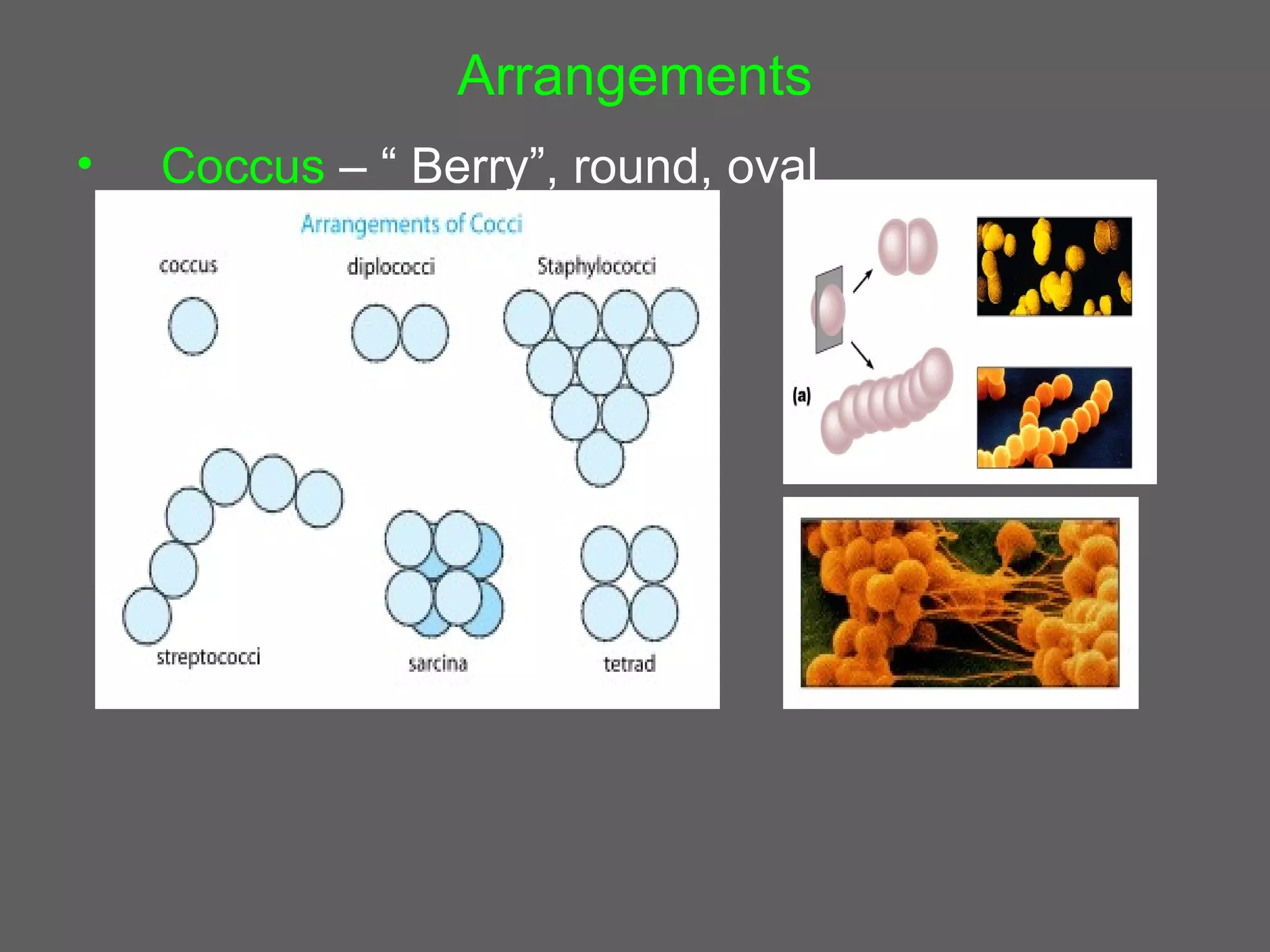
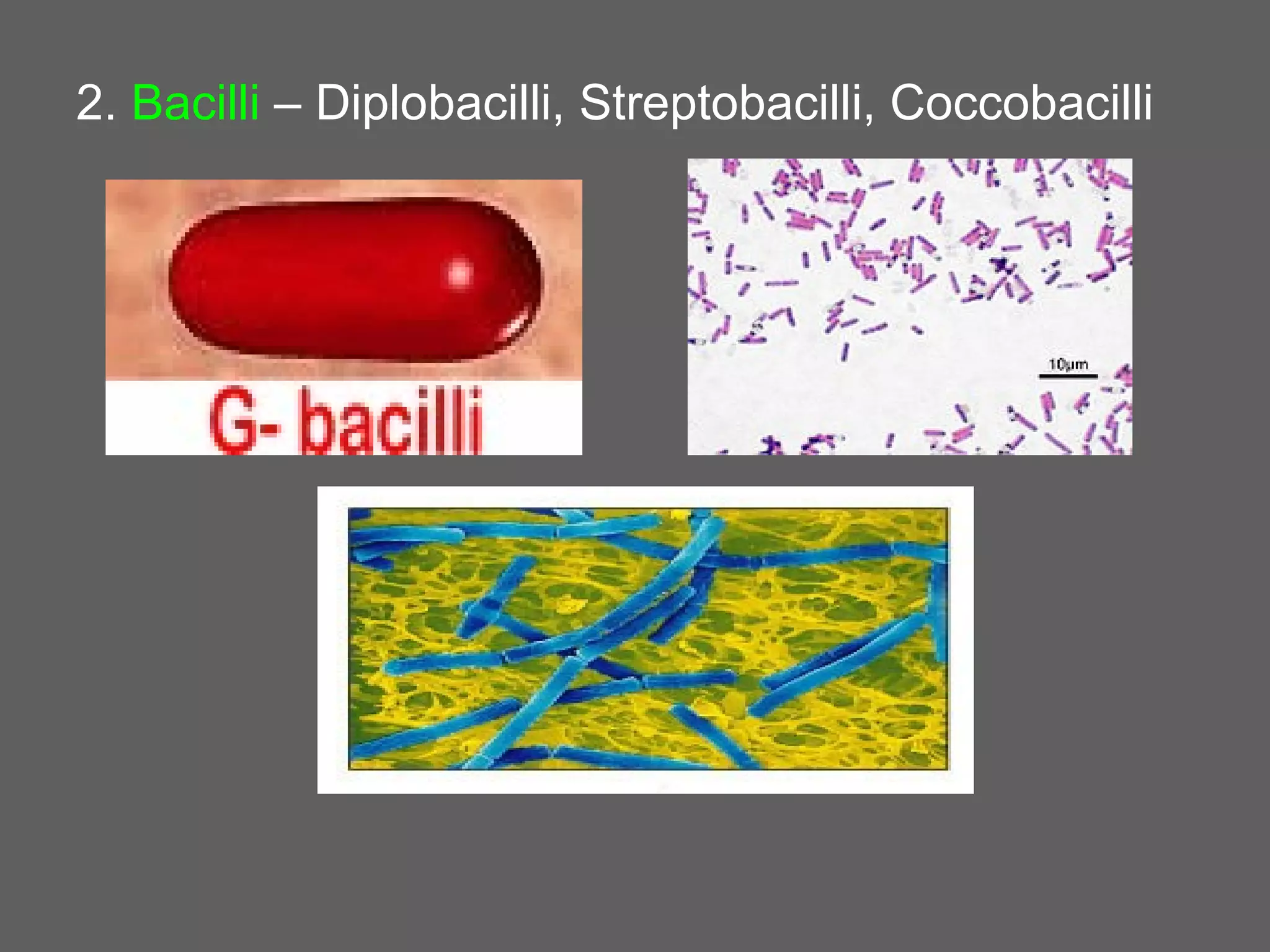
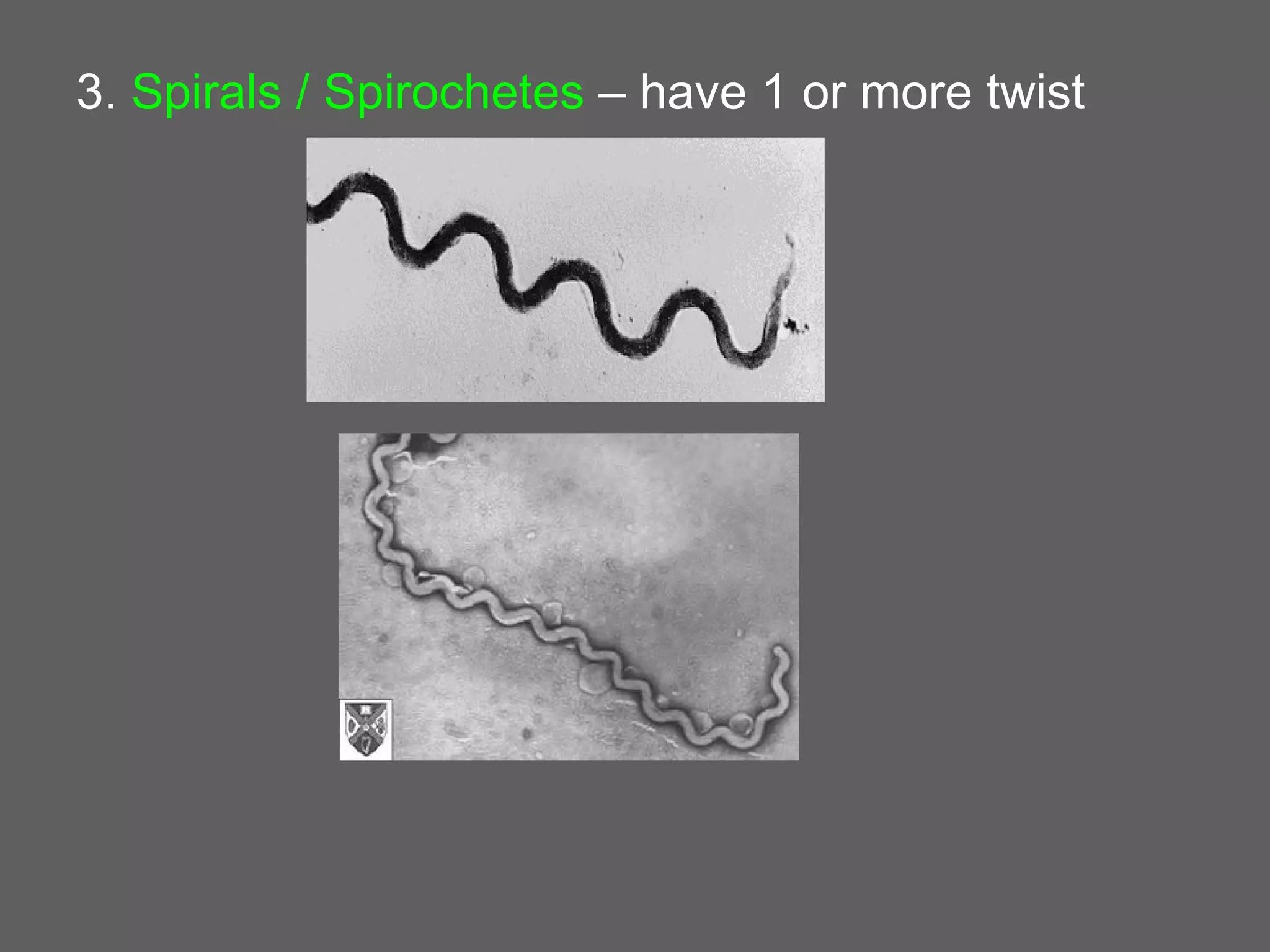
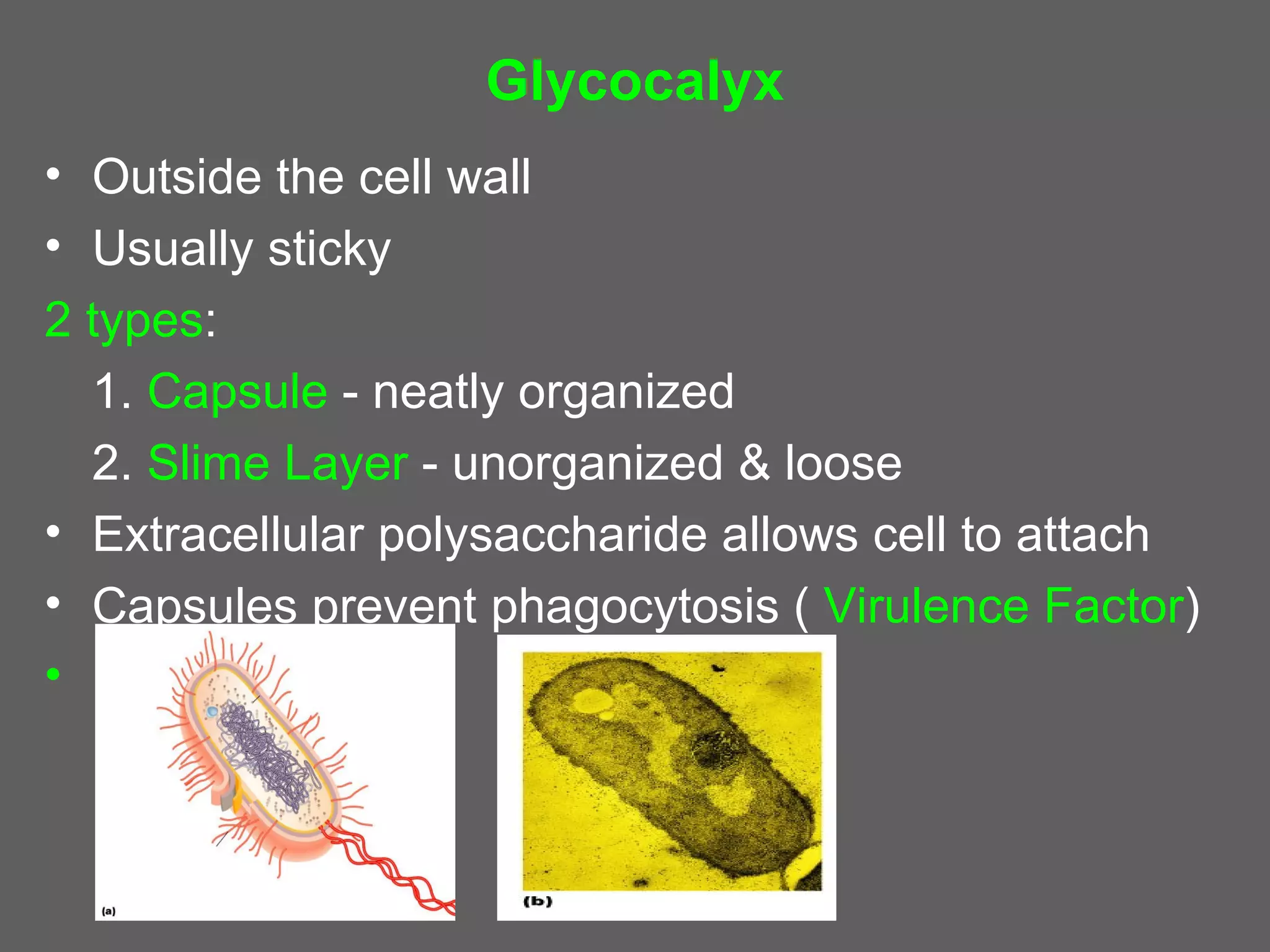
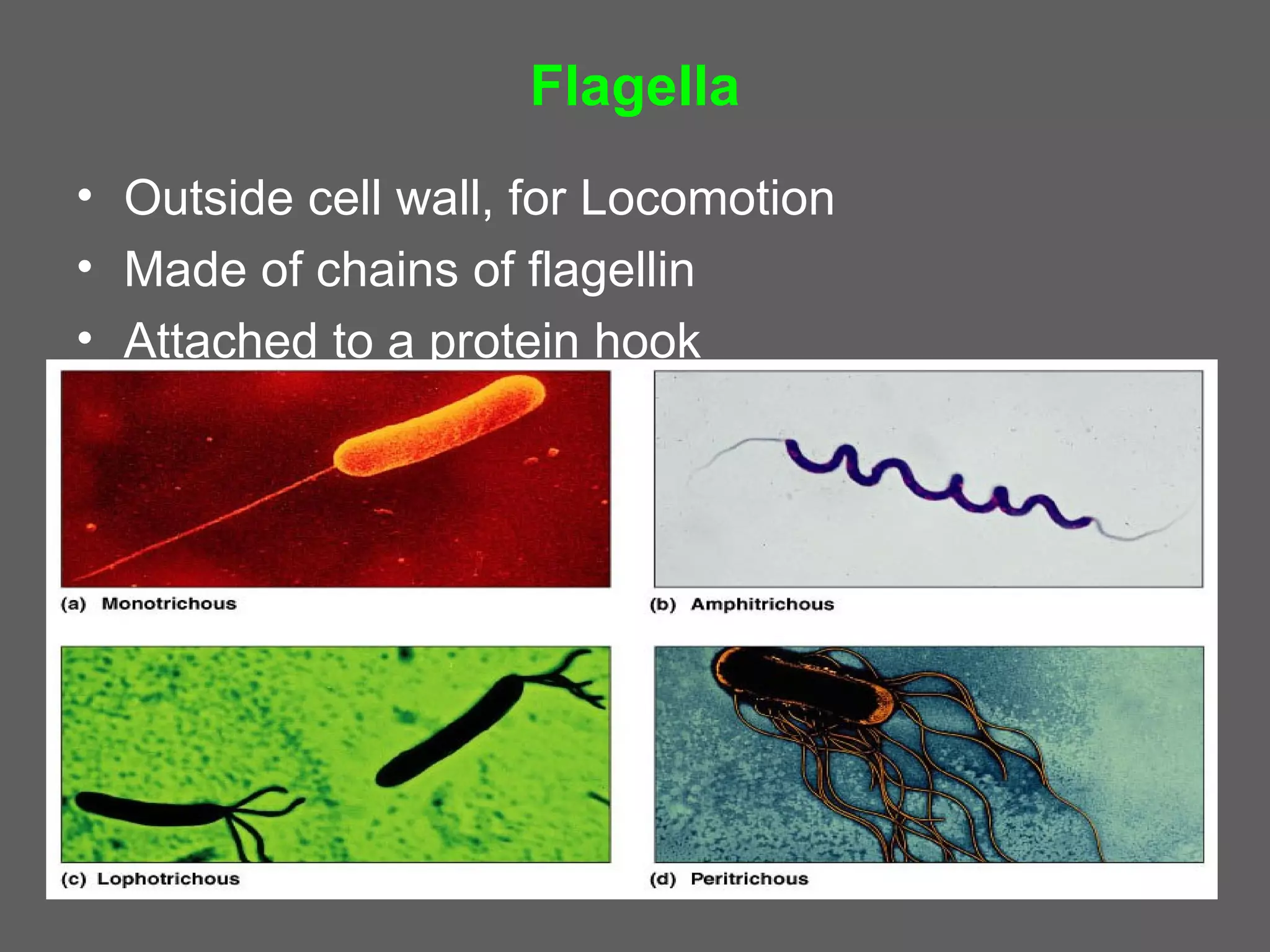
