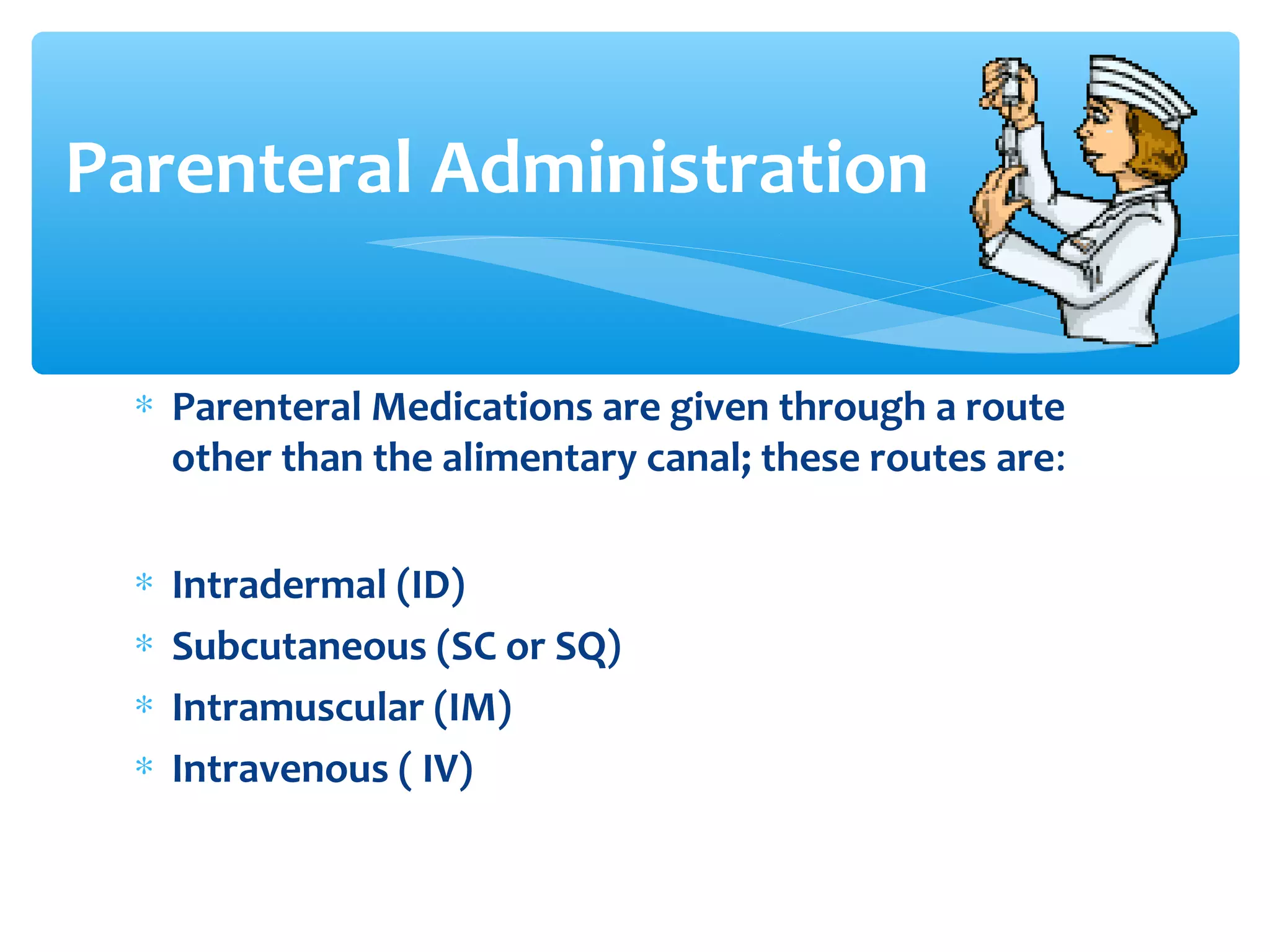
