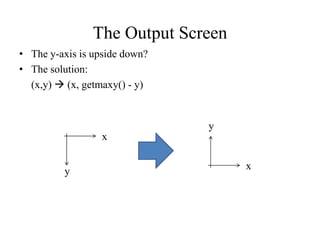
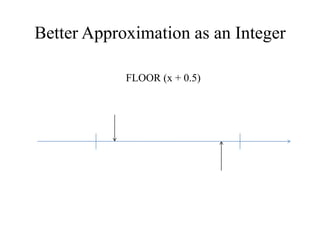
This document provides an overview of graphics programming in C using Turbo C++. It outlines the course content which includes drawing points, lines, polygons, circles and filling areas. It also discusses geometric transformations in 2D and 3D as well as line clipping algorithms. It provides details on setting up the integrated development environment and creating a graphics header file to initialize and exit graphics mode. It includes code examples to display a single point on the screen by approximating pixel coordinates as integers.