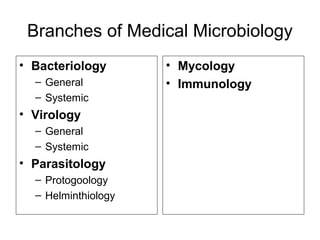
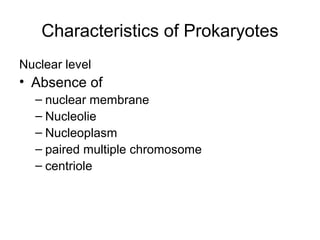
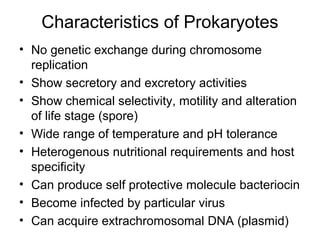
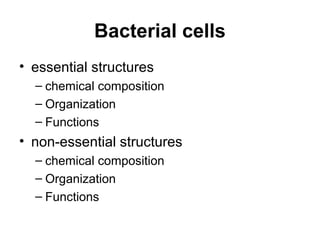
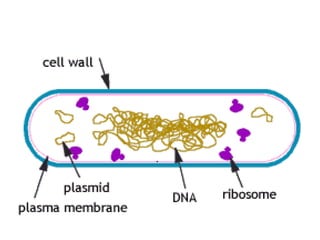
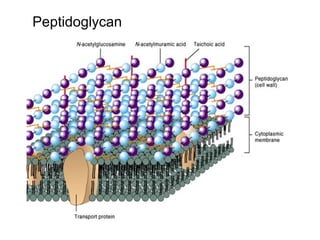
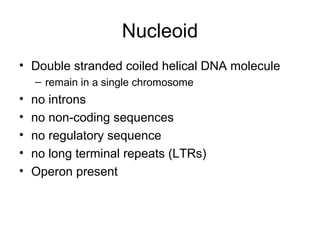
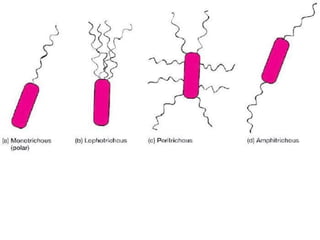
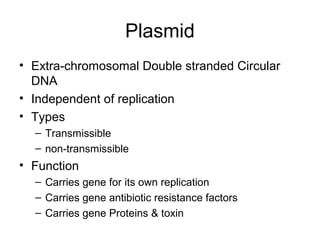
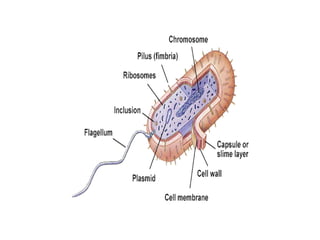
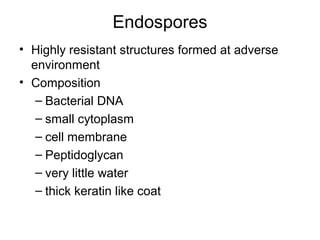
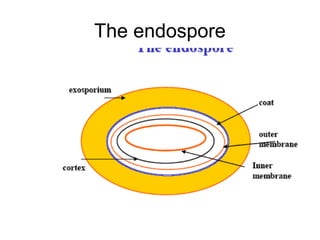
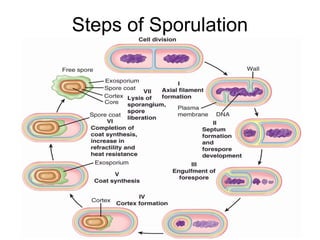
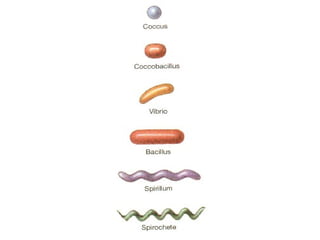
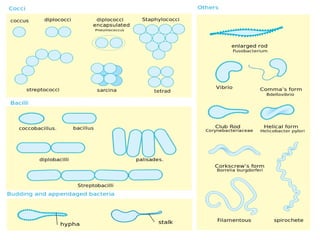
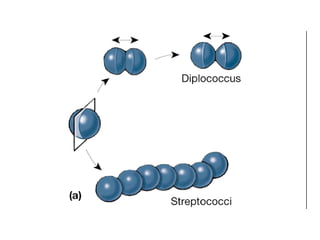
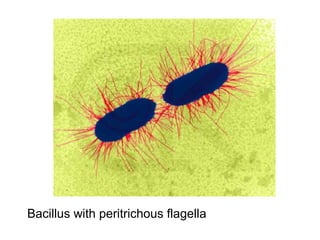
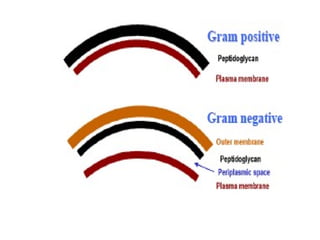
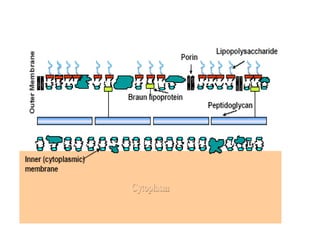
Medical Microbiology introduces important events in the history of microbiology such as the discovery of microbes by Anton van Leeuwenhoek in 1674. It discusses Koch's postulates for identifying pathogenic microbes and the branches of medical microbiology including bacteriology, virology, parasitology, and mycology. The document also describes the key structural differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and the essential and non-essential structures of bacterial cells such as the cell wall, cell membrane, flagella, and endospores.