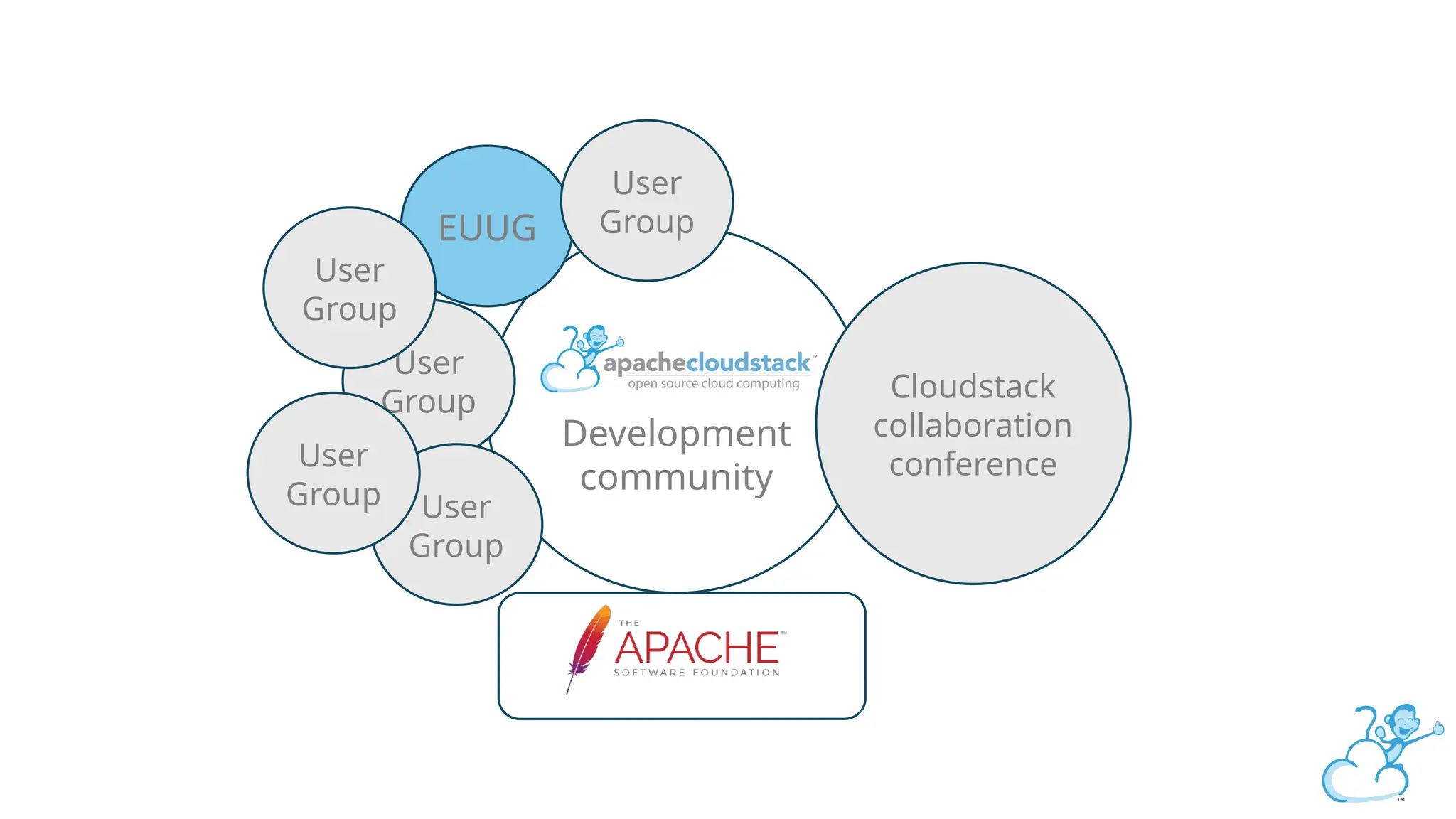
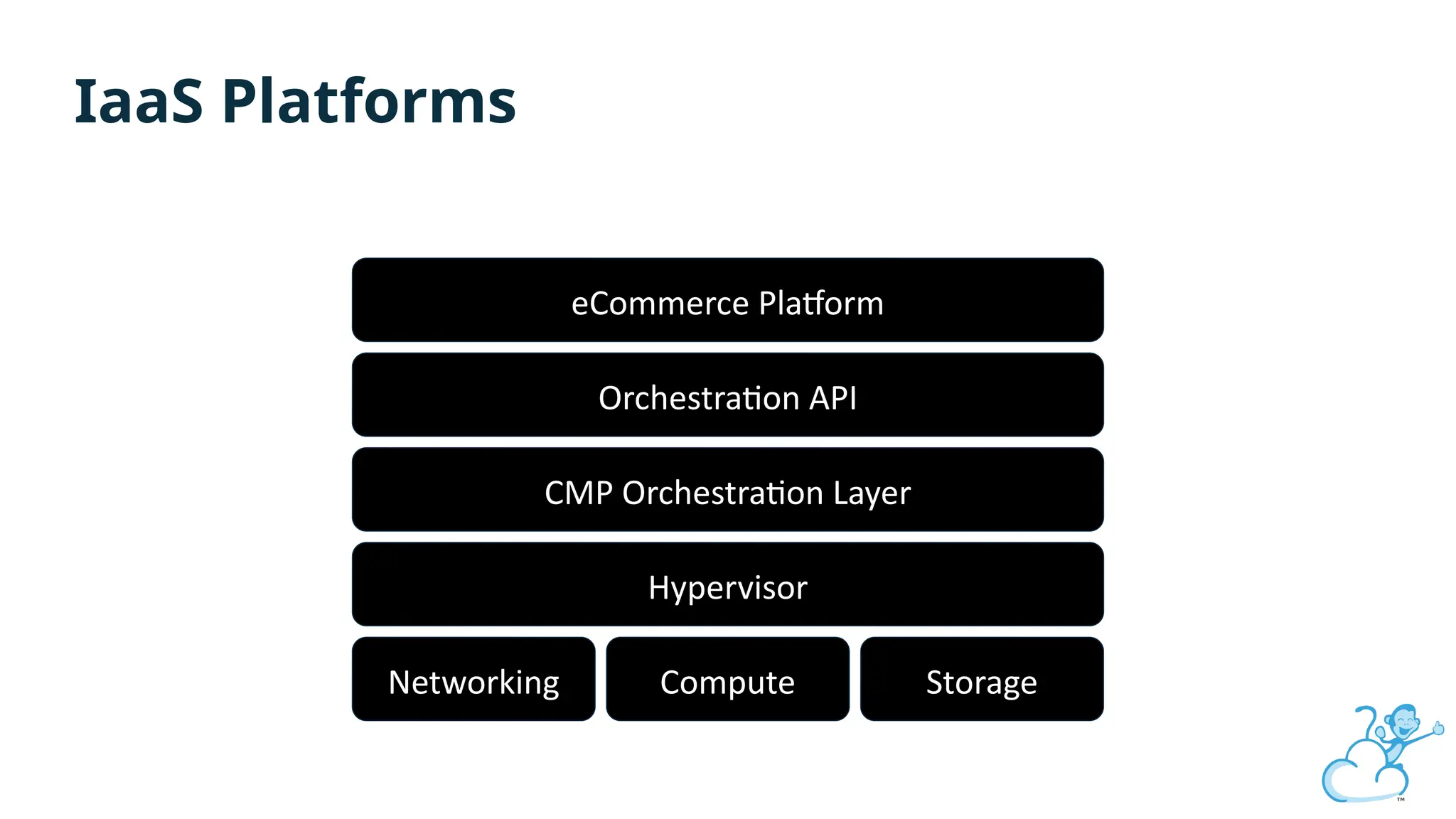
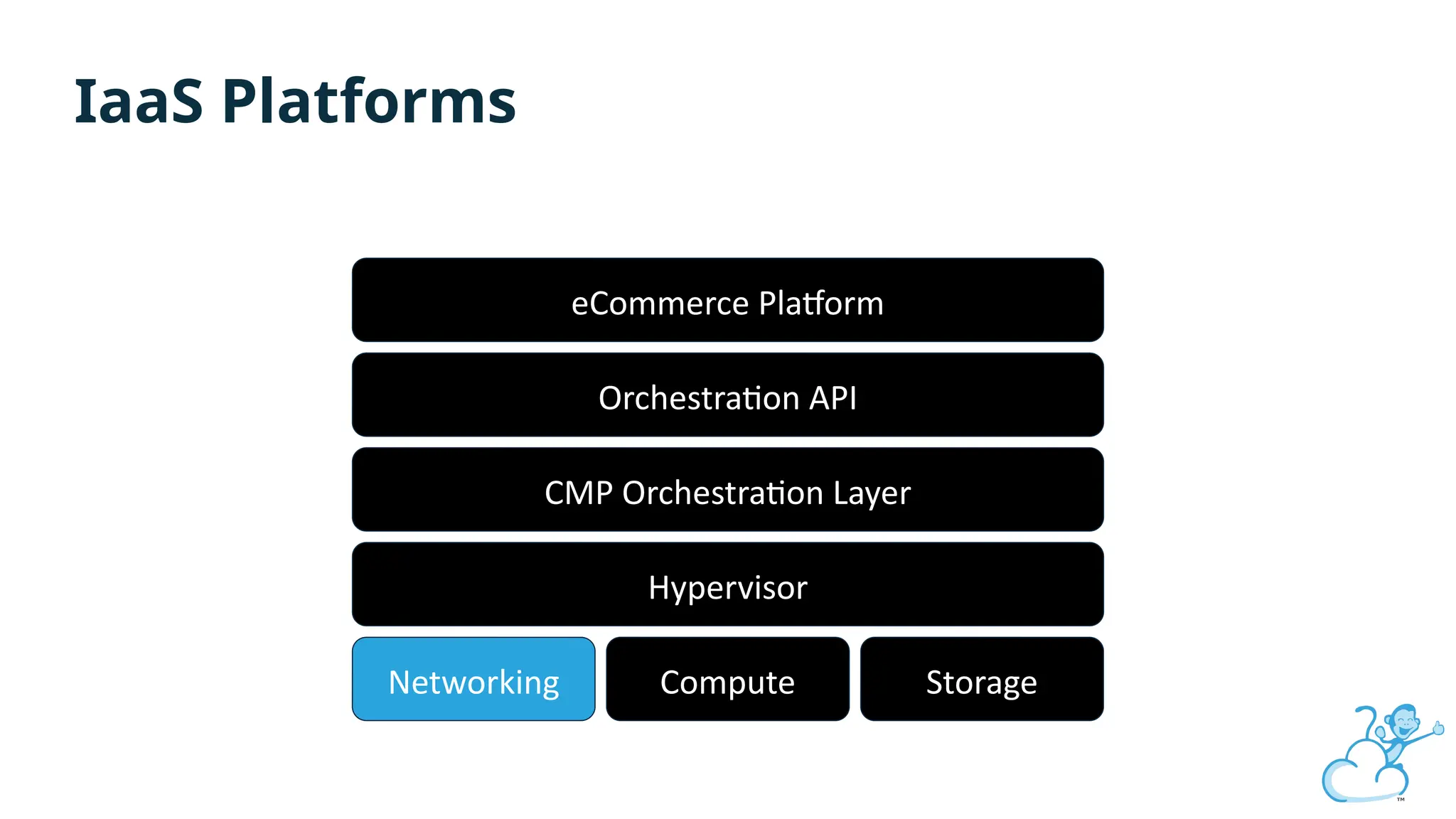
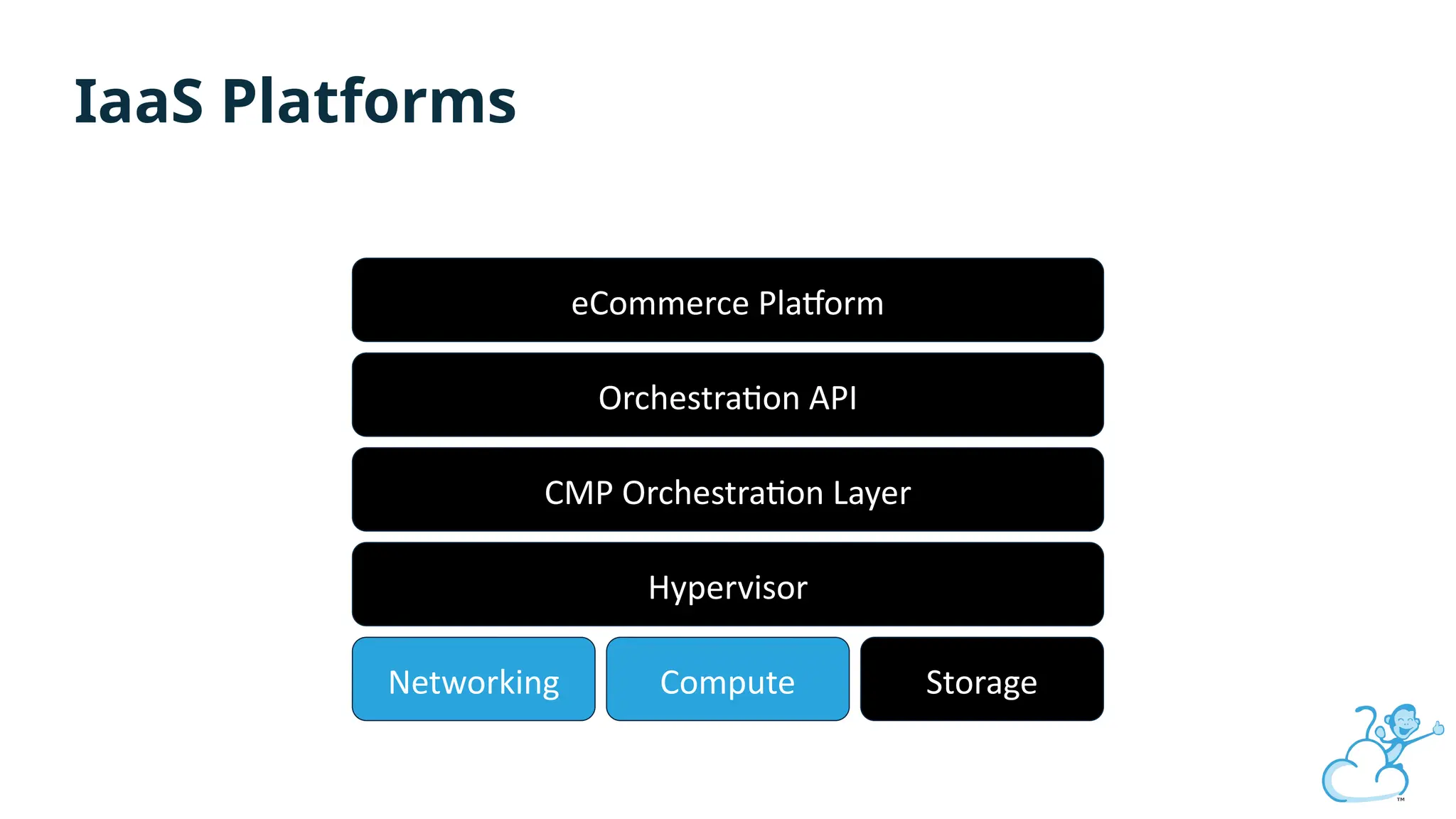
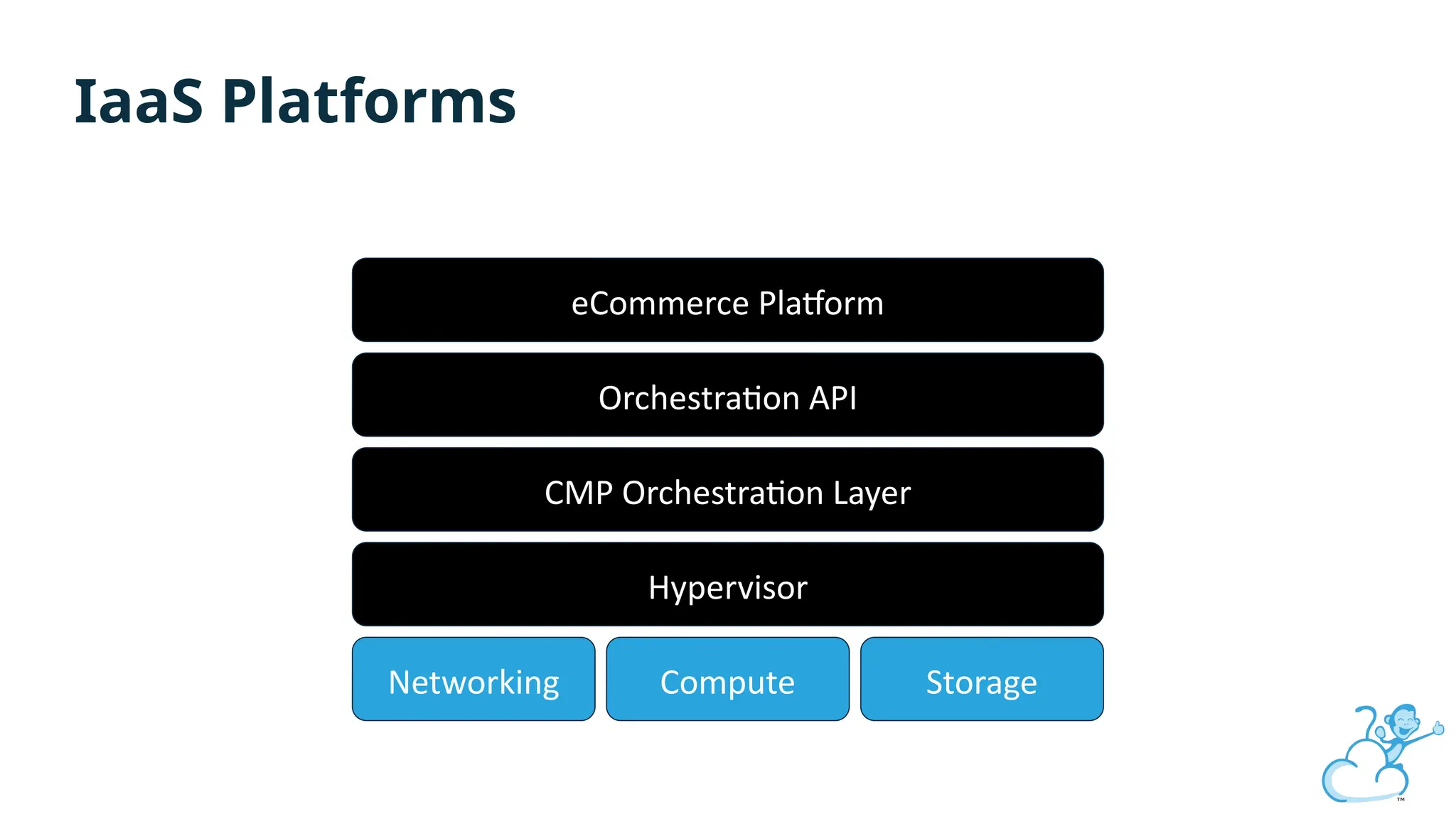
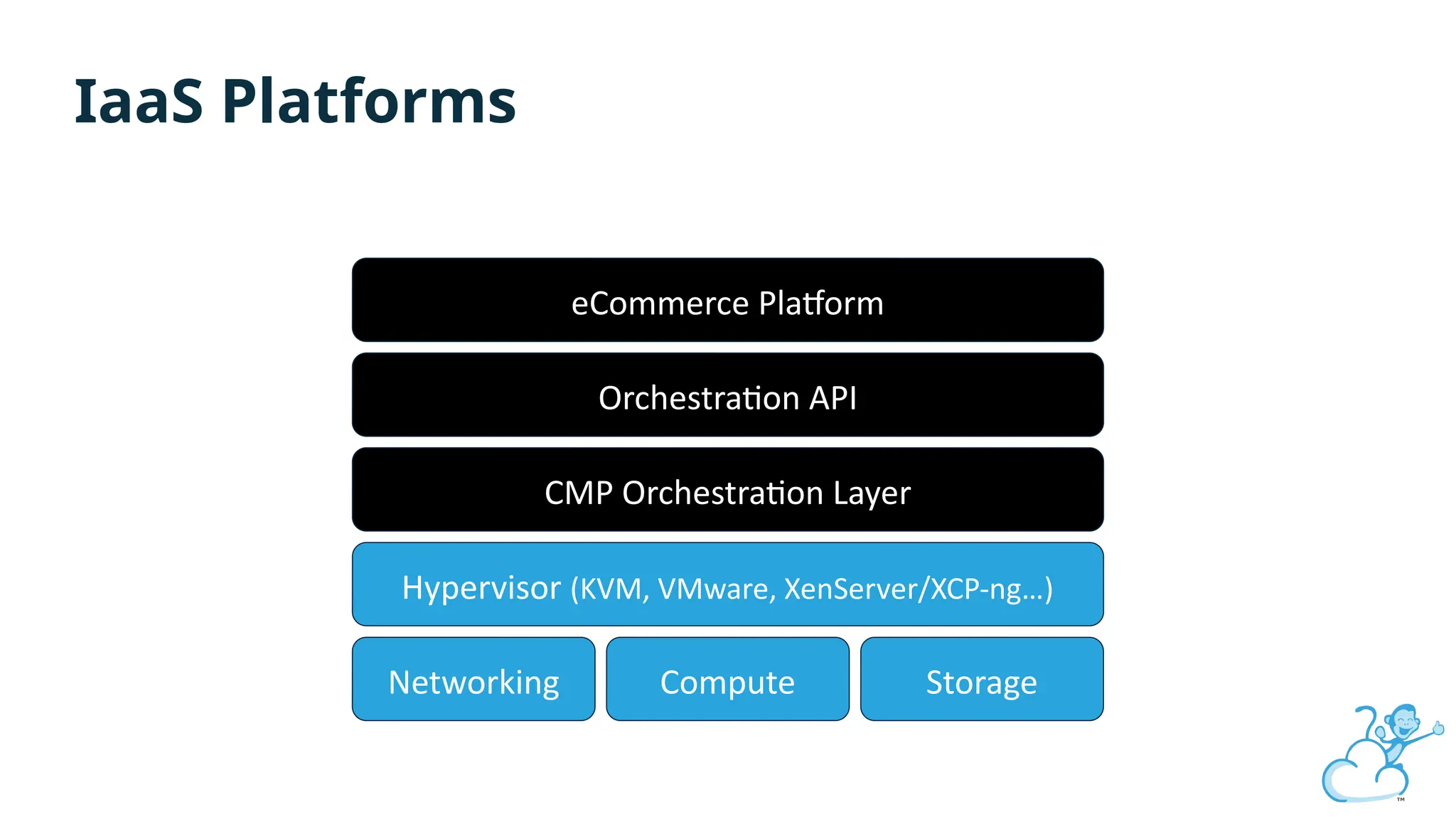
