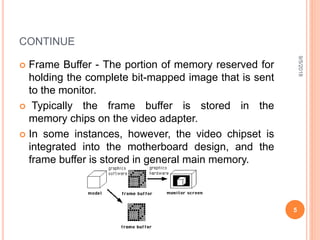
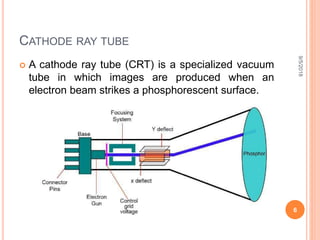
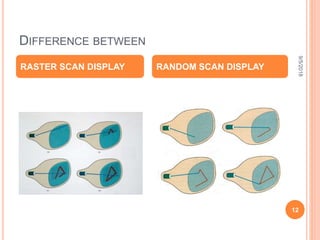
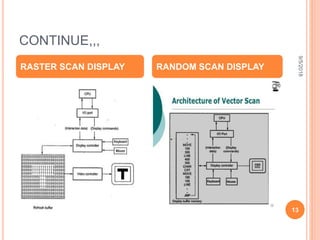
The document is a presentation on computer graphics by Ms. Nandini Sharma, highlighting its definition as the art of creating images using programming. It covers basic terminology such as pixels, resolution, frame buffers, and refresh rates, along with applications in various fields like graphic design, gaming, and virtual reality. The presentation also contrasts raster and random scan displays, explaining their characteristics.