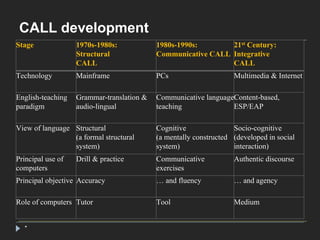
This document provides an introduction to ICT (Information and Communication Technology) and CALL (Computer-Assisted Language Learning). It defines the terms and discusses how CALL has evolved from mainly focusing on drills to more communicative and interactive approaches using newer technologies. It highlights how CALL has progressed from being text-based on mainframes to utilizing multimedia and the internet. The document concludes by listing some random tips for working with ICT/CALL, emphasizing the importance of problem-solving skills, pedagogical creativity, and keeping up with new technologies.