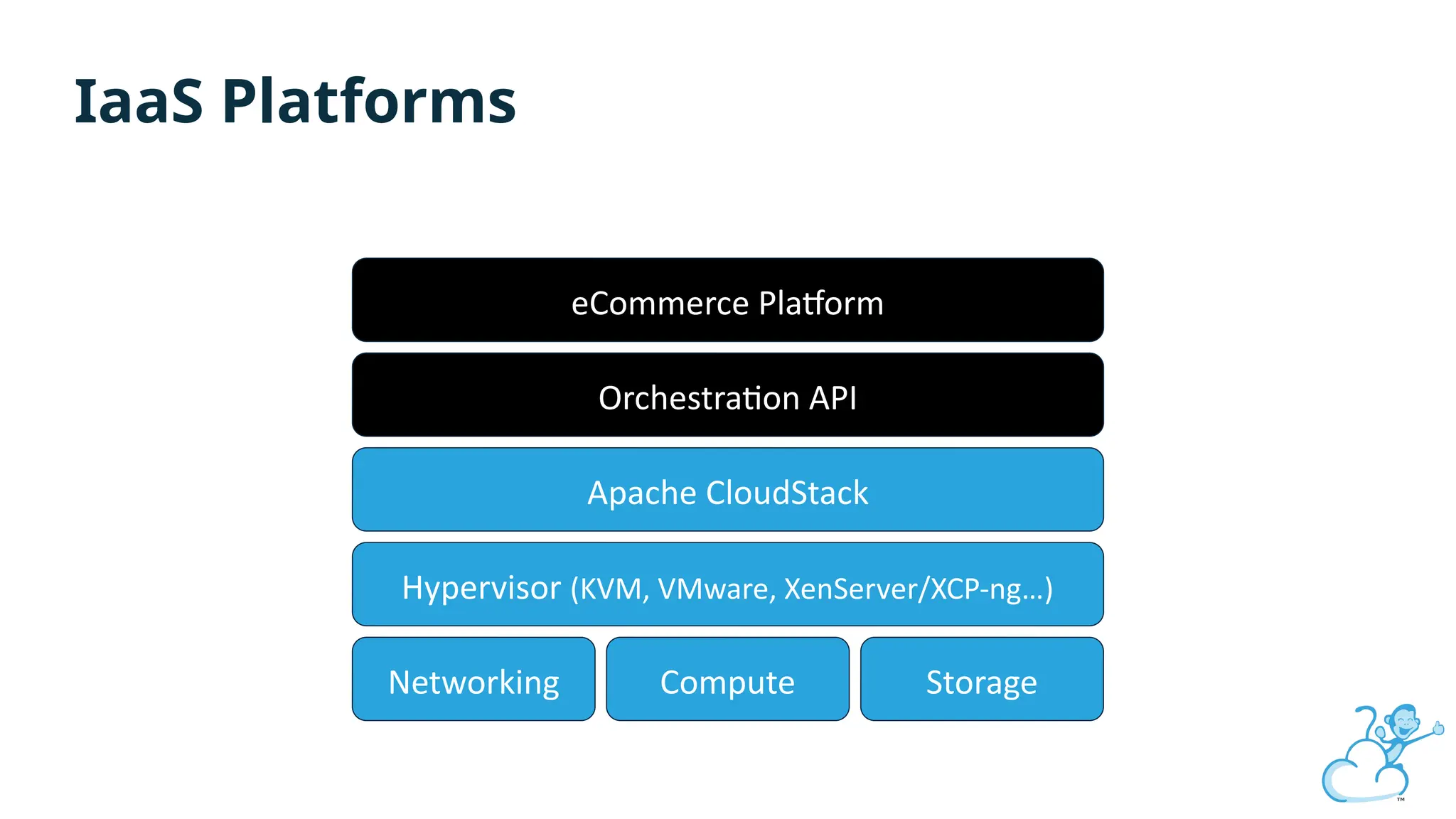
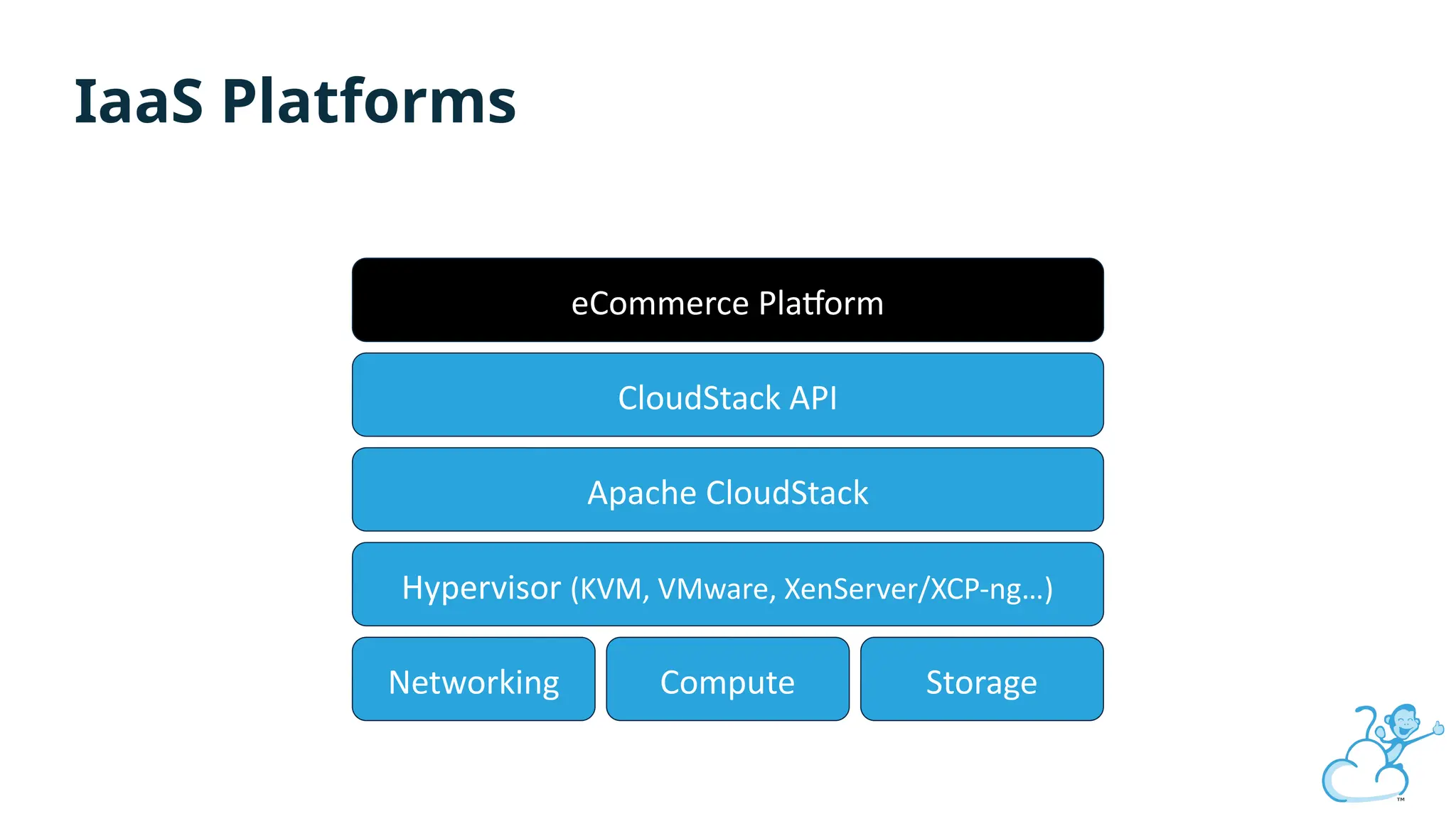
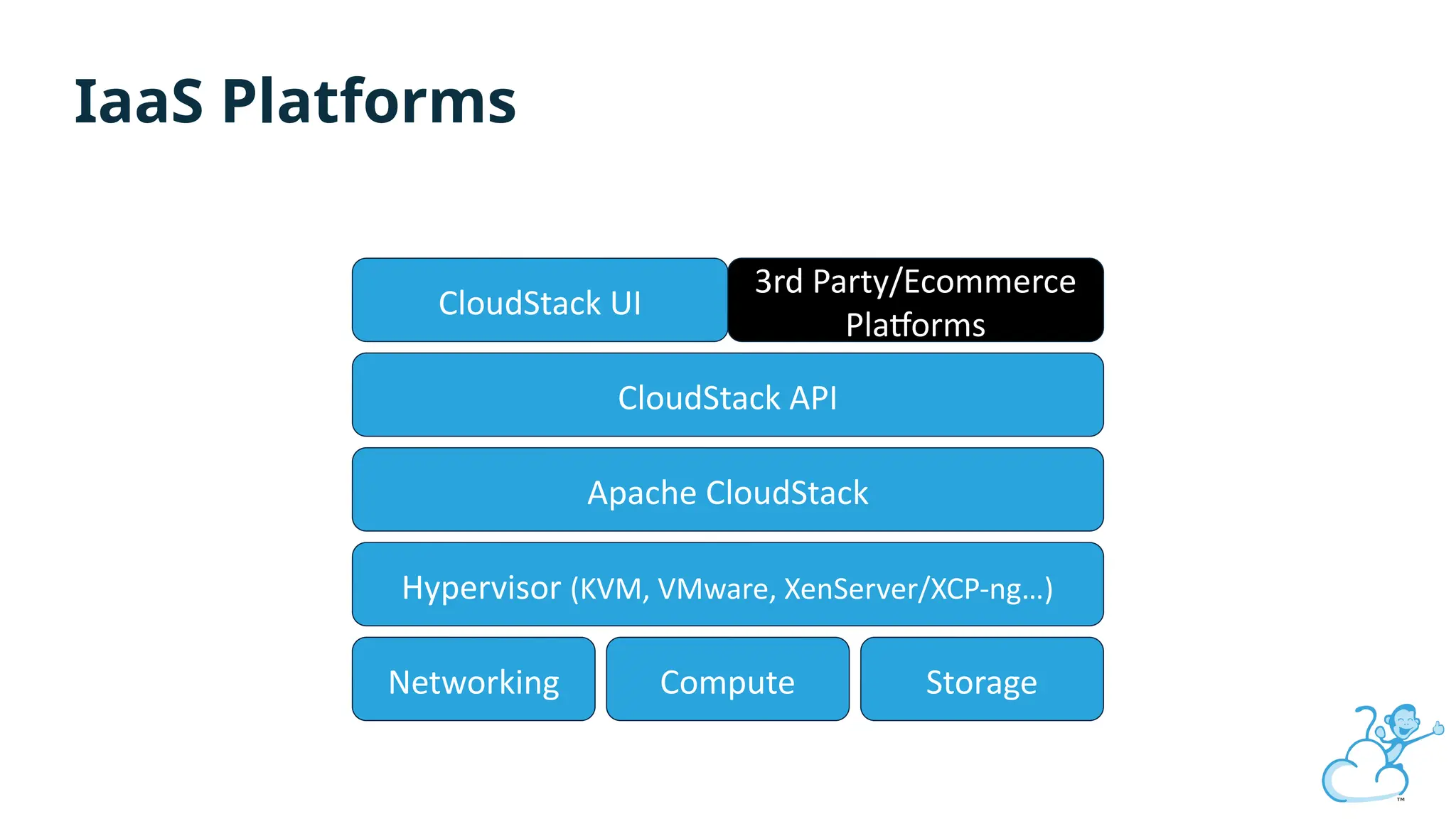
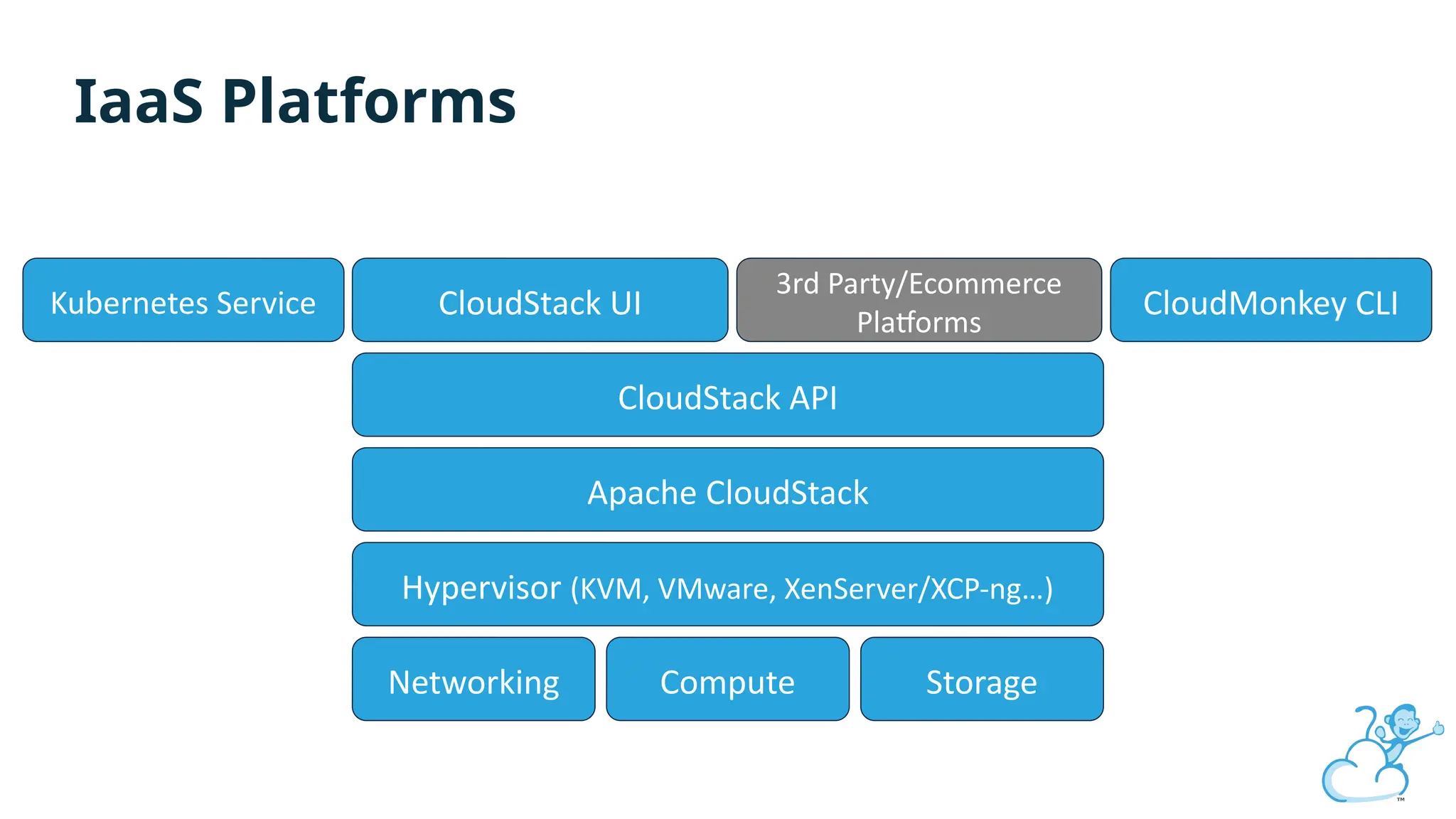
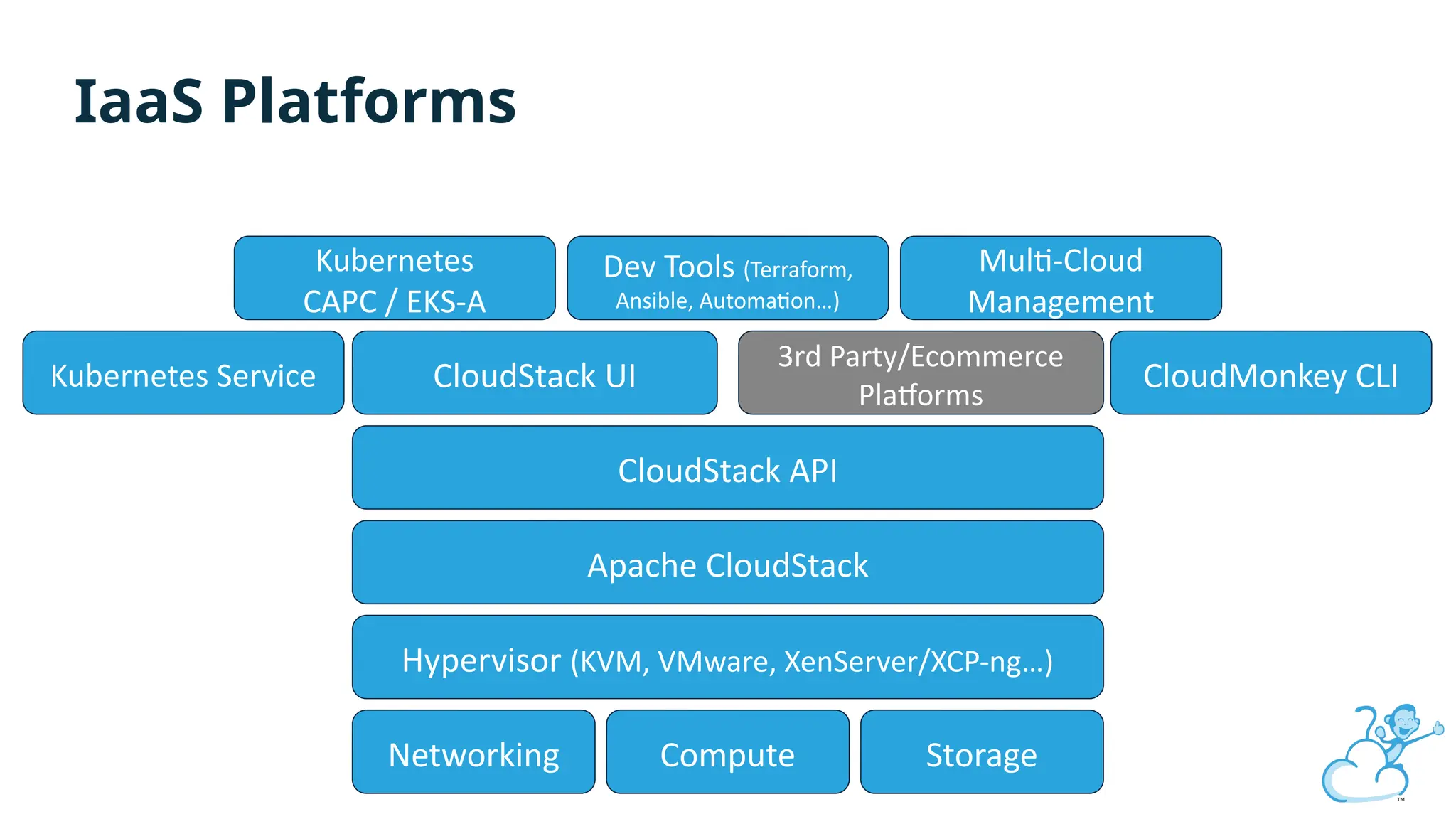
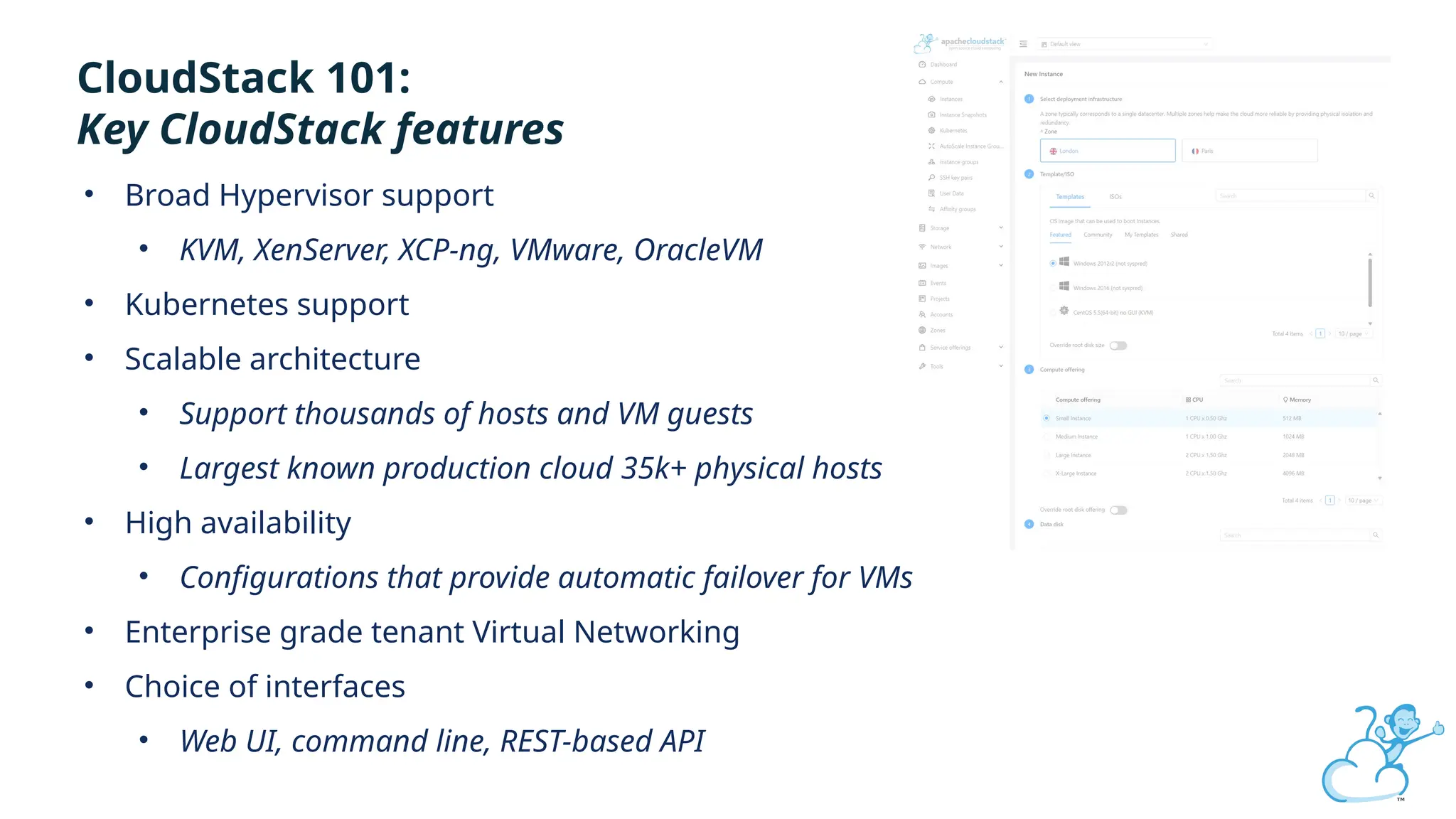
