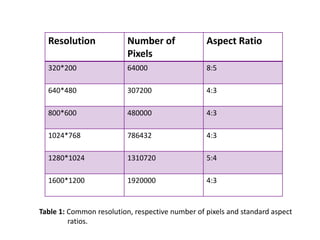
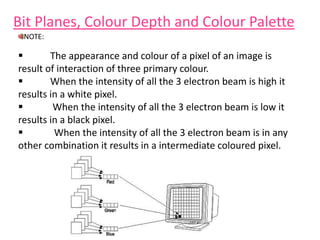
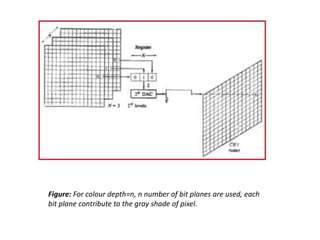
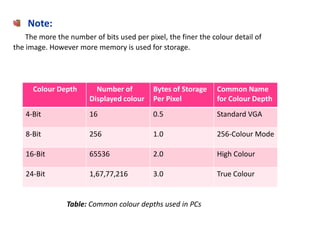
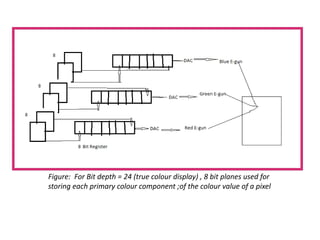
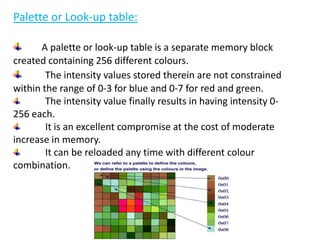
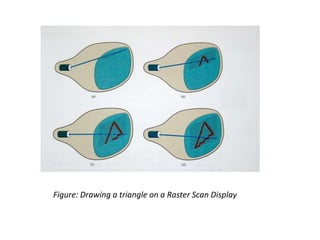
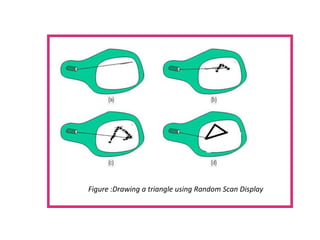
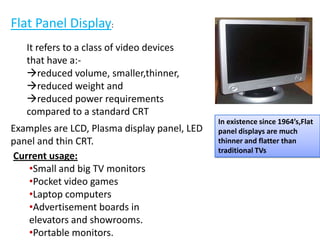
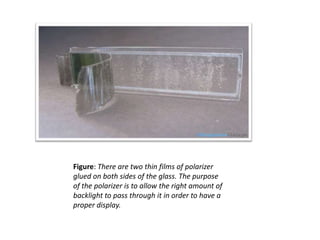
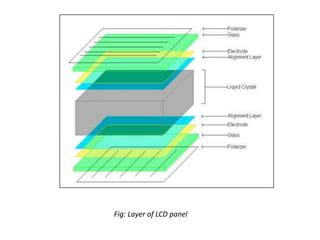
This document provides an introduction to computer graphics. It defines computer graphics as the creation, storage, and manipulation of pictures and drawings using digital computers. Computer graphics is used across diverse fields such as engineering, medicine, education, entertainment, and more. The document discusses basic terms related to display devices such as pixels, resolution, color depth, and frame buffers. It also describes different types of display devices including raster scan displays, random scan displays, direct view storage tubes, flat panel displays, and stereoscopic displays. Applications of computer graphics such as design, image processing, animation, simulation, and medical imaging are also summarized.