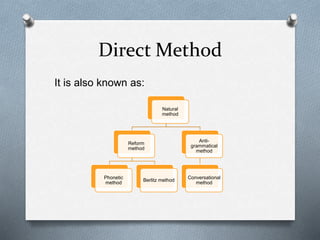
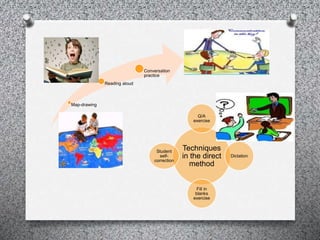
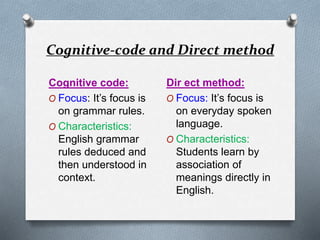
The Direct Method, developed in the late 19th century by figures like Maximilian Berlitz, emphasizes teaching a foreign language through oral skills and direct association with meaning, rather than translation. It advocates for an immersive approach that avoids grammar-focused instruction and encourages the use of simple vocabulary and situational grammar teaching. While effective for promoting speech and contextual learning, it requires skilled teachers and can be challenging to implement in public schools.