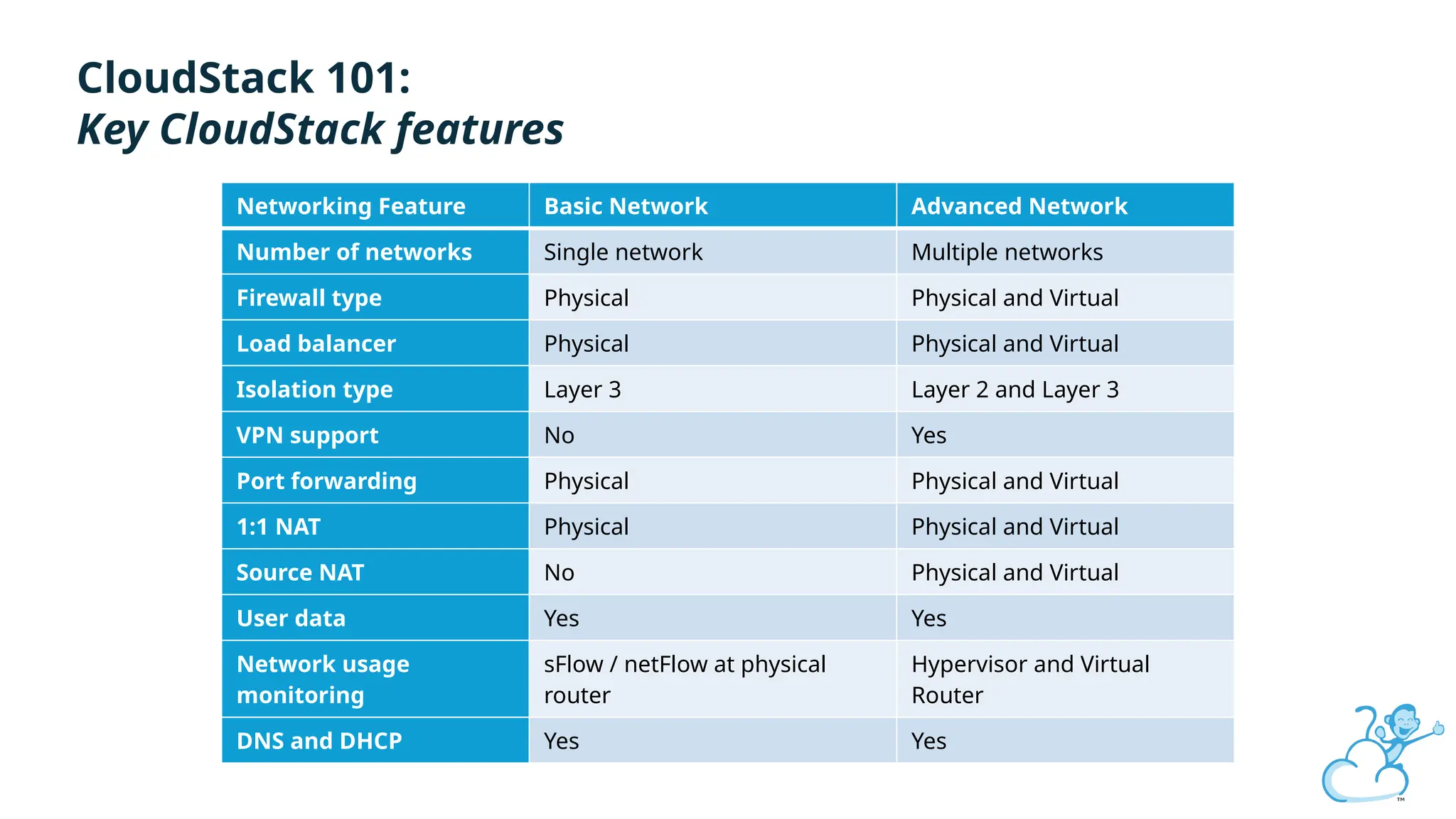
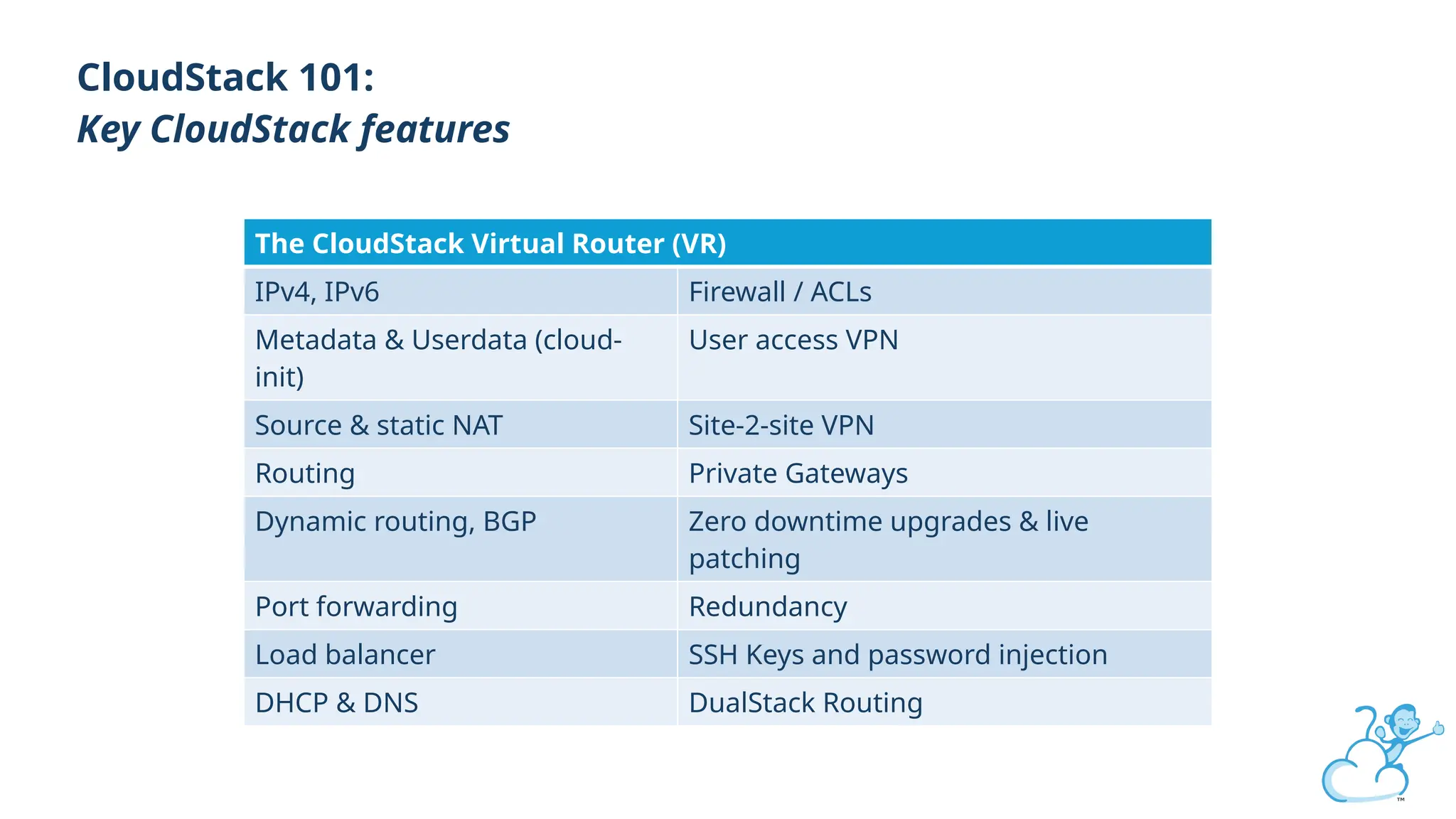
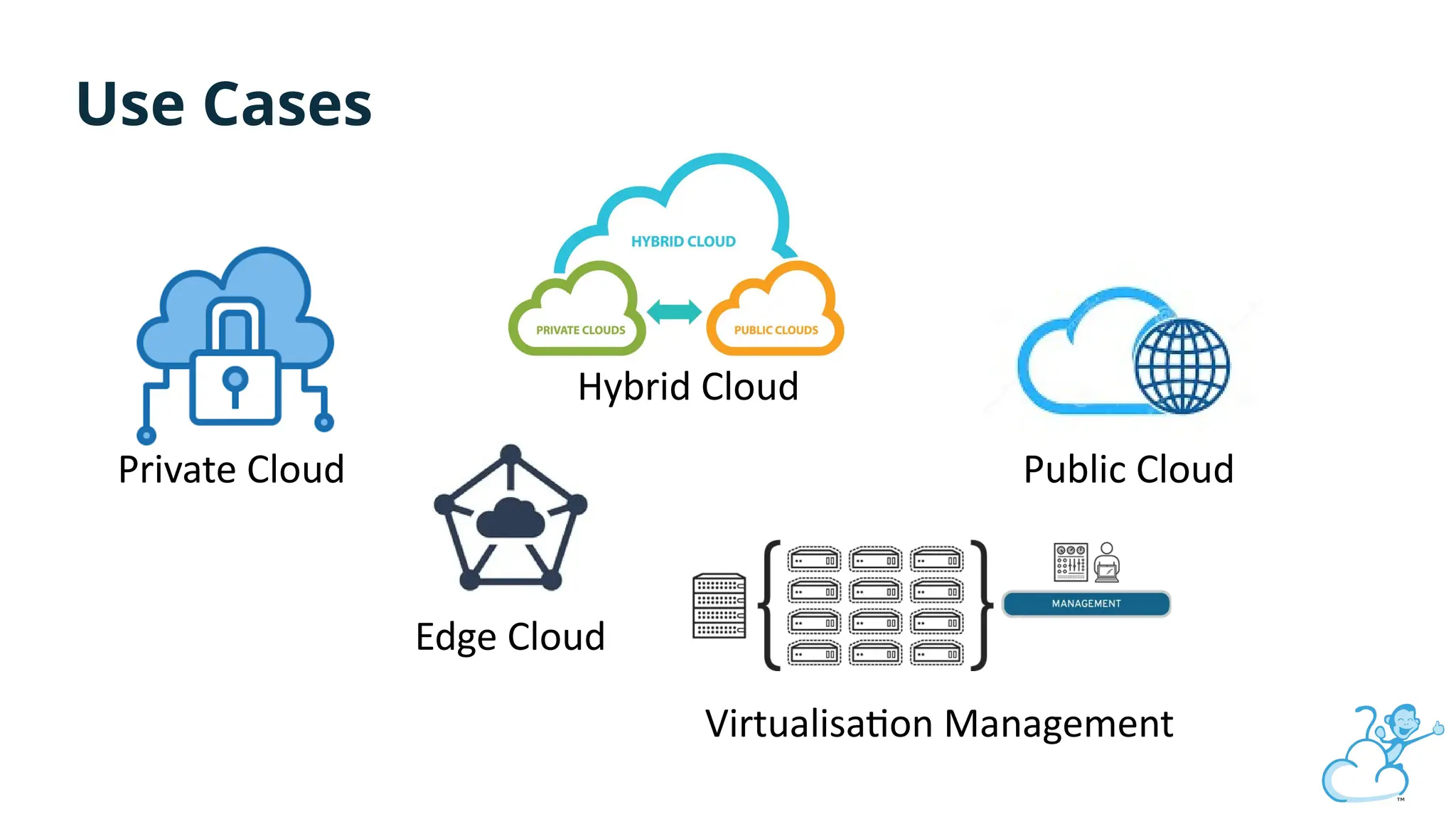
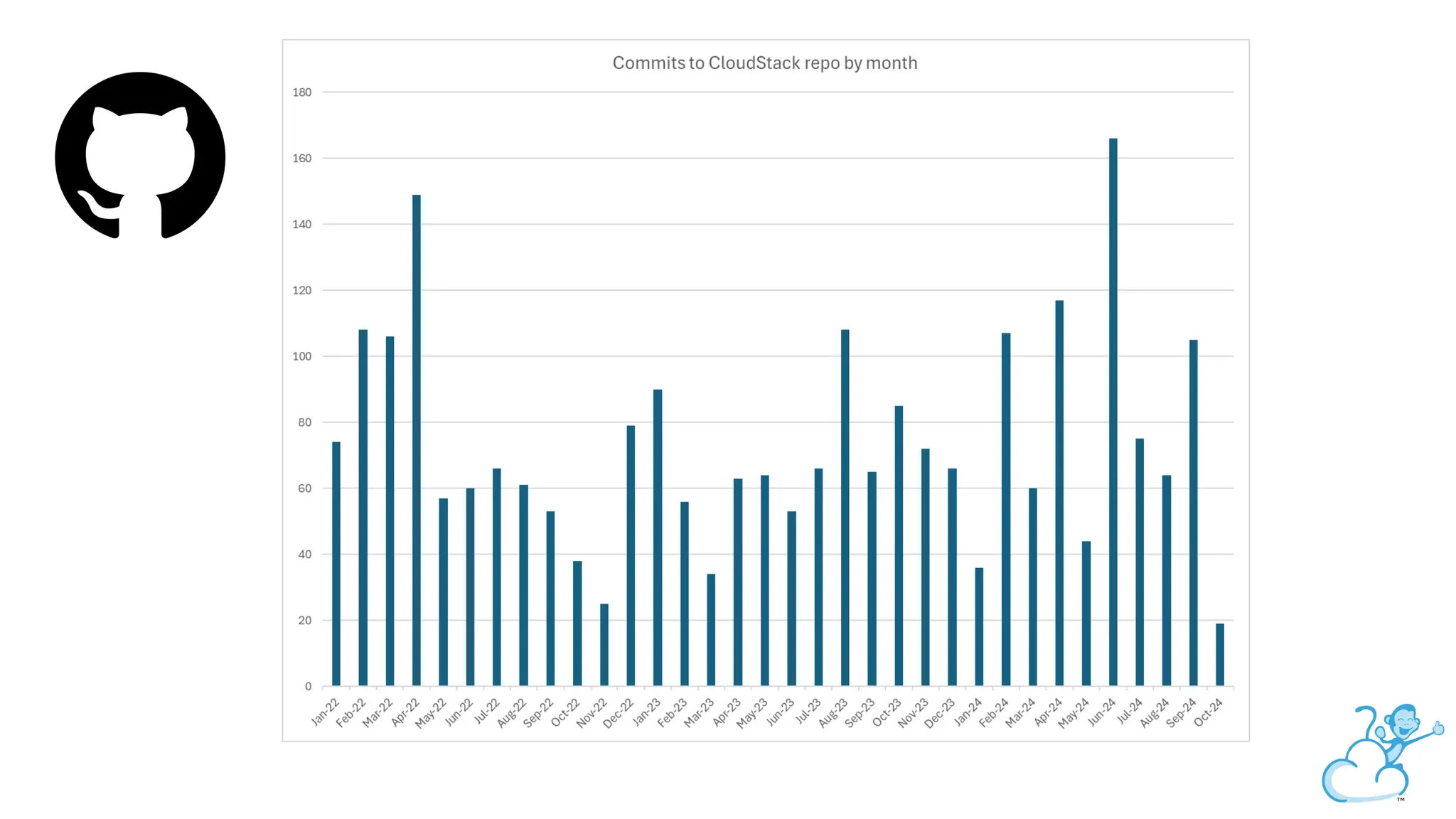
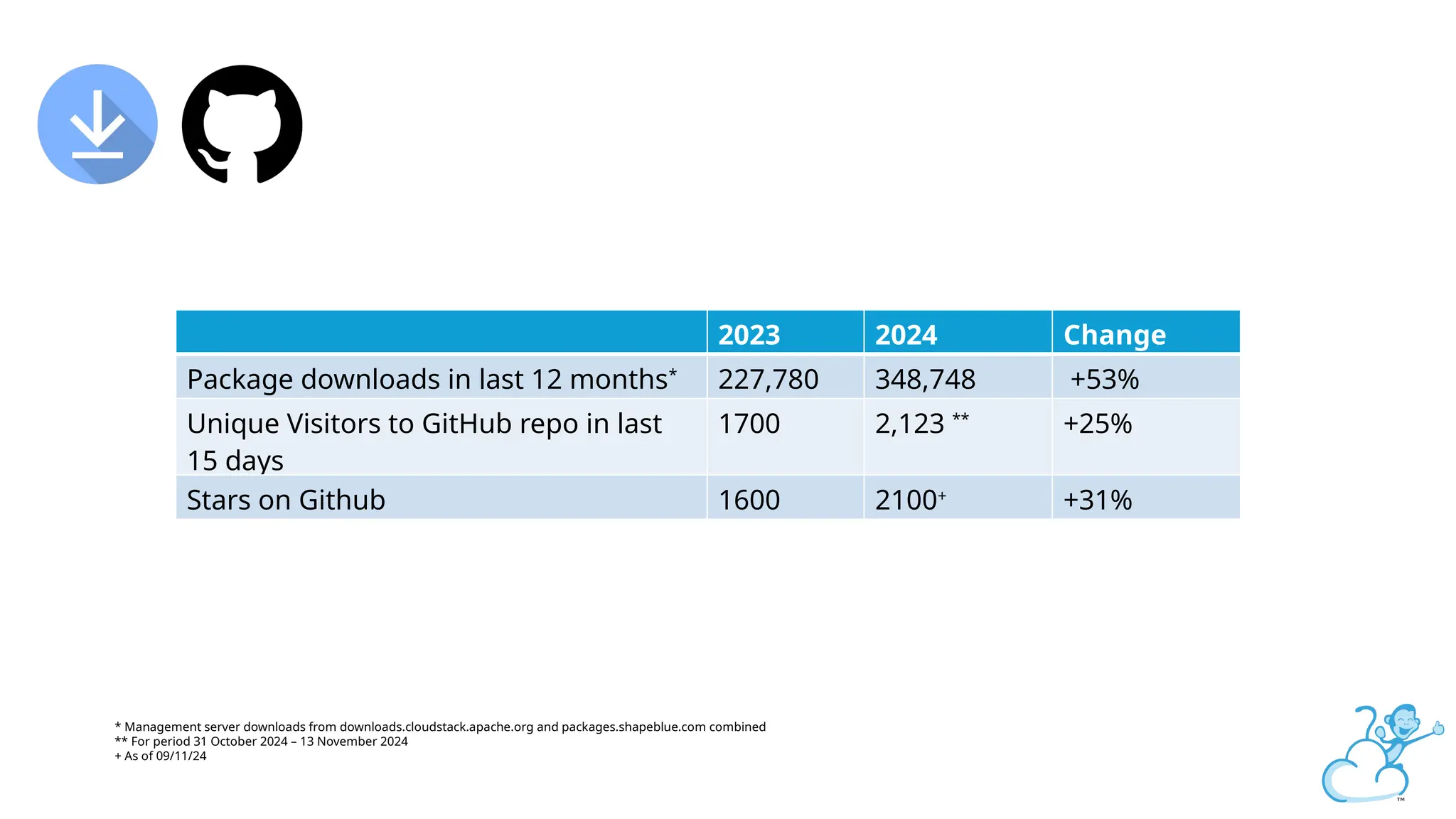
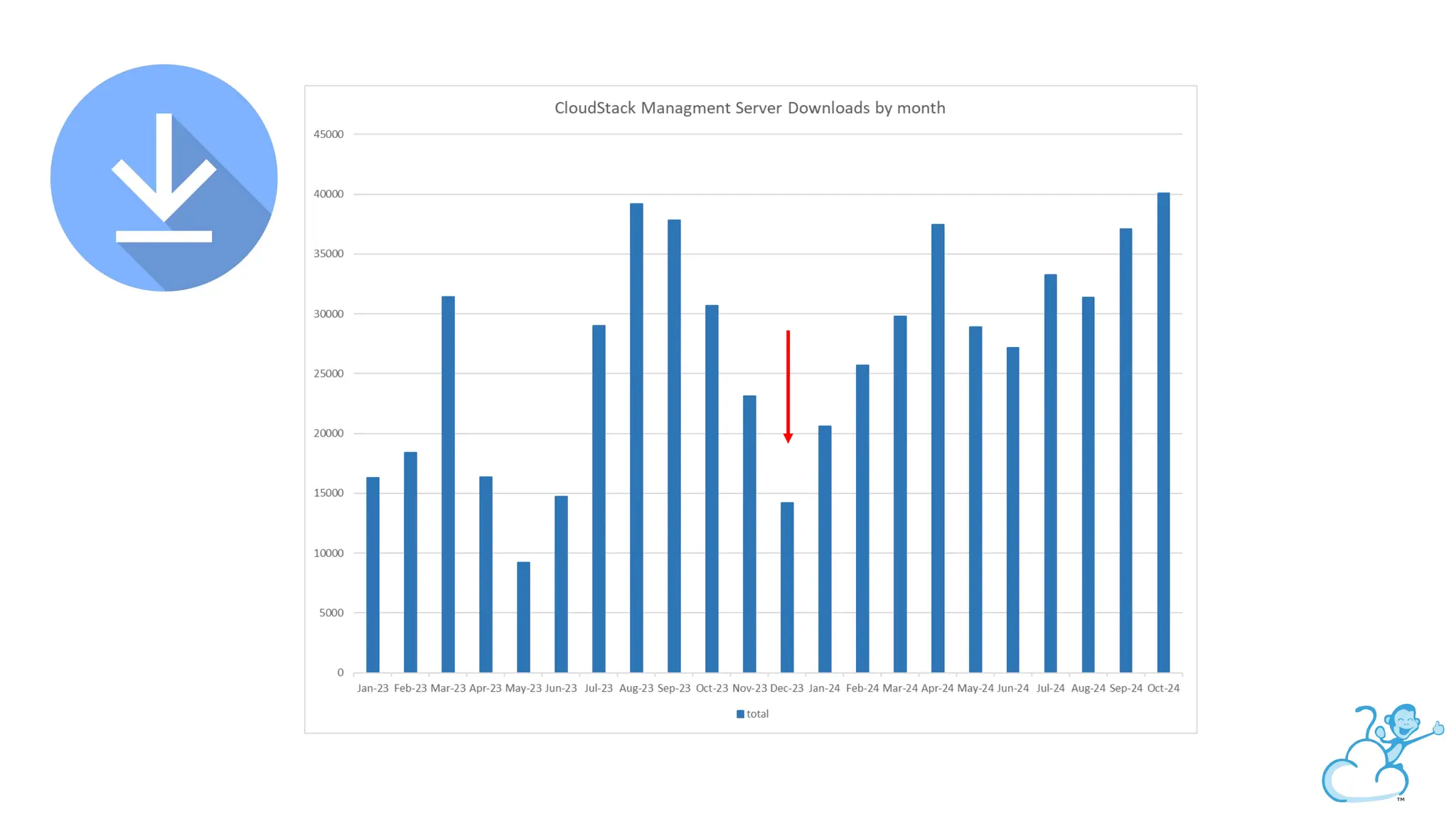
