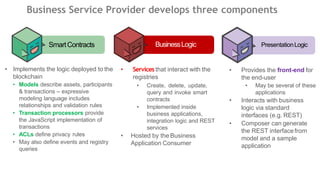
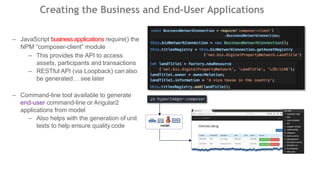
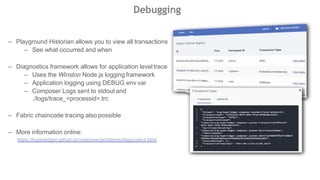
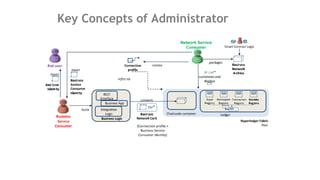
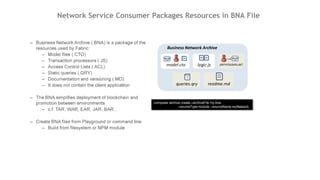
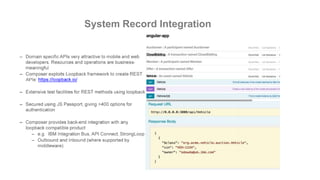
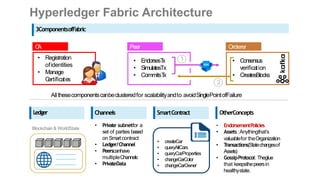
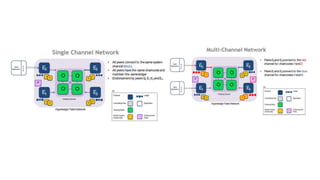
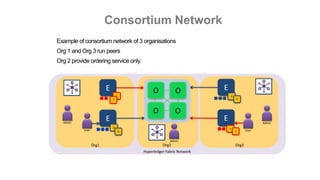
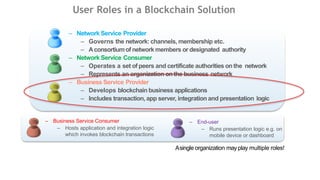
This document outlines a comprehensive roadmap for deploying blockchain solutions on Azure, specifically focusing on Hyperledger technologies. It covers various parts including architecture, deployment, and workflow integration, with emphasis on Hyperledger Composer for simplifying application development. Key concepts are explained such as roles within a blockchain network, transaction processing, access control, and the development of business applications.









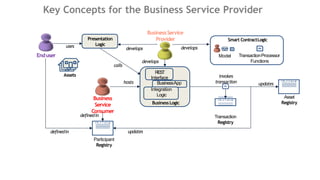
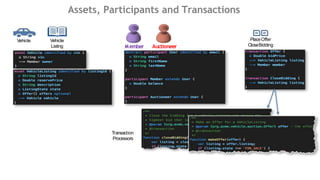
![Example: Vehicle Auction Developer
Vehicle
Registry
Vehicle
Listing
Registry
Auctioneer
develops
hosts
Auctioneer
Registry
Transaction
Registry
PlaceOffer
CloseBidding
definedin
Place Offer
CloseBidding
[Registryoperations]
Model
develops
VehicleAuction
Developer
Mobile
AuctionApp
develops
uses
Auction SmartContract
Member
calls
definedin
updates
updates
REST
Interface
AuctionBack-
endService
Systemof Record
Integration
BusinessLogic
Vehicle Vehicle
Listing
Member
Registry
Balance
$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchinarchitecture-azure-part-3-190821140733/85/Blockchin-Architecture-on-Azure-Part-3-15-320.jpg)