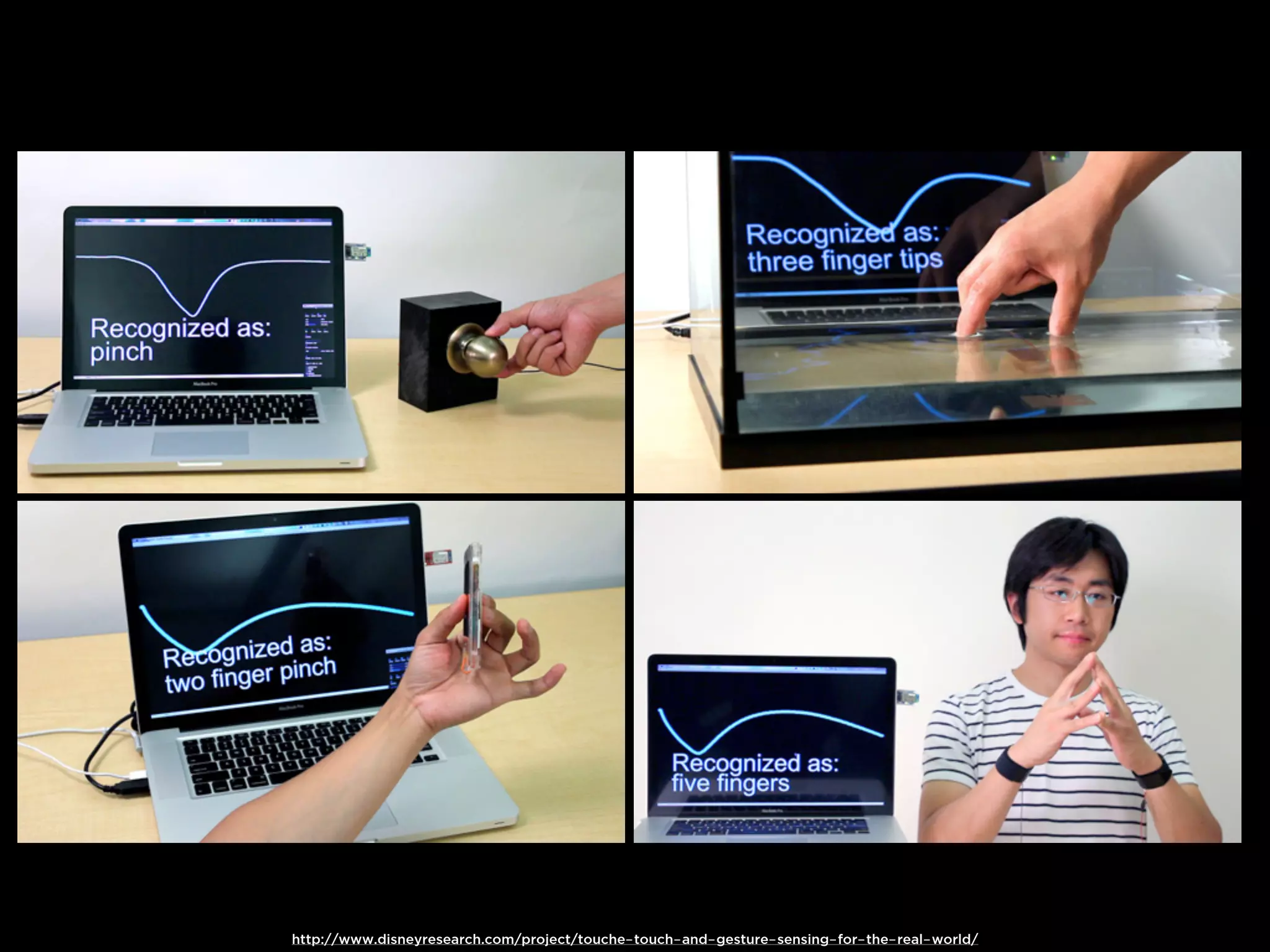
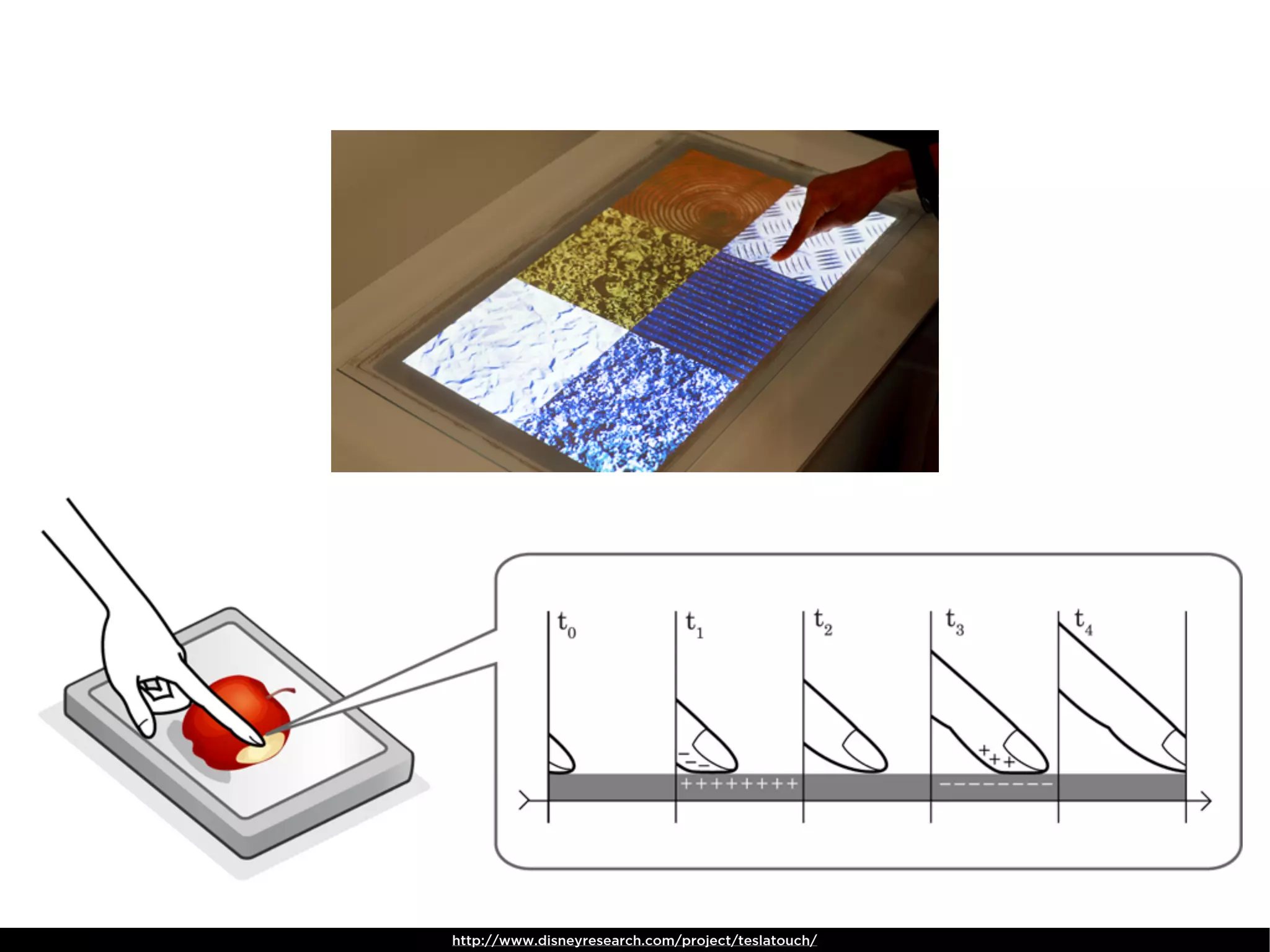
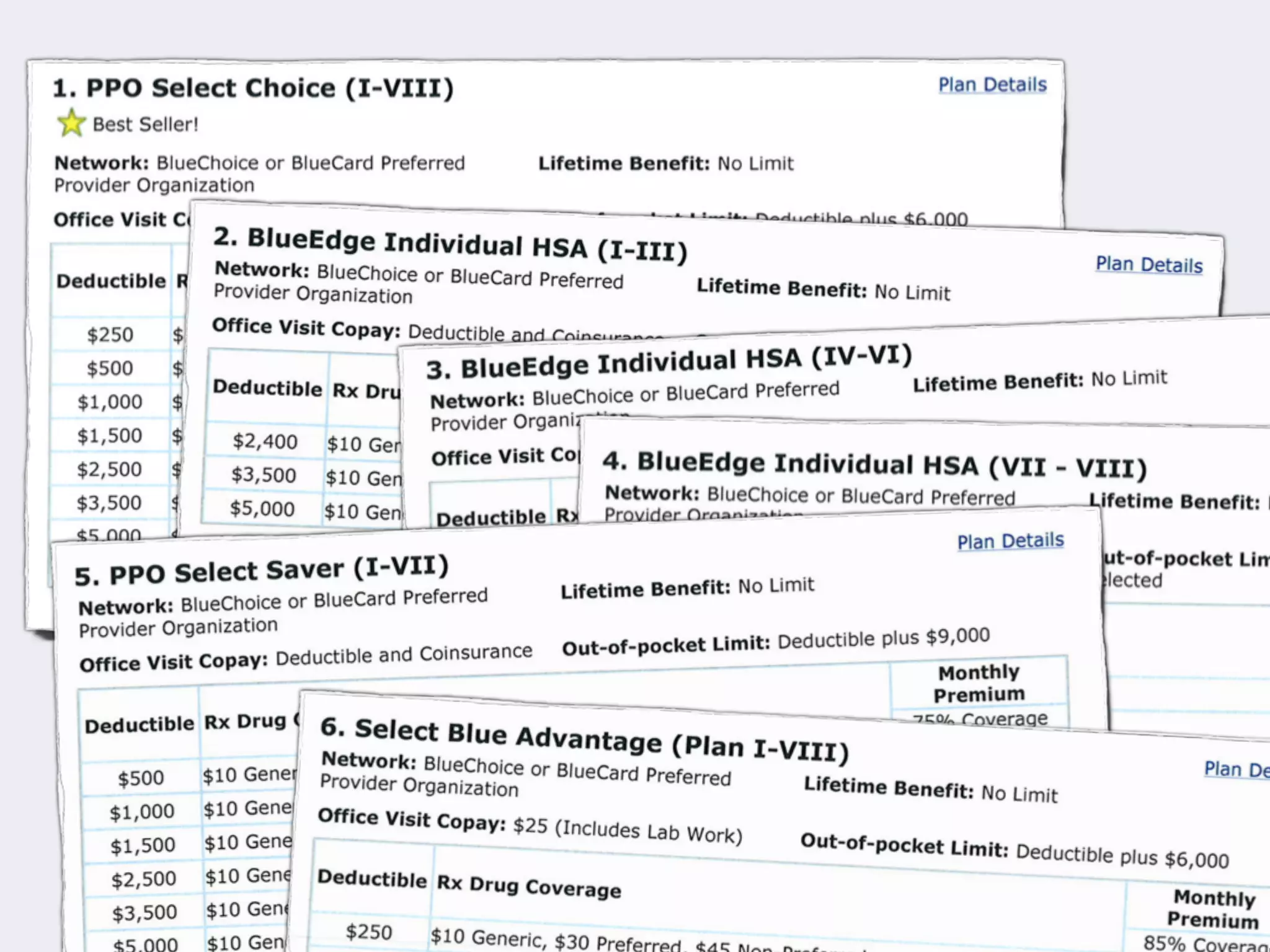