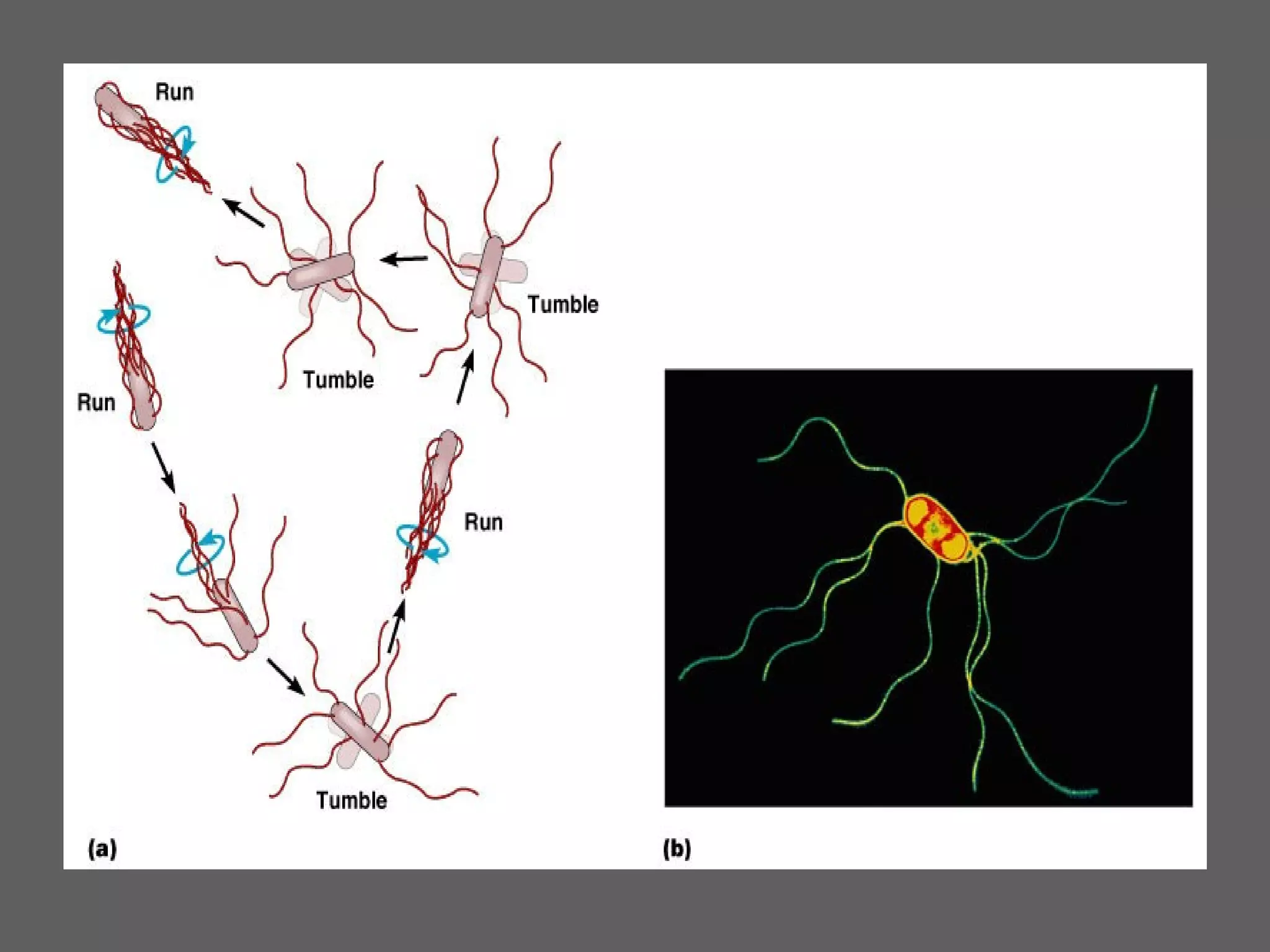
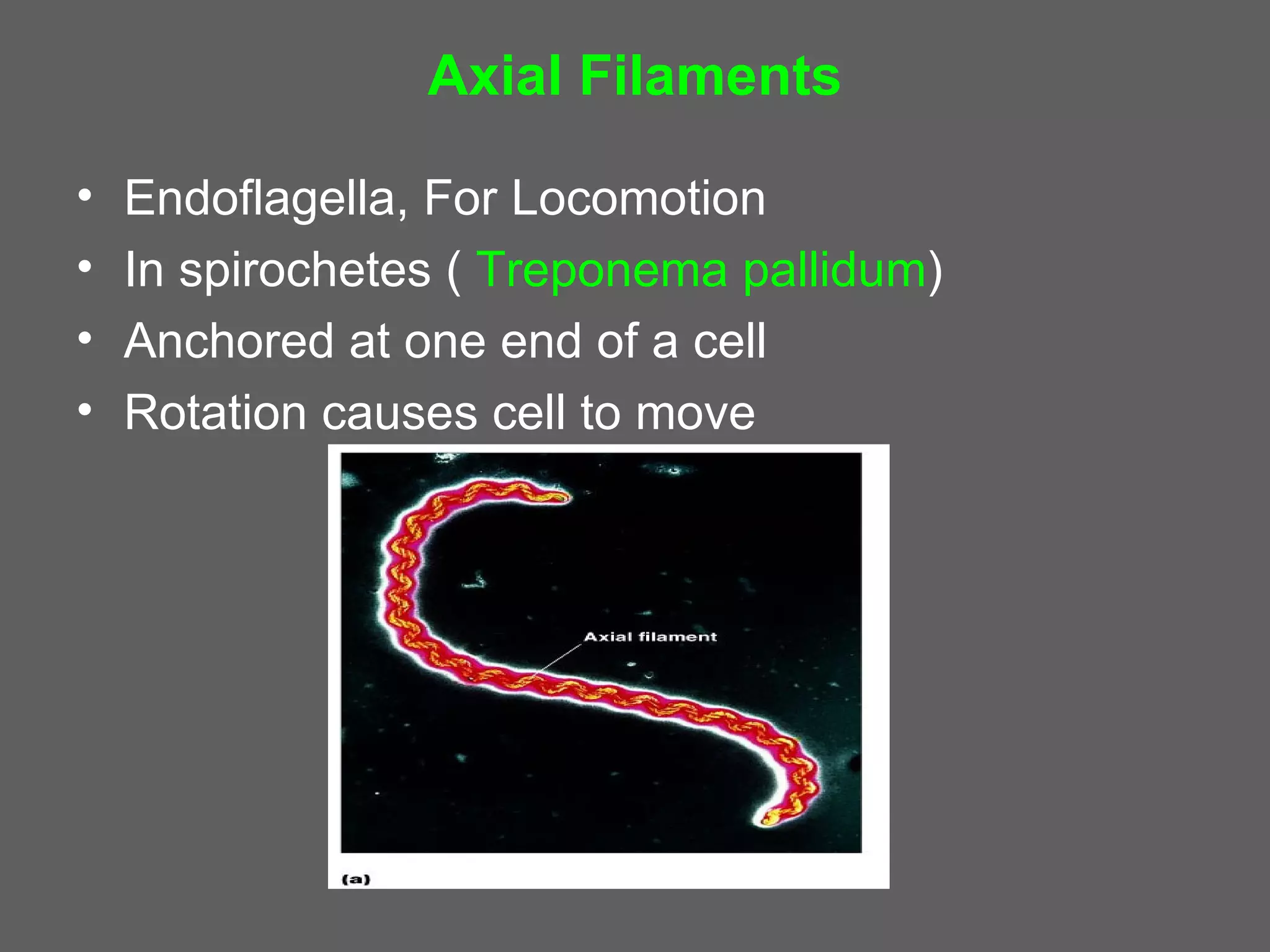
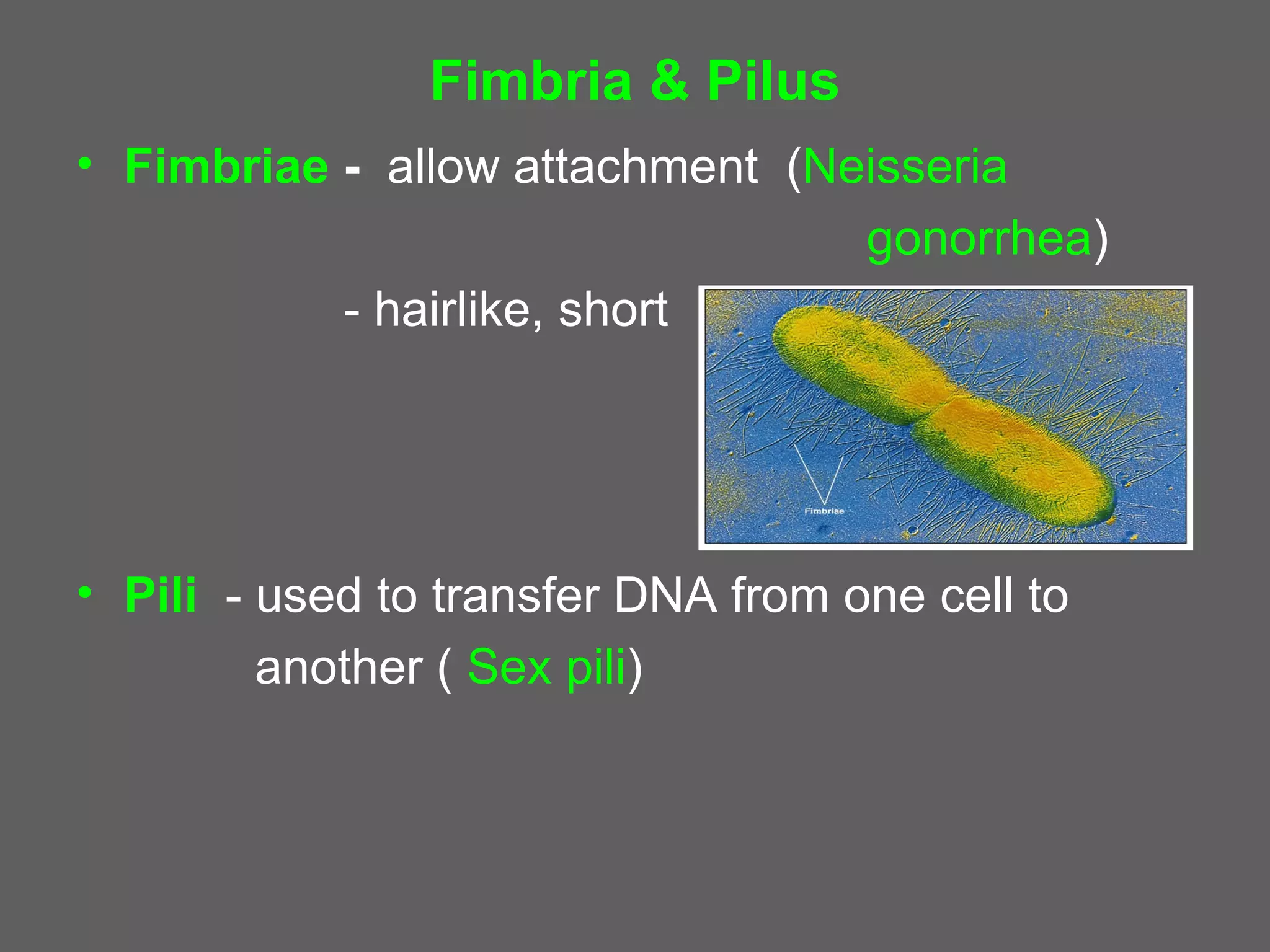
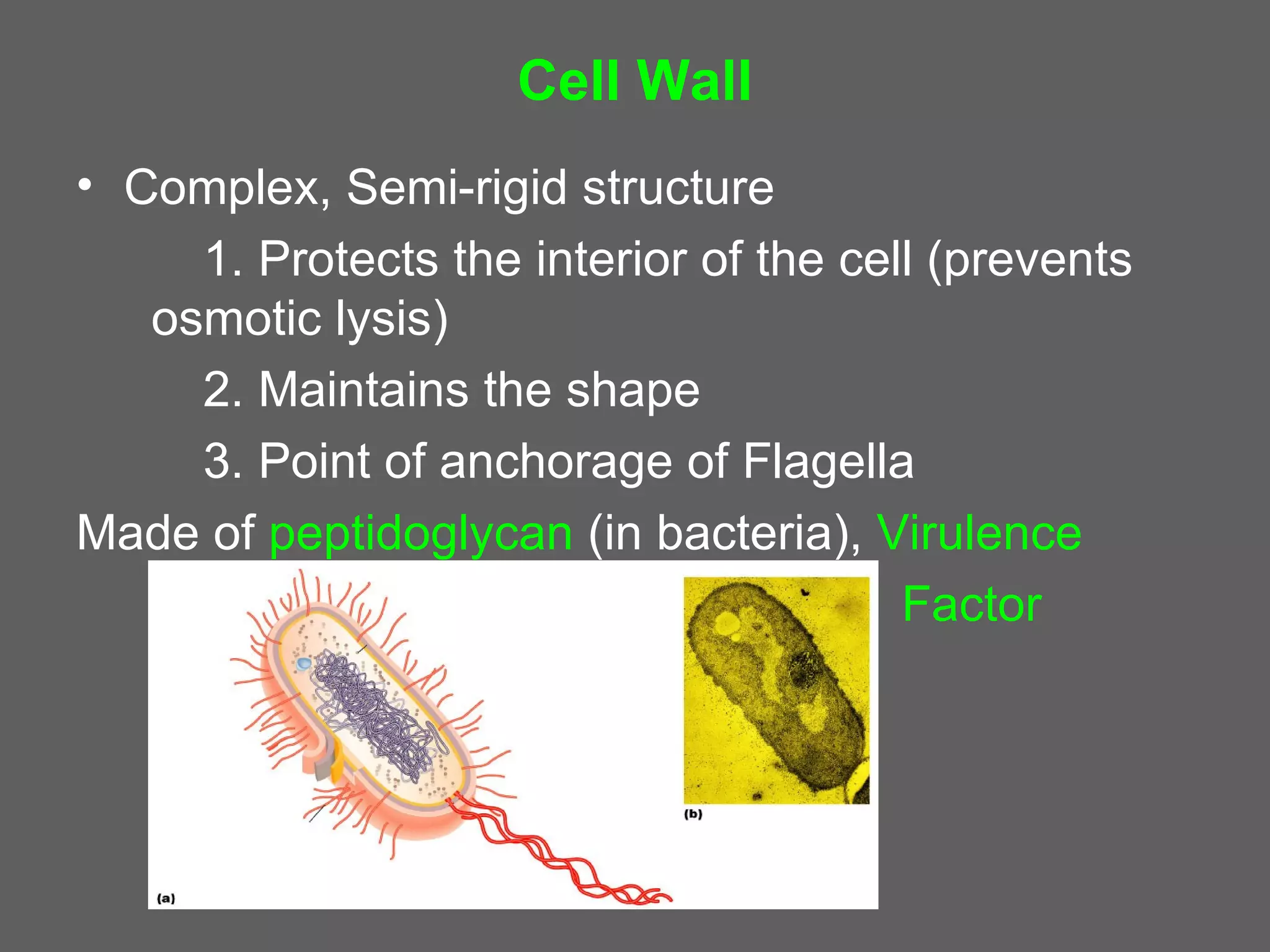
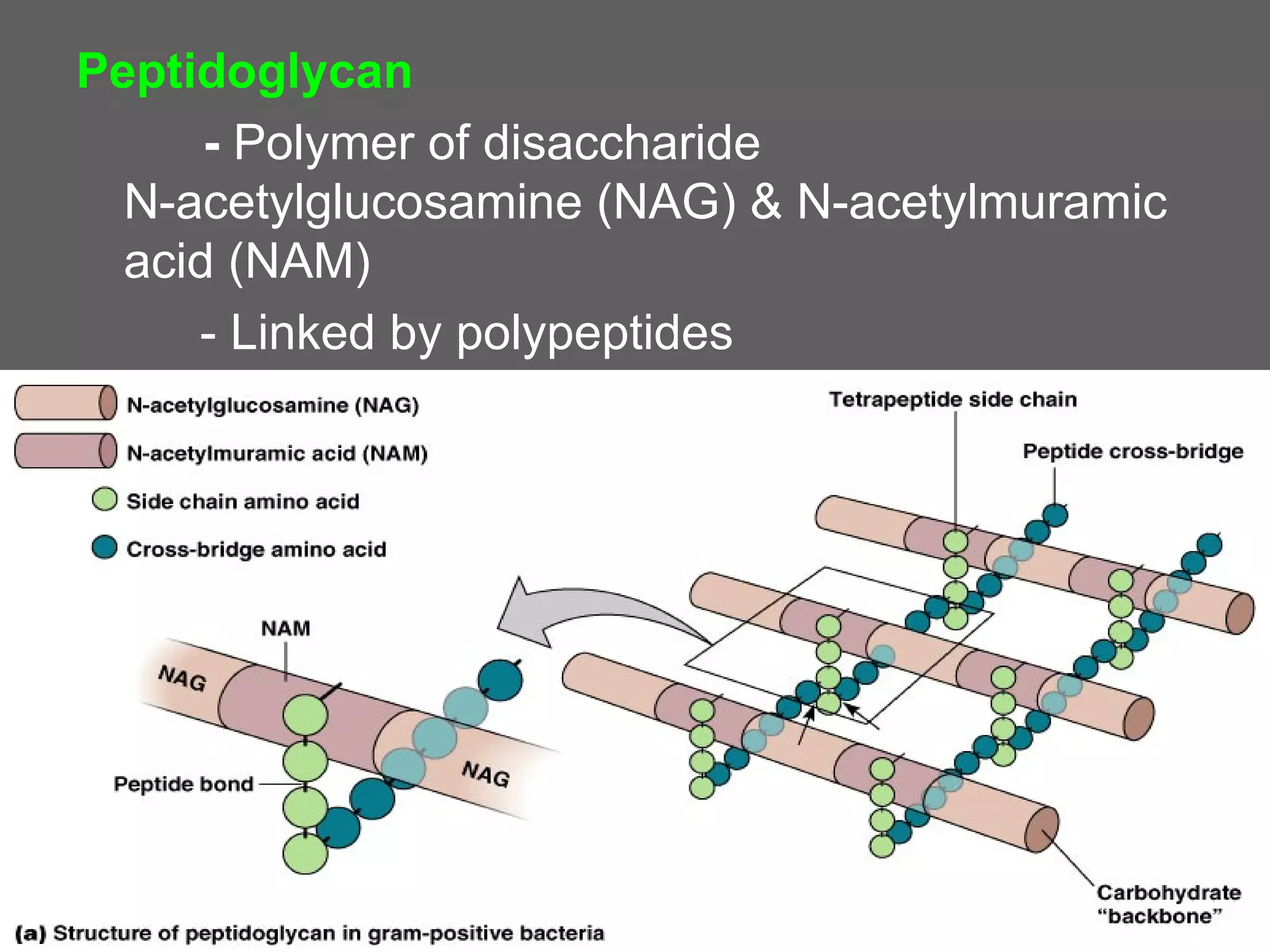
