The document provides explanations of various graphics functions from the graphics.h library in C language. It discusses functions for initializing graphics mode, drawing basic shapes like lines, rectangles, circles, getting and setting colors, reading and writing pixel values, loading and saving bitmap images, handling events and cleaning up graphics memory. It also includes code snippets to demonstrate drawing a rectangle, smiley and star using these graphics functions.





![*getmaxx function returns the maximum X coordinate for current graphics
mode and driver.
13)FILLPOLY,DRAWPOLY
DECLARATION
*void drawpoly( intnum, int *polypoints );
*void drawpoly( intnum, int *polypoints );
EXPLANATION
*Drawpoly function is used to draw polygons i.e. triangle, rectangle, pentagon,
hexagon etc.
*Fillpoly function draws and fills a polygon. It require same arguments as
drawpoly.
*num indicates (n+1) number of points where n is the number of vertices in a
polygon, polypoints points to a sequence of (n*2) integers . Each pair of
integers gives x and y coordinates of a point on the polygon. We specify (n+1)
points as first point coordinates should be equal to (n+1)th to draw a complete
figure.
*To understand more clearly we will draw a triangle using drawpoly, consider
for example the array :-
int points[] = { 320, 150, 420, 300, 250, 300, 320, 150};
points array contains coordinates of triangle which are (320, 150), (420, 300)
and (250, 300). Note that last point(320, 150) in array is same as first.
14)SETLINESTYLE
DECLARATION
*void setlinestyle( intlinestyle, unsigned upattern, int thickness );
EXPLANATION
*ItdrawsSOLID_LINE,DOTTED_LINE,CENTER_LINE,DASHED_LINE,US
ERBIT_LINE.