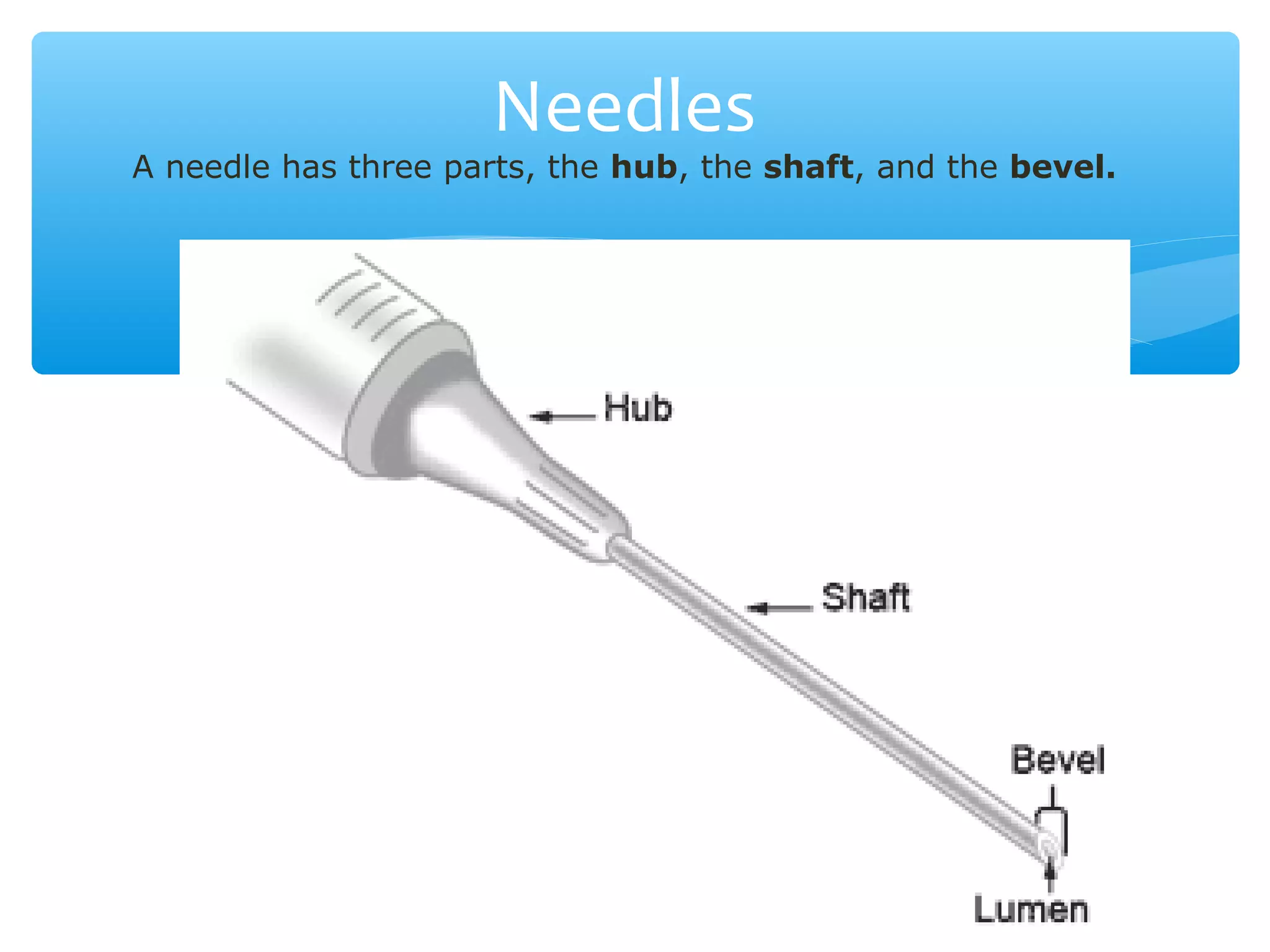