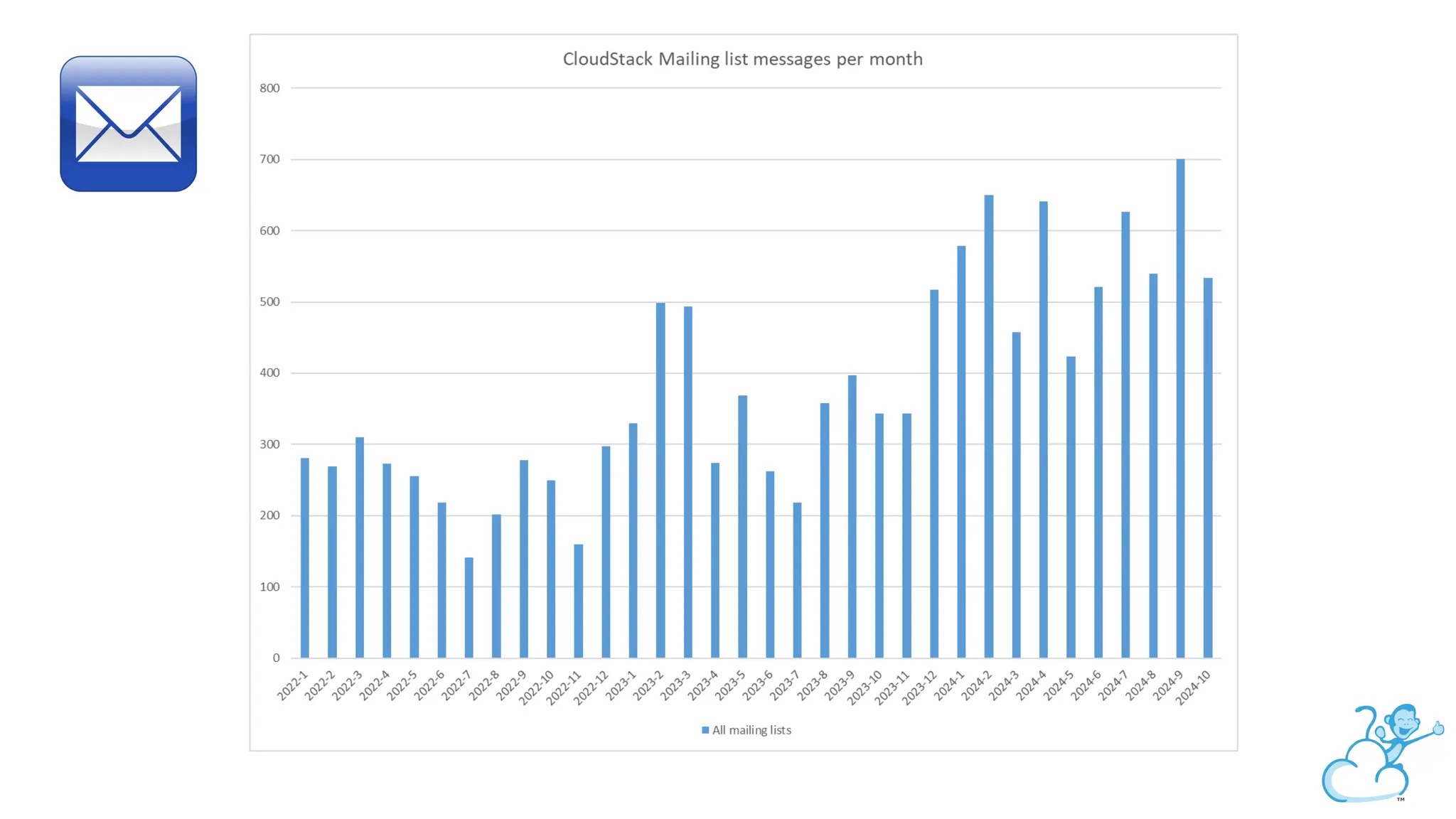
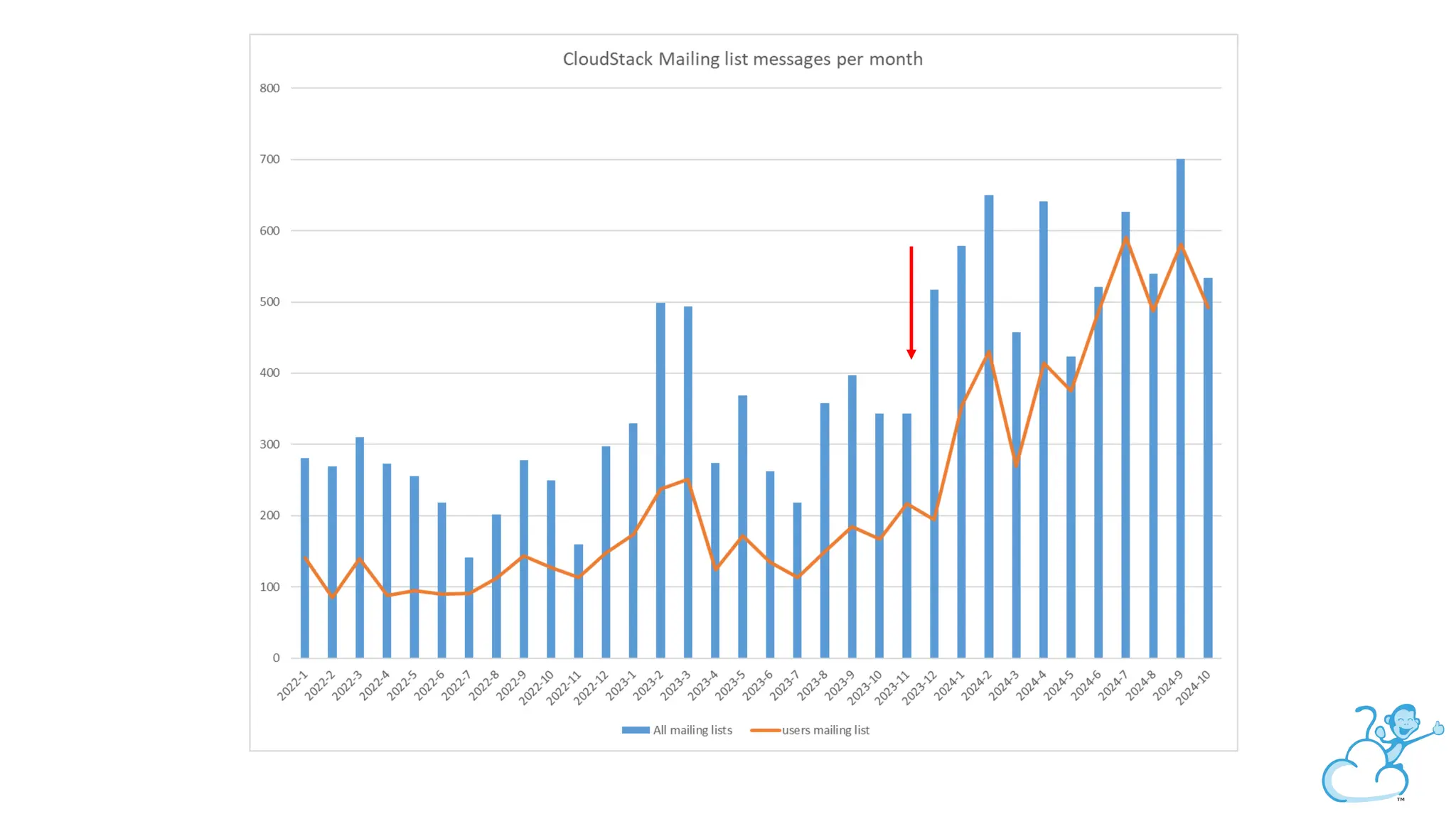
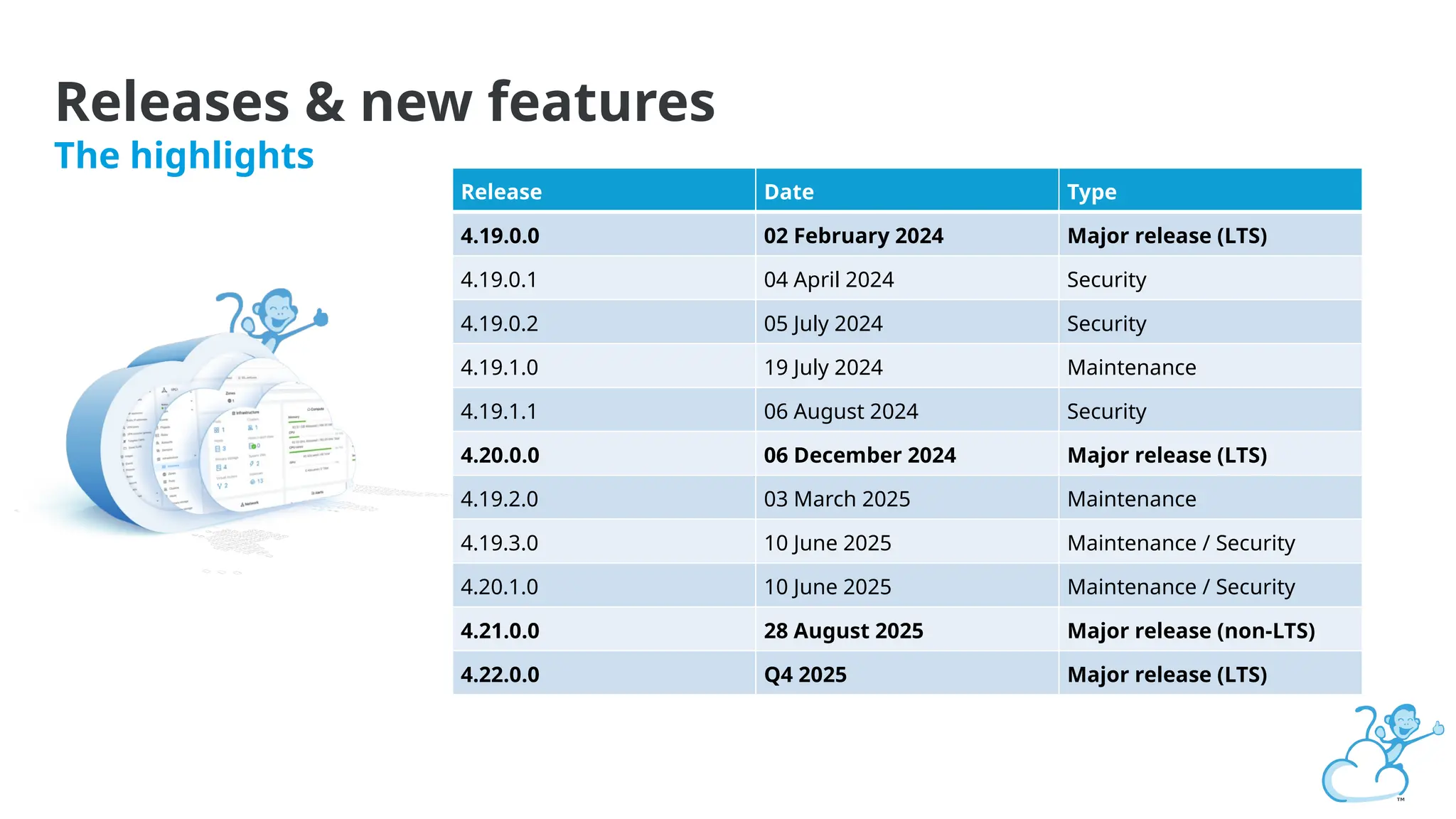
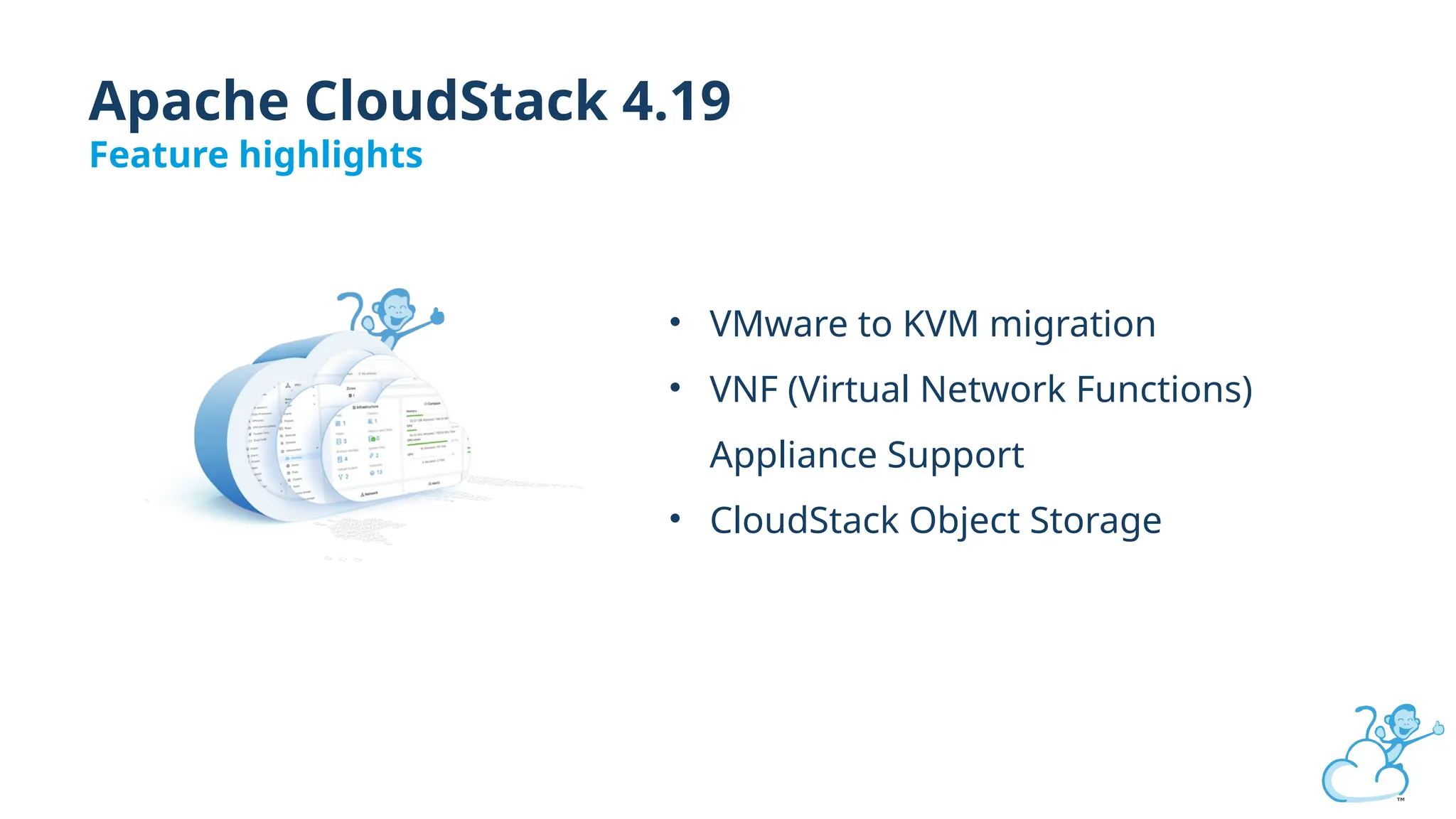
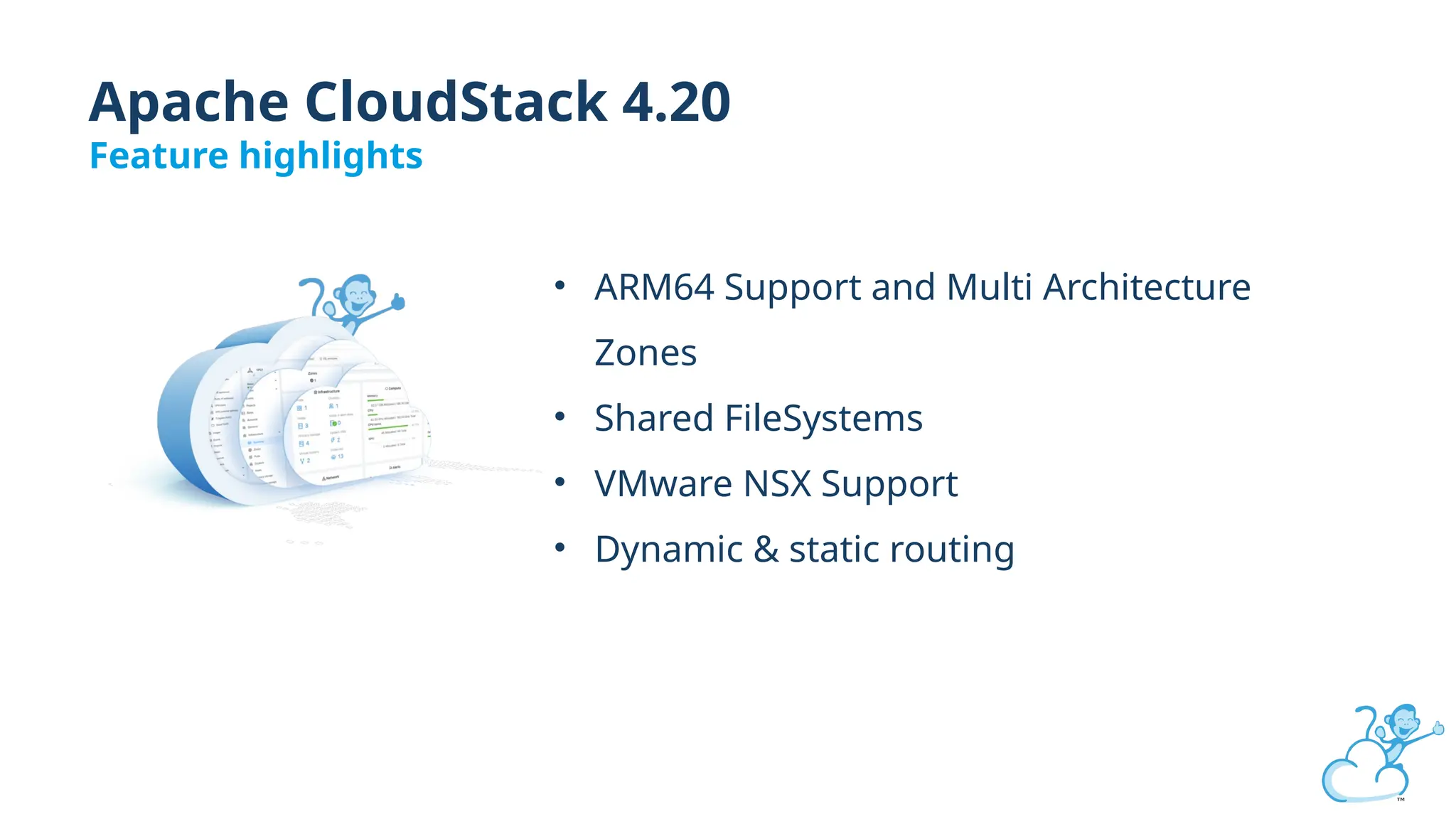
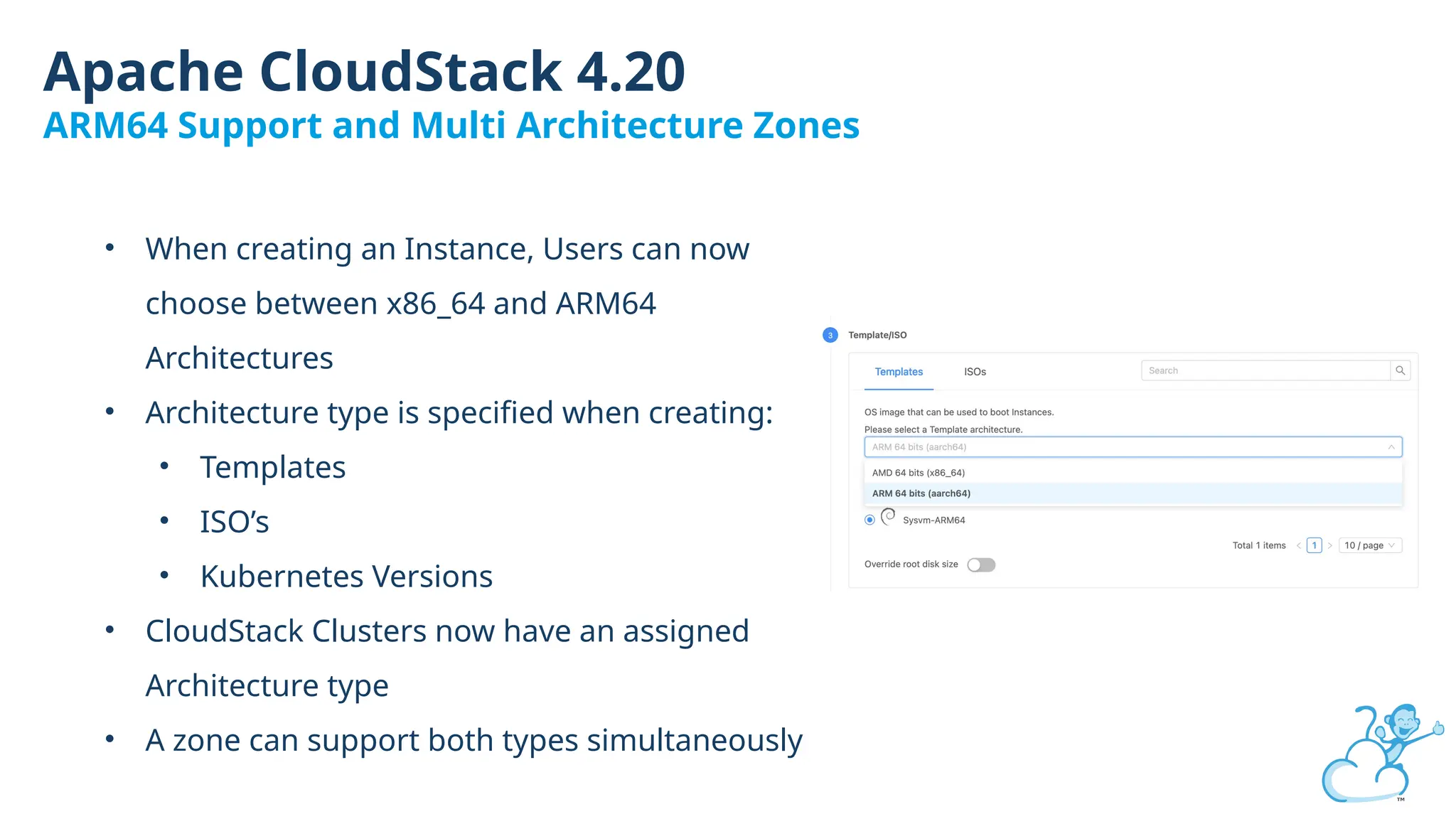
