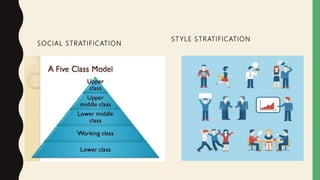
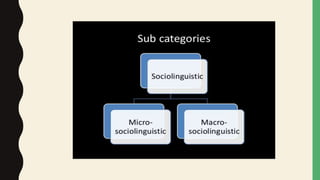
This document discusses key topics in sociolinguistics including language shift, language death, markers, and micro/macrosociolinguistics. It provides definitions and examples of language shift, where a community gradually abandons its original language for another, often occurring over 3-4 generations through a stage of bilingualism. Language death is the end point of shift when a language has no remaining native speakers. Markers are linguistic variables that correlate with social groups and speech styles. Microsociolinguistics examines language in relation to society at a small scale while macrosociolinguistics looks at larger societal behaviors and impacts on language.