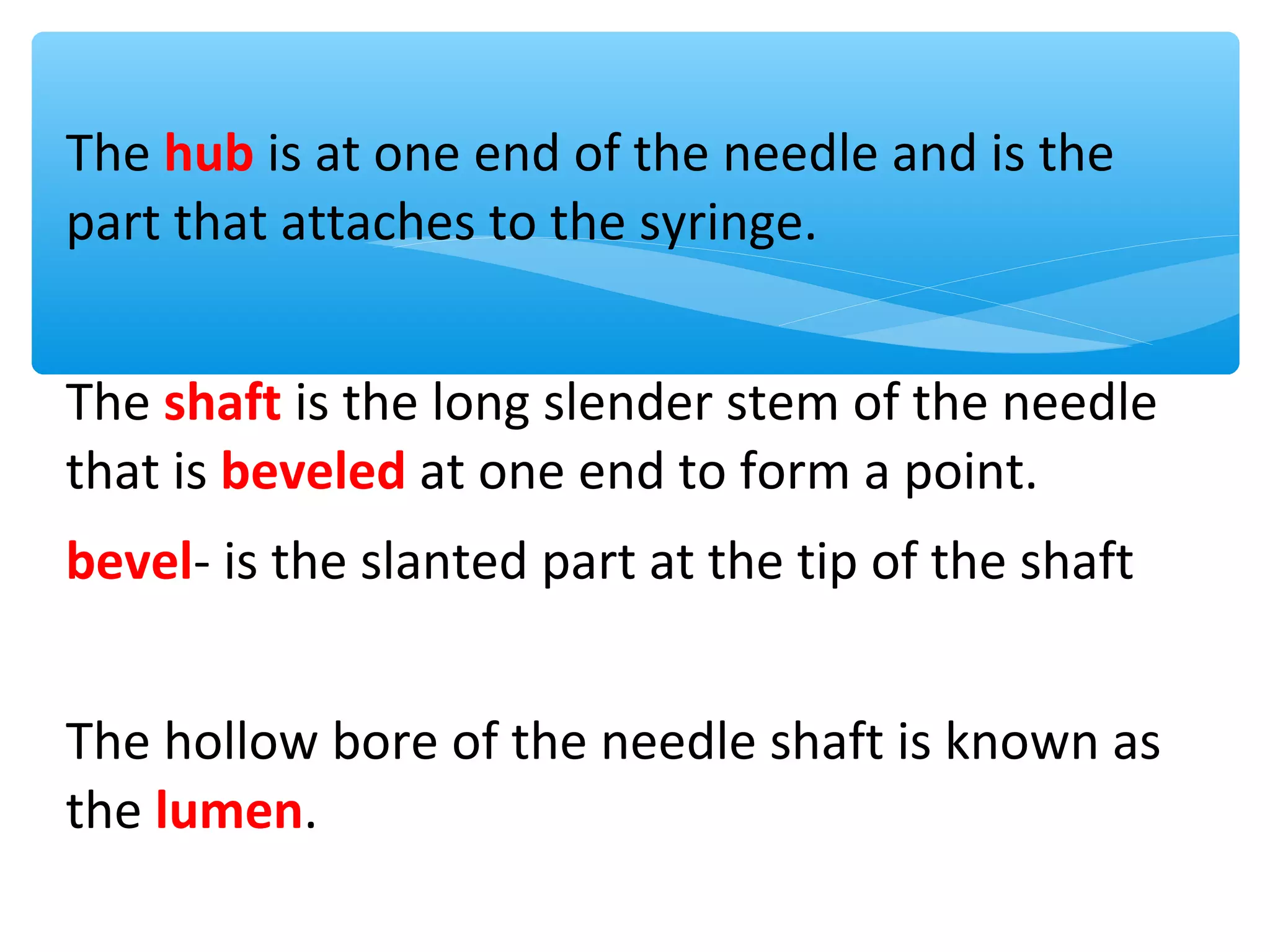
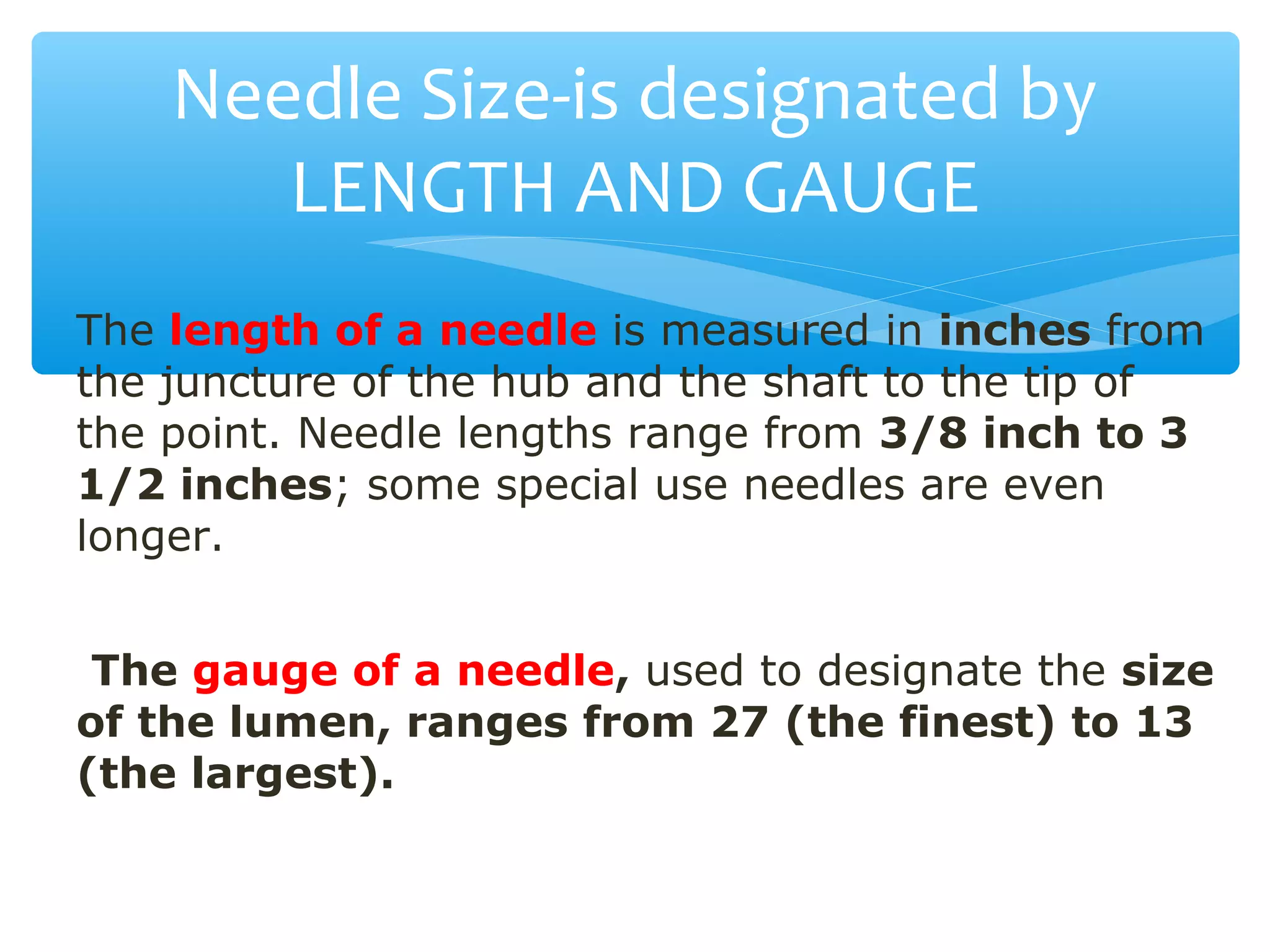
