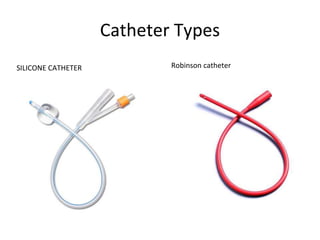
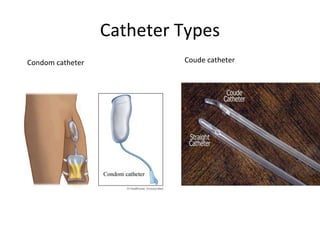
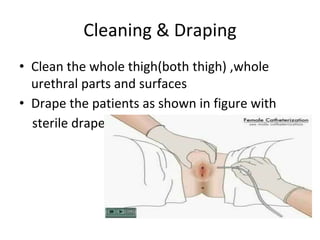
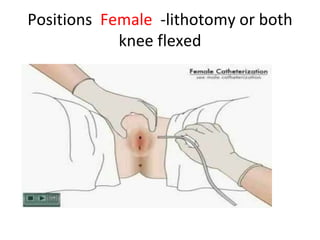
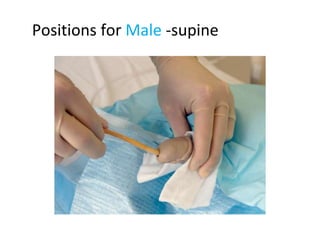
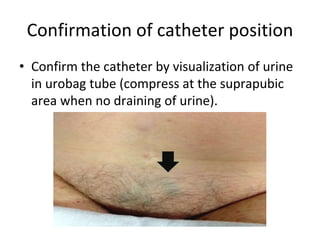
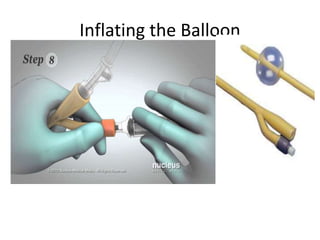
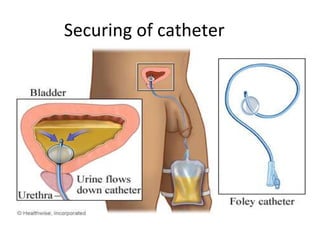
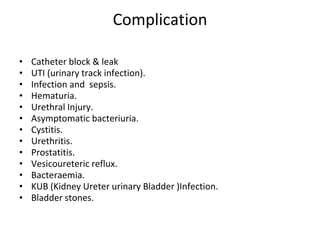
The document provides a comprehensive overview of urinary catheterisation, including its definition, indications, types of catheters, precautions, and detailed procedures for both male and female catheterisation. It also discusses potential complications and emphasizes the importance of proper catheter care and monitoring to prevent infections and other issues. Additionally, it outlines necessary equipment and steps for decatheterisation, ensuring patient comfort and safety throughout the process.