15)GETBKCOLOR,SETBKCOLOR
DECLARATION
*intgetbkcolor();
* void setbkcolor(intcolor);
EXPLANATION
*getbkcolor function returns the current background color
*setbkcolor function changes current background color e.g.
setbkcolor(YELLLOW) changes the current background color to YELLOW.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-6-2048.jpg)












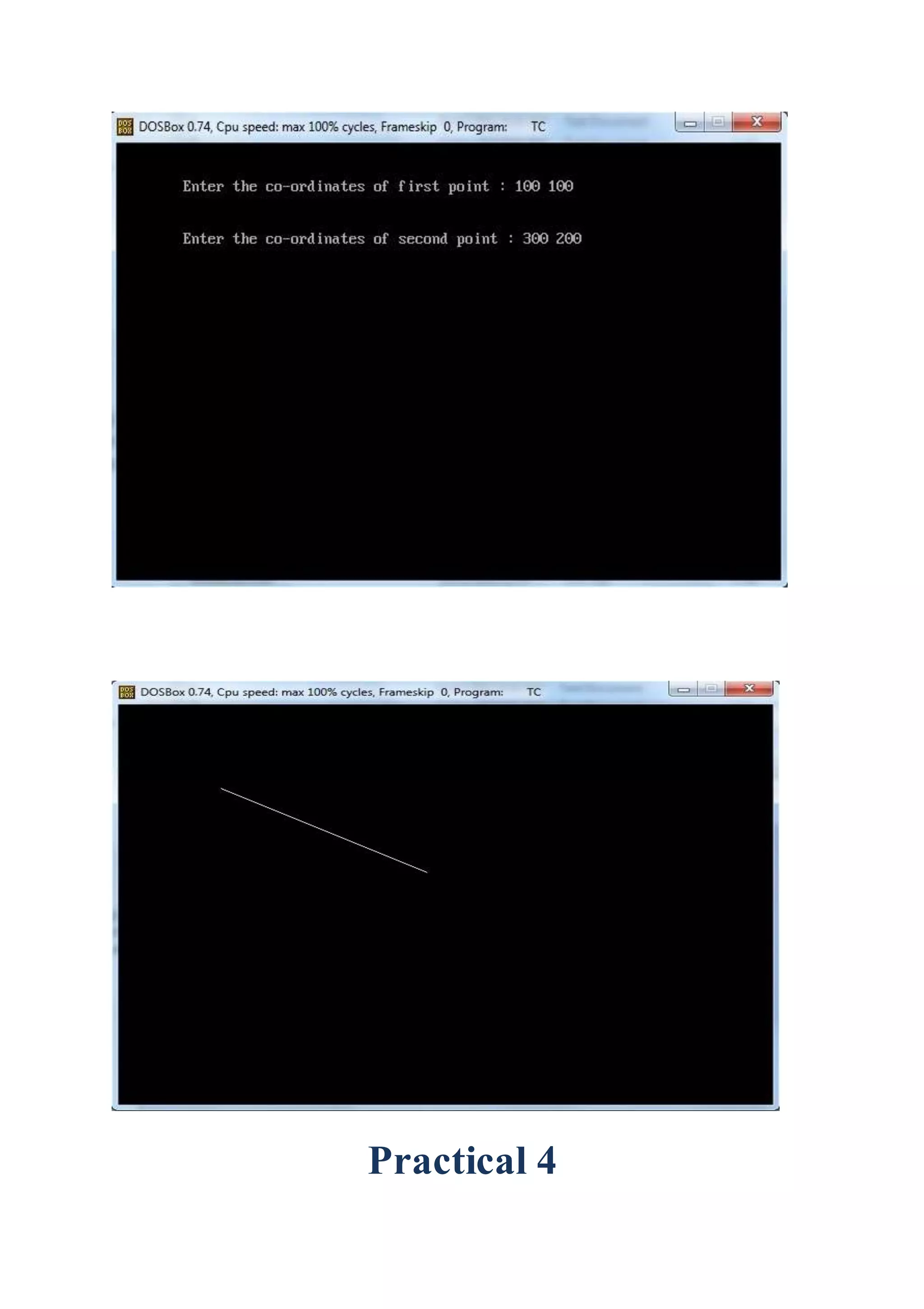





![Practical 5
Aim :- Implement PolygonFilling Algorithms.
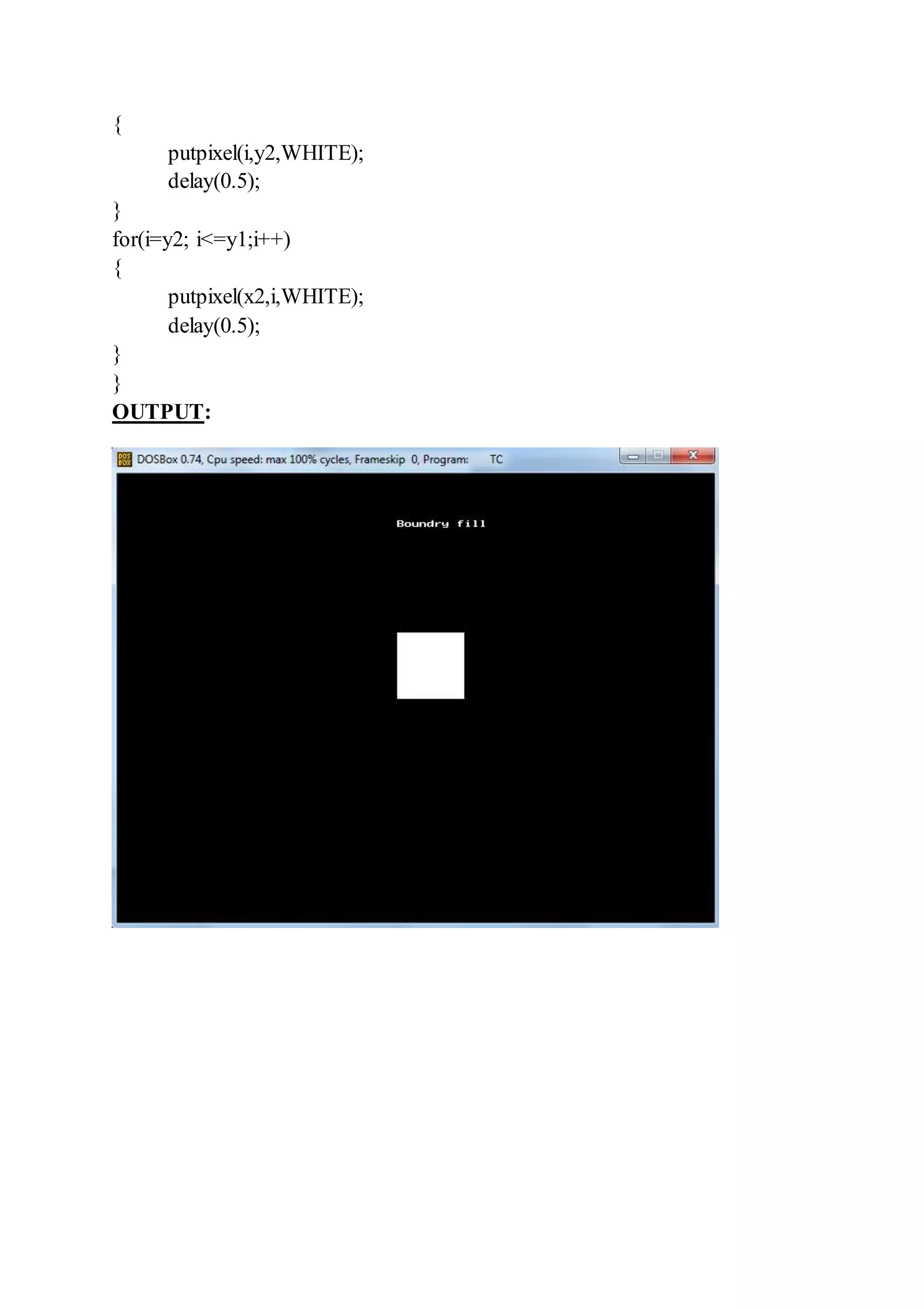
[A] Boundary Fill
CODE:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<dos.h>
void drawply();
void boundryfill(int x1, int x2, int y1, int y2);
main()
{
int gd=DETECT,gm,x,y,p[8],x1,x2,y1,y2;
initgraph(&gd,&gm," ");
cleardevice();
drawply();
getch();
x1=300;
x2=371;
y1=240;
y2=170;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-29-2048.jpg)

![[B] Flood Fill
CODE:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
void flood(int seed_x,int seed_y,int foreground_col,int background_col)
{
if (getpixel(seed_x,seed_y)!= background_col&& getpixel(seed_x,seed_y)!=
foreground_col)
{
putpixel(seed_x,seed_y,foreground_col);
flood(seed_x+1,seed_y,foreground_col,background_col);
flood(seed_x-1,seed_y,foreground_col,background_col);
flood(seed_x,seed_y+1,foreground_col,background_col);
flood(seed_x,seed_y-1,foreground_col,background_col);
}
}
void main()
{
int gd=DETECT,gm,gerror;
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"");
rectangle(50,50,100,100);
flood(55,55,15,15);
kgetch();
closegraph();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-32-2048.jpg)



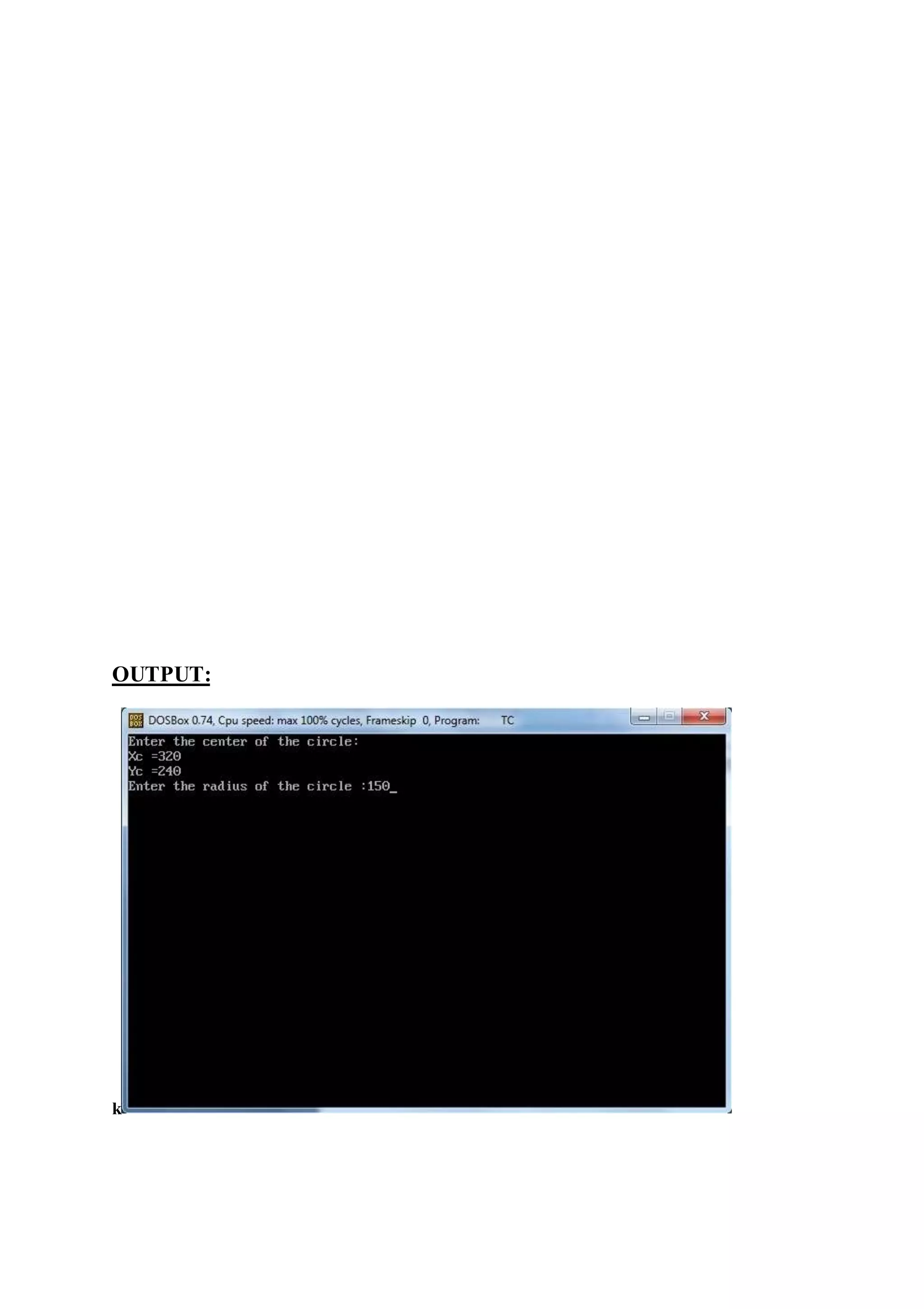
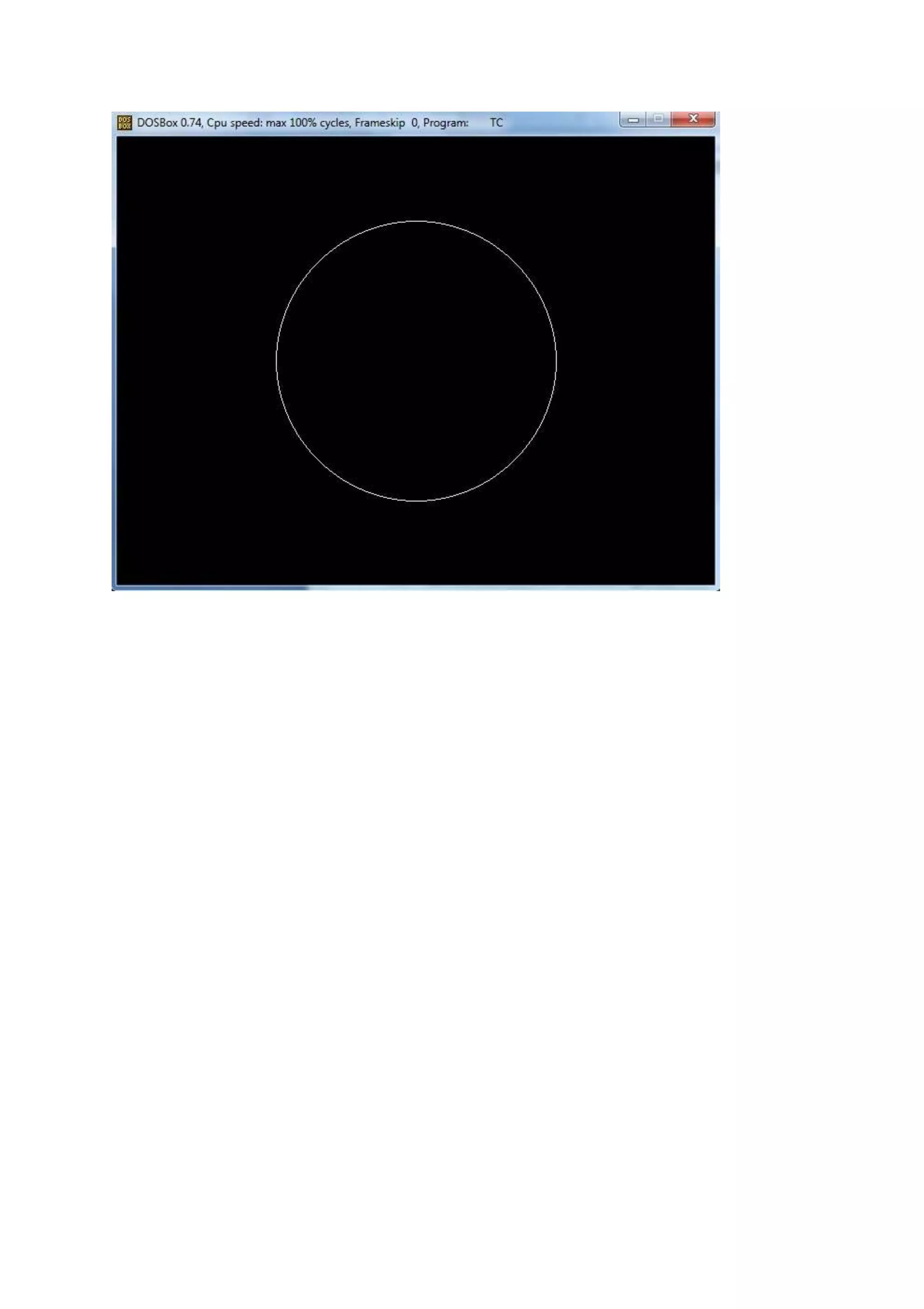


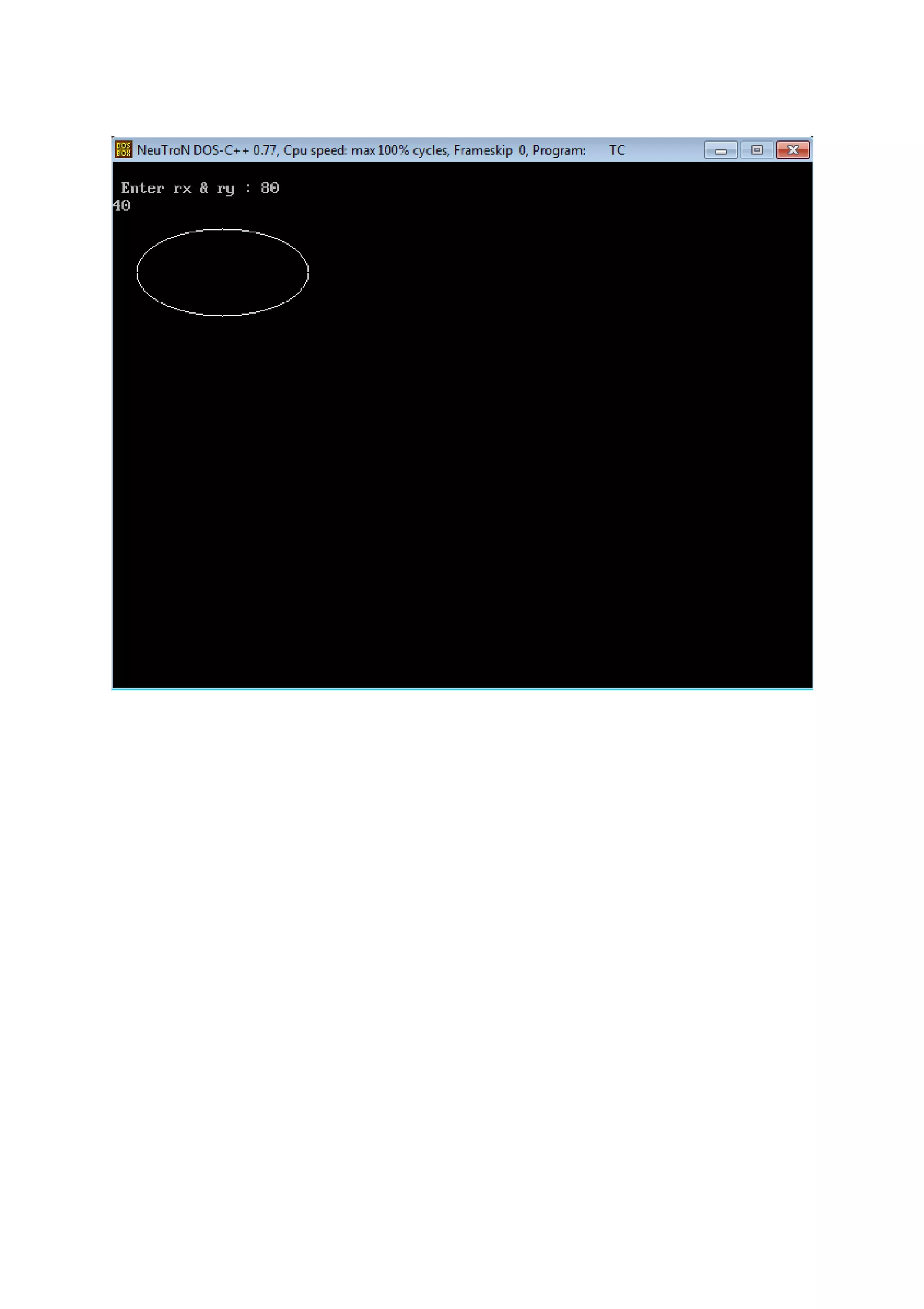