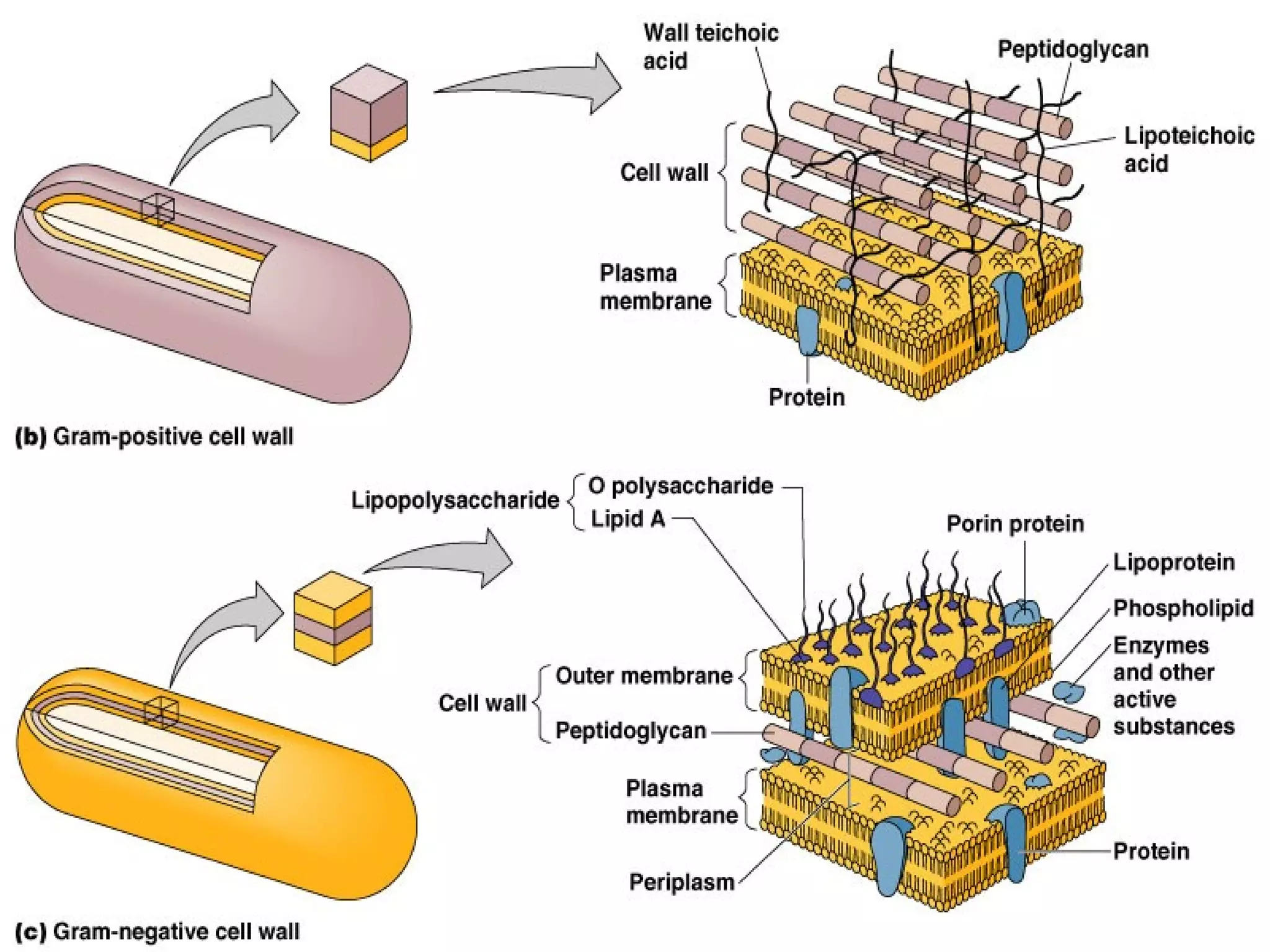
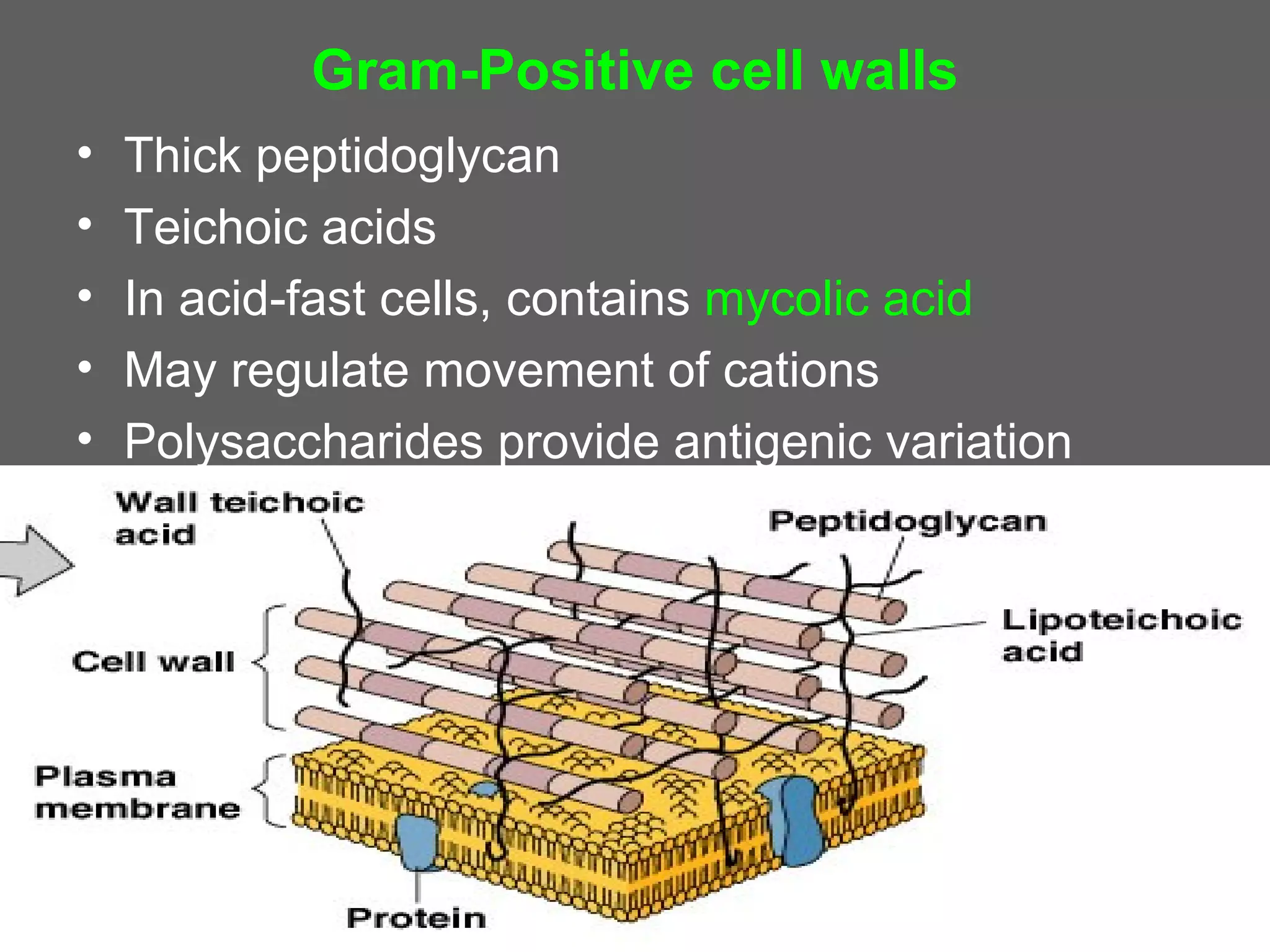
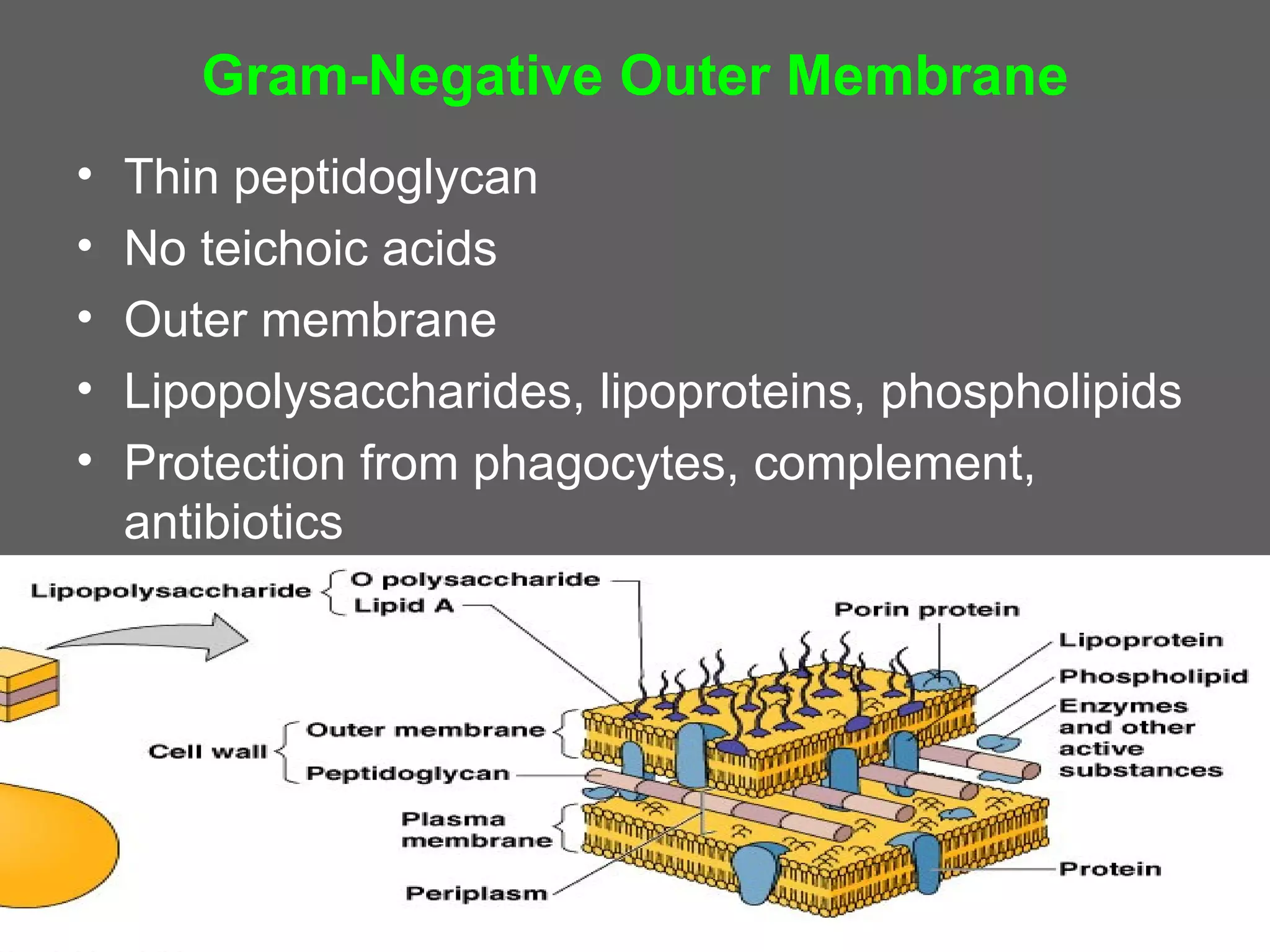
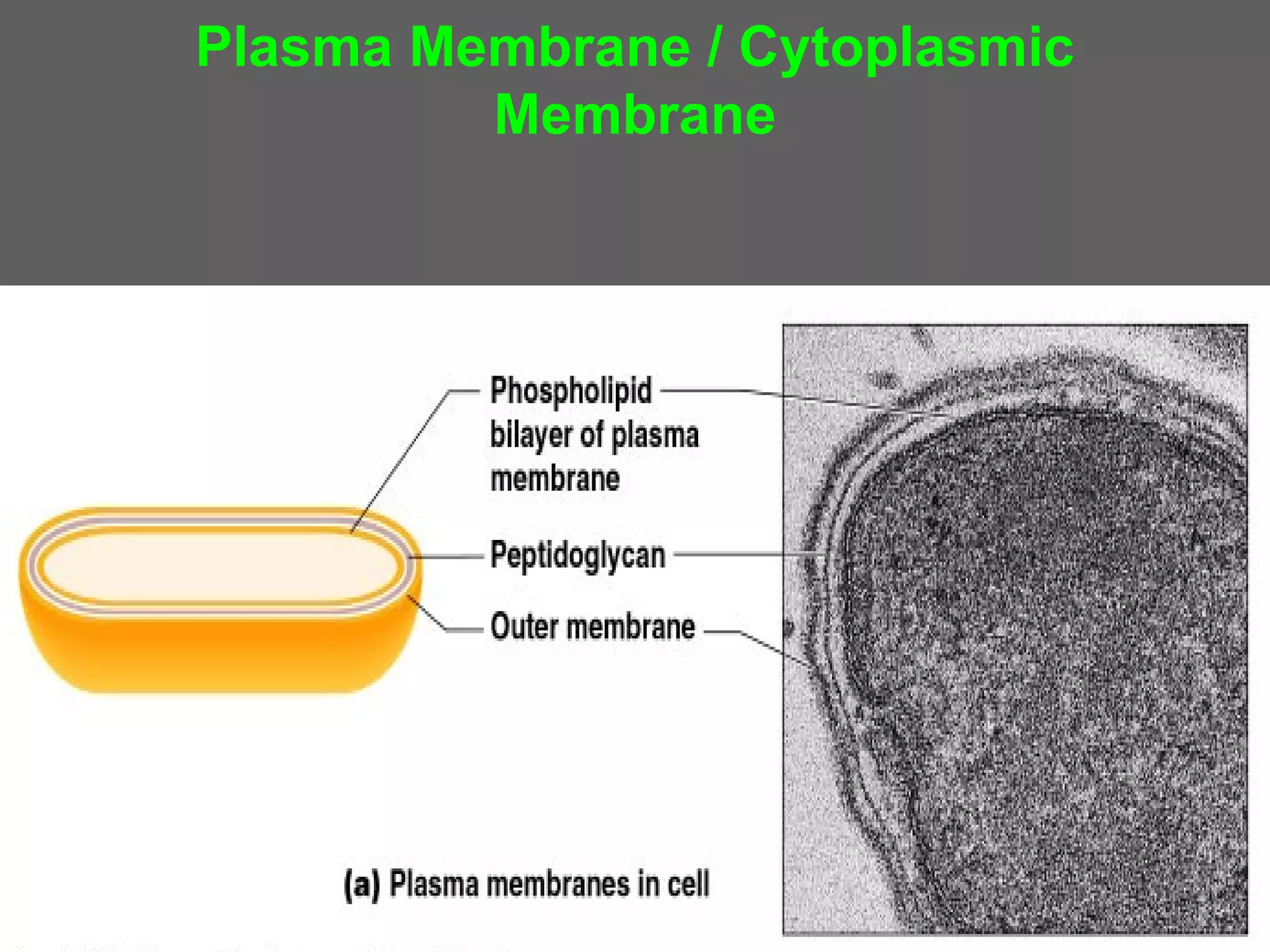
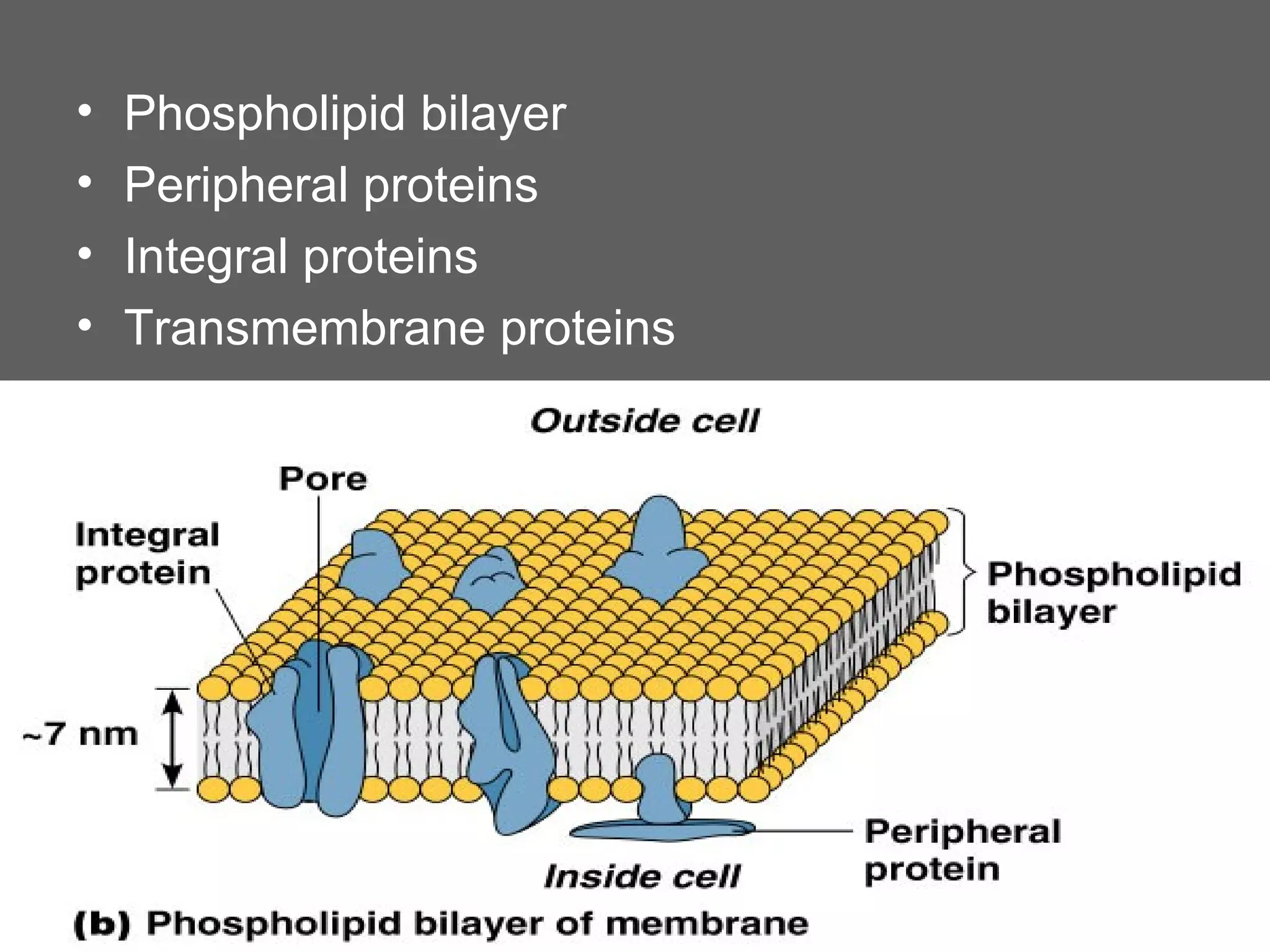