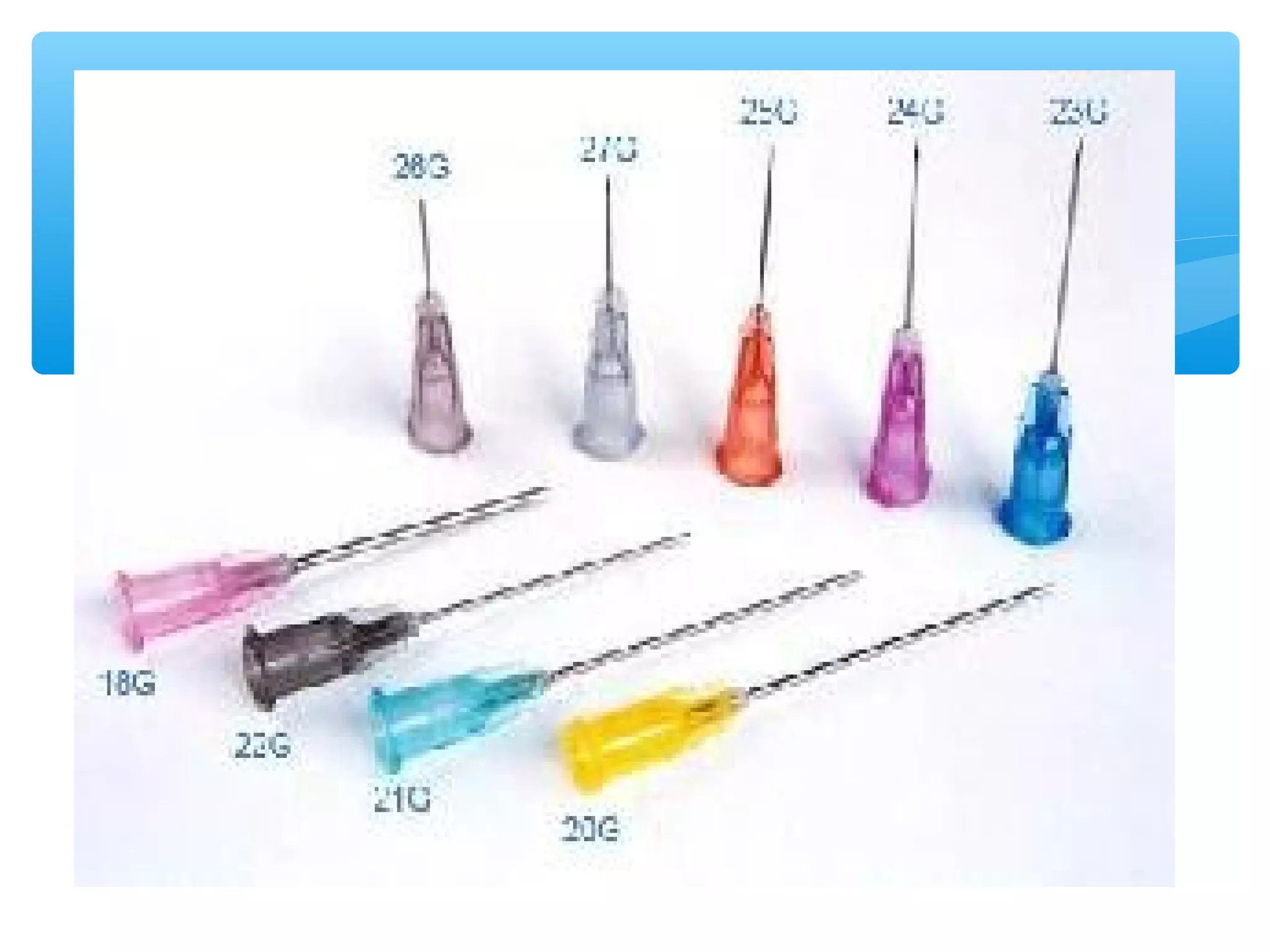