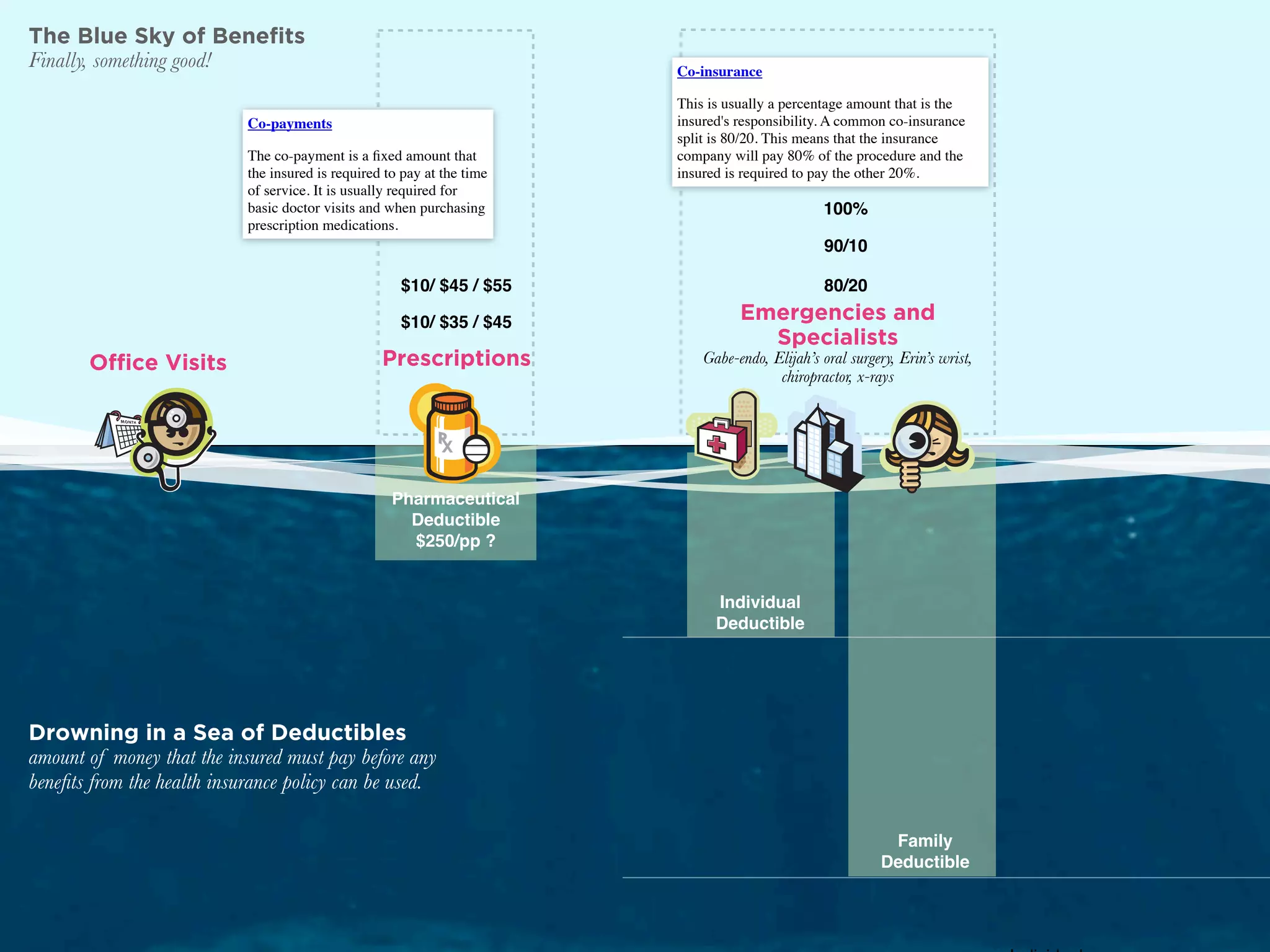
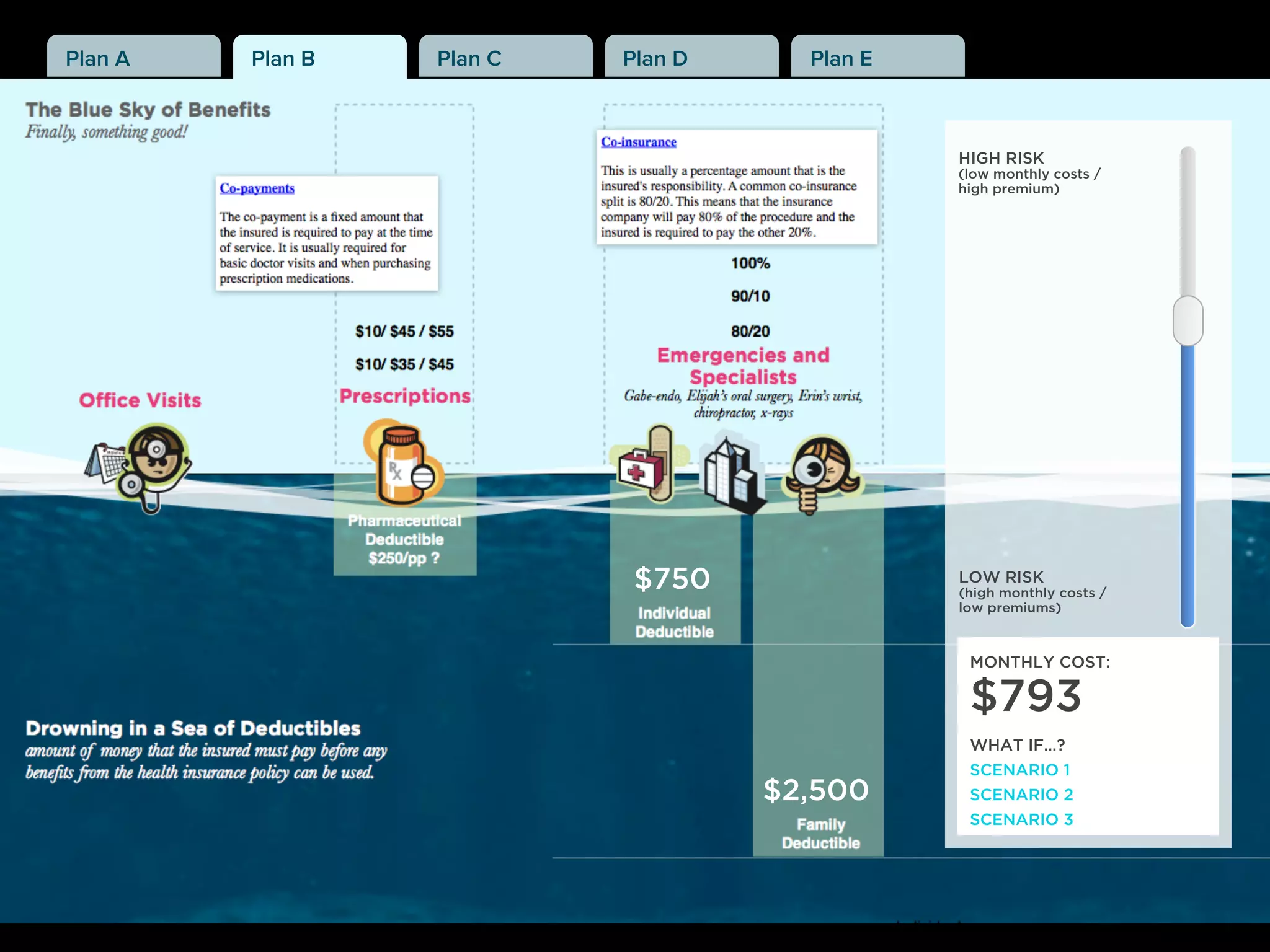
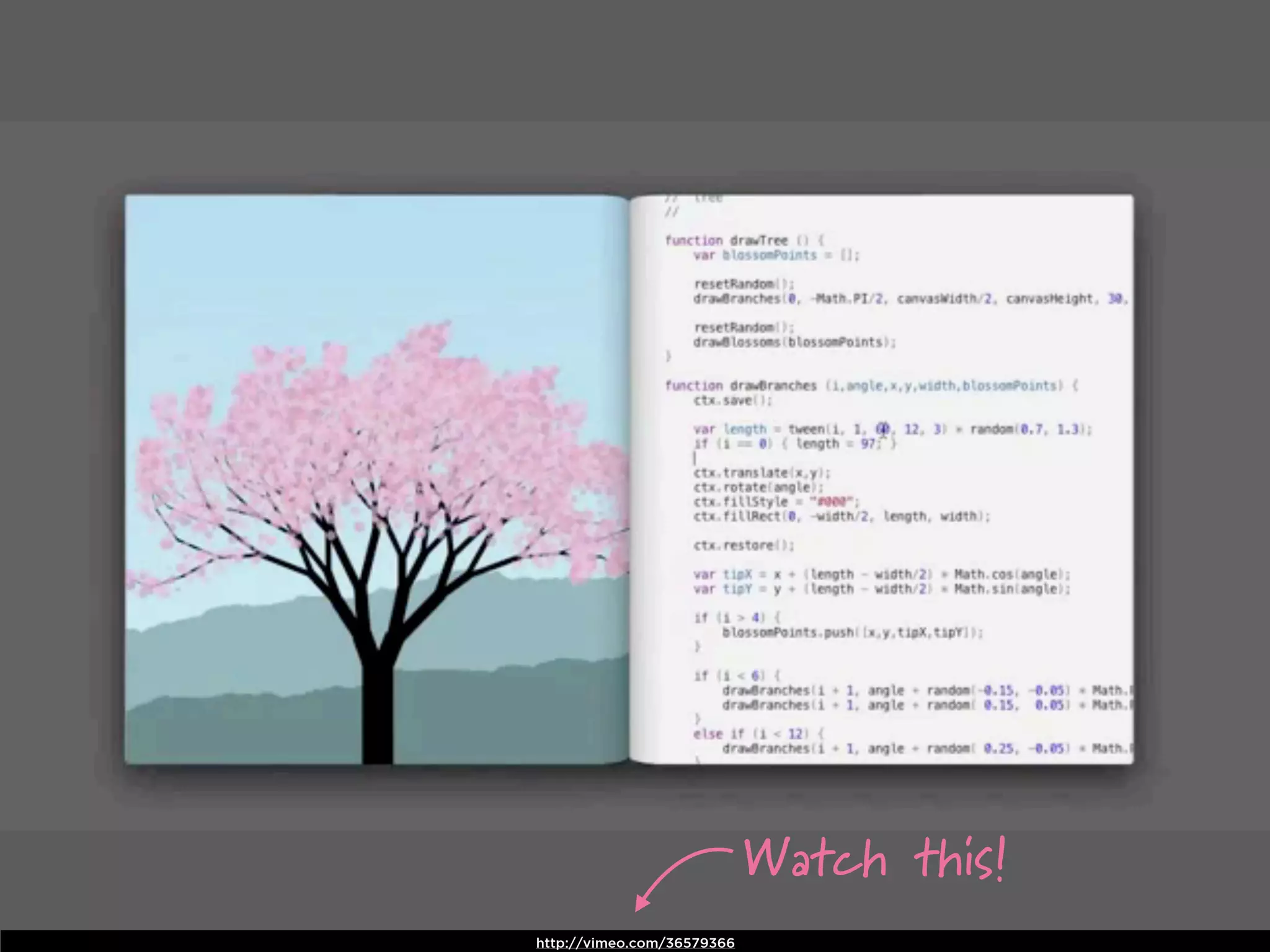
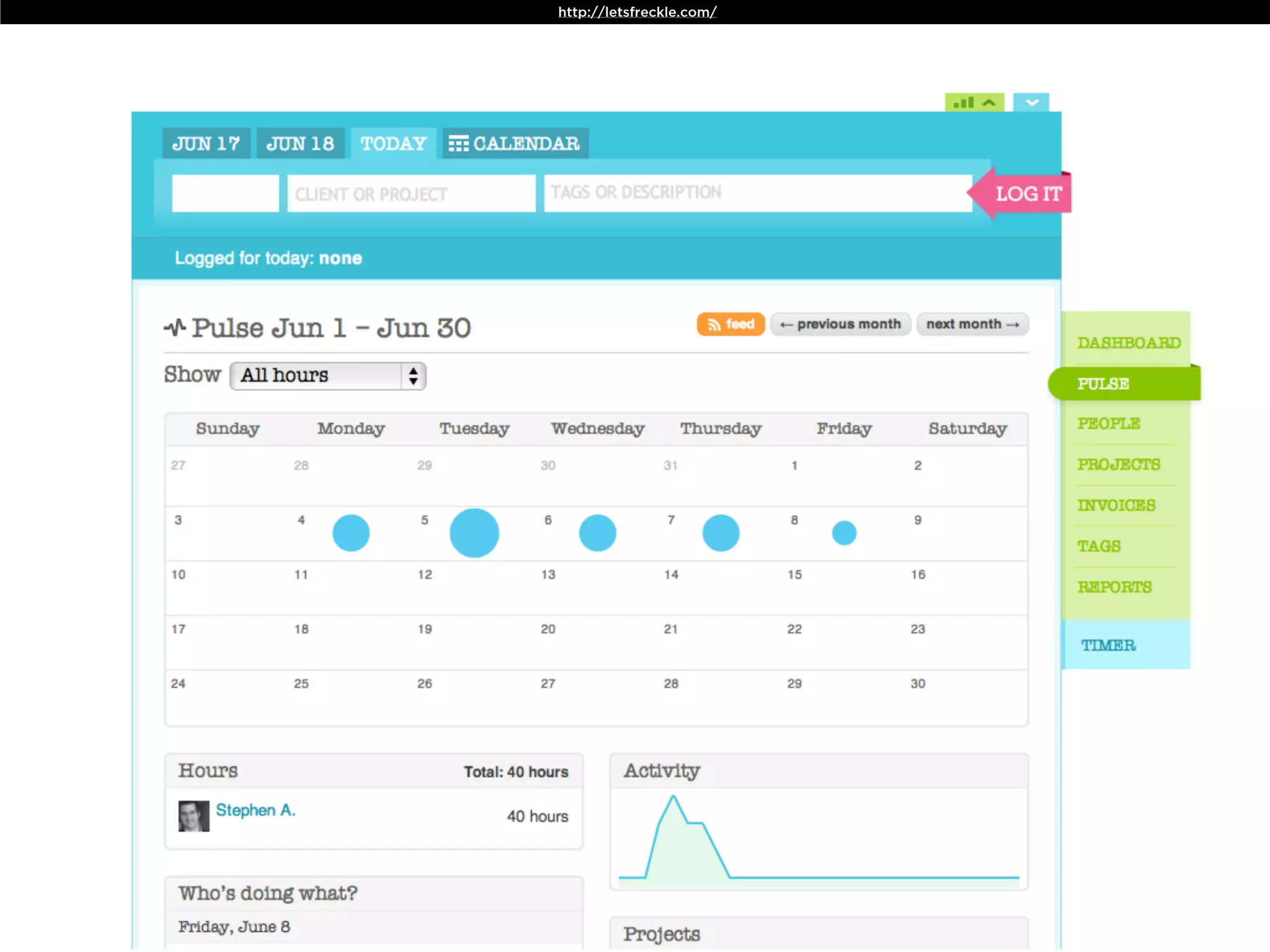
