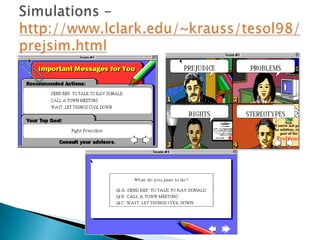
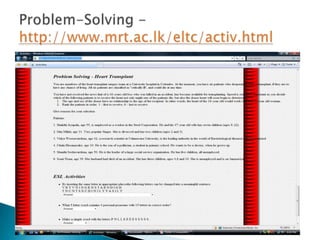
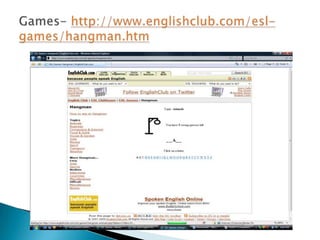
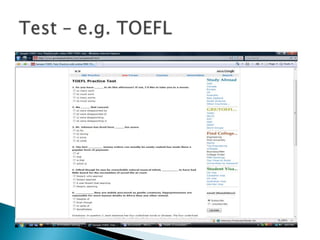
Computer-assisted language learning (CALL) involves using computers to support and enhance language teaching and learning. CALL encompasses issues related to materials design, technologies, pedagogical theories, and modes of instruction. CALL materials can be either generic software adapted for language learning, or software designed specifically for language learning. The history of CALL began in the 1960s with mainframe computers used for drill-and-practice activities. CALL expanded in the 1980s with the rise of microcomputers and word processing. Today, CALL utilizes various technologies like the Internet, blogs, podcasts, and more. Related disciplines include human-computer interaction, instructional technology, psychology, and applied linguistics.