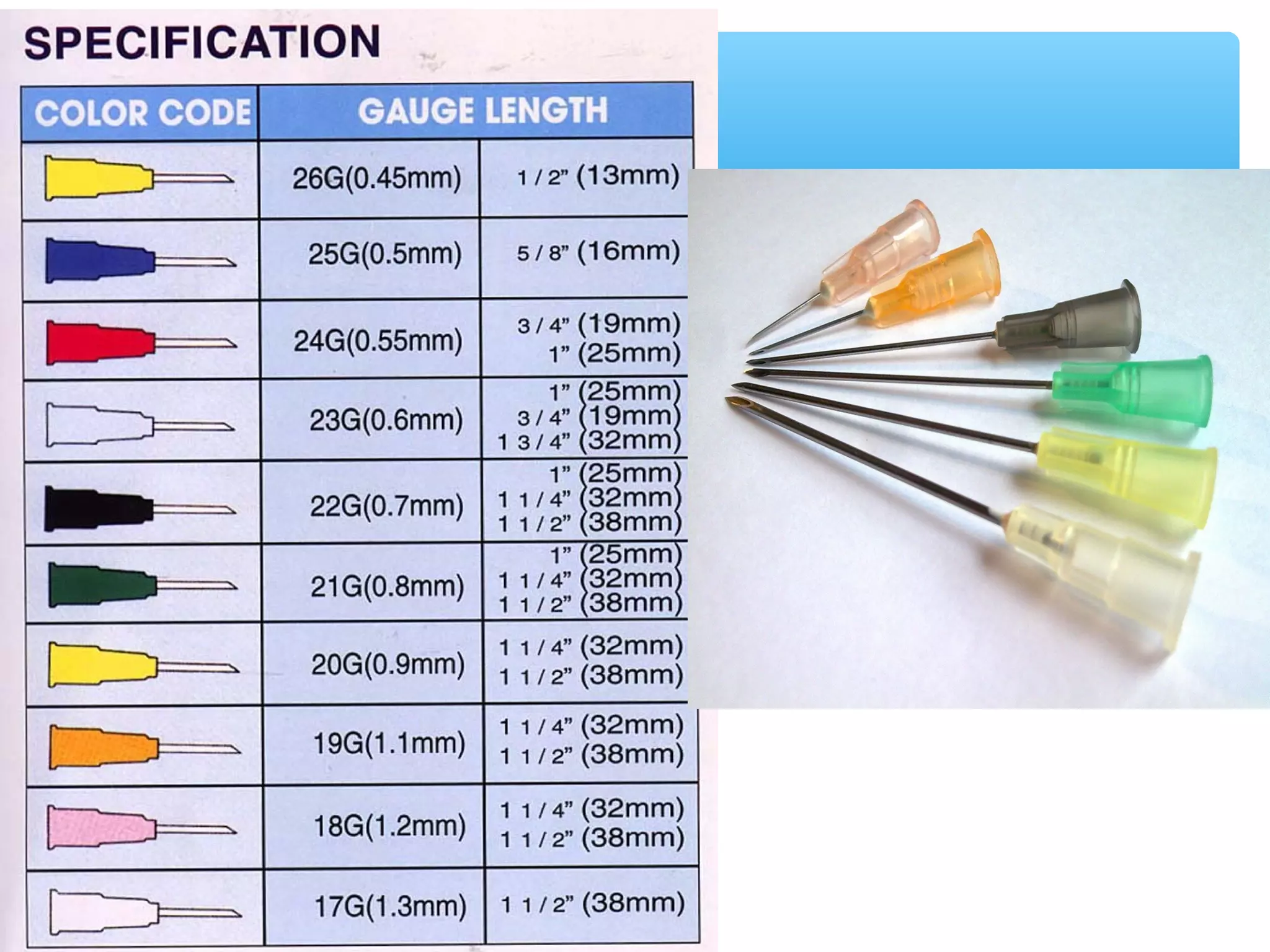