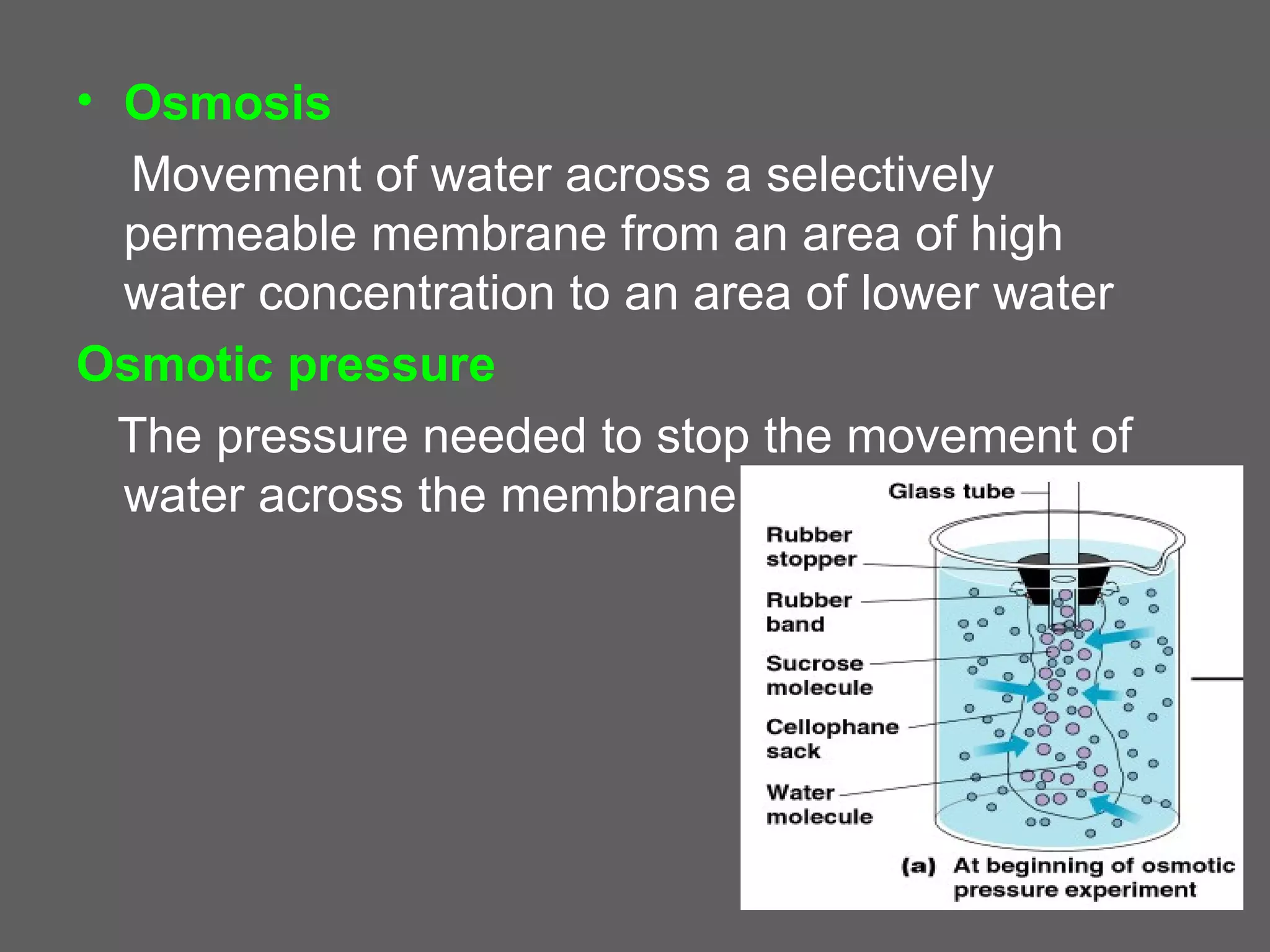
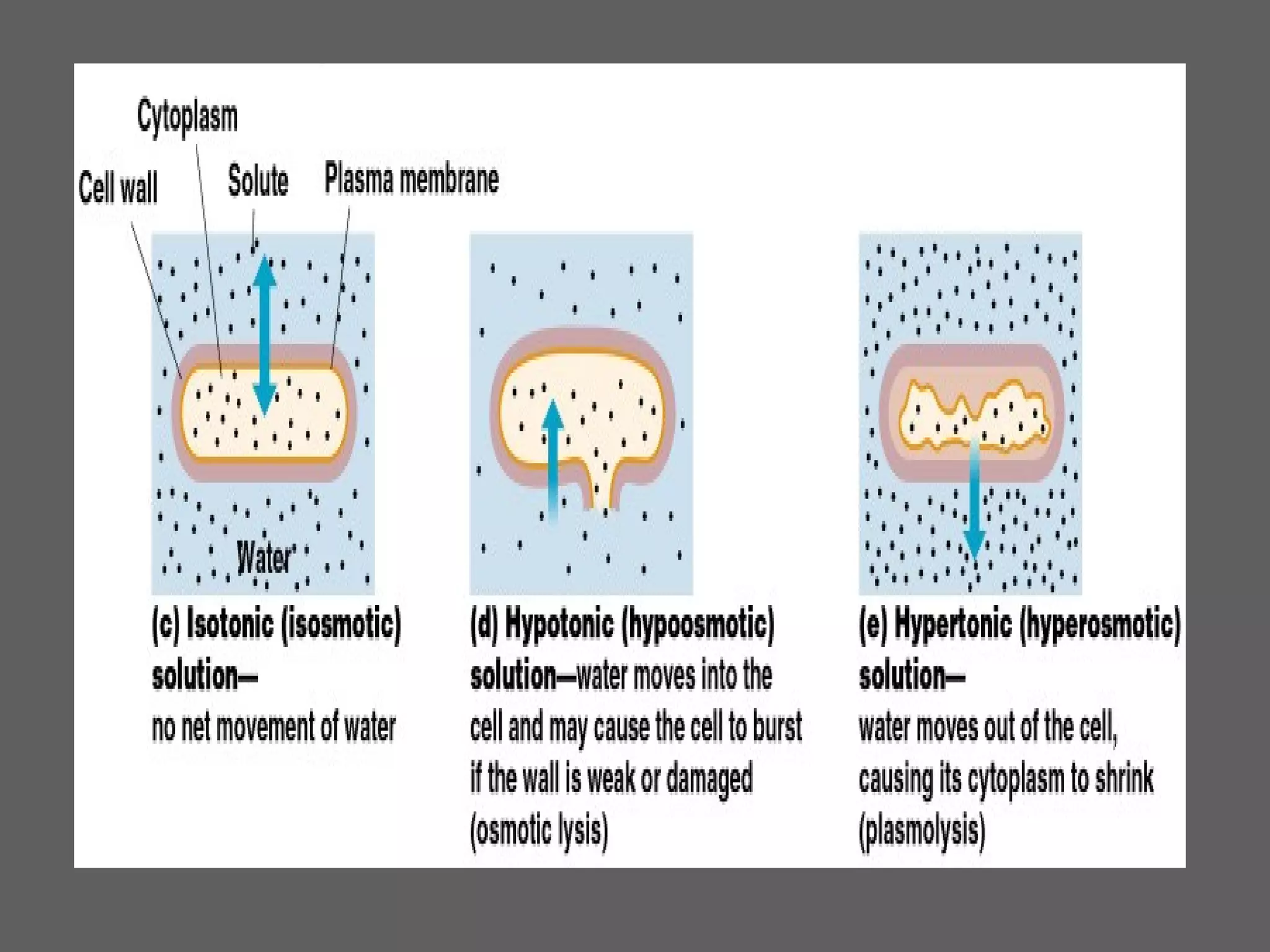
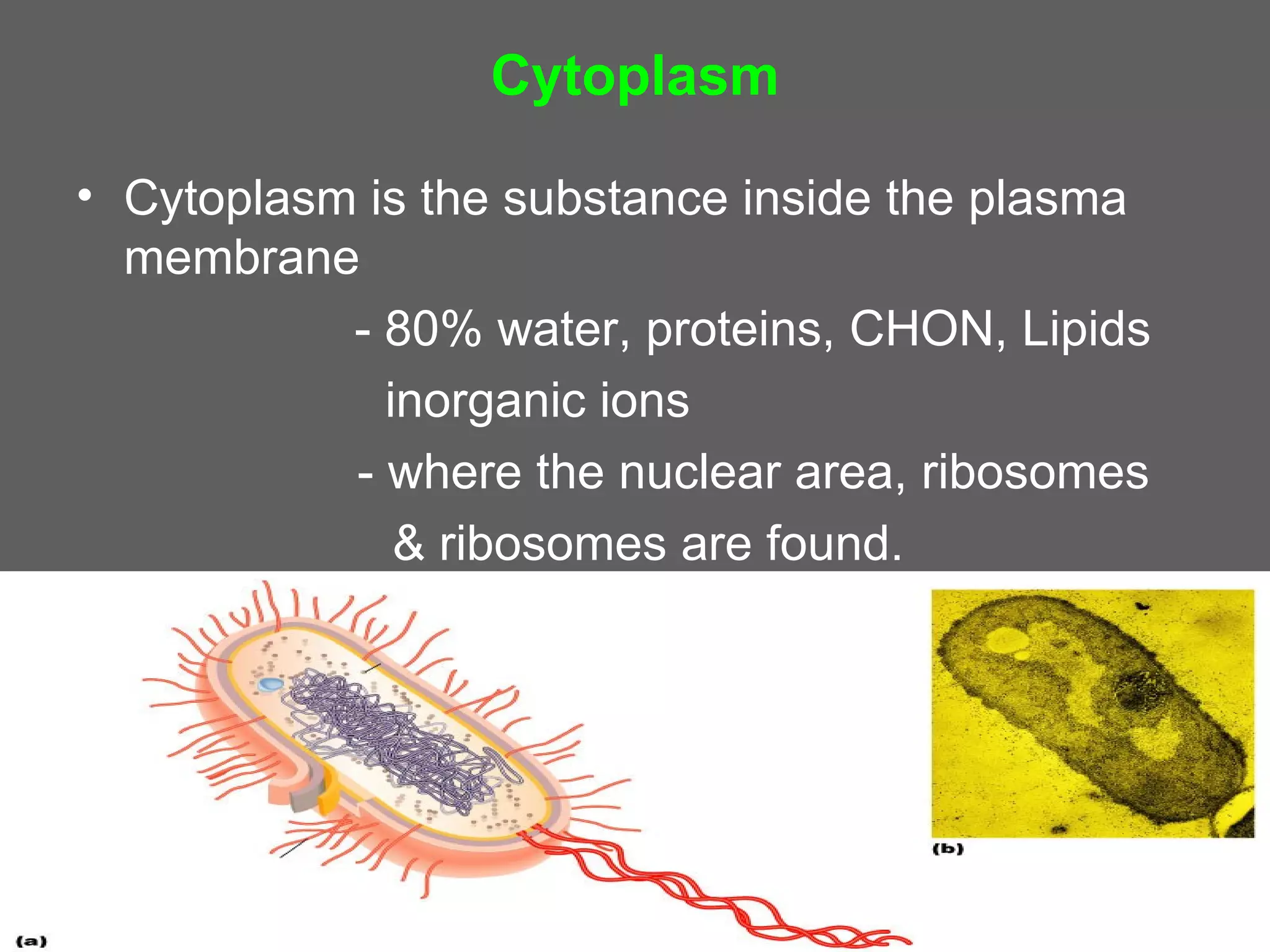
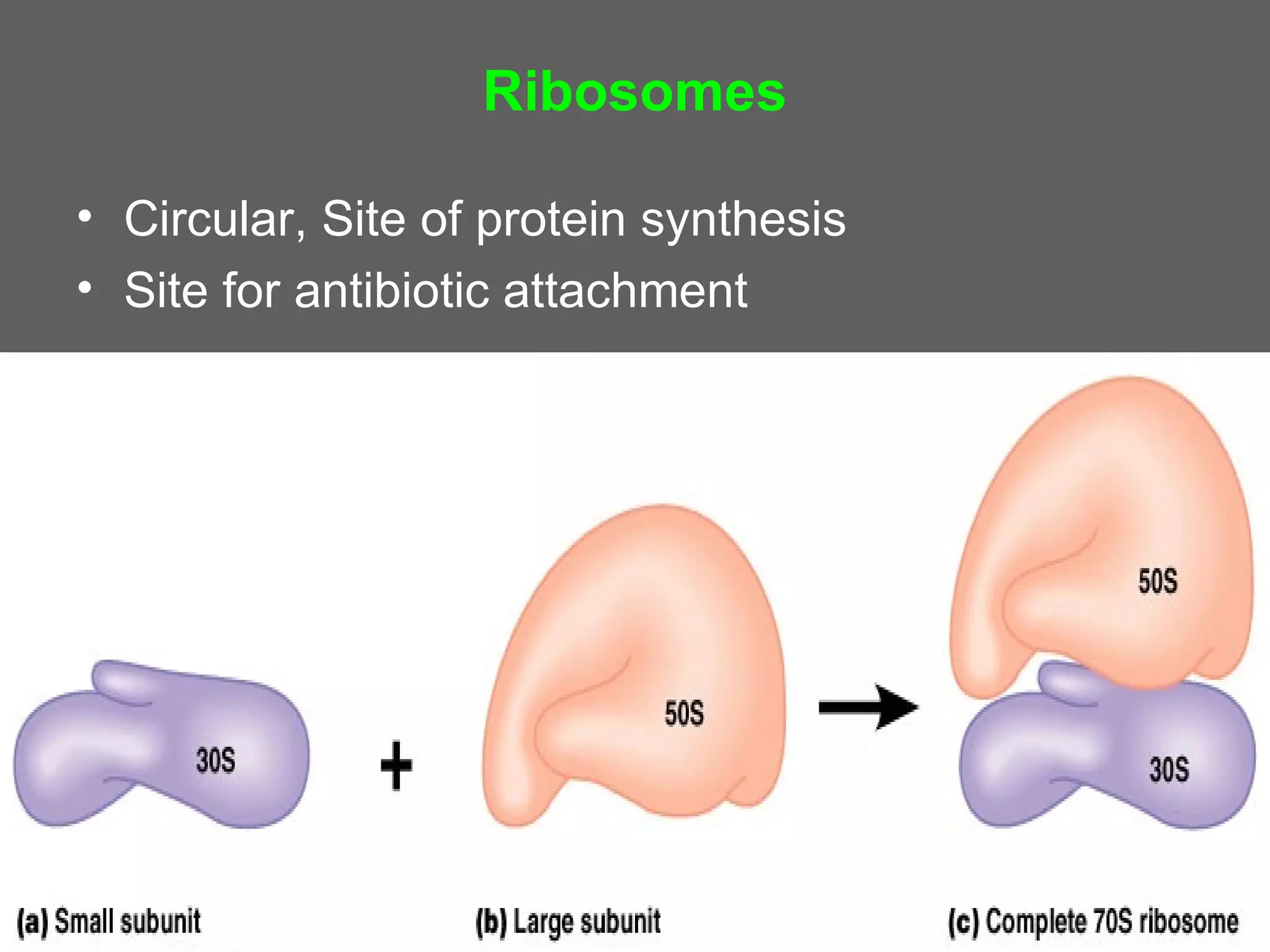
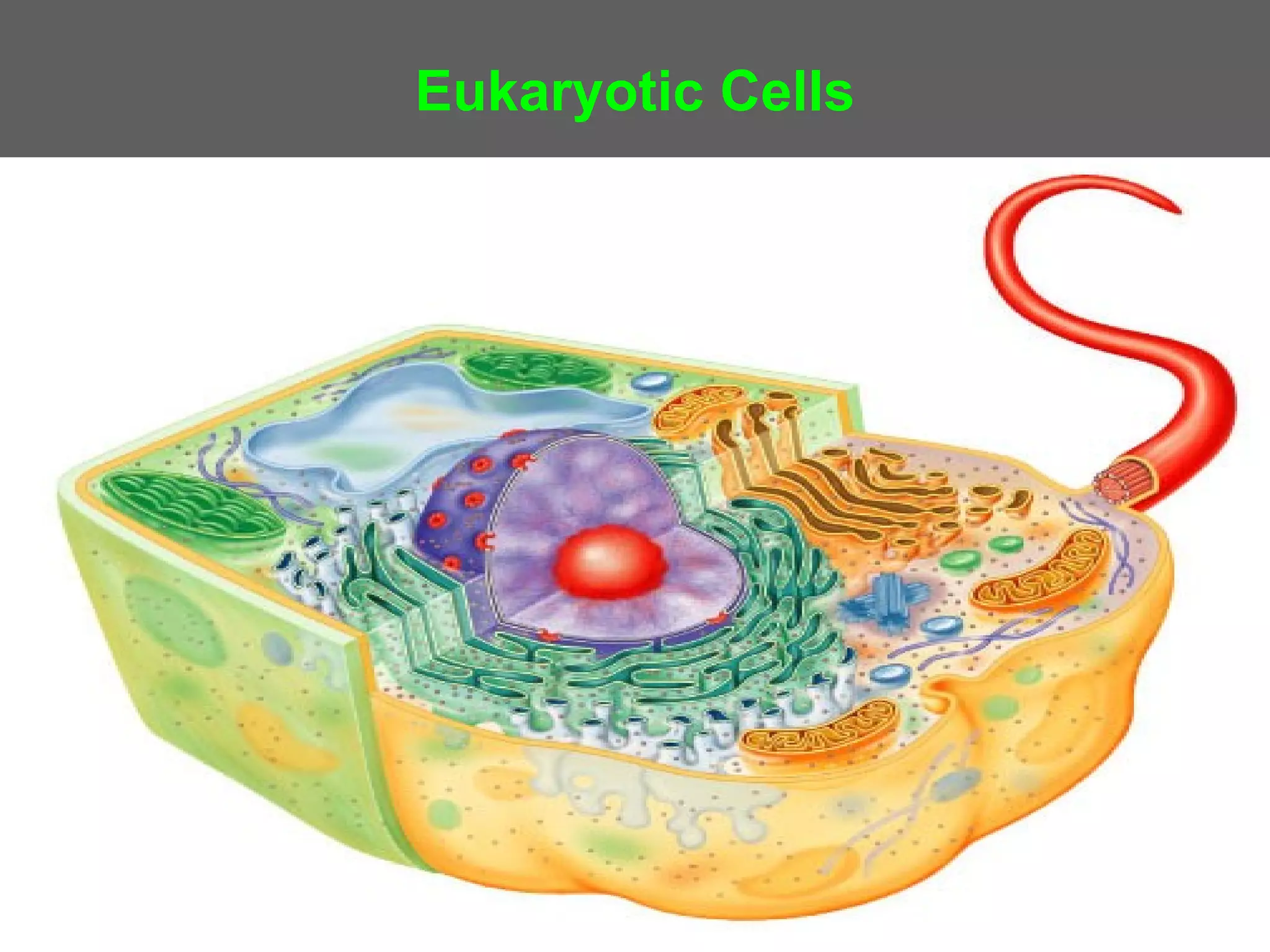