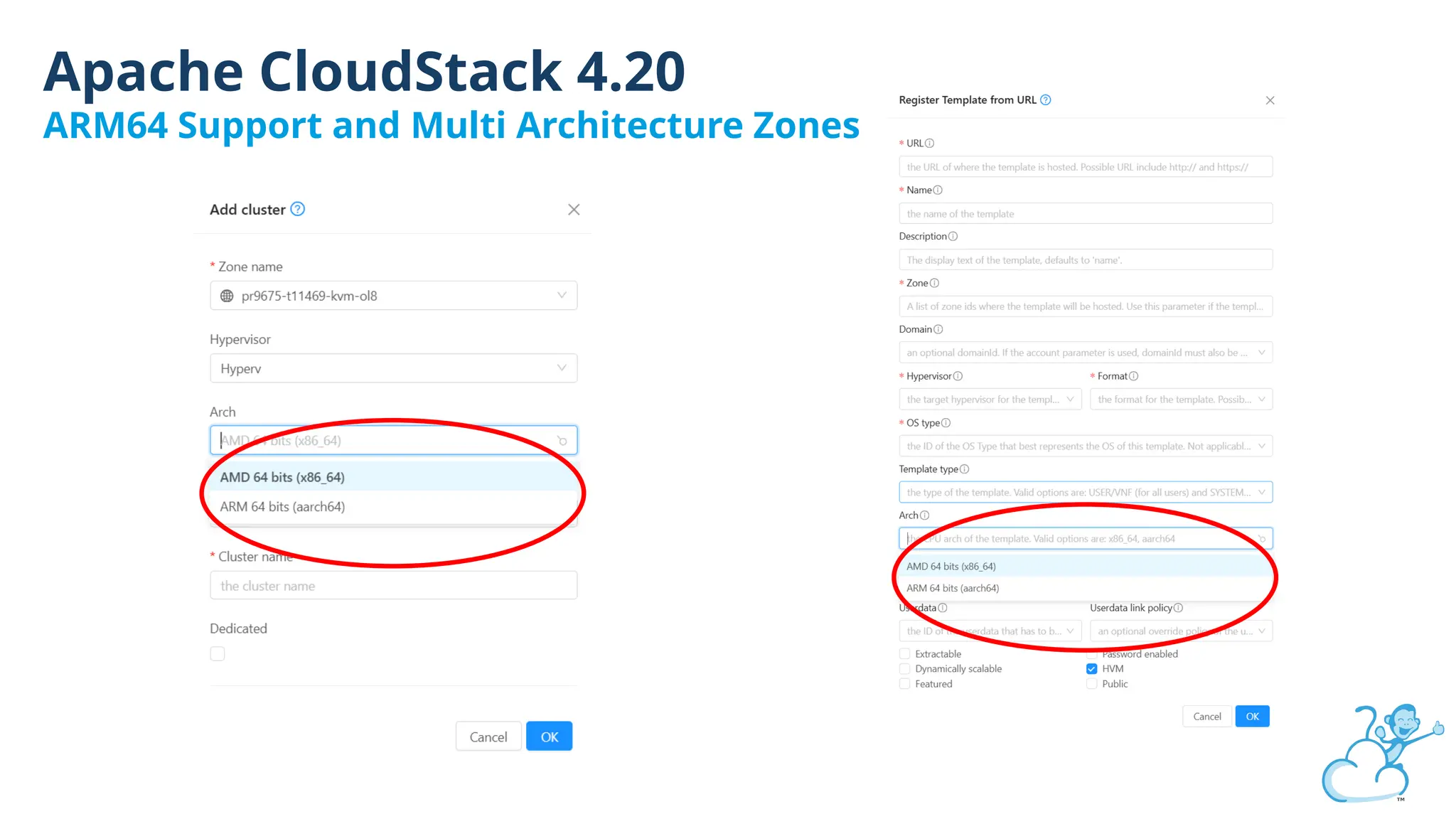
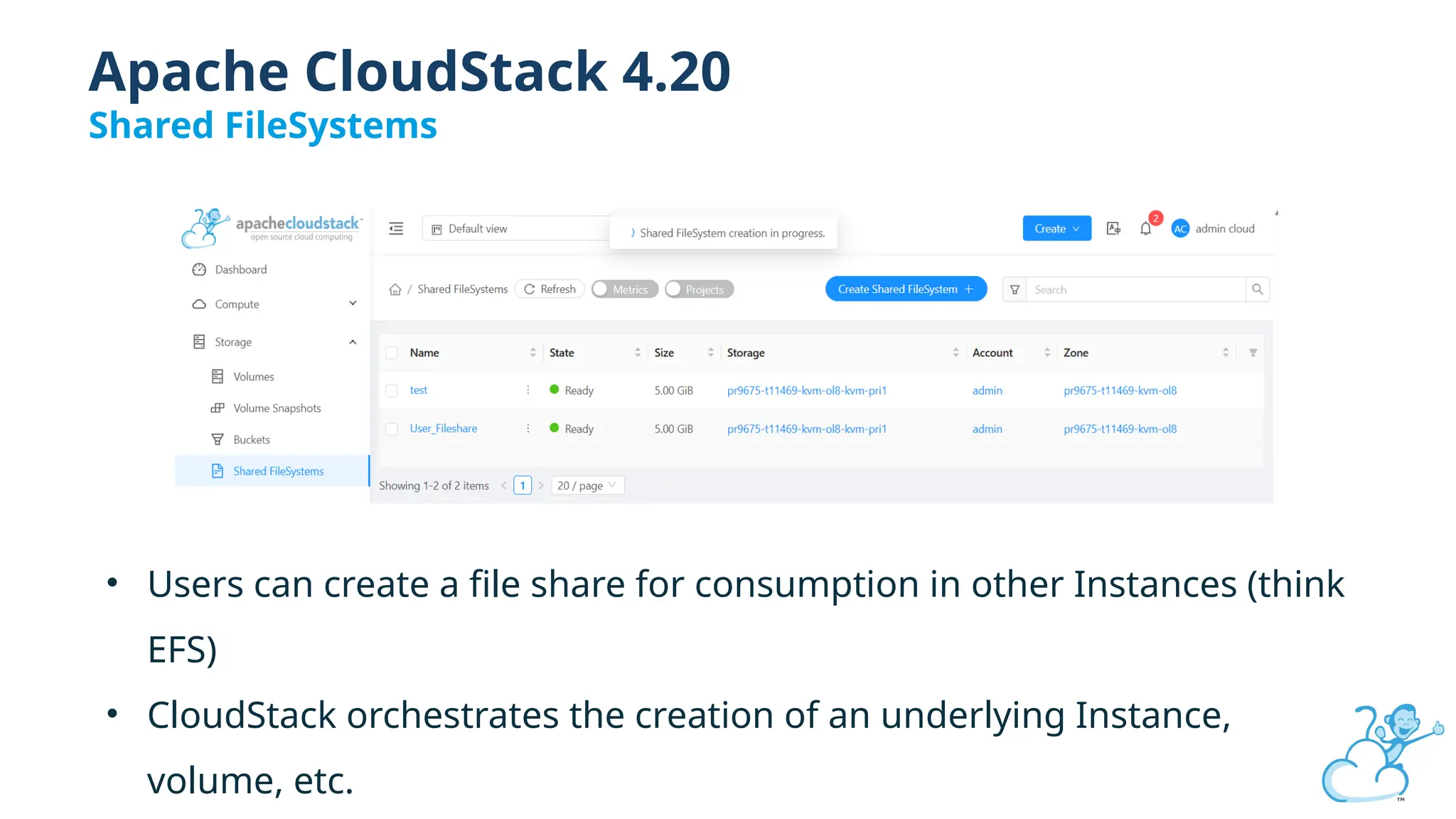
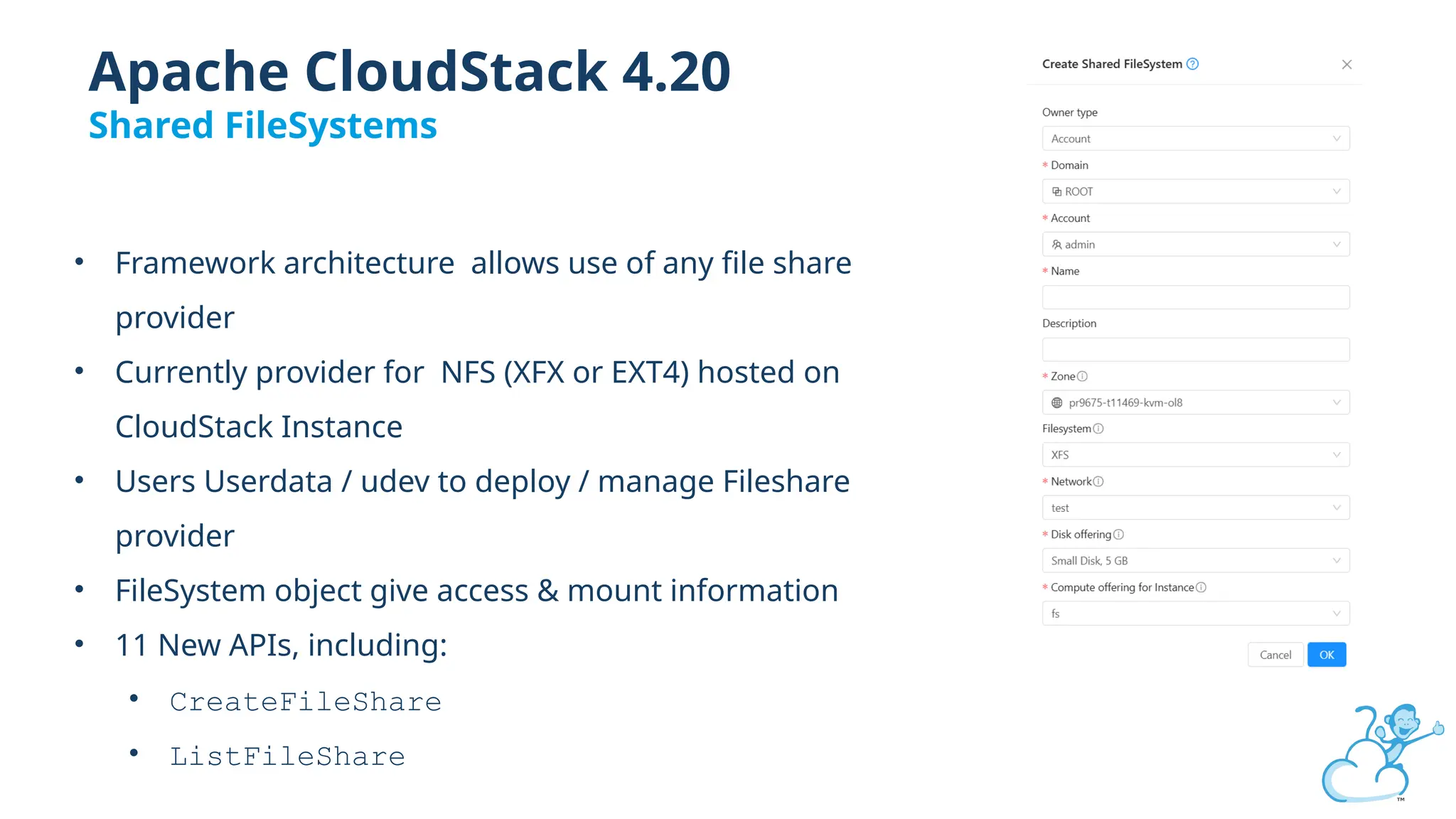
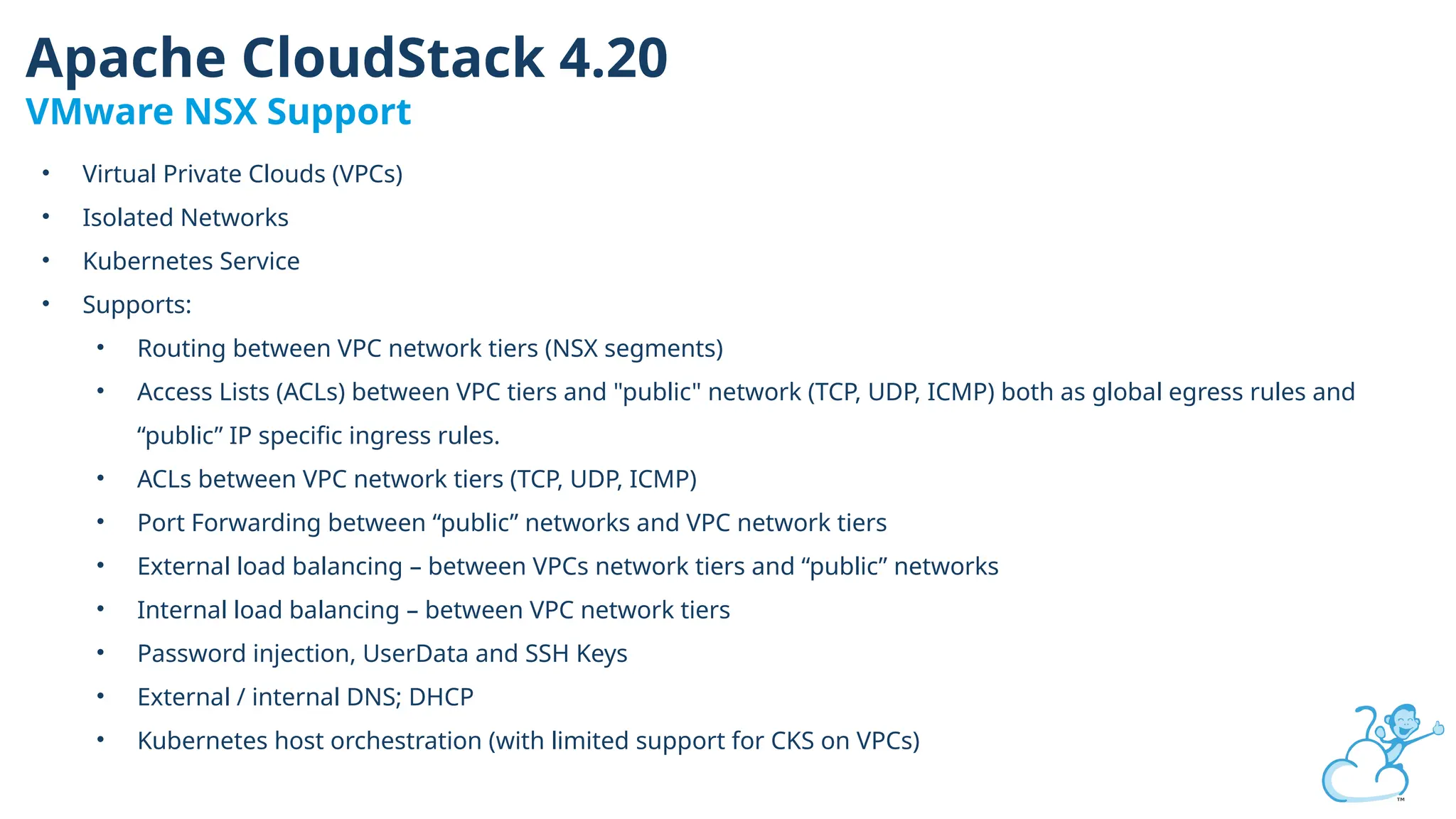
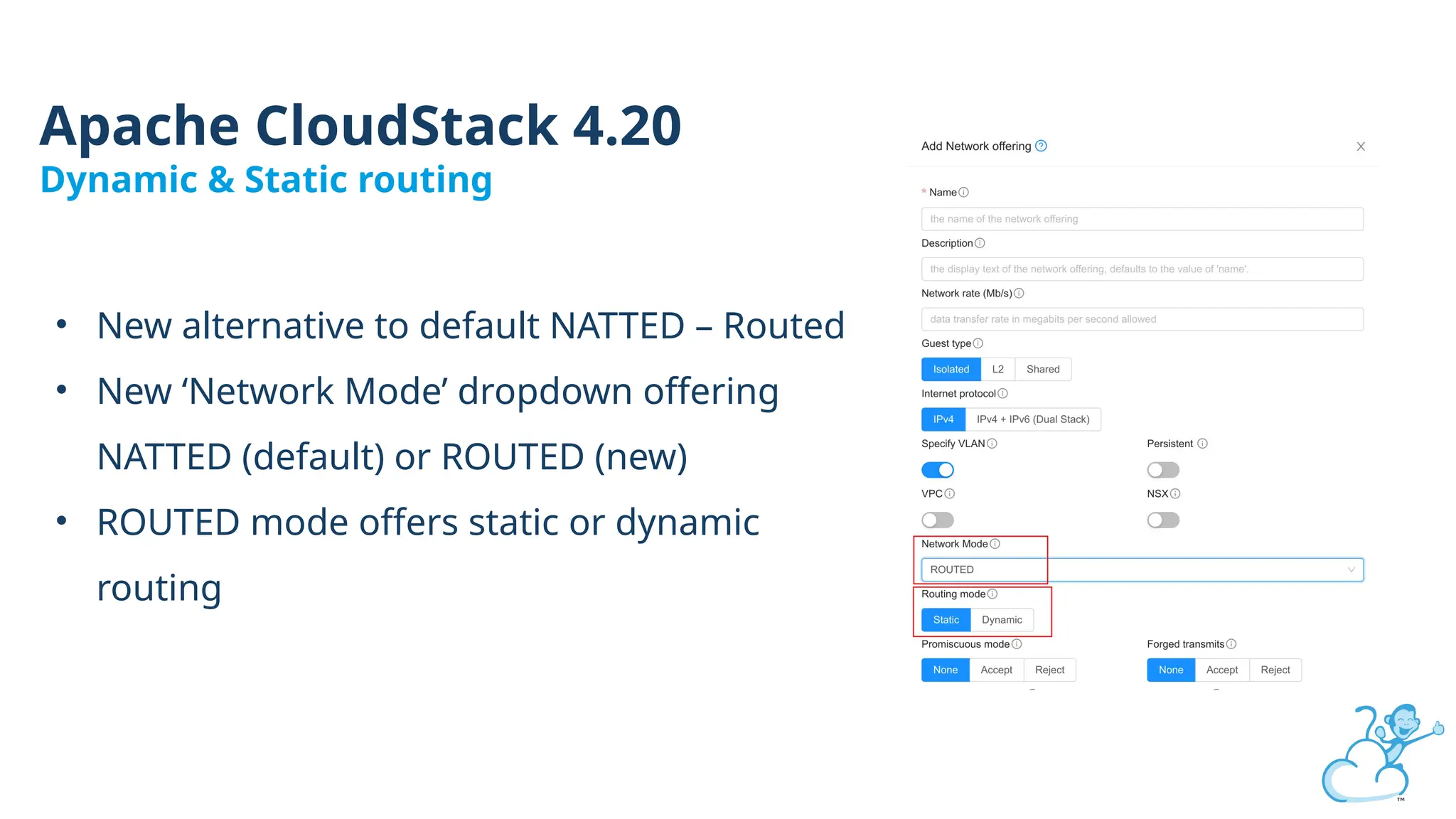
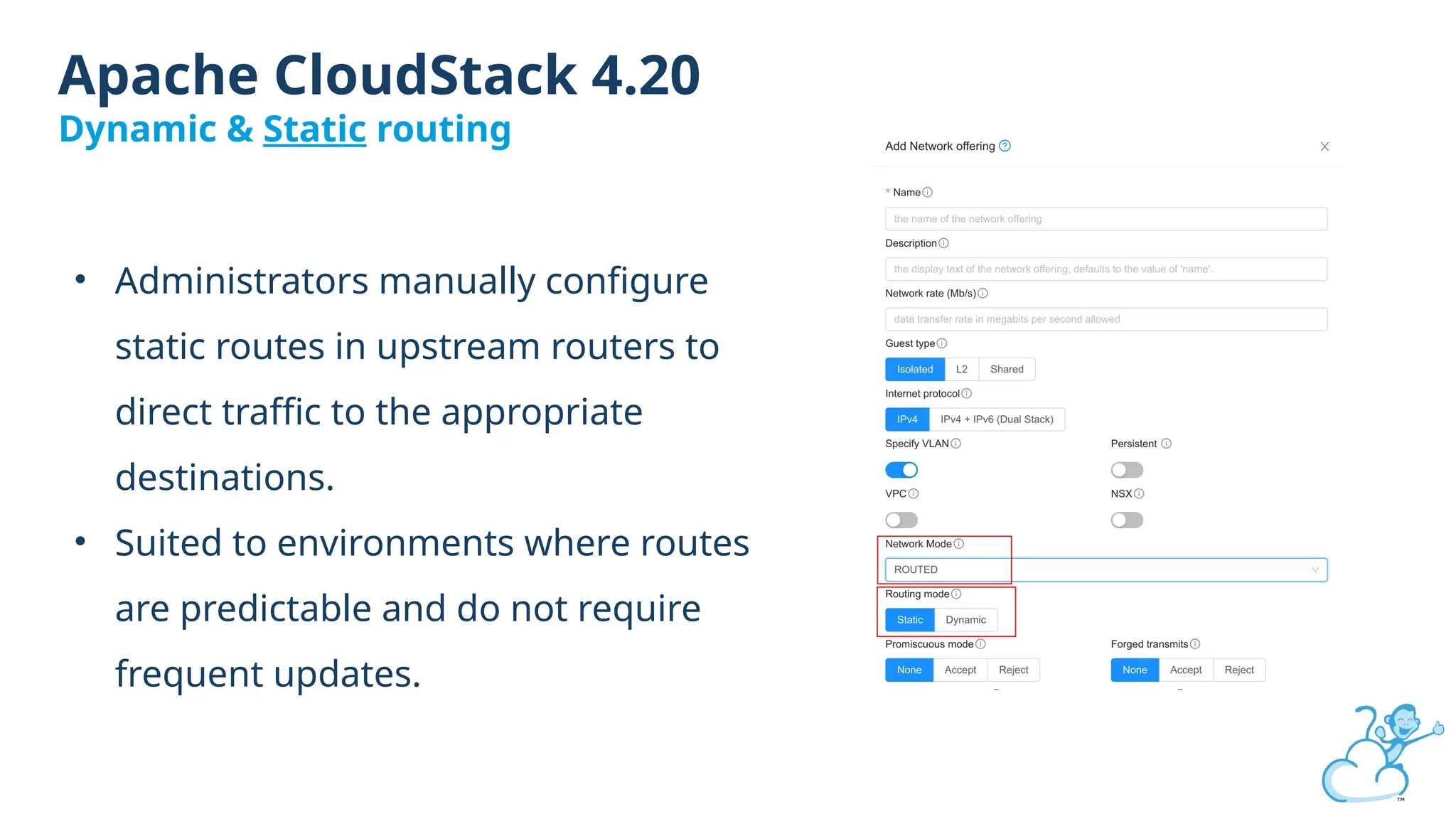