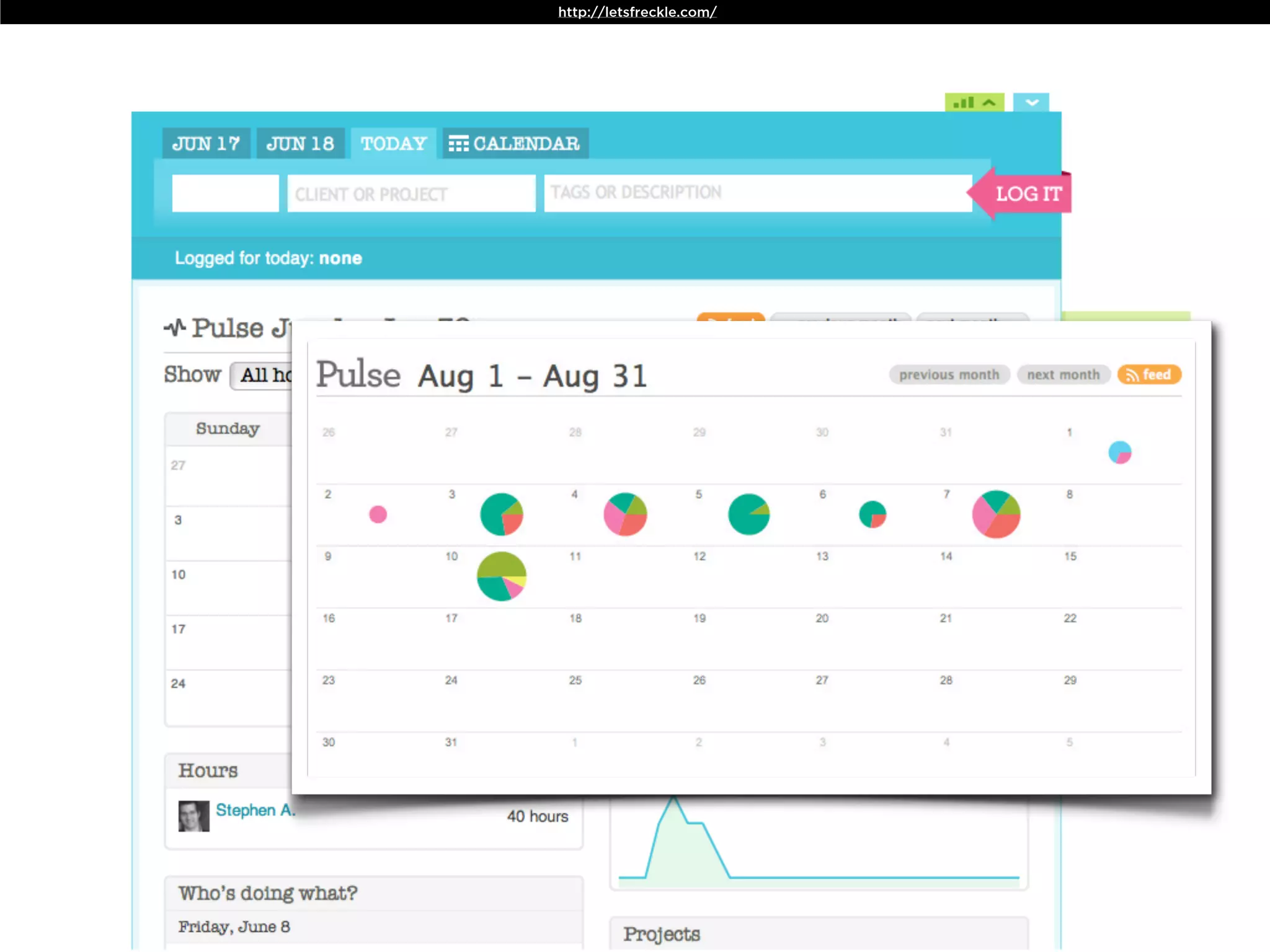
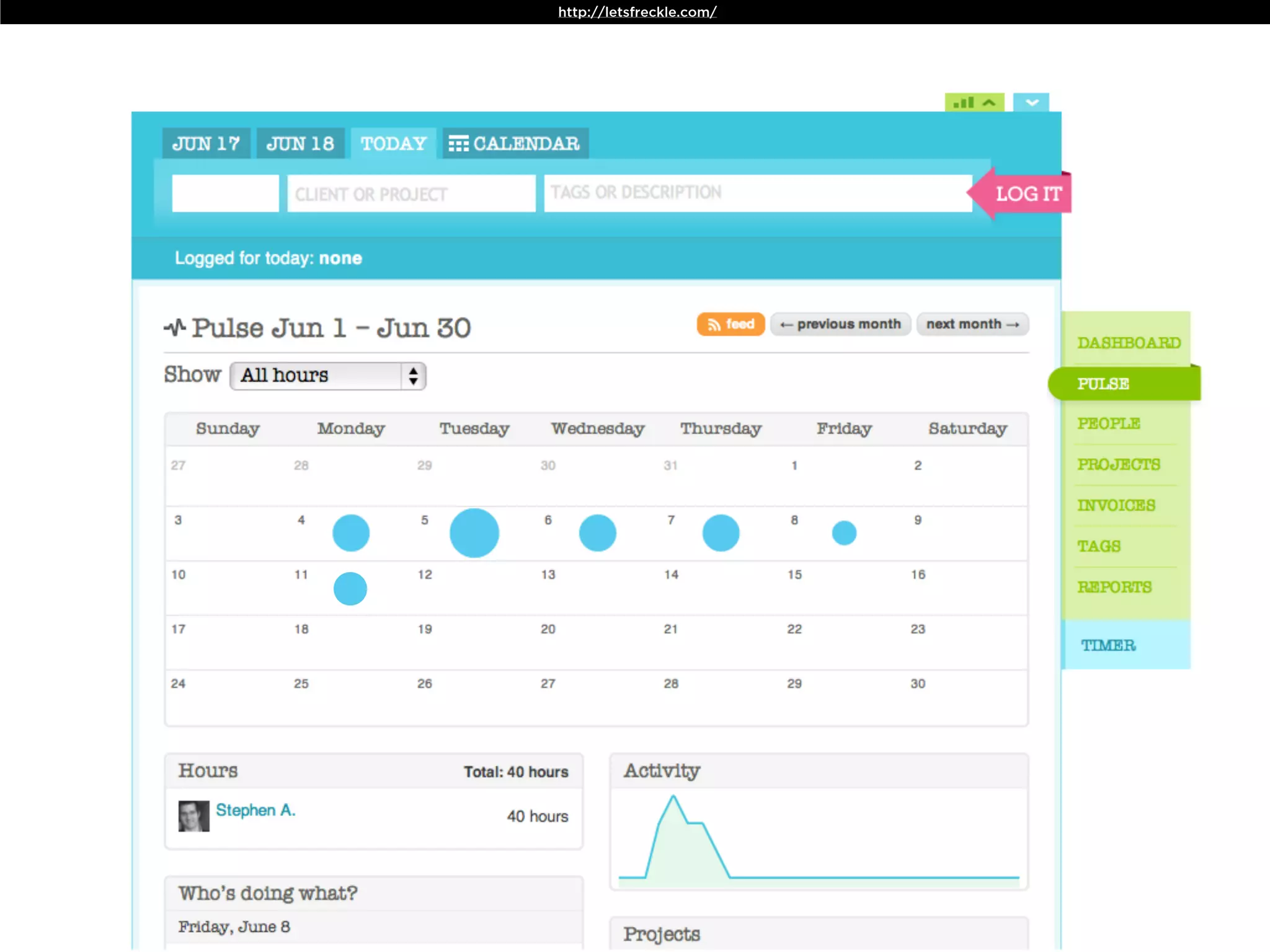
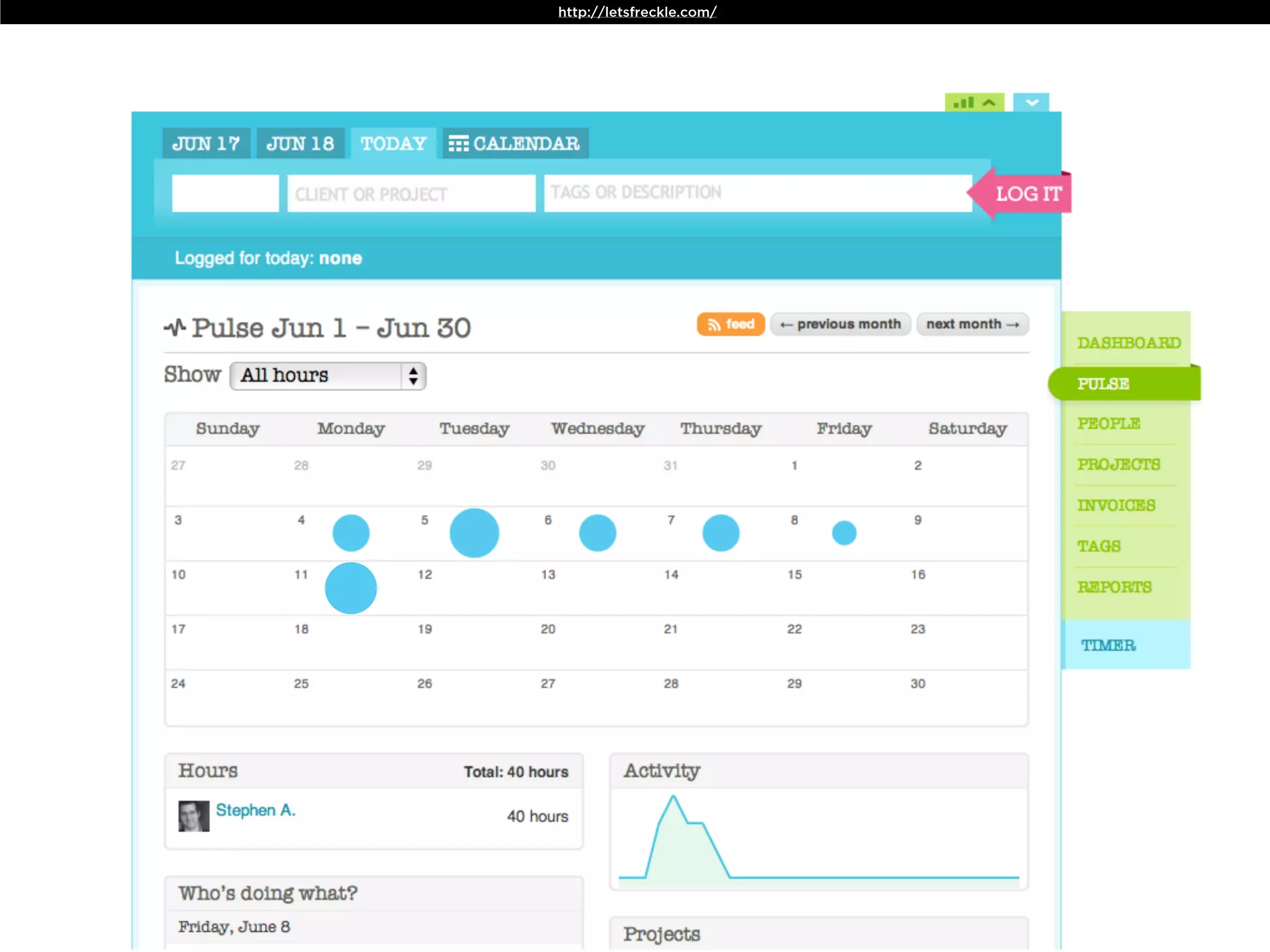