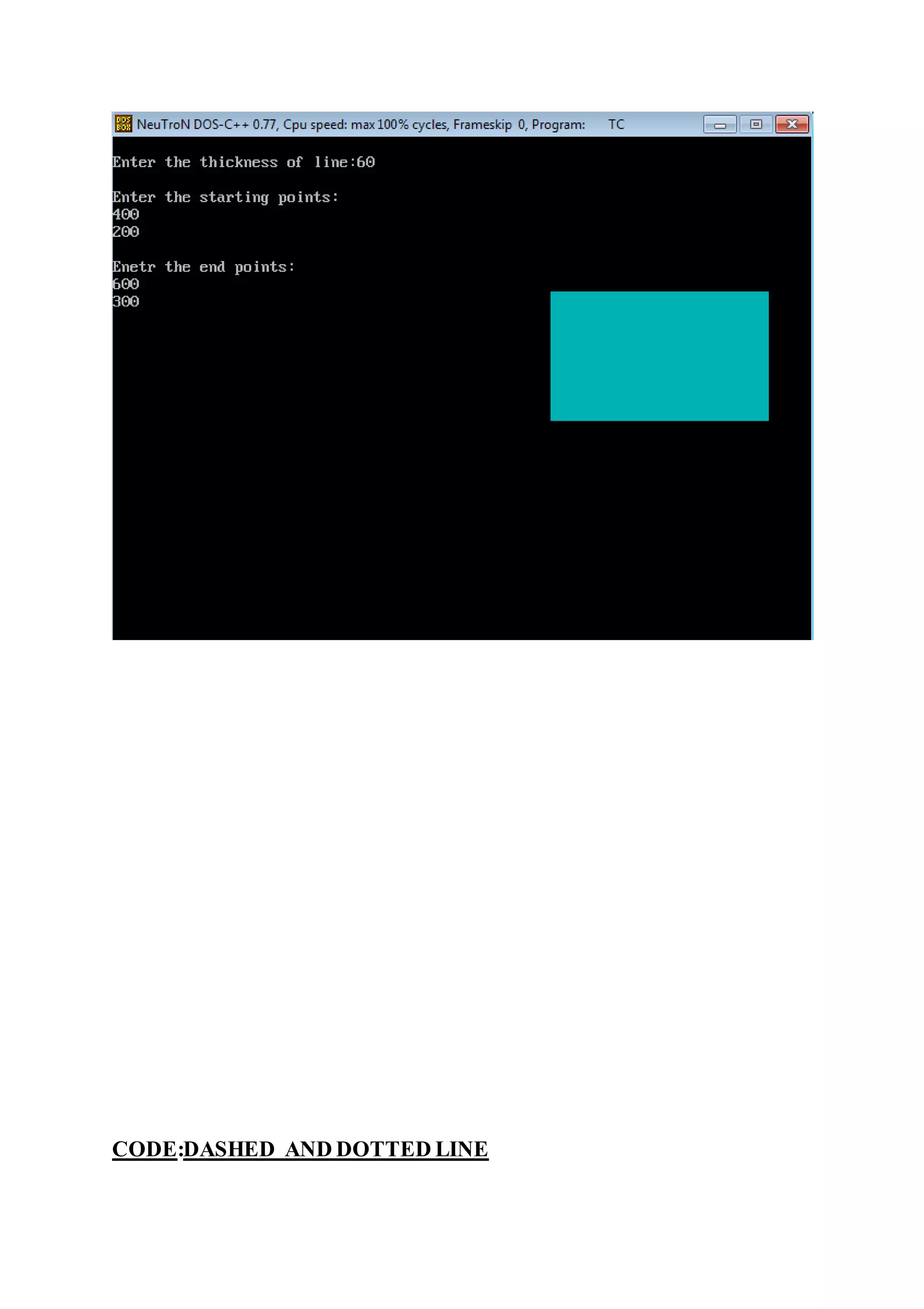
![Practical : 8
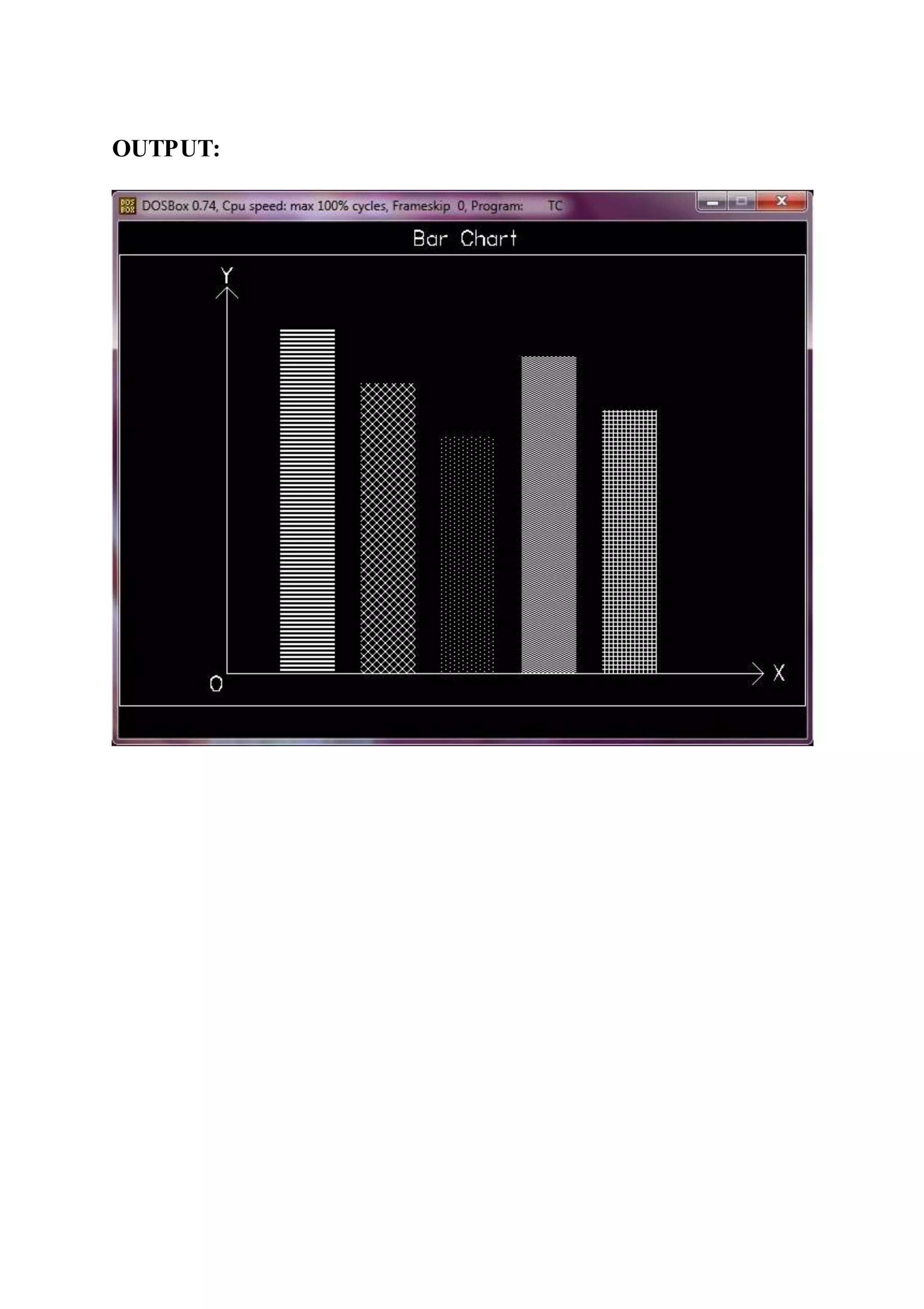
Aim :-Generate Bar Chart And Pie Chart.
[A] Bar Chart
#include<stdio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int gd = DETECT, gm;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "");
setcolor(WHITE);
rectangle(0,30,639,450);
settextstyle(SANS_SERIF_FONT,HORIZ_DIR,2);
setcolor(WHITE);
outtextxy(275,0,"Bar Chart");
setlinestyle(SOLID_LINE,0,2);
line(100,420,100,60);
line(100,420,600,420);
line(90,70,100,60);
line(110,70,100,60);
line(590,410,600,420);
line(590,430,600,420);
outtextxy(95,35,"Y");
outtextxy(610,405,"X");
outtextxy(85,415,"O");
setfillstyle(LINE_FILL, WHITE);
bar(150,100,200,419);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-41-2048.jpg)

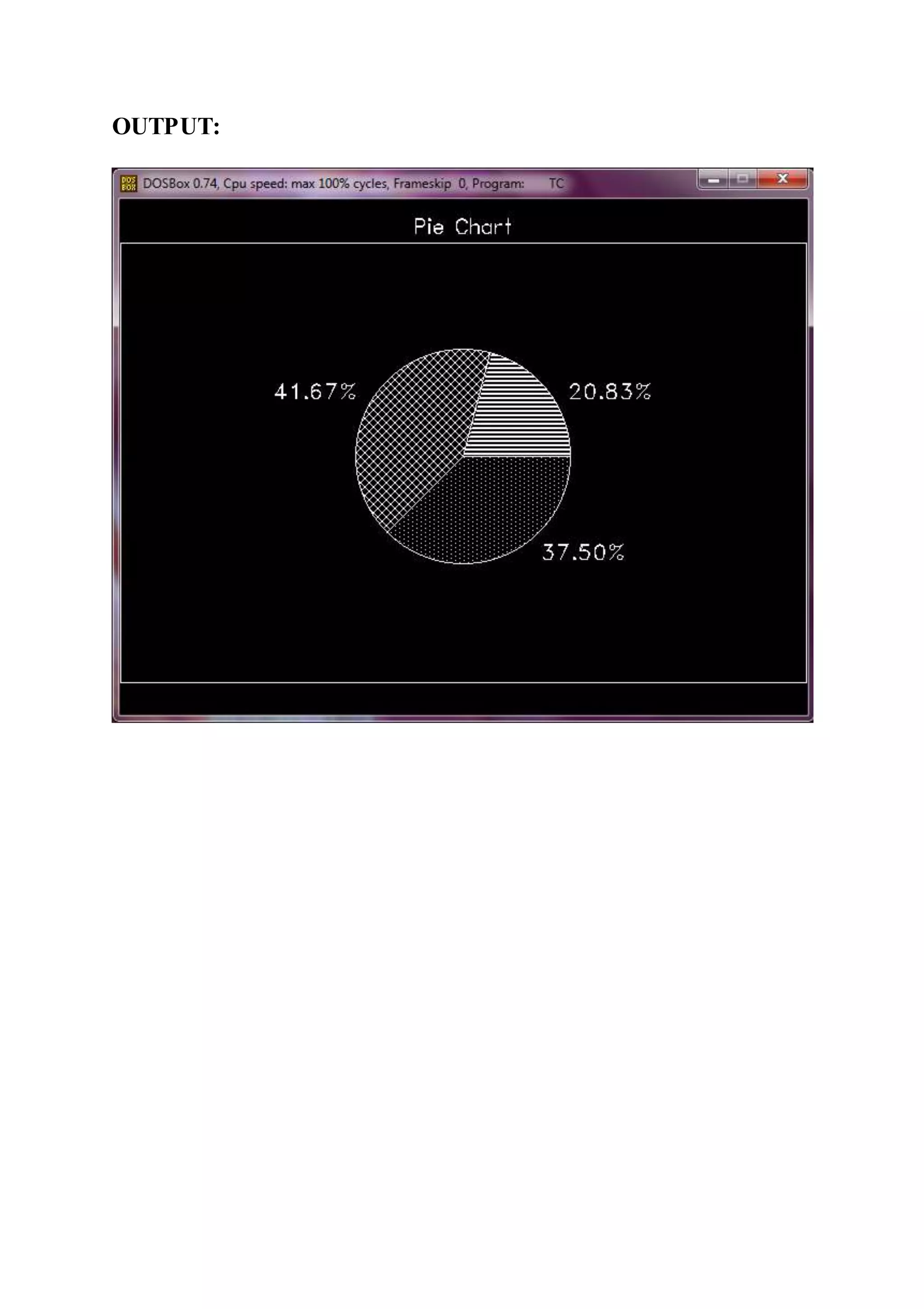
![[B] Pie Chart
#include<stdio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int gd = DETECT, gm, midx, midy;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "");
setcolor(WHITE);
rectangle(0,40,639,450);
settextstyle(SANS_SERIF_FONT,HORIZ_DIR,2);
setcolor(WHITE);
outtextxy(275,10,"Pie Chart");
midx = getmaxx()/2;
midy = getmaxy()/2;
setfillstyle(LINE_FILL, WHITE);
pieslice(midx, midy, 0, 75, 100);
outtextxy(midx+100, midy - 75, "20.83%");
setfillstyle(XHATCH_FILL, WHITE);
pieslice(midx, midy, 75, 225, 100);
outtextxy(midx-175, midy - 75, "41.67%");
setfillstyle(WIDE_DOT_FILL, WHITE);
pieslice(midx, midy, 225, 360, 100);
outtextxy(midx+75, midy + 75, "37.50%");
getch();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-44-2048.jpg)
![Practical: 9
Aim :2D Transformation -translation, rotation, scaling, fixed point
rotation, fixed point- scaling.