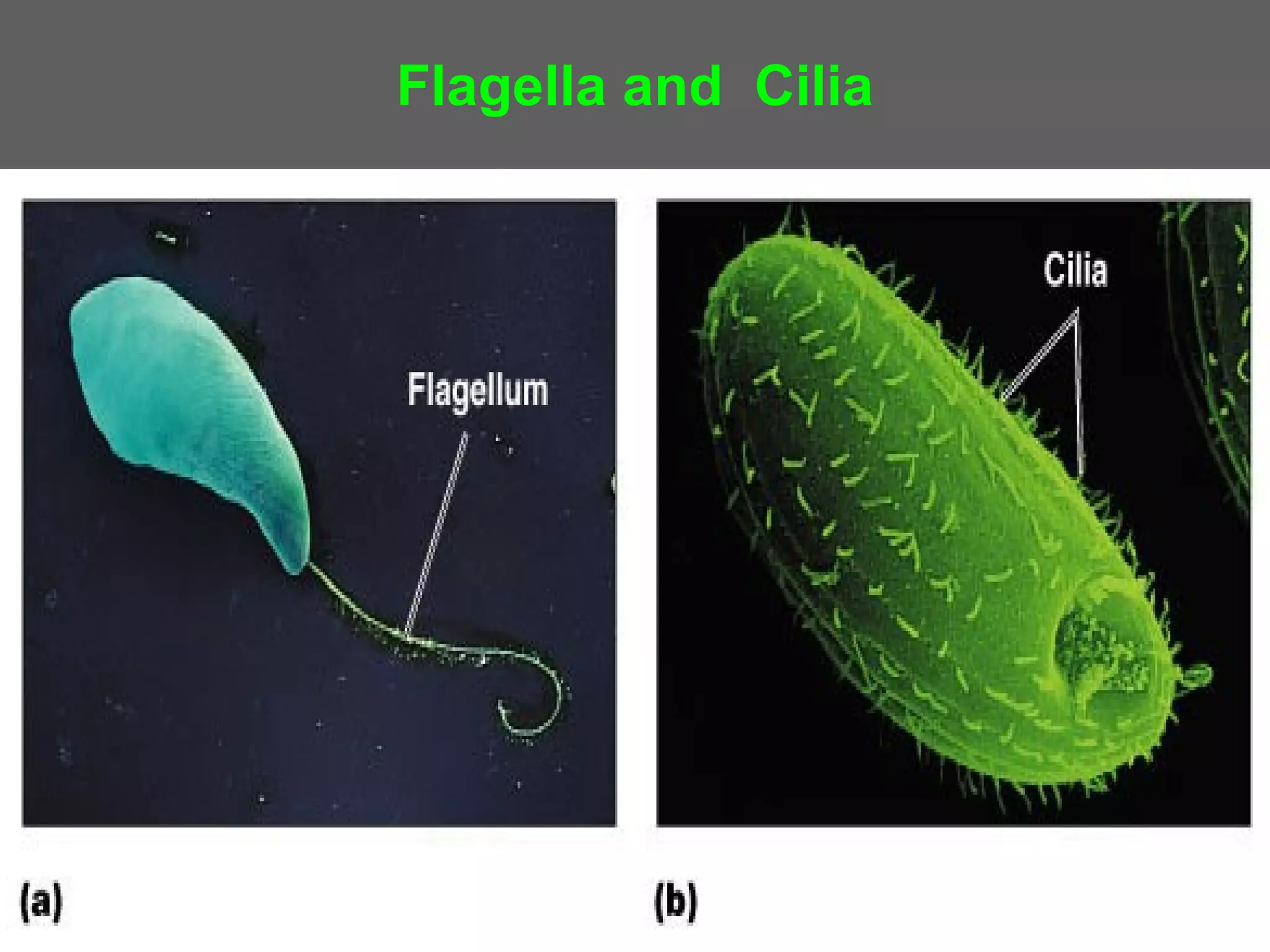
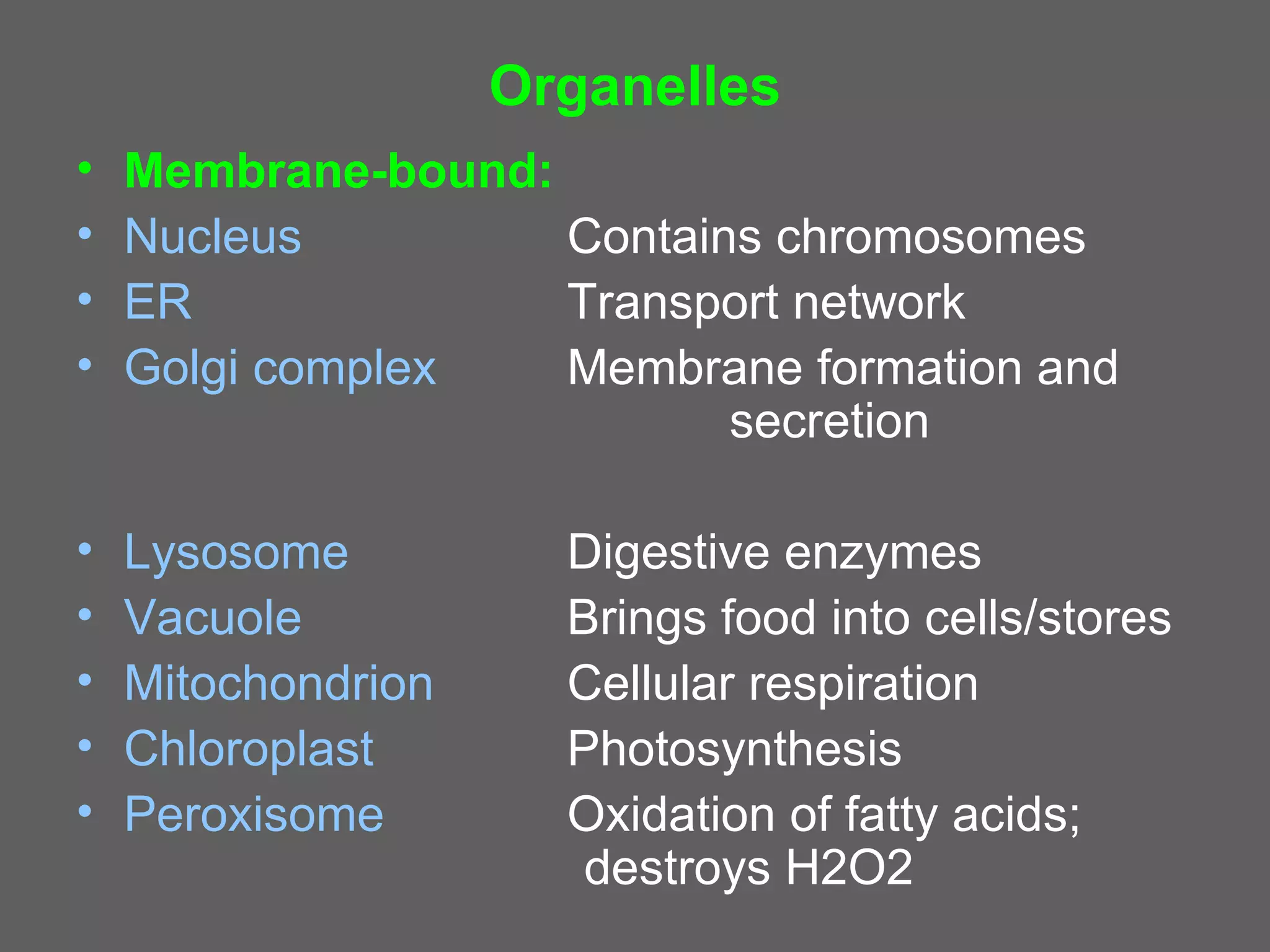
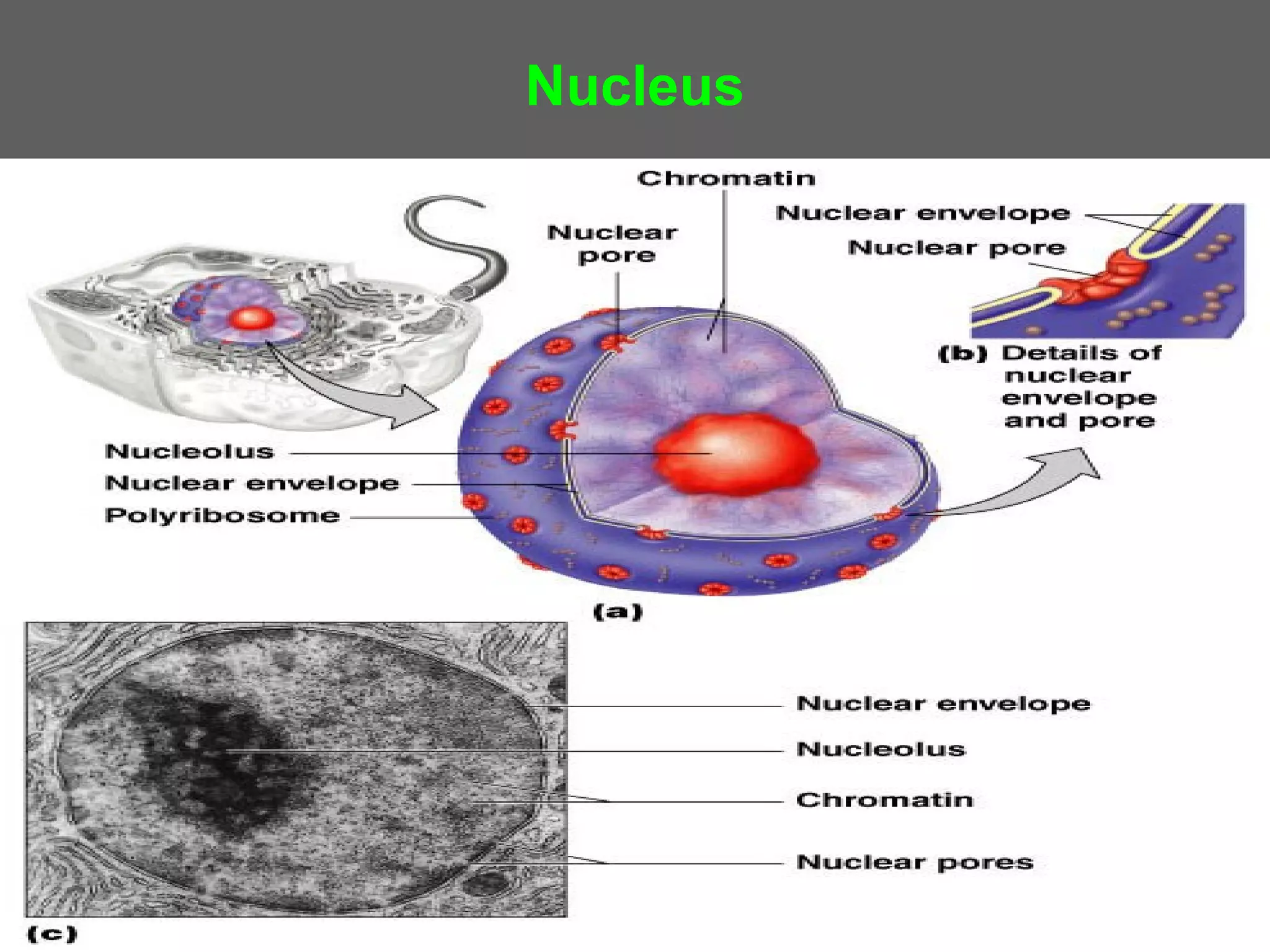
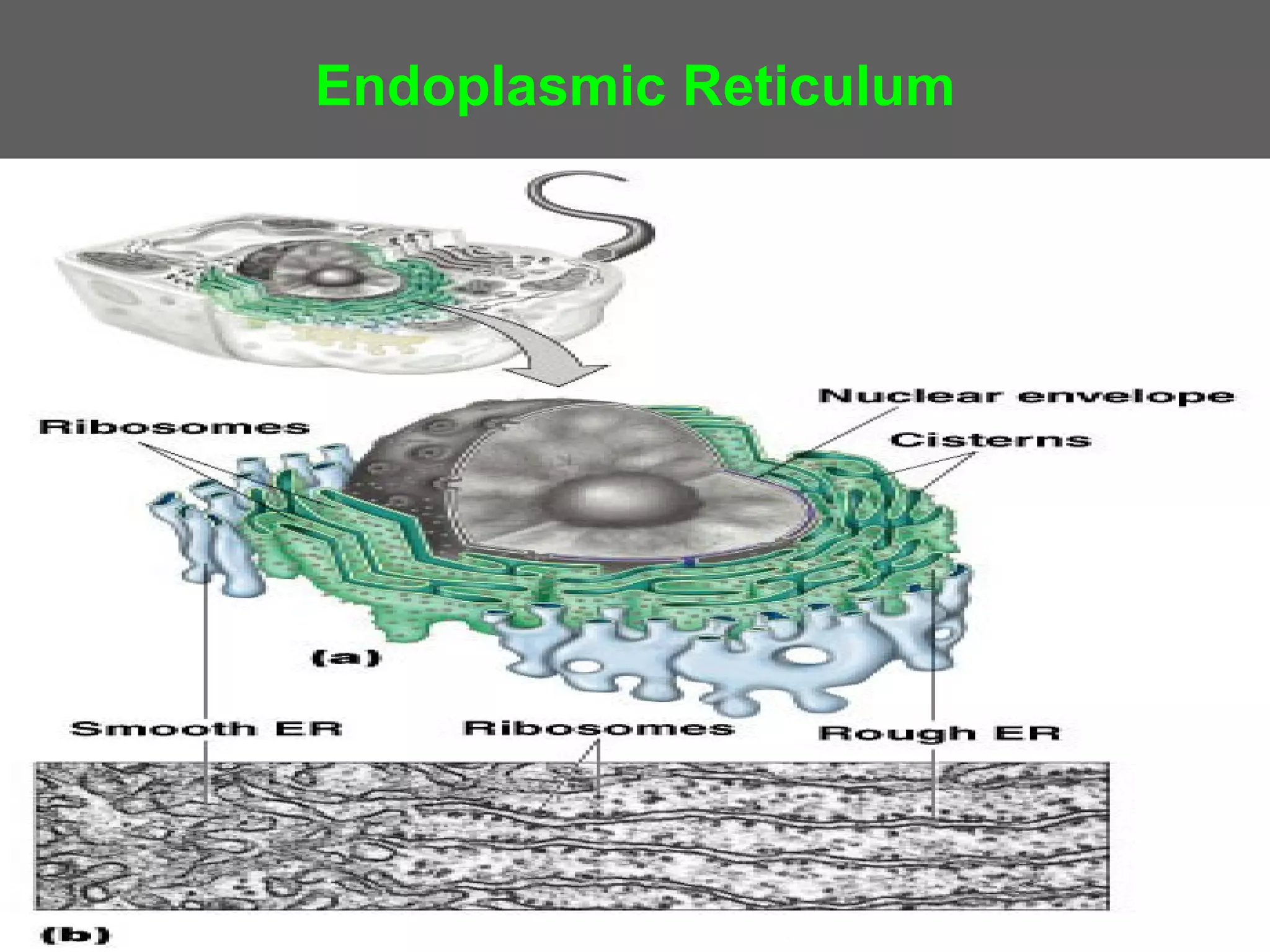
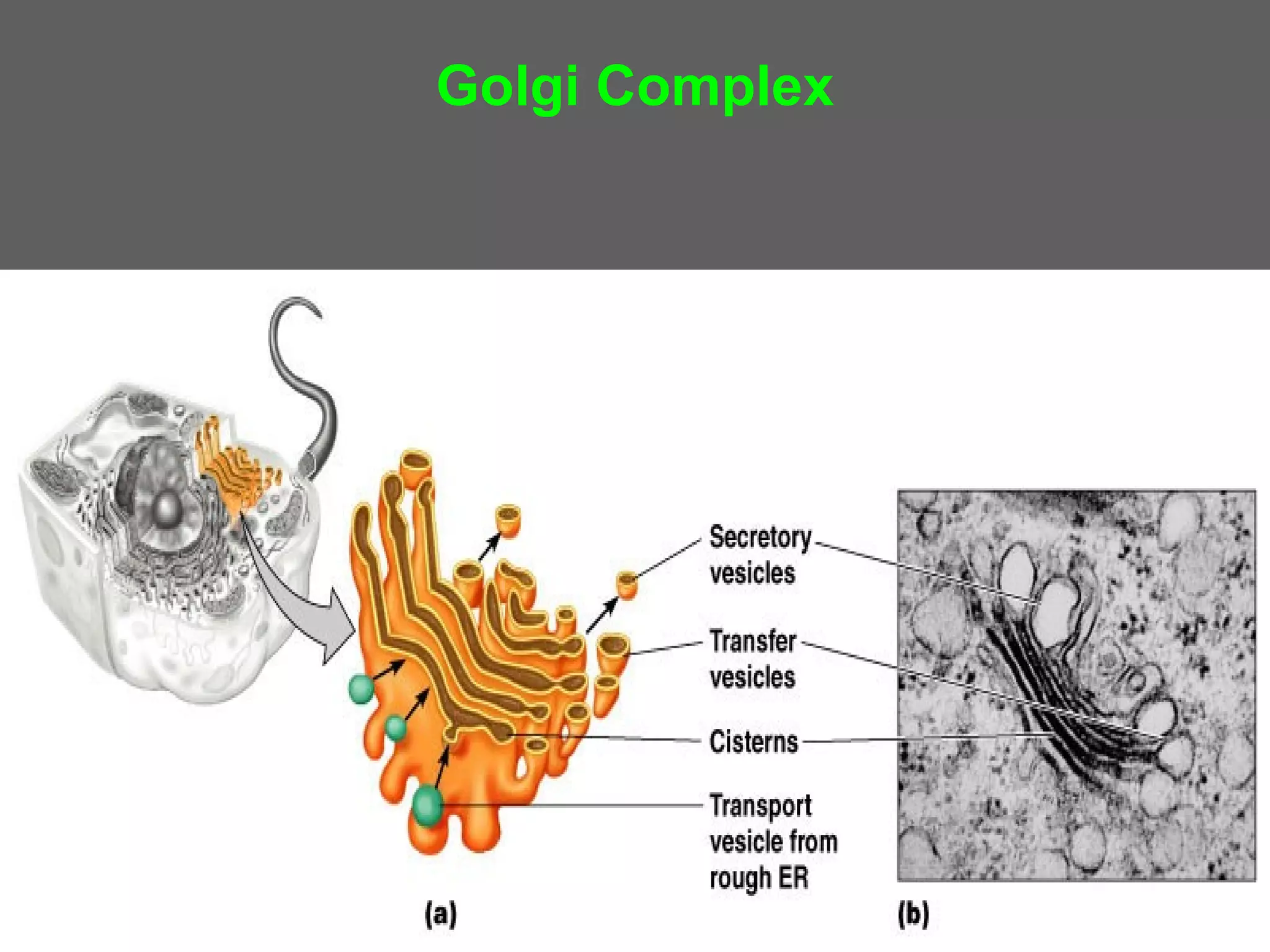
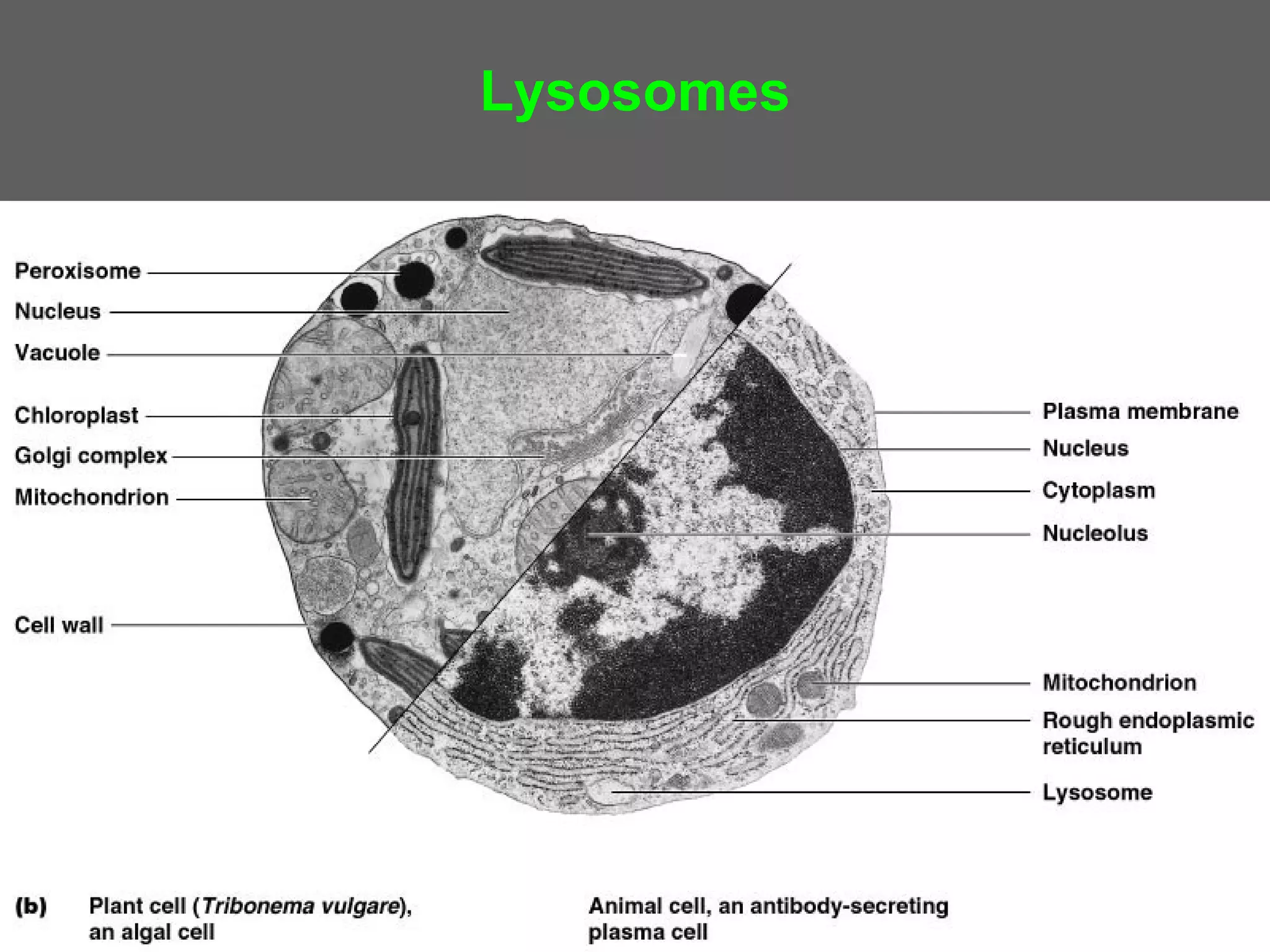
