The document discusses computer graphics and summarizes various graphics programming concepts in C, including:
- Two standard output modes: text and graphics mode, which allows pixel manipulation.
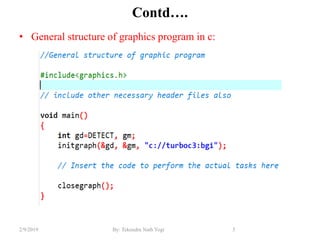
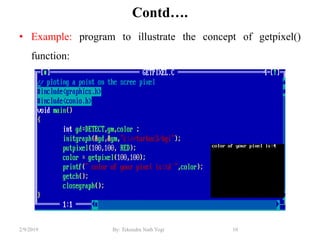
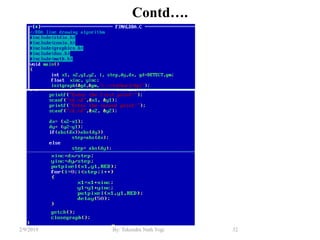
- Graphics library functions defined in "graphics.h" header file for drawing shapes, text and manipulating pixels.
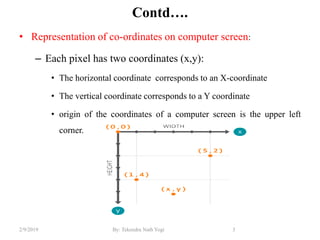
- Coordinate representation on screen with origin at upper left corner.
- Initialization of graphics mode using initgraph() and cleanup with closegraph().
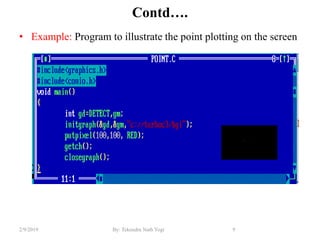
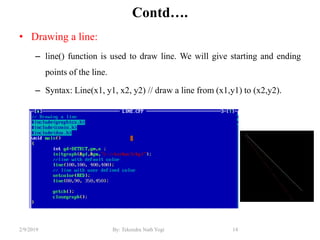
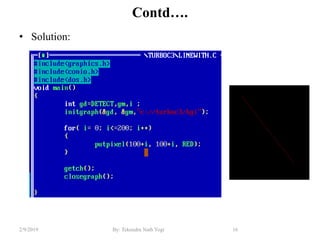
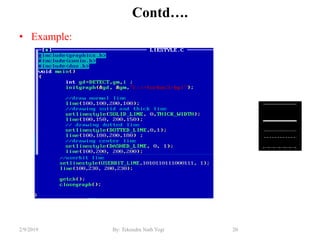
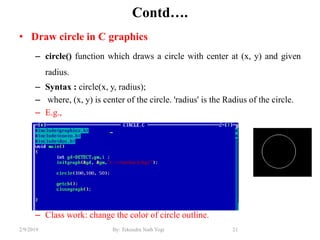
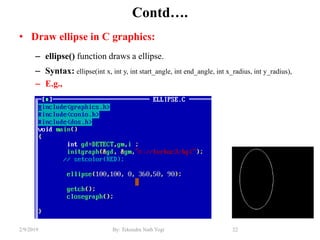
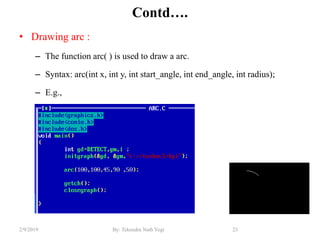
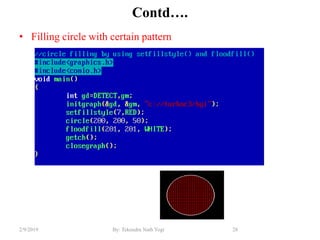
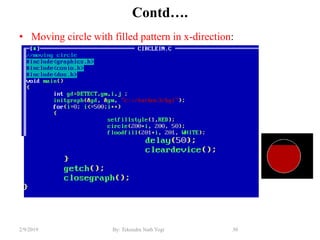
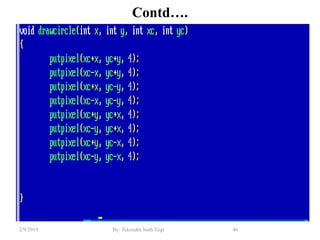
- Functions for drawing lines, circles, rectangles, text and filling areas with patterns.
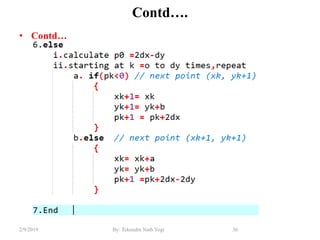
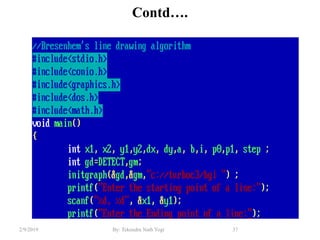
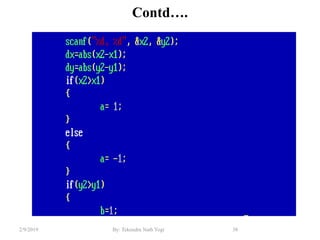
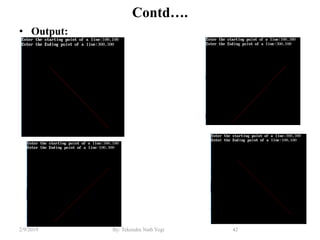
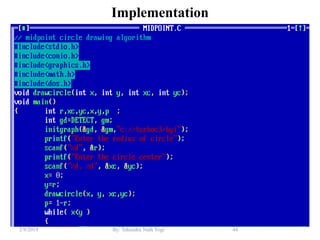
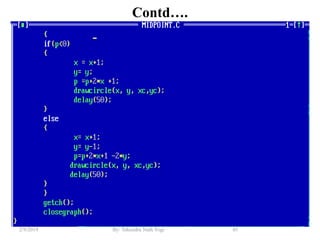
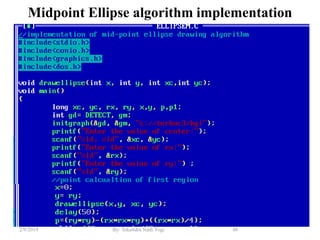
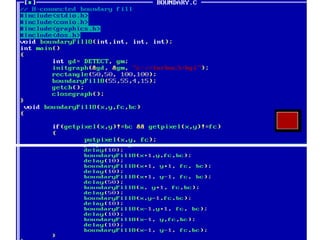
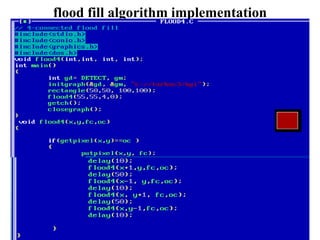
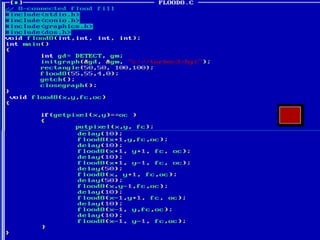
- Algorithms like DDA, Bresenham and midpoint circle/ellipse for drawing shapes.