TRANSLATION:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<math.h>
float ans[3][10];
void multi(float tmat[3][3],float coormat[3][10],int size);
void main()
{
float coormat[3][10],x[10],y[10];
int gd=DETECT,gm,no,tx,ty,sum=0,i,j,k;
float tmat[3][3]={{1,0,0},{0,1,0},{0,0,1}};
clrscr();
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"..bgi");
printf("enter (tx,ty):"),scanf("%d%d",&tx,&ty);
tmat[0][2]=tx;
tmat[1][2]=ty;
printf("Translation matrix is:n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf("%4.1ft",tmat[i][j]);
printf("n");
}
printf("enter no. of vertices:n"),scanf("%d",&no);
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
printf("enter (x%d,y%d):n",i+1,i+1),scanf("%f%f",&x[i],&y[i]);
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
coormat[0][i]=x[i];
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
coormat[1][i]=y[i];
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
coormat[2][i]=1;
printf("co ordinate matrix is:n");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-46-2048.jpg)
![for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<no;j++)
printf("%4.2ft",coormat[i][j]);
printf("n");
}//printing starting line
for(j=0;j<no-1;j++)
line(coormat[0][j],coormat[1][j],coormat[0][j+1],coormat[1][j+1]);
line(coormat[0][0],coormat[1][0],coormat[0][j],coormat[1][j]);
multi(tmat,coormat,no);
printf("answer matrix is:n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<no;j++)
printf("%4.2ft",ans[i][j]);
printf("n");
}
for(j=0;j<no-1;j++)
line(ans[0][j],ans[1][j],ans[0][j+1],ans[1][j+1]);
line(ans[0][0],ans[1][0],ans[0][j],ans[1][j]);
getch();
}
void multi(float tmat[3][3],float coormat[3][10],int no)
{
int i,j,k,sum=0;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<no;j++)
{
sum=0;
for(k=0;k<3;k++)
{
sum+=tmat[i][k]*coormat[k][j];
}
ans[i][j]=sum;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-47-2048.jpg)

![ROTATITON:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<math.h>
float ans[3][10];
void multi(float tmat[3][3],float coormat[3][10],int size);
void main()
{
float coormat[3][10],x[10],y[10],temp;
int gd=DETECT,gm,no,sx,sy,sum=0,i,j,k,theta;
float tmat[3][3]={{1,0,0},{0,1,0},{0,0,1}};
clrscr();
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"..bgi");
printf("enter theta:"),scanf("%d",&theta);
temp=(float)theta*3.14/180;
tmat[0][0]=cos(temp);
tmat[1][1]=cos(temp);
tmat[0][1]=-1*sin(temp);
tmat[1][0]=-1*sin(temp);
printf("Translation matrix is:n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf("%4.1ft",tmat[i][j]);
printf("n");
}
printf("enter no. of vertices:n"),scanf("%d",&no);
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
printf("enter (x%d,y%d):n",i+1,i+1),scanf("%f%f",&x[i],&y[i]);
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
coormat[0][i]=x[i];
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
coormat[1][i]=y[i];
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
coormat[2][i]=1;
printf("co ordinate matrix is:n");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-49-2048.jpg)
![for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<no;j++)
printf("%4.2ft",coormat[i][j]);
printf("n");
}
//printing starting line
for(j=0;j<no-1;j++)
line(coormat[0][j],coormat[1][j],coormat[0][j+1],coormat[1][j+1]);
line(coormat[0][0],coormat[1][0],coormat[0][j],coormat[1][j]);
multi(tmat,coormat,no);
printf("answer matrix is:n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<no;j++)
printf("%4.2ft",ans[i][j]);
printf("n");
}
for(j=0;j<no-1;j++)
line(ans[0][j],ans[1][j],ans[0][j+1],ans[1][j+1]);
line(ans[0][0],ans[1][0],ans[0][j],ans[1][j]);
getch();
}
void multi(float tmat[3][3],float coormat[3][10],int no)
{
int i,j,k,sum=0;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<no;j++)
{
sum=0;
for(k=0;k<3;k++)
{
sum+=tmat[i][k]*coormat[k][j];
}
ans[i][j]=sum;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-50-2048.jpg)

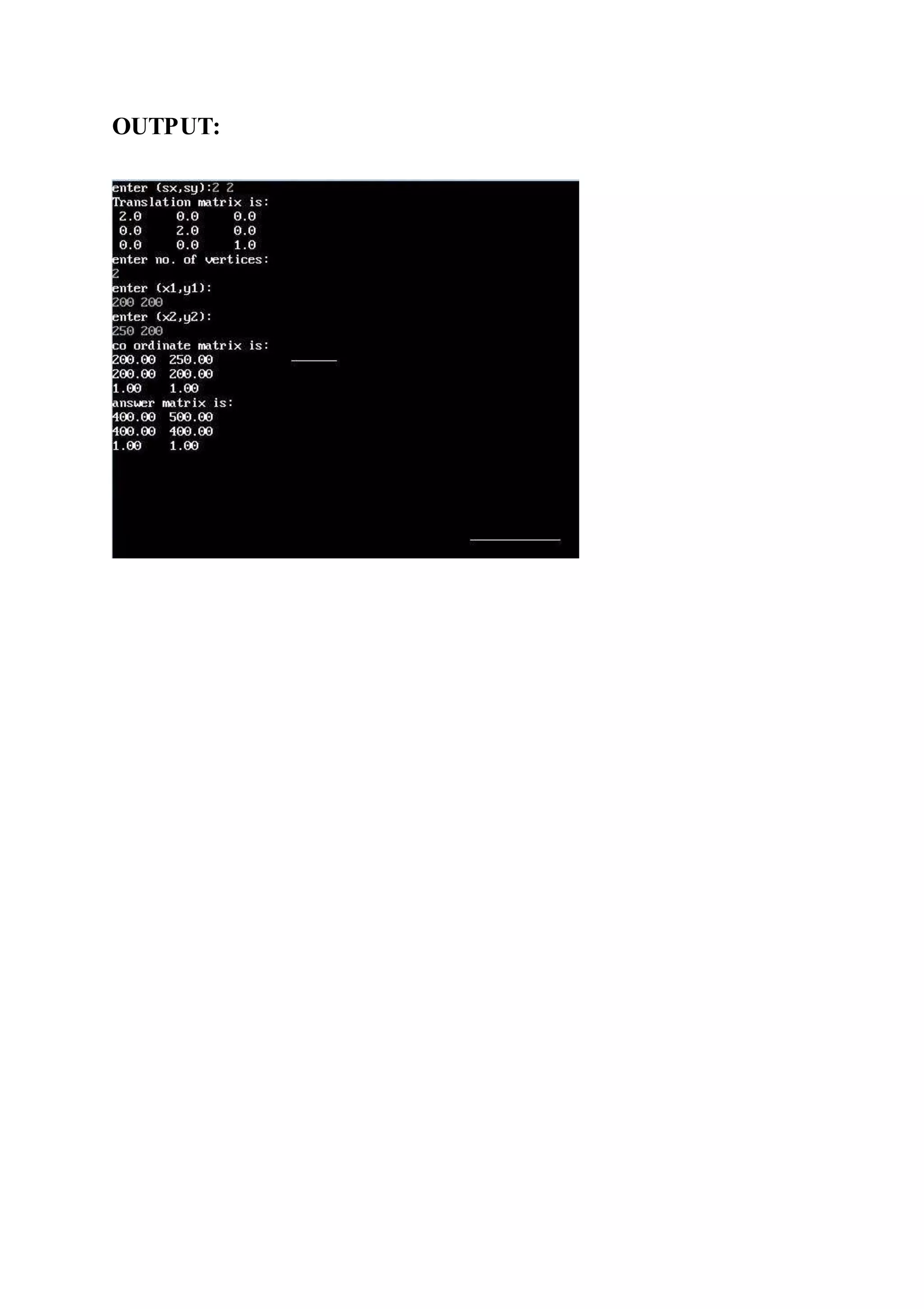
![SCALING:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<math.h>
float ans[3][10];