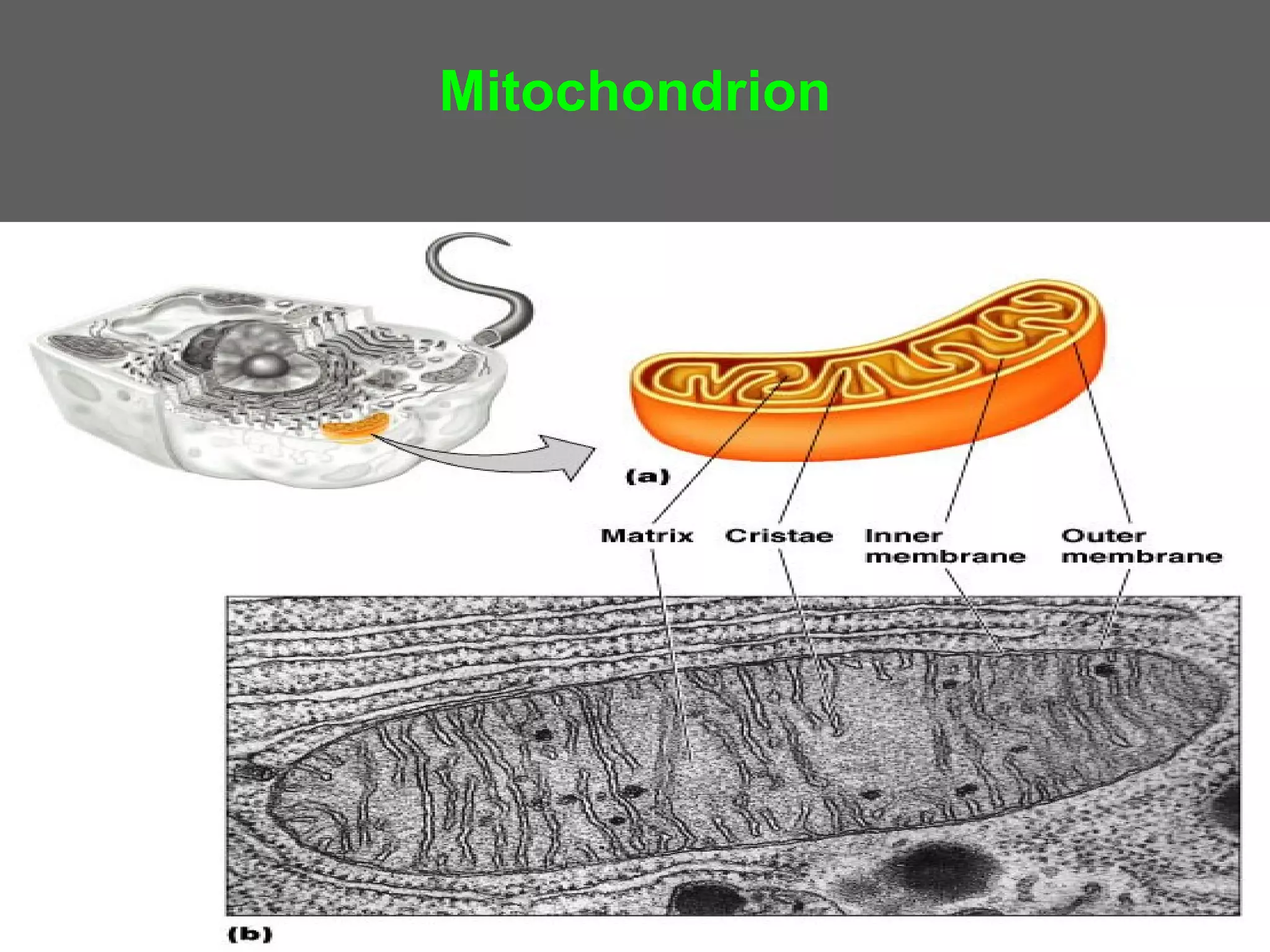
The document compares and contrasts the key structures and features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes like bacteria have no nucleus, organelles or histones. They have a single circular chromosome, peptidoglycan cell walls and divide via binary fission. Eukaryotes like plants and animals cells have a nucleus containing chromosomes, histones and membrane-bound organelles. They have polysaccharide cell walls and divide via mitosis using a spindle apparatus. The document outlines the major internal and external structures of both types of cells.