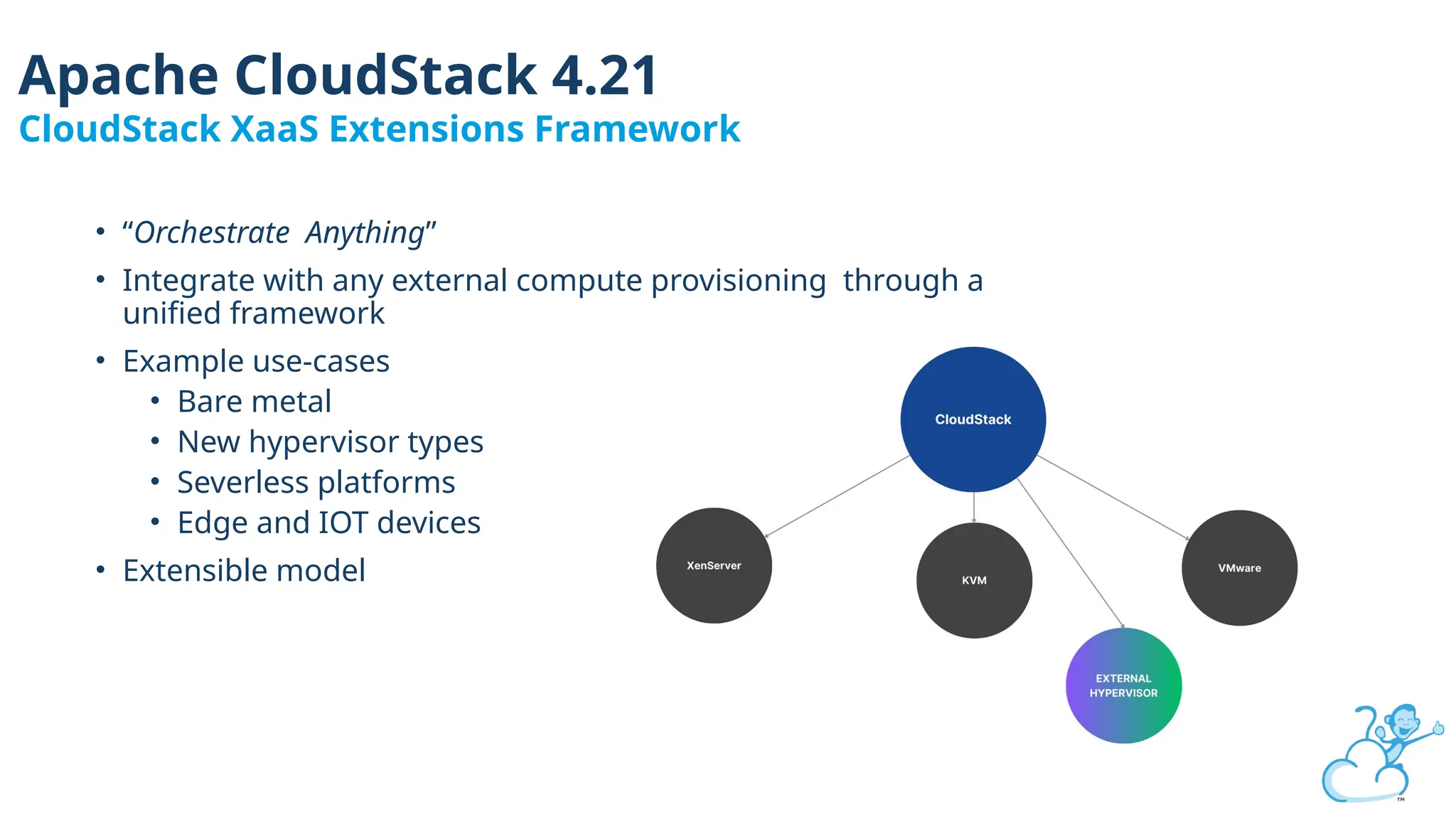
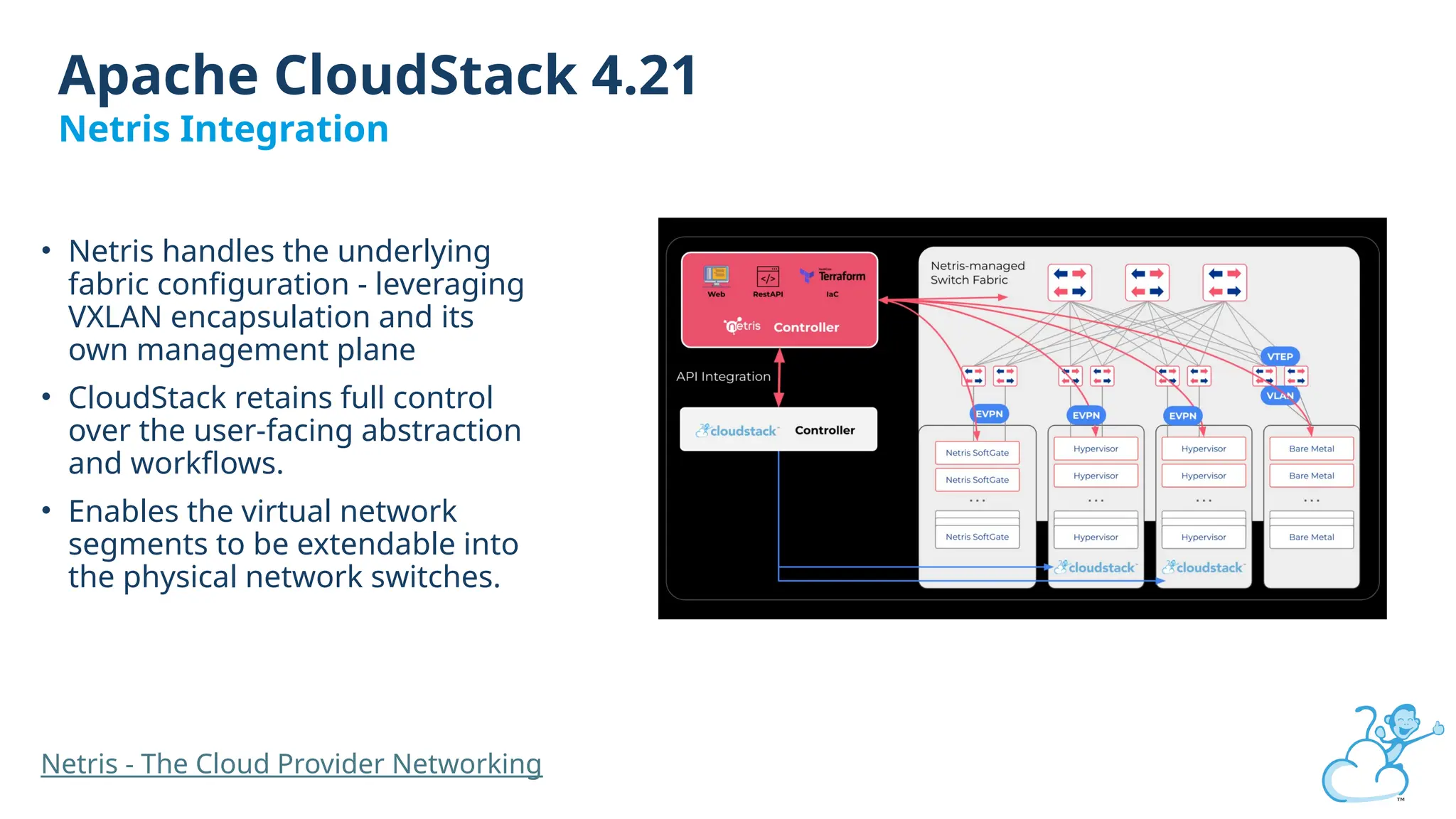
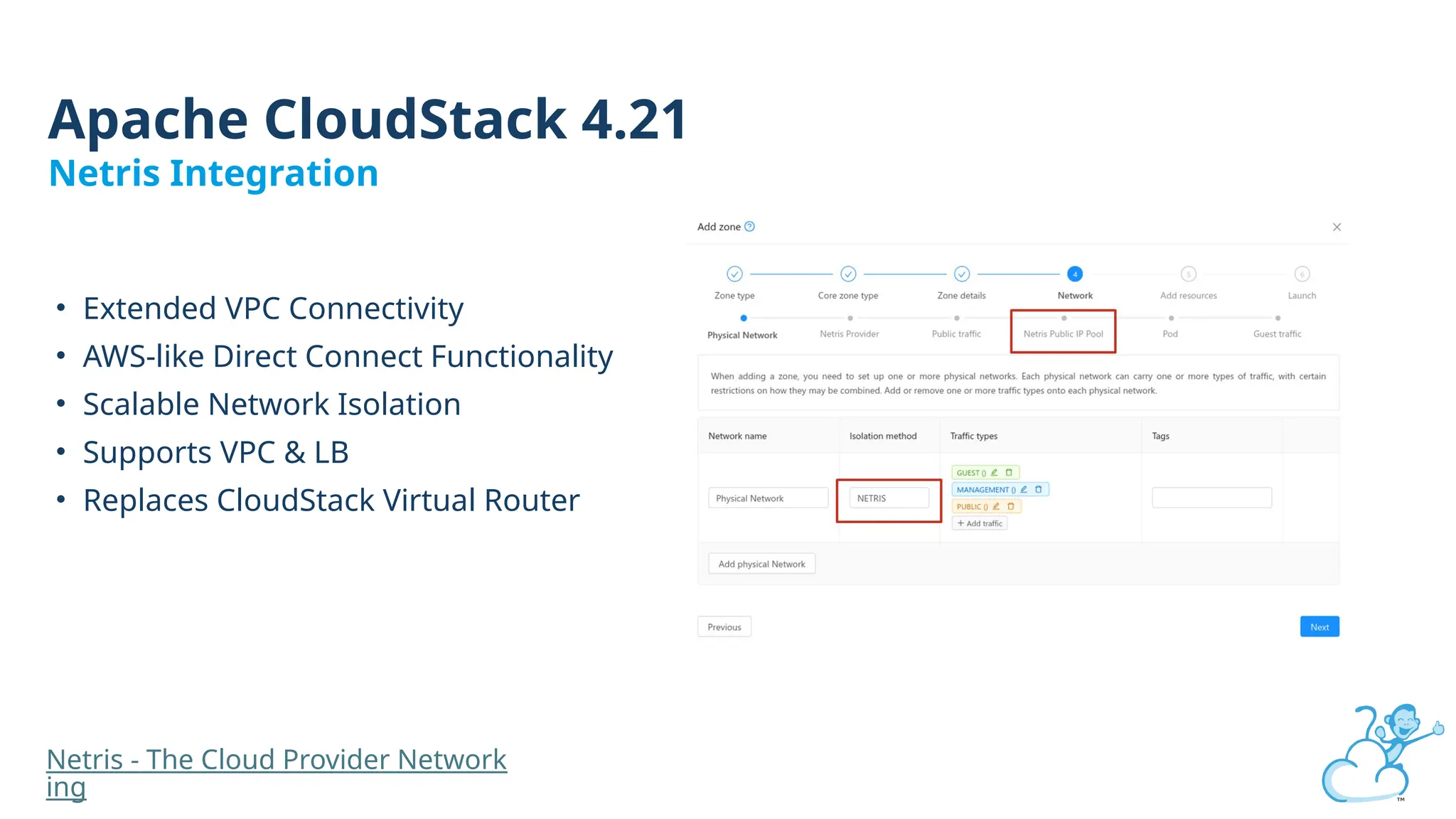
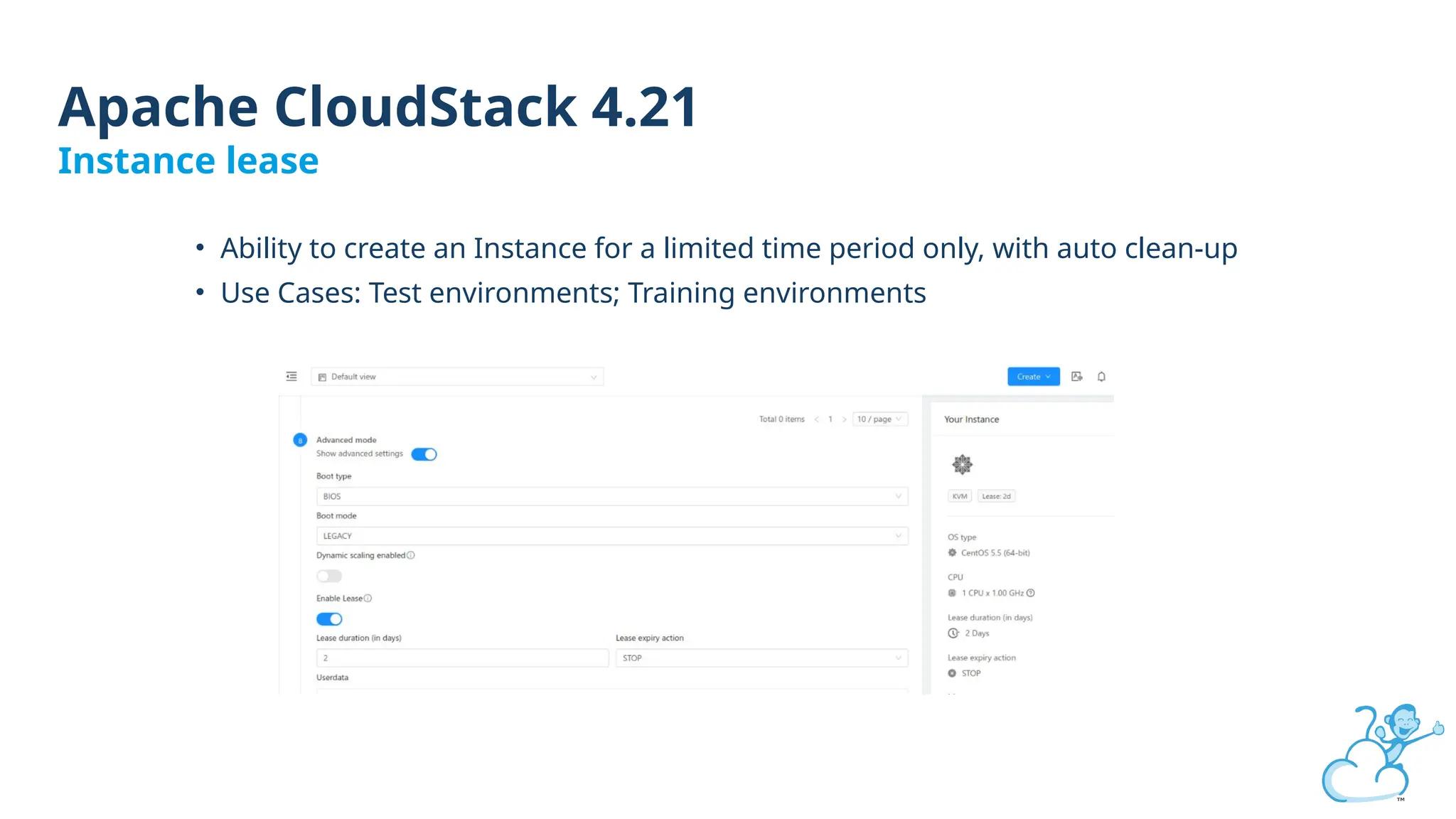
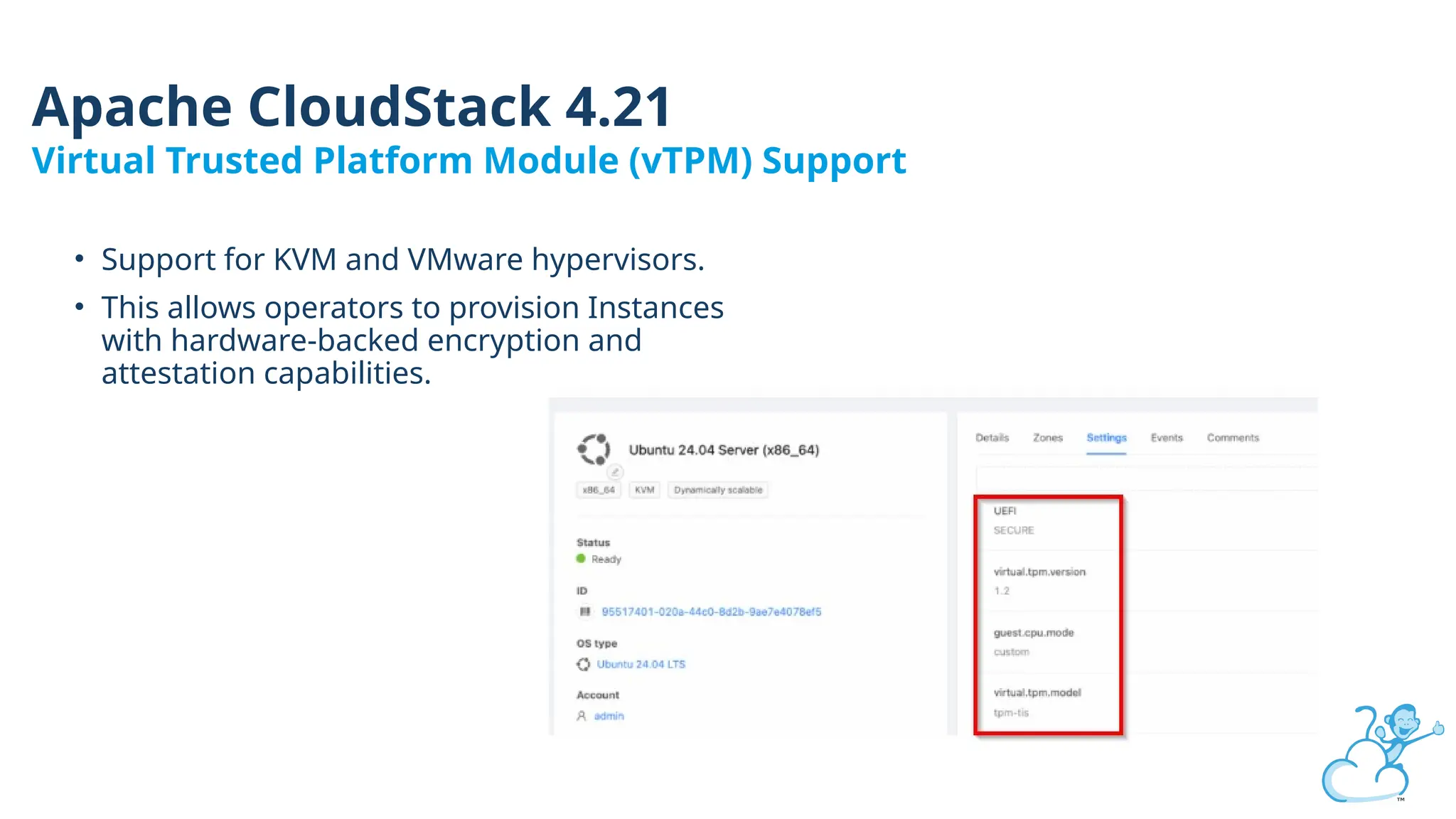
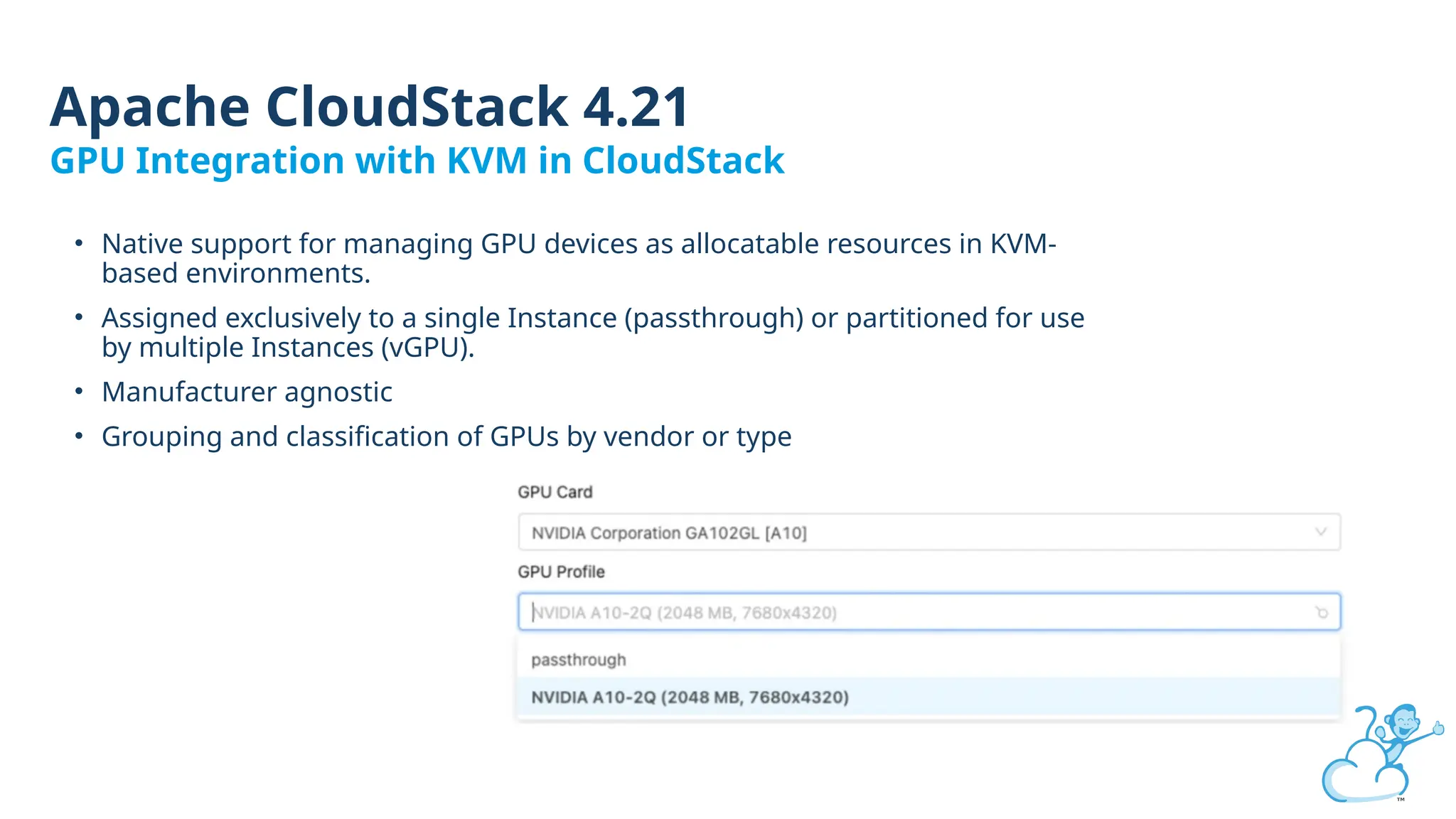