void multi(float tmat[3][3],float coormat[3][10],int size);
void main()
{
float coormat[3][10],x[10],y[10];
int gd=DETECT,gm,no,sx,sy,sum=0,i,j,k;
float tmat[3][3]={{1,0,0},{0,1,0},{0,0,1}};
clrscr();
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"..bgi");
printf("enter (sx,sy):"),scanf("%d%d",&sx,&sy);
tmat[0][0]=sx;
tmat[1][1]=sy;
printf("Translation matrix is:n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf("%4.1ft",tmat[i][j]);
printf("n");
}
printf("enter no. of vertices:n"),scanf("%d",&no);
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
printf("enter (x%d,y%d):n",i+1,i+1),scanf("%f%f",&x[i],&y[i]);
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
coormat[0][i]=x[i];
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
coormat[1][i]=y[i];
for(i=0;i<no;i++)
coormat[2][i]=1;
printf("co ordinate matrix is:n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<no;j++)
printf("%4.2ft",coormat[i][j]);
printf("n");
} //printing starting line](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-52-2048.jpg)
![for(j=0;j<no-1;j++)
line(coormat[0][j],coormat[1][j],coormat[0][j+1],coormat[1][j+1]);
line(coormat[0][0],coormat[1][0],coormat[0][j],coormat[1][j]);
multi(tmat,coormat,no);
printf("answer matrix is:n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<no;j++)
printf("%4.2ft",ans[i][j]);
printf("n"); }
for(j=0;j<no-1;j++)
line(ans[0][j],ans[1][j],ans[0][j+1],ans[1][j+1]);
line(ans[0][0],ans[1][0],ans[0][j],ans[1][j]);
getch();
}
void multi(float tmat[3][3],float coormat[3][10],int no)
{
int i,j,k,sum=0;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<no;j++)
{
sum=0;
for(k=0;k<3;k++)
{
sum+=tmat[i][k]*coormat[k][j];
}
ans[i][j]=sum;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-53-2048.jpg)
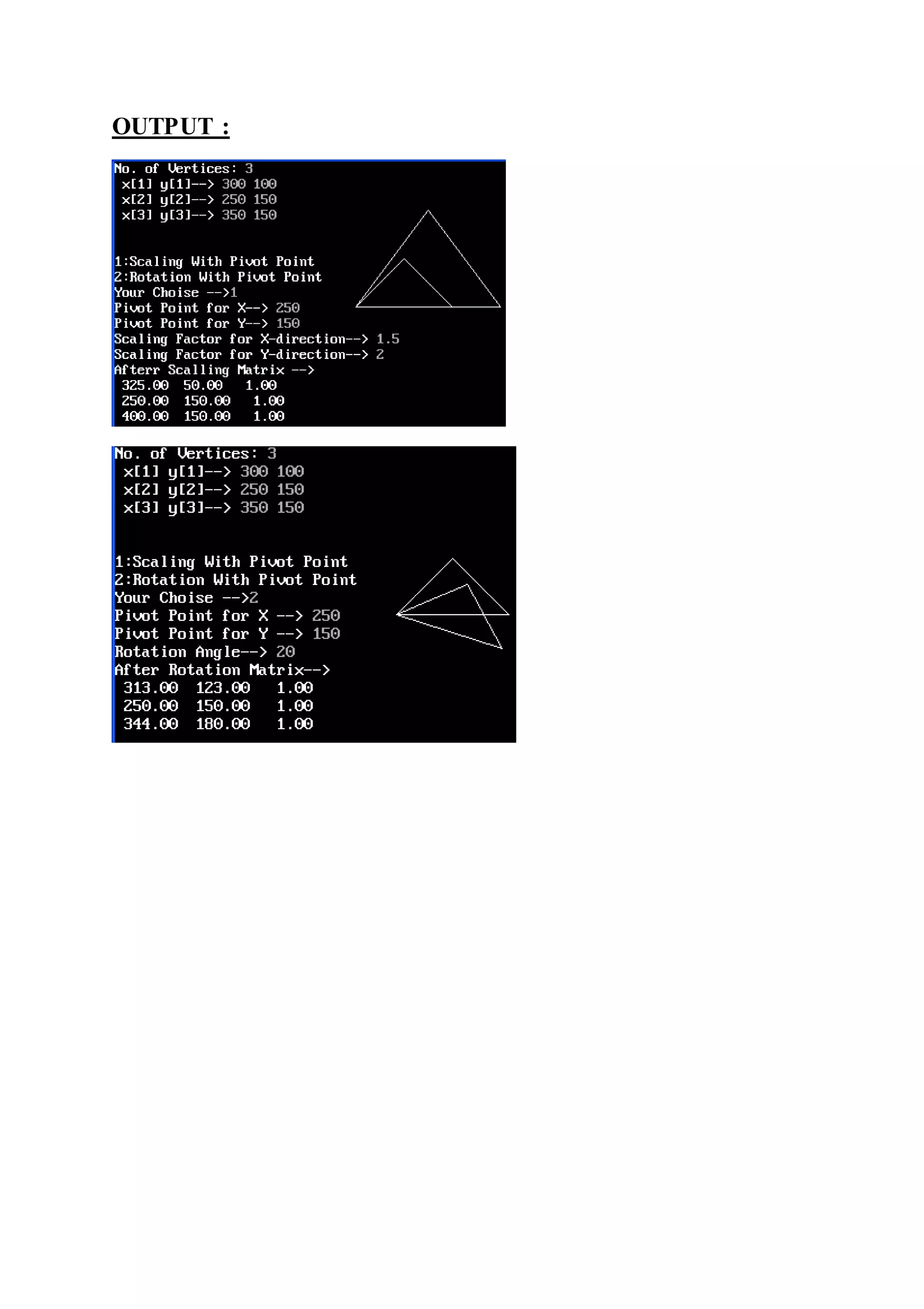
![2D SCALLING AND ROTATION WITH FIXED POINT:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#define PI 22/7
float mat2[3][3]={{1,0,0},{0,1,0},{0,0,1}};
float sx,sy,angle,mat1[10][3],x[10],y[10];
int i,j,n;
void pivoting(float,float);
void pivot_scaling();
void pivot_rotation();
void mat_multi();
void identity();
void main()
{
int gd=DETECT,gm,ch;
float px,py;
clrscr();
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"c:tcbgi");
printf("No. of Vertices: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf(" x[%d] y[%d]--> ",(i+1),(i+1));
scanf("%f%f",&x[i],&y[i]);
mat1[i][0]=x[i];
mat1[i][1]=y[i];
mat1[i][2]=1;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
if(i==(n-1))
line(mat1[i][0],mat1[i][1],mat1[0][0],mat1[0][1]);
else
line(mat1[i][0],mat1[i][1],mat1[i+1][0],mat1[i+1][1]); }
getch();
printf("nn1:Scaling With Pivot Pointn2:Rotation With Pivot PointnYour
Choise -->");
scanf("%d",&ch);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-55-2048.jpg)
![switch(ch)
{
case 1:
scanf("%f",&px, printf("Pivot Point for X--> "));
scanf("%f",&py, printf("Pivot Point for Y--> "));
pivoting(-px,-py);
identity();
pivot_scaling();
identity();
pivoting(px,py);
printf("Afterr Scalling Matrix --> n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf(" %5.2f ",mat1[i][j]);
printf("n"); }
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
if(i==(n-1))
line(mat1[i][0],mat1[i][1],mat1[0][0],mat1[0][1]);
else
line(mat1[i][0],mat1[i][1],mat1[i+1][0],mat1[i+1][1]);
}
break;
case 2:
scanf("%f",&px, printf("Pivot Point for X--> "));
scanf("%f",&py, printf("Pivot Point for Y--> "));
pivoting(-px,-py);
identity();
pivot_rotation();
identity();
pivoting(px,py);
printf("After Rotation Matrix--> n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf(" %5.2f ",mat1[i][j]);
printf("n"); }
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
if(i==(n-1))
line(mat1[i][0],mat1[i][1],mat1[0][0],mat1[0][1]);
else
line(mat1[i][0],mat1[i][1],mat1[i+1][0],mat1[i+1][1]); }
break;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-56-2048.jpg)
![default:
printf("Wrong Choice!");
}
getch();
}
void identity()
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(i==j)
mat2[i][j]=1;
else
mat2[i][j]=0;
}
}
void mat_multi()