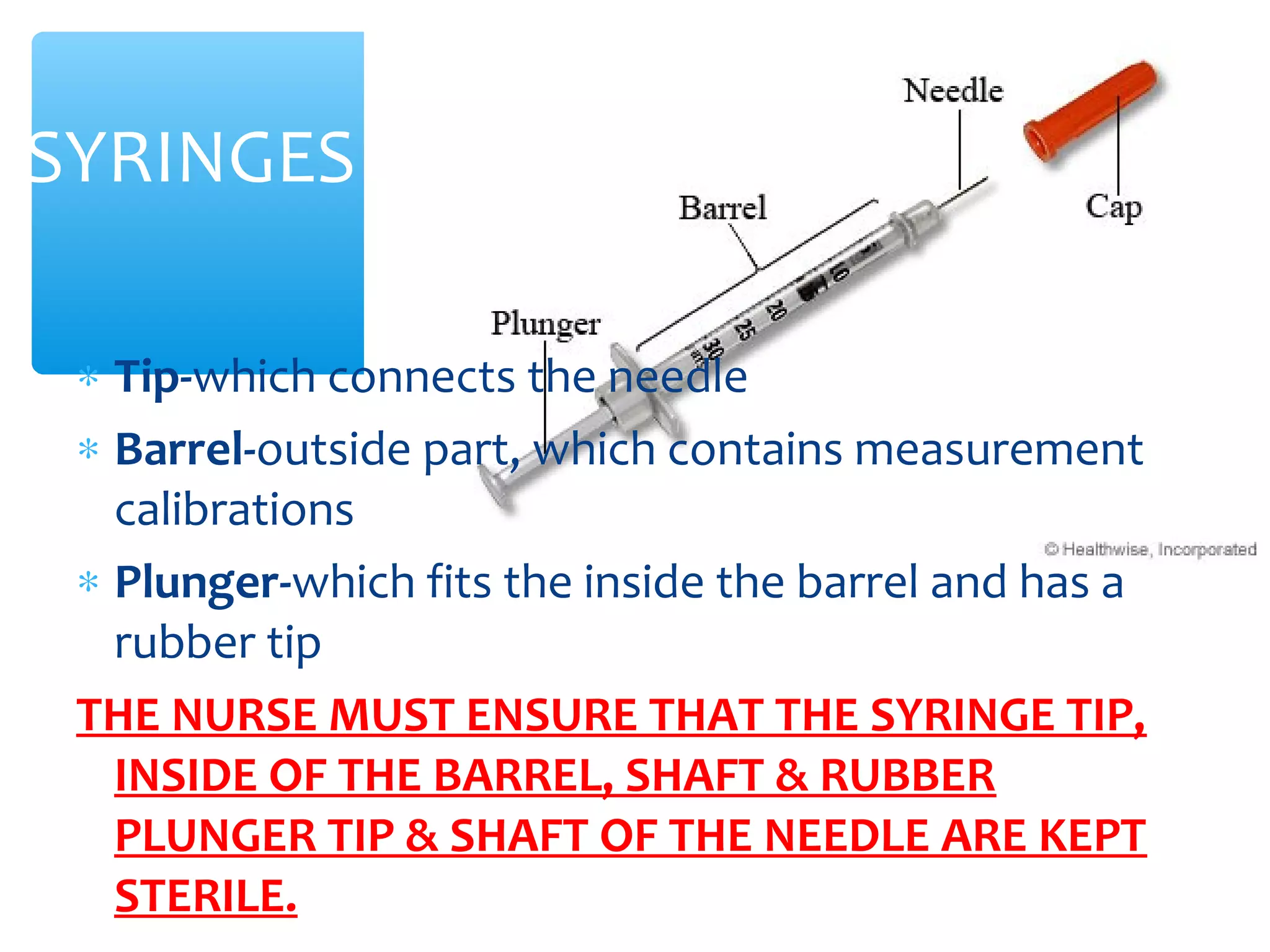
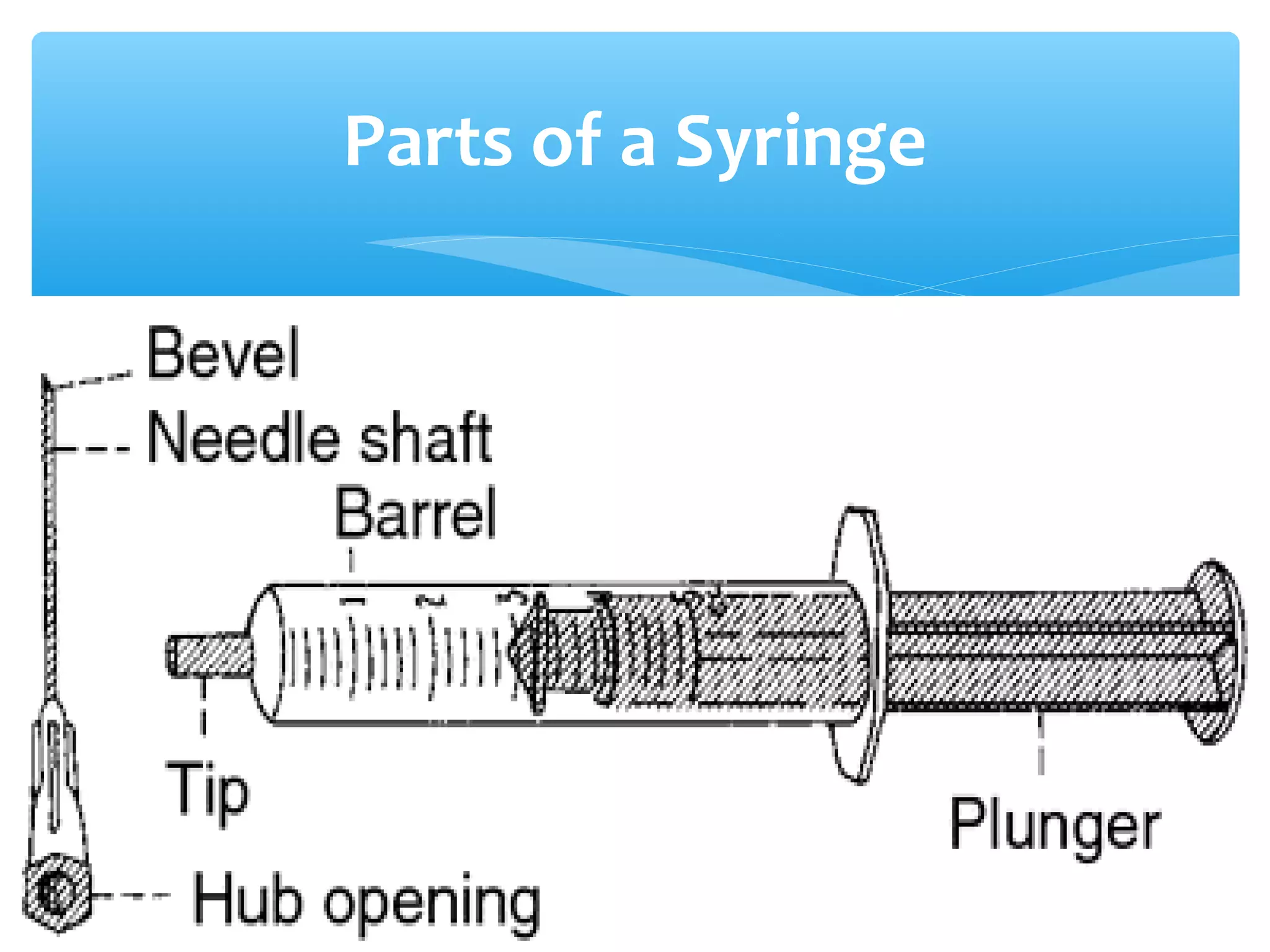