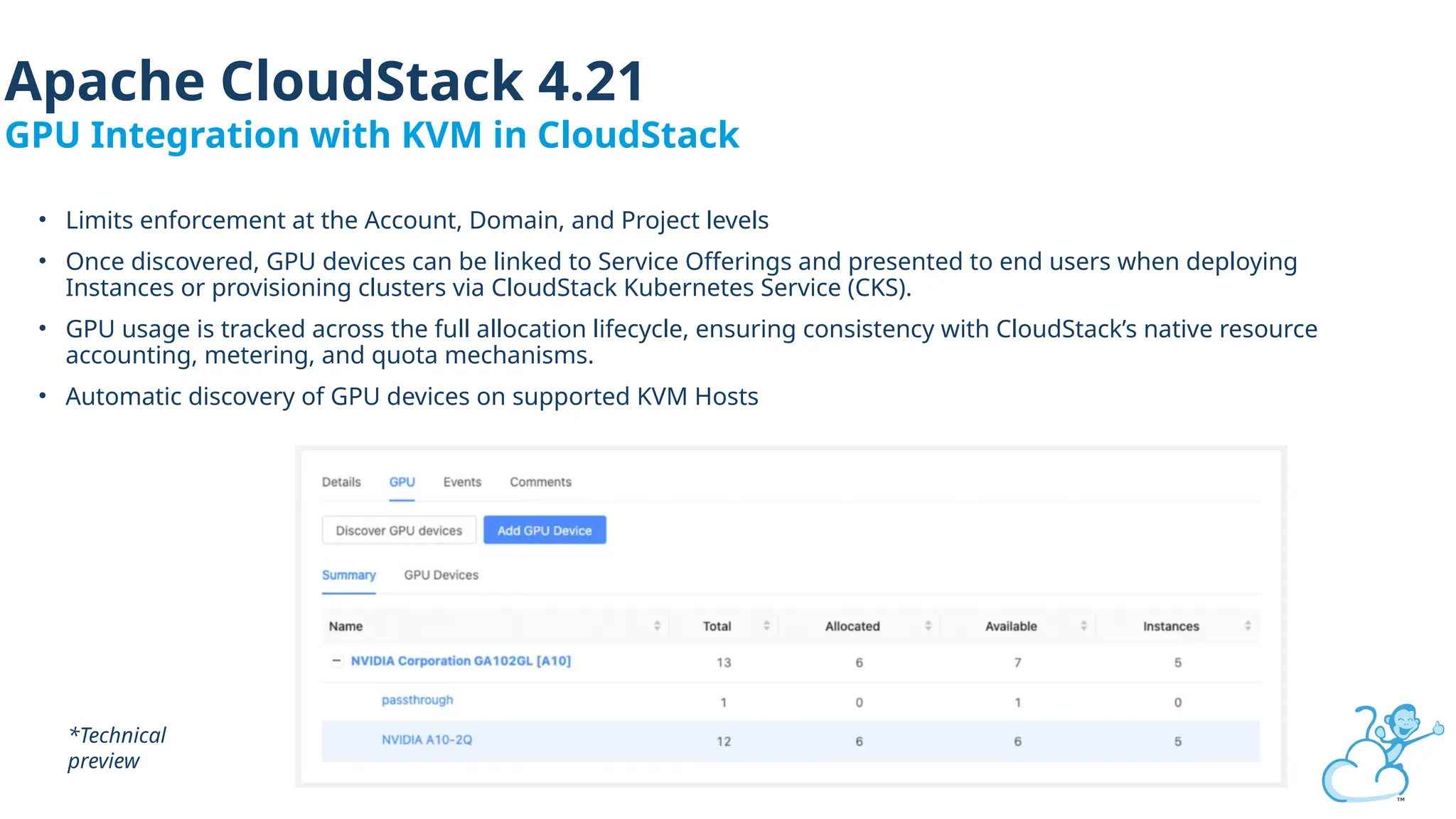
Steve's talk is about this group and the community, and also provides an introductory overview of CloudStack, covering its core features, architecture, and practical use cases. Attendees can gain insights into how CloudStack simplifies cloud orchestration, supports multiple hypervisors, and integrates seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure. He also presents the CloudStack news, talking through recent releases and new features.