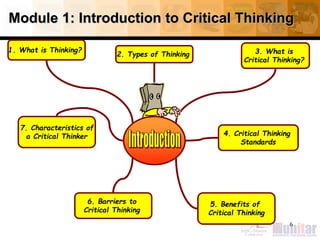
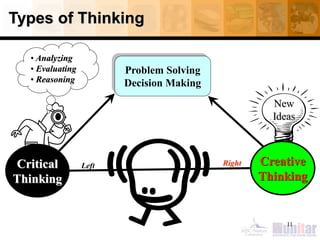
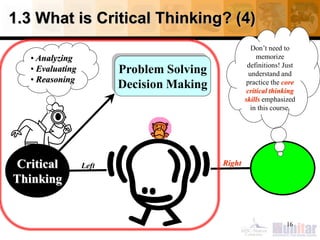
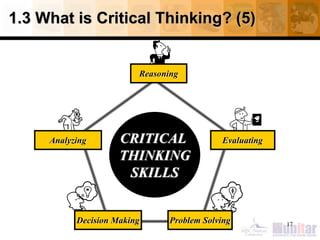
This document provides an introduction to critical thinking. It begins with definitions of thinking and critical thinking. It then discusses different types of thinking including problem solving, decision making, and creative thinking.
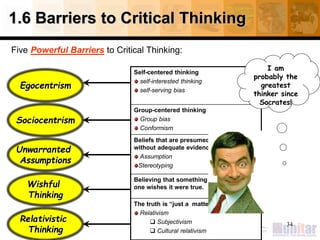
The document outlines critical thinking standards such as clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, and fairness. It discusses barriers to critical thinking like biases, assumptions, stereotyping, and relativism. Benefits of critical thinking are also mentioned including improved academic and job performance.
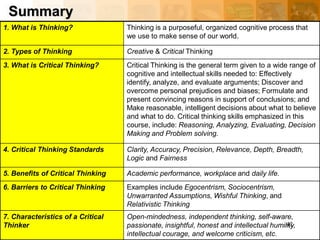
The summary highlights the key topics covered in the introduction to critical thinking document, which are definitions, types of thinking, critical thinking standards, barriers, and benefits. It is concise at 3 sentences while capturing the most important information and high




























![1.6 Mini Quiz – Question 2
36
Which critical thinking barrier does Ali display in this
passage?
A) Self-interested thinking
B) Group bias
C) Self-serving bias
D) Conformism
Muhammad Ali [speaking in Zaire, Africa]: "There's no country
as great as the smallest city in America. I mean [here in Zaire]
you can't watch television. The water won't even run right.
The toilets won't flush. The roads, the cars- there's nothing as
great as America."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/criticalthinking-190206070931/85/Critical-thinking-36-320.jpg)