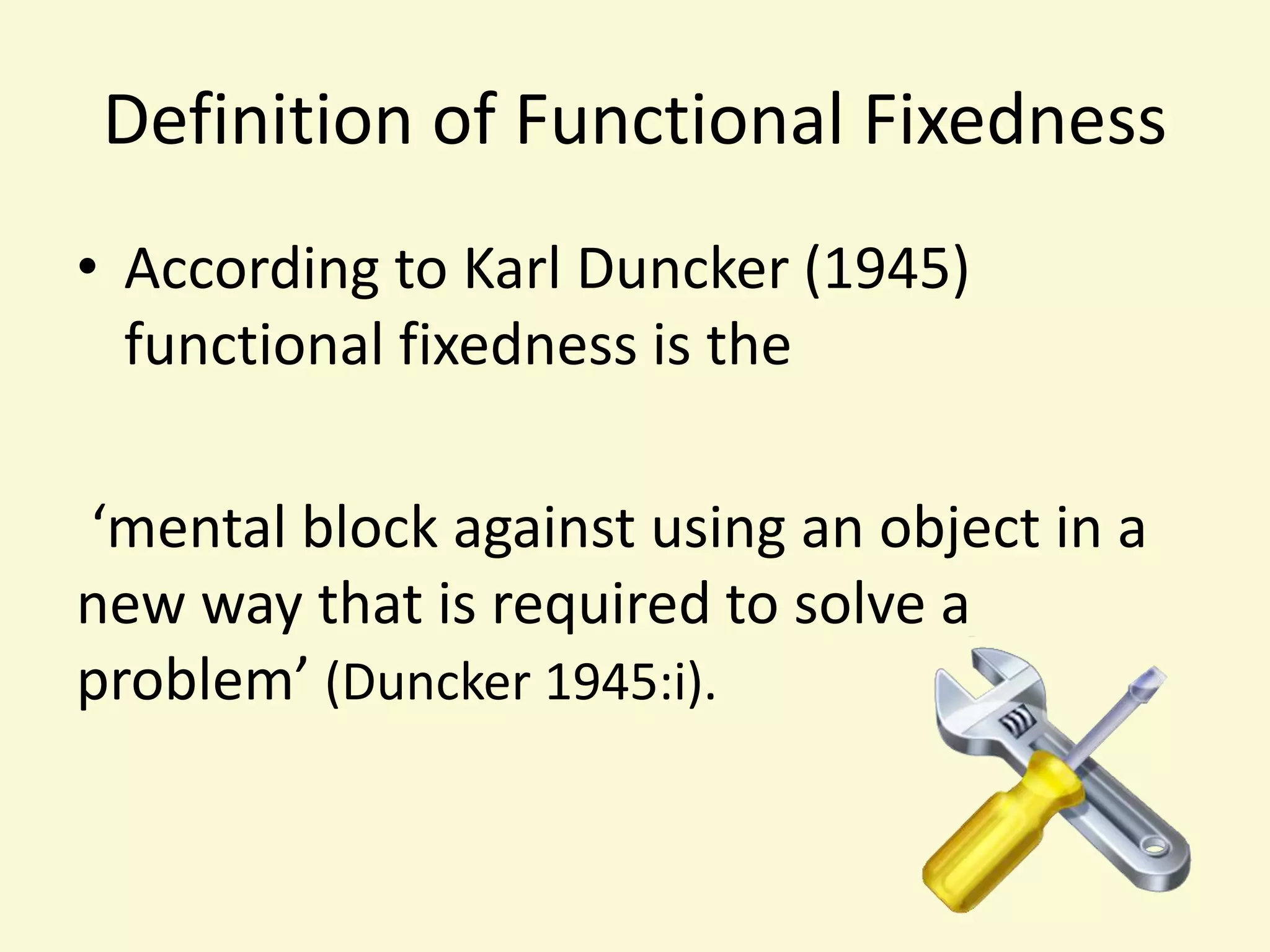
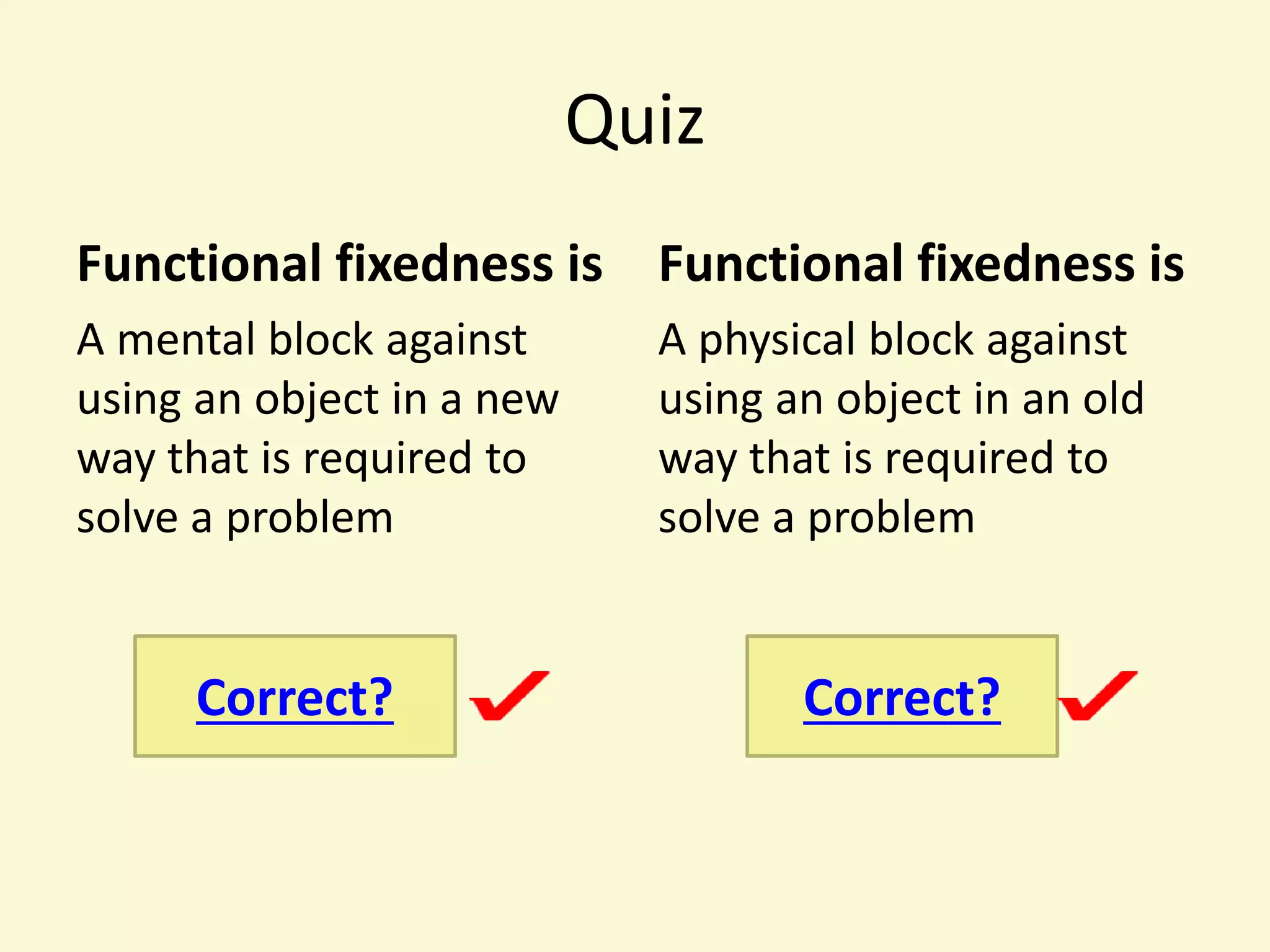
The document presents a lecture on functional fixedness, defining it as a mental block that limits creativity by restricting how objects are perceived and used. It emphasizes the importance of imagination and associations in problem-solving, highlighting methods to encourage creativity through tasks and group discussions. Recommendations include adopting 'what if' thinking and challenging existing associations to foster a more open and imaginative approach to problem-solving.