{
int i,j,k,m;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
m=0;
for(k=0;k<3;k++)
m+=mat1[i][k]*mat2[k][j];
mat1[i][j]=m;
}
}
}
void pivoting(float px,float py)
{
mat2[2][0]=px;
mat2[2][1]=py;
mat_multi();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-57-2048.jpg)
![void pivot_scaling()
{
scanf("%f",&sx, printf("Scaling Factor for X-direction--> "));
scanf("%f",&sy, printf("Scaling Factor for Y-direction--> "));
mat2[0][0]=sx;
mat2[1][1]=sy;
mat_multi();
}
void pivot_rotation()
{
printf("Rotation Angle--> ");
scanf("%f",&angle);
angle=(PI*angle/180);
mat2[0][0]=cos(angle);
mat2[1][1]=cos(angle);
mat2[0][1]=sin(angle);
mat2[1][0]=-1*sin(angle);
mat_multi();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-58-2048.jpg)
![Practical: 10
Aim: 2D Transformation- 2D Reflection, 2D Shearing.
REFLECTION :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
float rmat[3][3],cor[3][10];
int n;
void mul(float c[3][10], float c1[3][3], int n);
void polygon(float cor[3][10], int n);
void id(float rmat[3][3]);
void id(float rmat[3][3])
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
if(i==j)
rmat[i][j]=1;
else
rmat[i][j]=0;
}}}
void polygon(float cor[3][10],int n)
{
int j;
cor[0][n]=cor[0][0];
cor[1][n]=cor[1][0];
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
line(320+cor[0][j],240-cor[1][j],320+cor[0][j+1],240-cor[1][j+1]);
}
void mul(float c[3][10], float c1[3][3],int n)
{
float ans[3][10];
int i,j,k;
float sum;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-60-2048.jpg)
![for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
sum=0;
for(k=0;k<3;k++)
sum=sum+c1[i][k]*c[k][j];
ans[i][j]=sum;
}}
polygon(ans,n);
}
void main()
{
int ch,gd,gm,x,y,i,j;
gd=DETECT;
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"d:tcbgi");
cleardevice();
printf("ENTER NUMBER OF VERTICES-->>");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("nENTER CO-ORDINATE VALUES -->>");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
if(j==2)
cor[j][i]=1;
else
scanf("%f",&cor[j][i]);
}}
label:
moveto(0,0);
getch();
cleardevice();
line(0,240,640,240);
line(320,0,320,480);
polygon(cor,n);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-61-2048.jpg)
![printf("1.REFLECTION ABOUT X-AXIS n2.REFLECTION ABOUT Y-
AXIS n3.REFLECTION ABOUT BOTH AXISn4.REFLECTION AT
Y=Xn5.REFLECTION ABOUT Y=-Xn6.EXIT");
printf("nENTER YOUR CHOICE-->>");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
id(rmat);
rmat[1][1]=-1;
mul(cor,rmat,n);
break;
case 2:
id(rmat);
rmat[0][0]=-1;
mul(cor,rmat,n);
break;
case 3:
id(rmat);
rmat[0][0]=-1;
rmat[1][1]=-1;
mul(cor,rmat,n);
break;
case 4:
id(rmat);
rmat[0][0]=0;
rmat[1][0]=1;
rmat[0][1]=1;
rmat[1][1]=0;
mul(cor,rmat,n);
break;
case 5:
id(rmat);
rmat[0][0]=0;
rmat[1][0]=-1;
rmat[0][1]=-1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-62-2048.jpg)
![rmat[1][1]=0;
mul(cor,rmat,n);
break;
case 6:
exit(0);
}
getch();
}
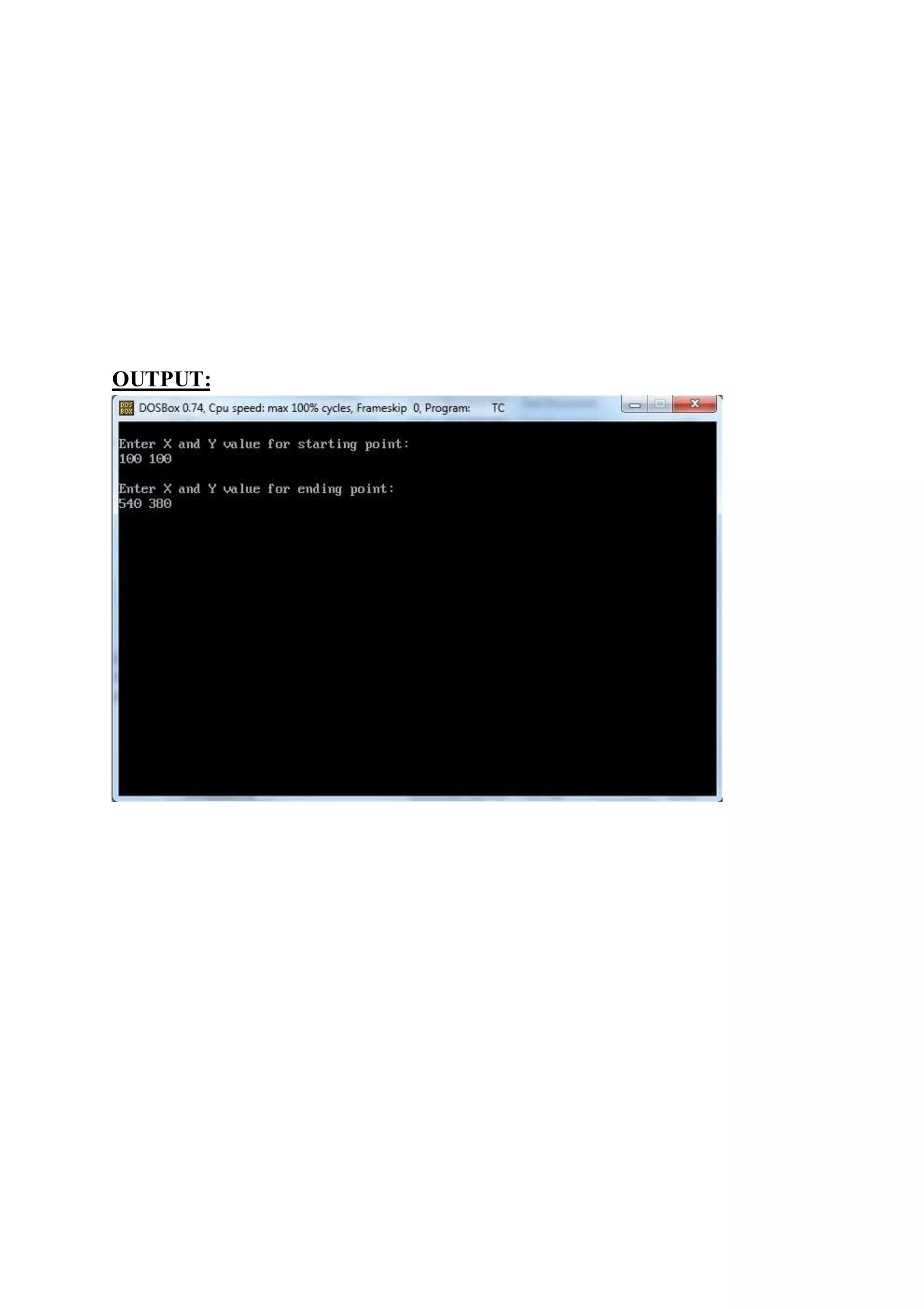
OUTPUT:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-63-2048.jpg)
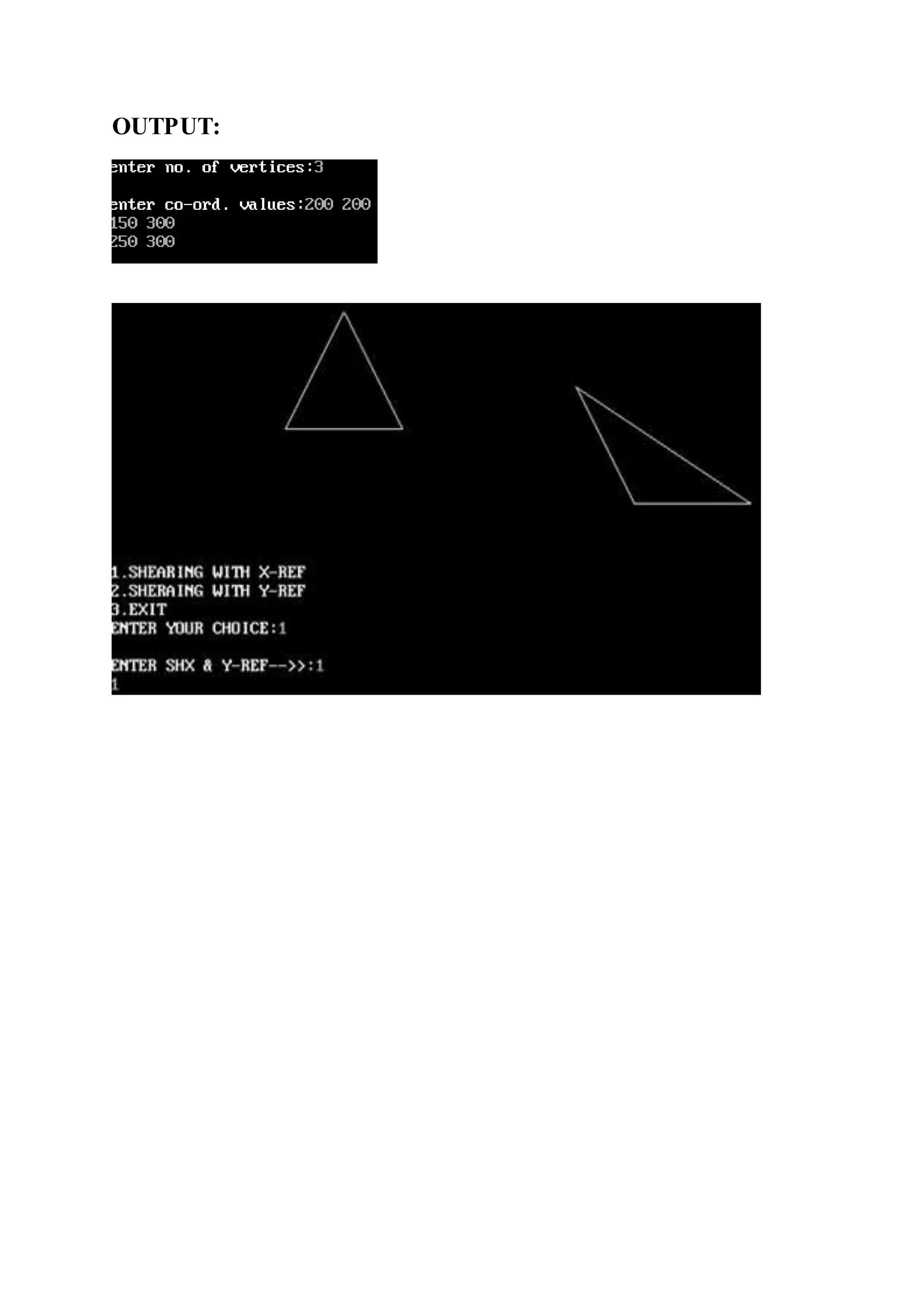
![SHEARING:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
float smat[3][3],cor[3][10];
int n;
void mul(float c[3][10], float c1[3][3], int n);
void polygon(float cor[3][10], int n);
void id(float smat[3][3]);
void polygon(float cor[3][10],int n)
{
int j;
cor[0][n]=cor[0][0];
cor[1][n]=cor[1][0];
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
line(cor[0][j],cor[1][j],cor[0][j+1],cor[1][j+1]);
}
void mul(float c[3][10], float c1[3][3],int n)
{
float ans[3][10];
int i,j,k;
float sum;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
sum=0;
for(k=0;k<3;k++)
sum=sum+c1[i][k]*c[k][j];
ans[i][j]=sum;
}
}
polygon(ans,n);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-64-2048.jpg)
![void id(float smat[3][3])
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
if(i==j)
smat[i][j]=1;
else
smat[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
void main()
{
int ch,gd=DETECT,gm,x,y,i,j;
float sh,ref;
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"d:tcbgi");