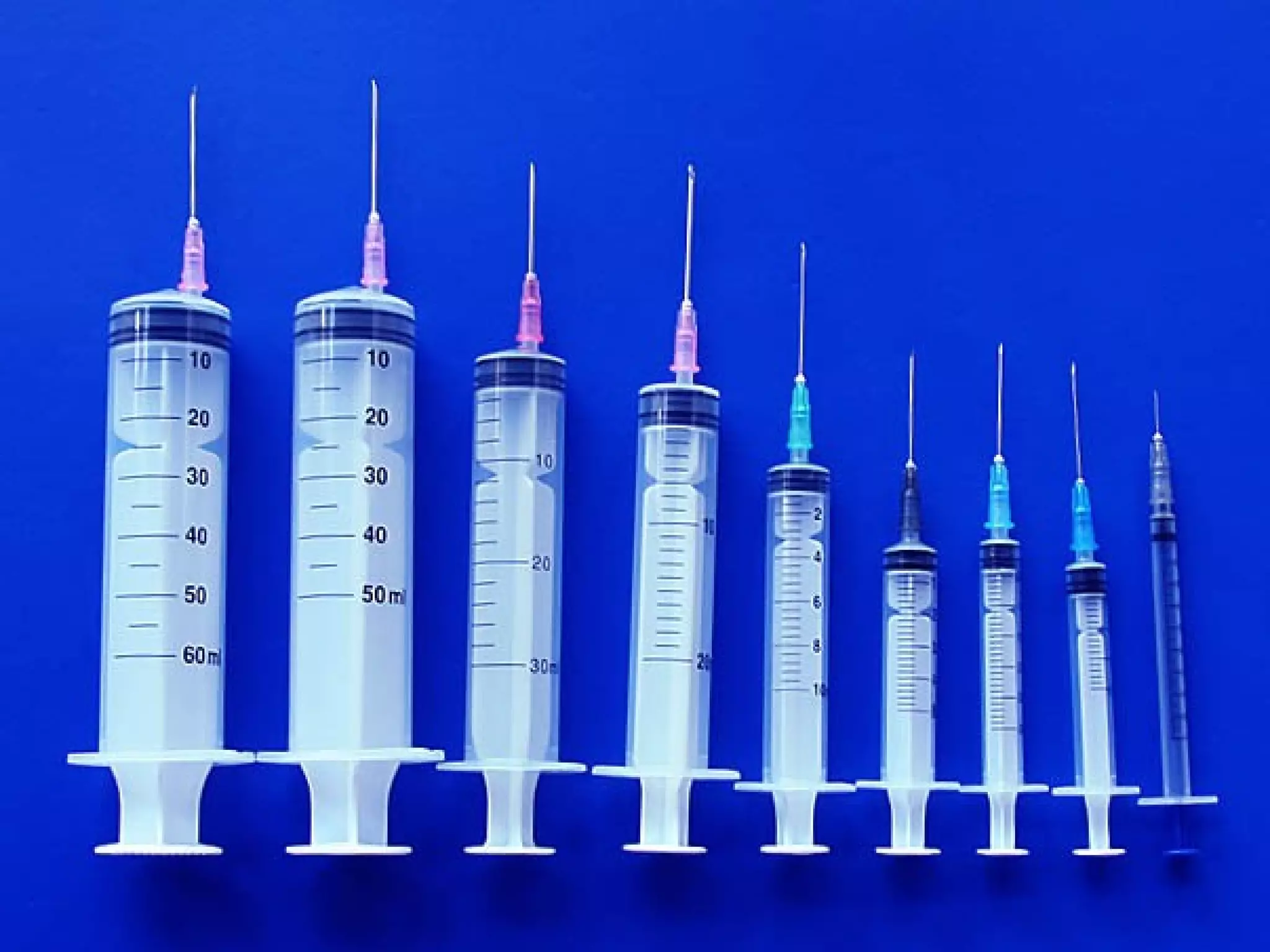
