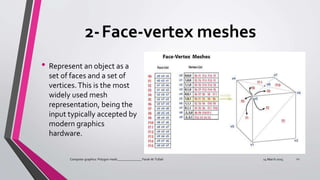
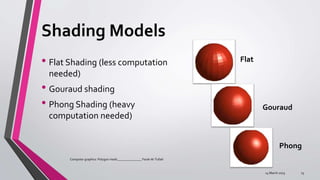
A polygon mesh is a 3D surface made of vertices, edges, and faces that defines the shape of a polyhedral object. It can be constructed using box modeling with subdivision and extrusion tools, inflation modeling by extruding a 2D shape, or connecting primitive 3D shapes. Polygon meshes are commonly represented through face-vertex or winged-edge structures and can be rendered with flat, Gouraud, or Phong shading models. However, polygons only approximate curved surfaces and lose geometric information.