cleardevice();
printf("enter no. of vertices:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("nenter co-ord. values:");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
if(j==2)
cor[j][i]=1;
else
scanf("%f",&cor[j][i]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-65-2048.jpg)
![label:getch();
cleardevice();
polygon(cor,n);
while(1)
{
printf("1.SHEARING WITH X-REF n2.SHERAING WITH Y-
REFn3.EXIT");
printf("nENTER YOUR CHOICE:");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
printf("nENTER SHX & Y-REF-->>:");
scanf("%f %f",&sh,&ref);
id(smat);
smat[0][1]=sh;
smat[0][2]=(-1)*sh*ref;
mul(cor,smat,n);
goto label;
break;
case 2:
printf("nENTER VALUES FOR SHY & Y-REF-->>");
scanf("%f %f",&sh,&ref);
id(smat);
smat[1][0]=sh;
smat[1][2]=(-1)*sh*ref;
mul(cor,smat,n);
goto label;
break;
case 3:
exit(0);
}
getch();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-66-2048.jpg)

![Practical : 11
Aim :-Implement Cohen-Sutherland Line Clipping Algorithm.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<dos.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<graphics.h>
int w1,w2,w3,w4;
typedef struct coordinate
{
int x,y;
char code[4];
}PT;
void drawwindow();
void drawline (PT p1,PT p2,int cl);
PT setcode(PT p);
int visibility (PT p1,PT p2);
PT resetendpt (PT p1,PT p2);
void main()
{
int gd=DETECT, gm,v;
PT p1,p2,ptemp;
initgraph(&gd,&gm," ");
cleardevice();
printf("nnttENTER END-POINT 1 (x,y): ");
scanf("%d,%d",&p1.x,&p1.y);
printf("nnttENTER END-POINT 2 (x,y): ");
scanf("%d,%d",&p2.x,&p2.y);
printf("nnttENTER WINDOW (left,top,right,bottom) : ");
scanf("%d,%d,%d,%d",&w1,&w2,&w3,&w4);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-69-2048.jpg)

![void drawwindow()
{
setcolor(WHITE);
rectangle(w1,w2,w3,w4);
}
void drawline (PT p1,PT p2,int cl)
{
setcolor(cl);
line(p1.x,p1.y,p2.x,p2.y);
}
PT setcode(PT p)
{
PT ptemp;
if(p.y<w2)
ptemp.code[0]='1';
else
ptemp.code[0]='0';
if(p.y>w4)
ptemp.code[1]='1';
else
ptemp.code[1]='0';
if (p.x>w3)
ptemp.code[2]='1';
else
ptemp.code[2]='0';
if (p.x<w1)
ptemp.code[3]='1';
else
ptemp.code[3]='0';
ptemp.x=p.x;
ptemp.y=p.y;
return(ptemp);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-71-2048.jpg)
![int visibility (PT p1,PT p2)
{
int i,flag=0;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
if((p1.code[i]!='0')||(p2.code[i]!='0'))
flag=1;
}
if(flag==0)
return(0);
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
if((p1.code[i]==p2.code[i]) &&(p1.code[i]=='1'))
flag=0;
}
if(flag==0)
return(1);
return(2);
}
PT resetendpt (PT p1,PT p2)
{
PT temp;
int x,y,i;
float m,k;
if( p1.code[3]=='1')
x=w1;
if(p1.code[2]=='1')
x=w3;
if((p1.code[3]=='1')||(p1.code[2]=='1'))
{
m=(float) (p2.y-p1.y)/(p2.x-p1.x);
k=(p1.y+(m*(x-p1.x)));
temp.y=k;
temp.x=x;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-72-2048.jpg)
![for(i=0;i<4;i++)
temp.code[i]=p1.code[i];
if(temp.y<=w4&&temp.y>=w2)
return(temp);
}
if(p1.code[0]=='1')
y=w2;
if(p1.code [1]=='1')
y=w4;
if((p1.code[0]=='1')||(p1.code[1]=='1'))
{
m=(float)(p2.y-p1.y)/(p2.x-p1.x);
k=(float)p1.x+(float)(y-p1.y)/m;
temp.x=k;
temp.y=y;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
temp.code[i]=p1.code[i];
return(temp);
}
else
return(p1);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-73-2048.jpg)

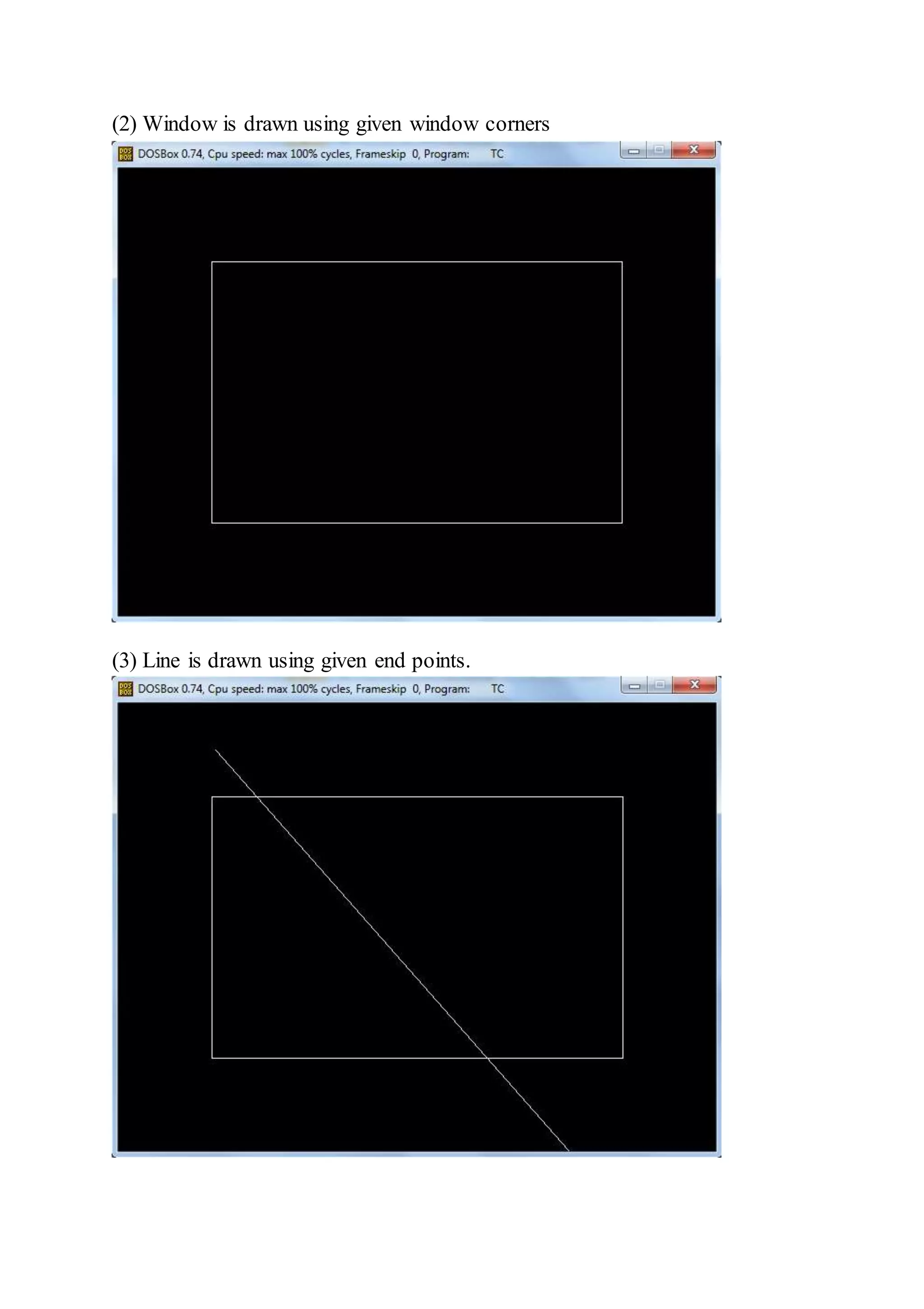
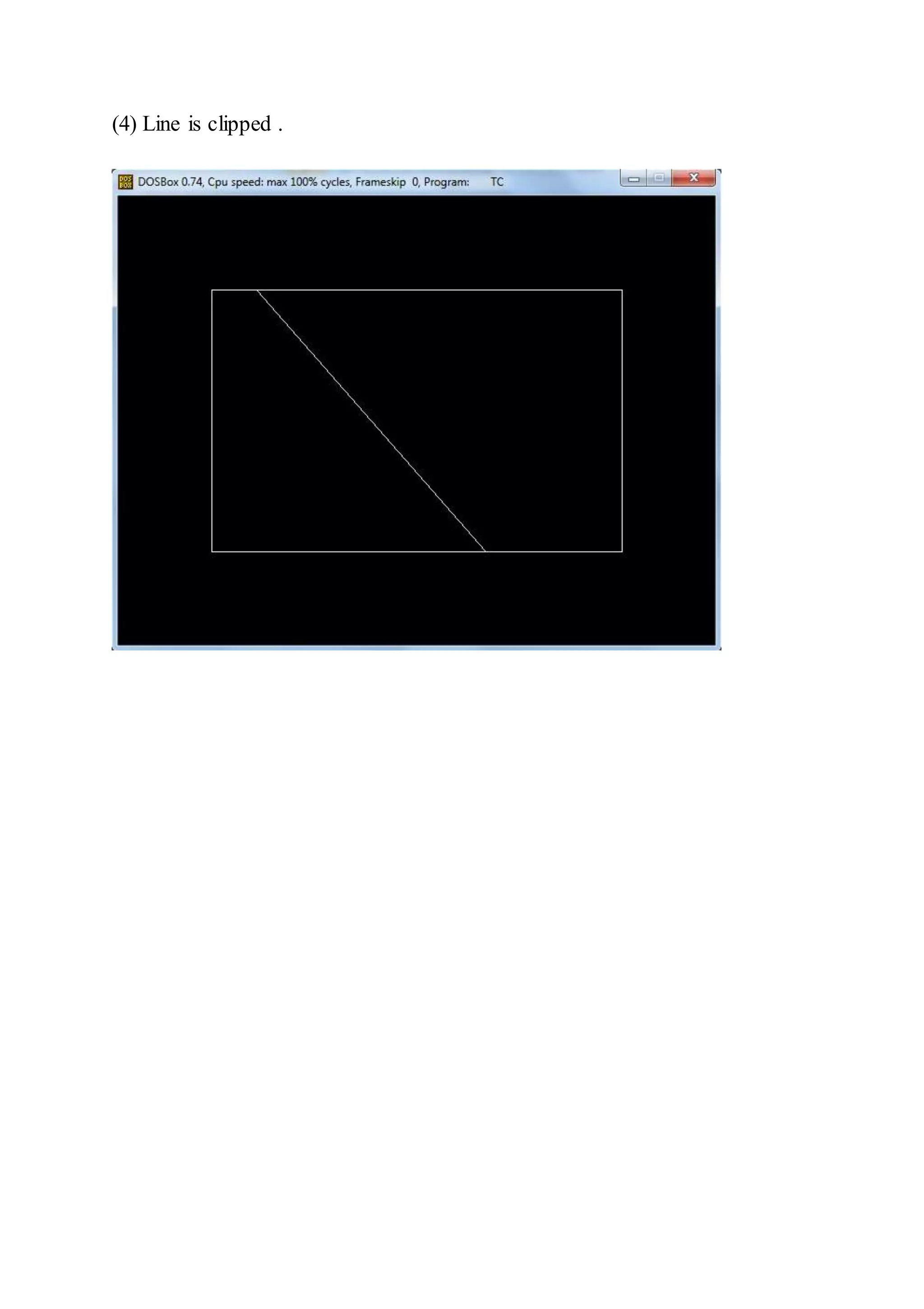
![Practical : 12
Aim :-Implement Sutherland-Hodgeman Polygon Clipping
Algorithm.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<math.h>
typedef struct
{
float x;
float y;
}PT;
int n;
void left(PT p1,PT p[20],PT pp[20])
{
int i,j=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(p[i].x < p1.x && p[i+1].x >= p1.x)
{
if(p[i+1].x-p[i].x!=0)
{
pp[j].y = (p[i+1].y-p[i].y)/(p[i+1].x-p[i].x)* (p1.x-p[i].x)+p[i].y;
}
else
{
pp[j].y = p[i].y;
}
pp[j].x = p1.x;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-77-2048.jpg)
![j++;
pp[j].x=p[i+1].x;
pp[j].y=p[i+1].y;
j++;
}
if(p[i].x > p1.x && p[i+1].x >= p1.x)
{
pp[j].y = p[i+1].y;
pp[j].x = p[i+1].x;