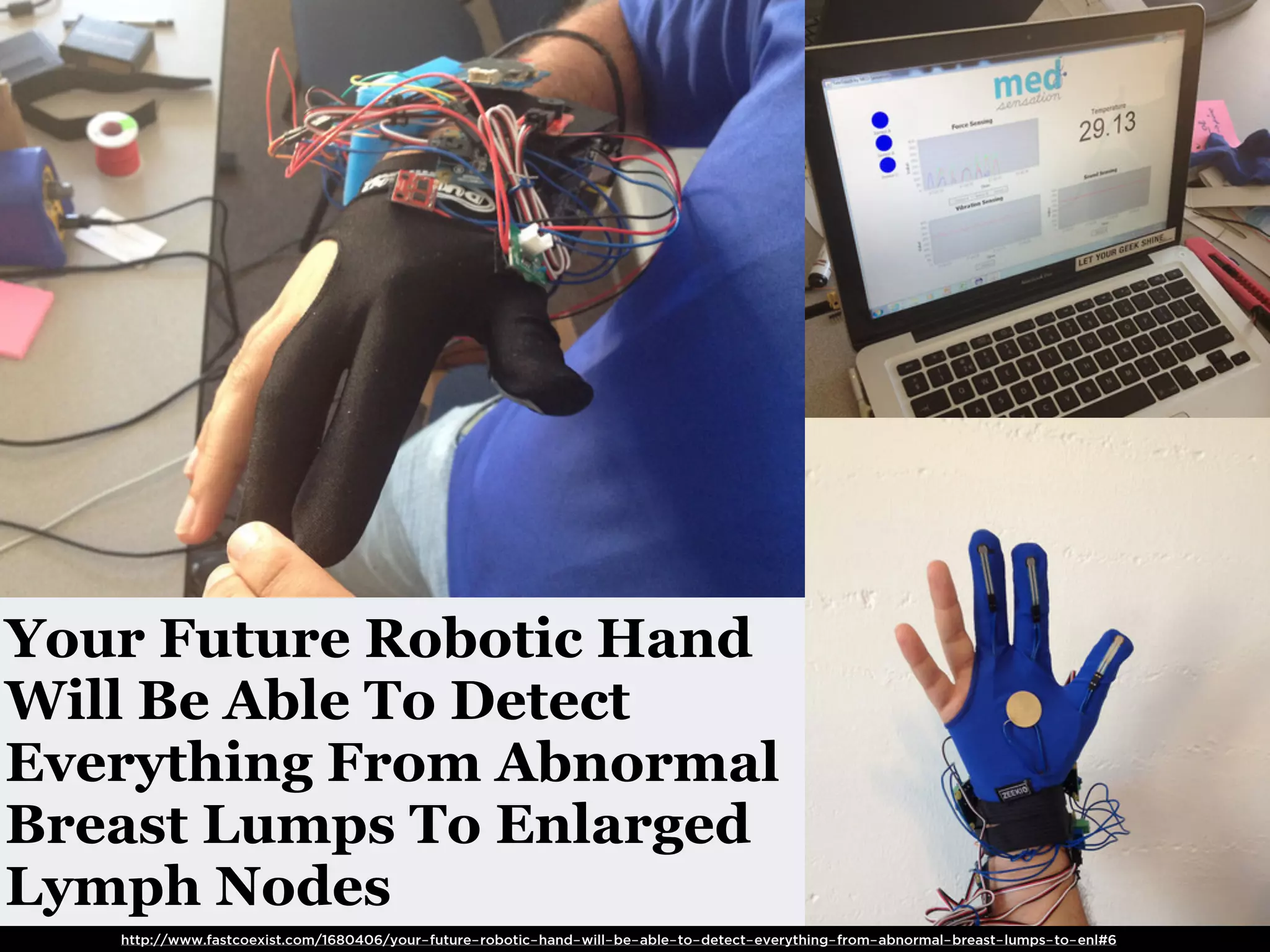
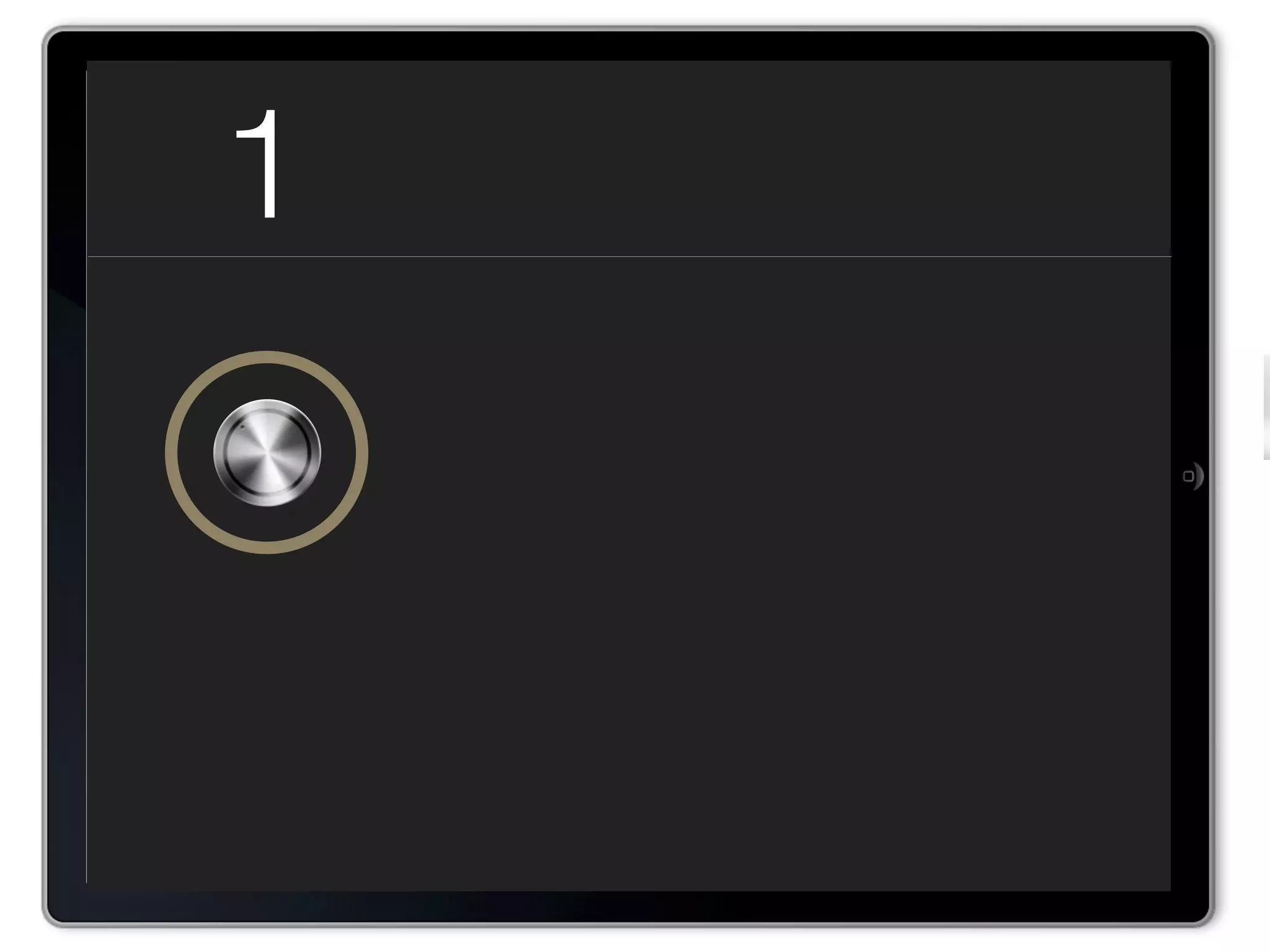
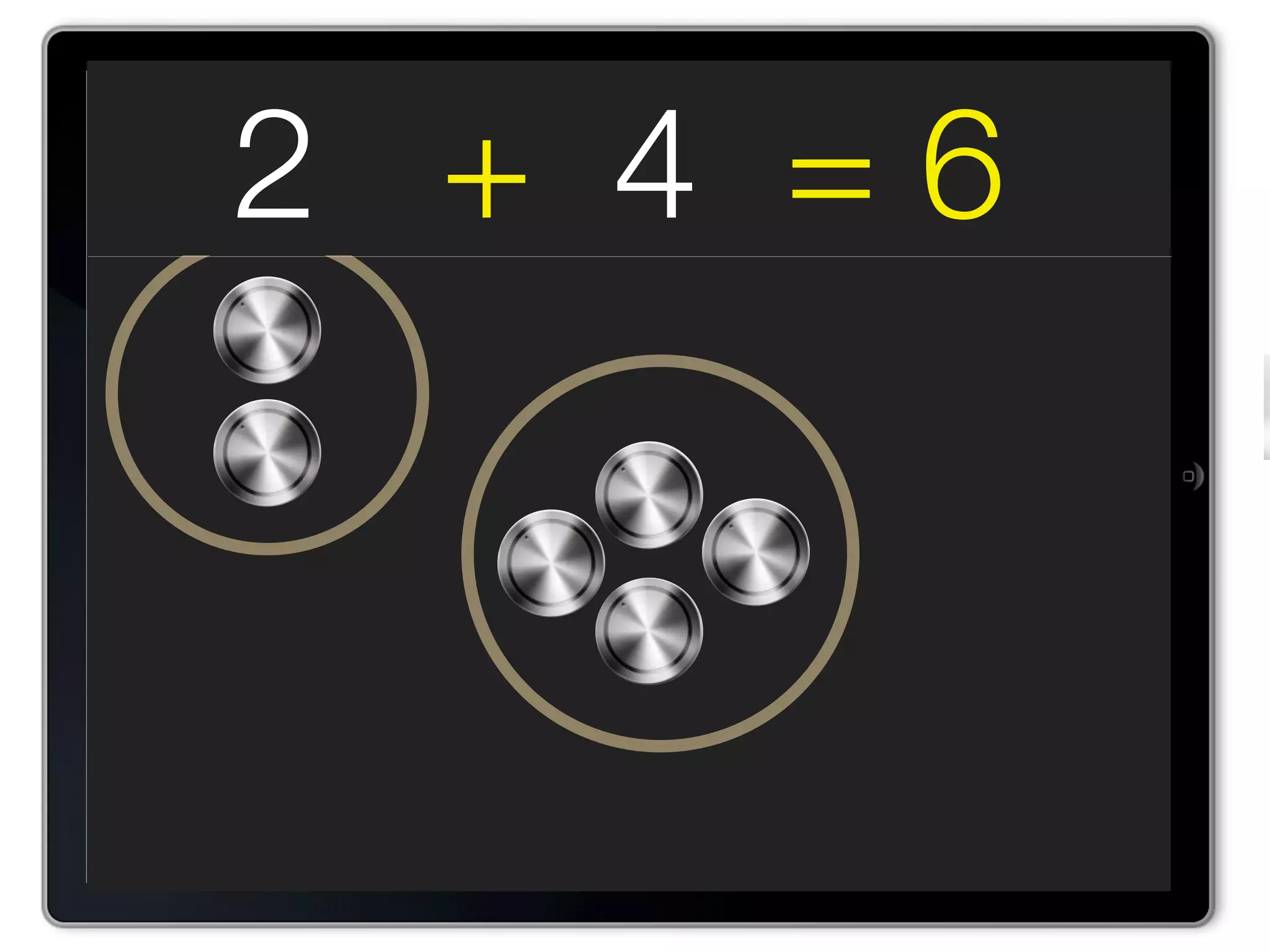
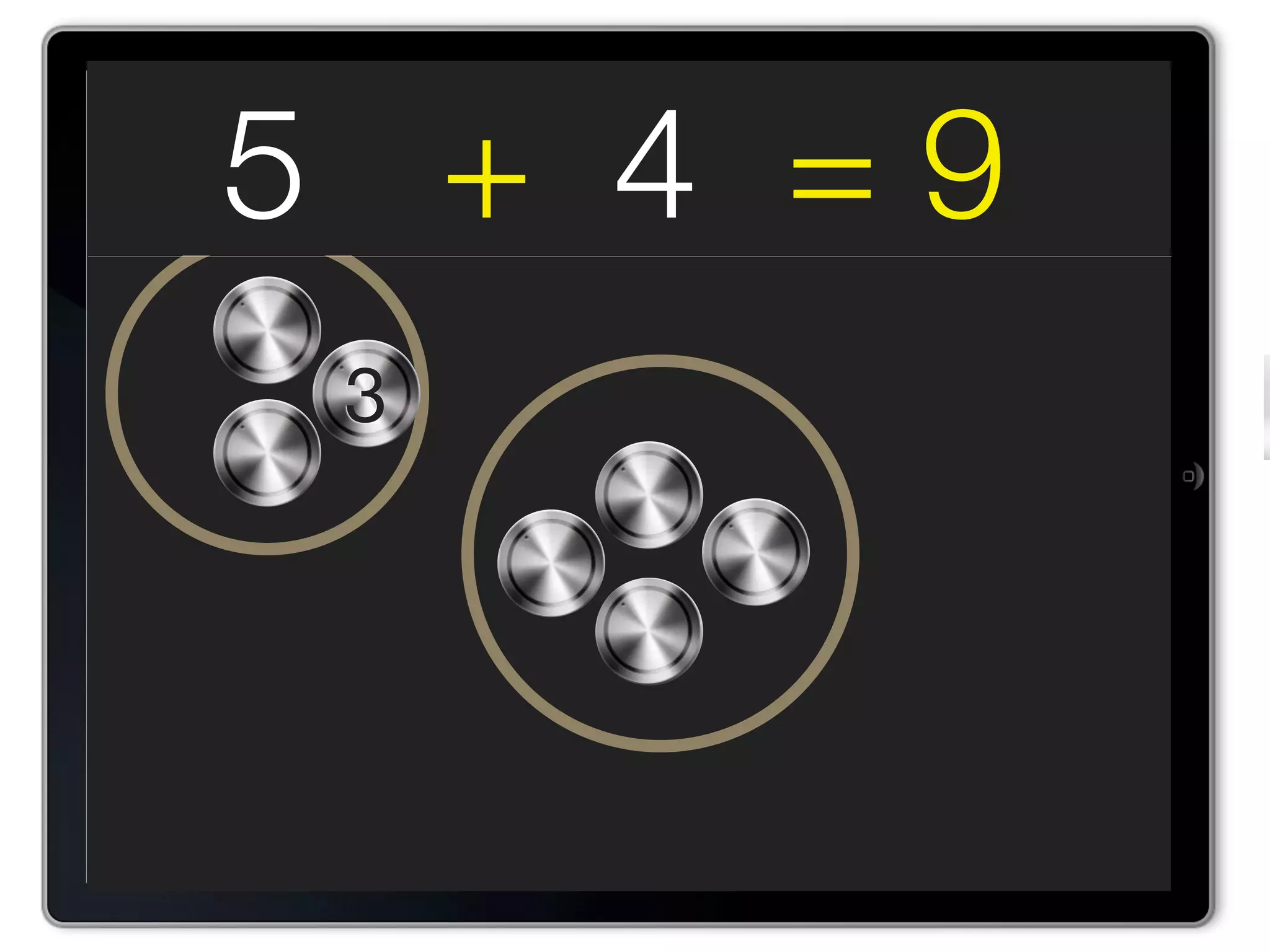
The document discusses Walt Disney's early experiments with animation techniques from the 1920s to 1940s. It notes that Disney borrowed a stop motion camera from his boss in the early 1920s to create hand-drawn animated films called "Laugh-O-Grams". In 1928, Disney experimented with synchronizing audio with film animation. From 1929-1939, more than 75 "Silly Symphonies" were created to further explore advances in sound, color, and animation. The Walt Disney Studios was also the first to experiment with technicolor in 1932 for the animated short "Flowers and Trees".