j++;
}
if(p[i].x > p1.x && p[i+1].x <= p1.x)
{
if(p[i+1].x-p[i].x!=0)
{
pp[j].y = (p[i+1].y-p[i].y)/(p[i+1].x-p[i].x)* (p1.x-p[i].x)+p[i].y;
}
else
{
pp[j].y = p[i].y;
}
pp[j].x = p1.x;
j++;
} }
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
p[i].x = pp[i].x;
p[i].y = pp[i].y;
}
p[i].x = pp[0].x;
p[i].y = pp[0].y;
n=j;
}
void right(PT p2,PT p[20],PT pp[20])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-78-2048.jpg)
![{
int i,j=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(p[i].x > p2.x && p[i+1].x <= p2.x)
{
if(p[i+1].x-p[i].x!=0)
{
pp[j].y = (p[i+1].y-p[i].y)/(p[i+1].x-p[i].x)* (p2.x-p[i].x)+p[i].y;
}
else
{
pp[j].y = p[i].y;
}
pp[j].x = p2.x;
j++;
pp[j].x=p[i+1].x;
pp[j].y=p[i+1].y;
j++;
}
if(p[i].x < p2.x && p[i+1].x <= p2.x)
{
pp[j].y = p[i+1].y;
pp[j].x = p[i+1].x;
j++;
}
if(p[i].x < p2.x && p[i+1].x >= p2.x)
{
if(p[i+1].x-p[i].x!=0)
{
pp[j].y = (p[i+1].y-p[i].y)/(p[i+1].x-p[i].x)* (p2.x-p[i].x)+p[i].y;
}
else](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-79-2048.jpg)
![{
pp[j].y = p[i].y;
}
pp[j].x = p2.x;
j++;
} }
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
p[i].x = pp[i].x;
p[i].y = pp[i].y;
}
p[i].x = pp[0].x;
p[i].y = pp[0].y;
n=j;
}
void top(PT p1,PT p[20],PT pp[20])
{
int i,j=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(p[i].y < p1.y && p[i+1].y >= p1.y)
{
if(p[i+1].y-p[i].y!=0)
{
pp[j].x = (p[i+1].x-p[i].x)/(p[i+1].y-p[i].y)* (p1.y-p[i].y)+p[i].x;
}
else
{
pp[j].x = p[i].x;
}
pp[j].y = p1.y;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-80-2048.jpg)
![j++;
pp[j].x=p[i+1].x;
pp[j].y=p[i+1].y;
j++;
}
if(p[i].y > p1.y && p[i+1].y >= p1.y)
{
pp[j].y = p[i+1].y;
pp[j].x = p[i+1].x;
j++;
}
if(p[i].y > p1.y && p[i+1].y <= p1.y)
{
if(p[i+1].y-p[i].y!=0)
{
pp[j].x = (p[i+1].x-p[i].x)/(p[i+1].y-p[i].y)* (p1.y-p[i].y)+p[i].x;
}
else
{
pp[j].x = p[i].x;
}
pp[j].y = p1.y;
j++;
} }
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
p[i].x = pp[i].x;
p[i].y = pp[i].y;
}
p[i].x = pp[0].x;
p[i].y = pp[0].y;
n=j;
}
void bottom(PT p2,PT p[20],PT pp[20])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-81-2048.jpg)
![{
int i,j=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(p[i].y > p2.y && p[i+1].y <= p2.y)
{
if(p[i+1].y-p[i].y!=0)
{
pp[j].x = (p[i+1].x-p[i].x)/(p[i+1].y-p[i].y)* (p2.y-p[i].y)+p[i].x;
}
else
{
pp[j].x = p[i].x;
}
pp[j].y = p2.y;
j++;
pp[j].x=p[i+1].x;
pp[j].y=p[i+1].y;
j++;
}
if(p[i].y < p2.y && p[i+1].y <= p2.y)
{
pp[j].y = p[i+1].y;
pp[j].x = p[i+1].x;
j++;
}
if(p[i].y < p2.y && p[i+1].y >= p2.y)
{
if(p[i+1].y-p[i].y!=0)
{
pp[j].x = (p[i+1].x-p[i].x)/(p[i+1].y-p[i].y)* (p2.y-p[i].y)+p[i].x;
}
else](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-82-2048.jpg)
![{
pp[j].x = p[i].x;
}
pp[j].y = p2.y;
j++;
} }
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
p[i].x = pp[i].x;
p[i].y = pp[i].y;
}
p[i].x = pp[0].x;
p[i].y = pp[0].y;
n=j;
}
void drawpolygon(PT x[20],int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
line(x[i].x,x[i].y,x[i+1].x,x[i+1].y);
}
line(x[i].x,x[i].y,x[0].x,x[0].y);
}
void main()
{
int i,j,gd=DETECT,gm;
PT d,p1,p2,p[20],pi1,pi2,pp[20];
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"");
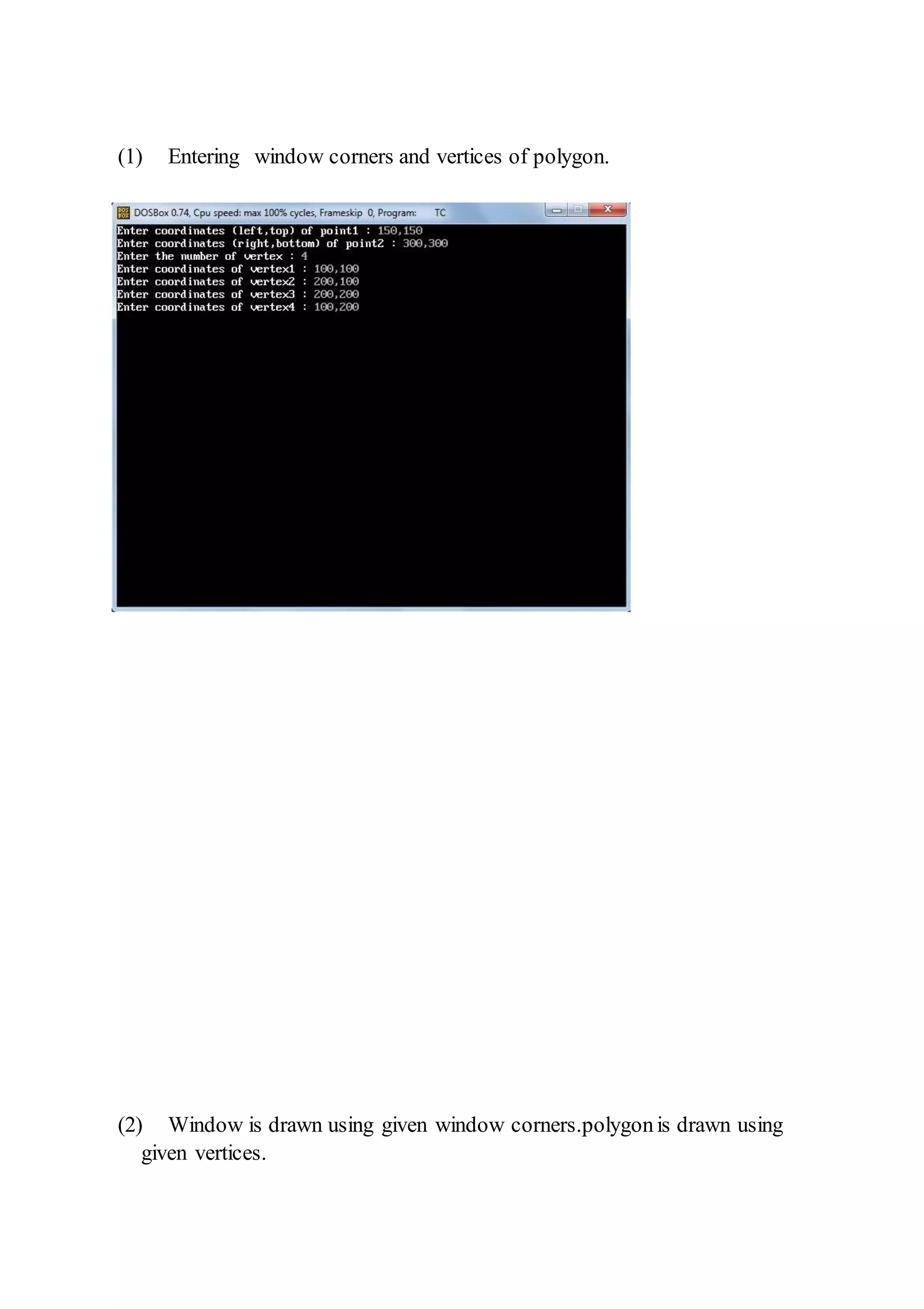
printf("Enter coordinates (left,top) of point1 : ");
scanf("%f,%f",&p1.x,&p1.y);
printf("Enter coordinates (right,bottom) of point2 : ");
scanf("%f,%f",&p2.x,&p2.y);
printf("Enter the number of vertex : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-83-2048.jpg)
![{
printf("Enter coordinates of vertex%d : ",i+1);
scanf("%f,%f",&p[i].x,&p[i].y);
}
p[i].x = p[0].x;
p[i].y = p[0].y;
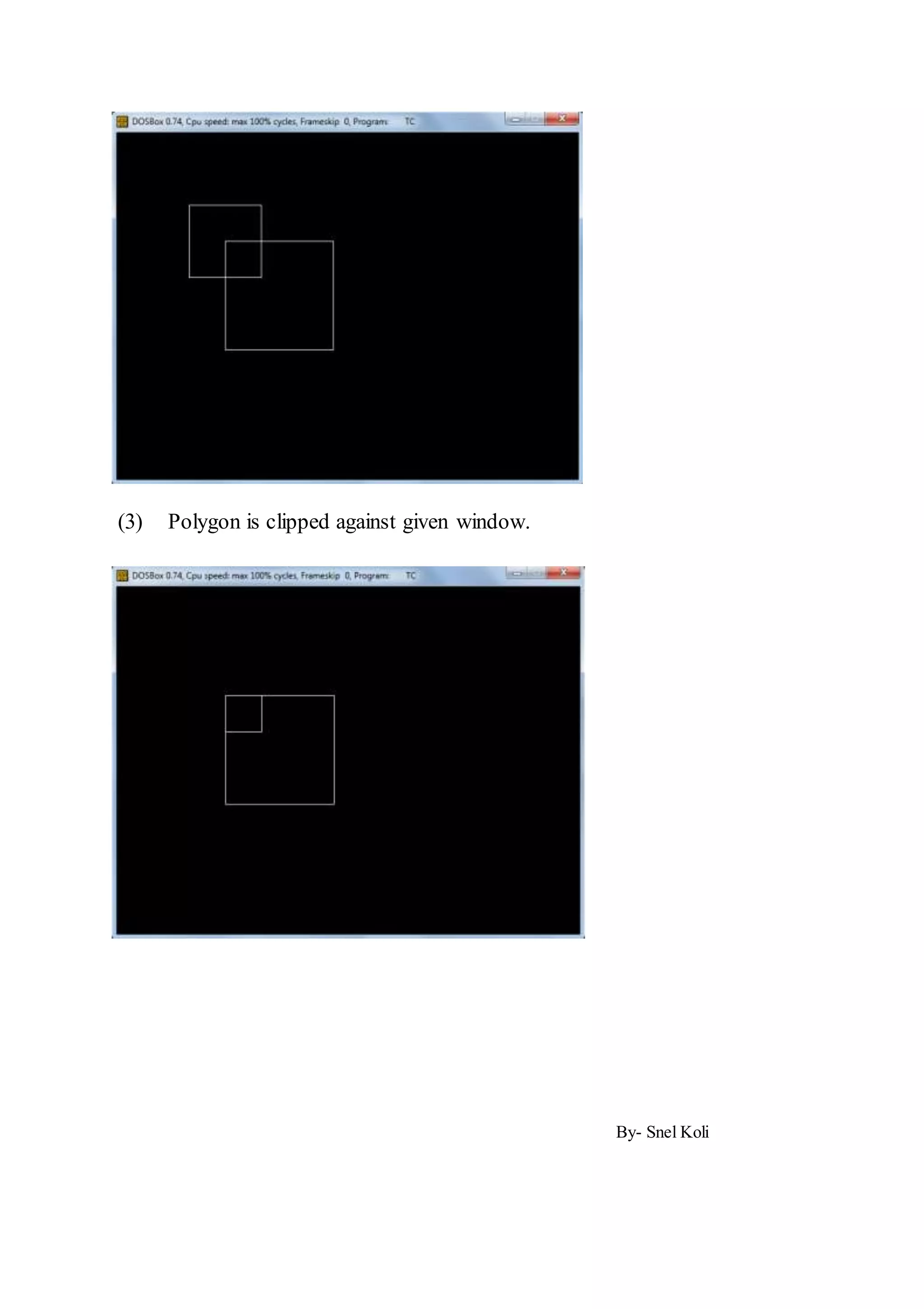
cleardevice();
drawpolygon(p,n);
rectangle(p1.x,p1.y,p2.x,p2.y);
getch();
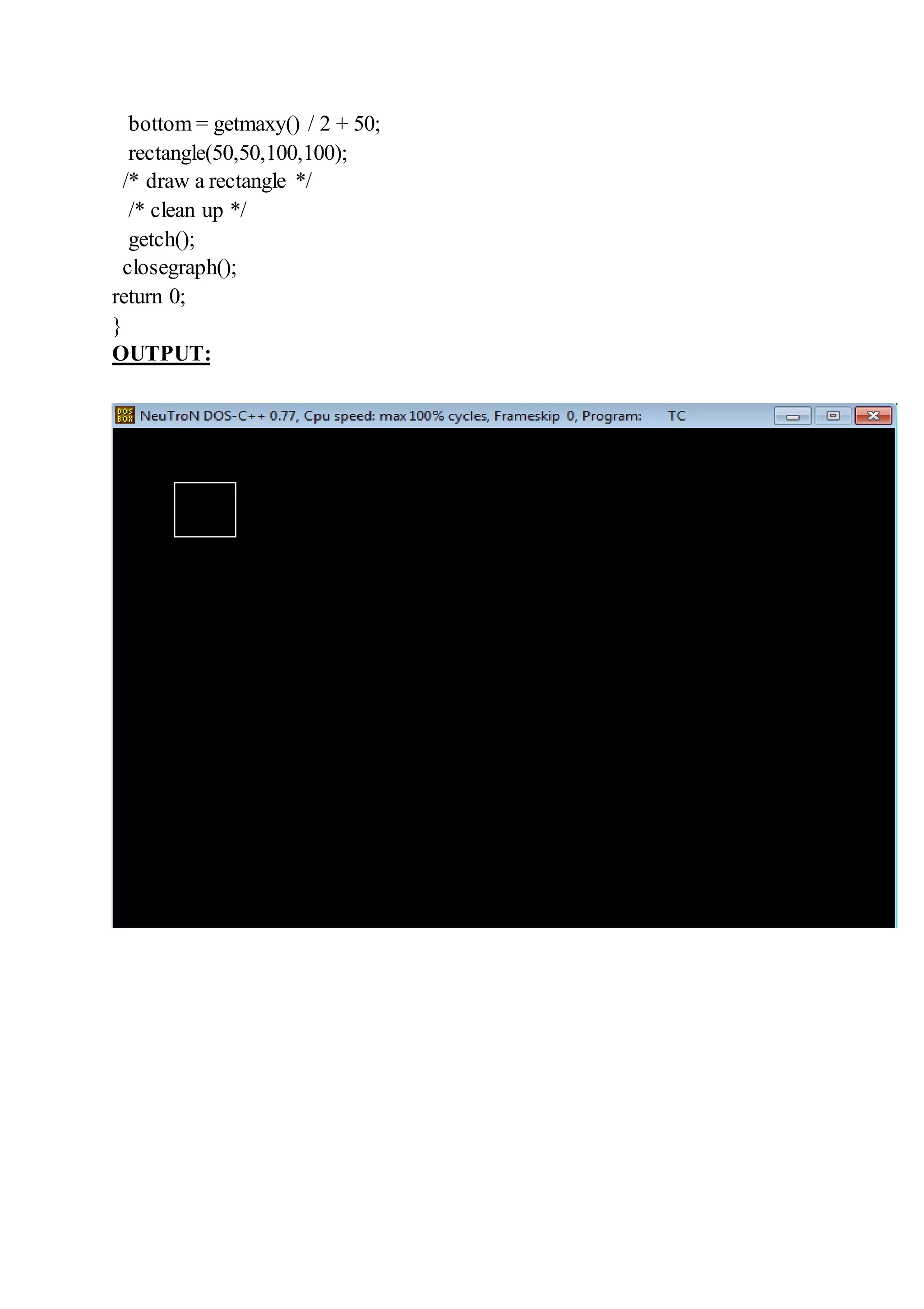
left(p1,p,pp);
right(p2,p,pp);
top(p1,p,pp);
bottom(p2,p,pp);
cleardevice();
rectangle(p1.x,p1.y,p2.x,p2.y);
drawpolygon(p,n);
getch();
closegraph();
}
OUTPUT:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphics-150824064523-lva1-app6892/75/Computer-graphics-84-2048.jpg)