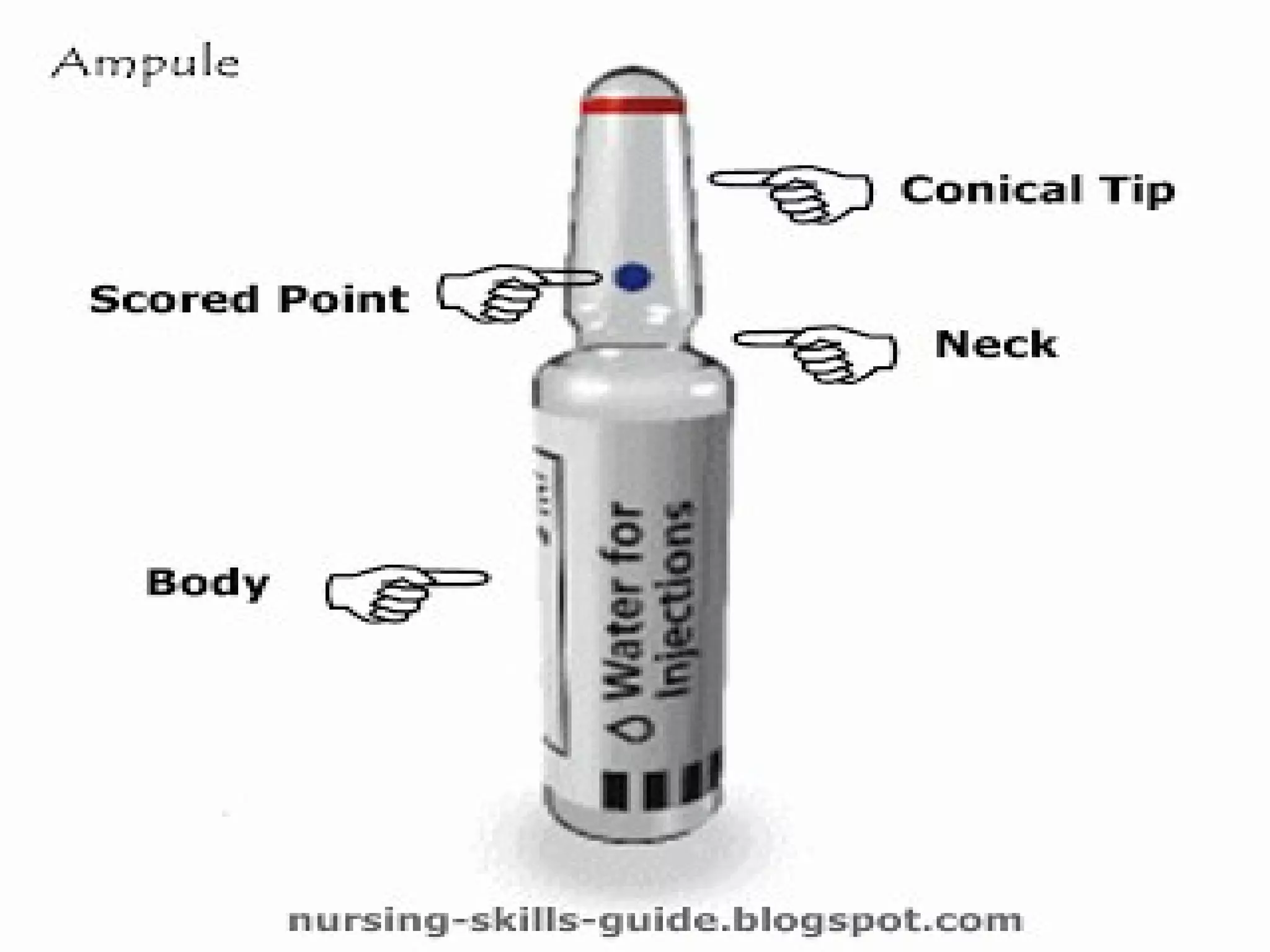
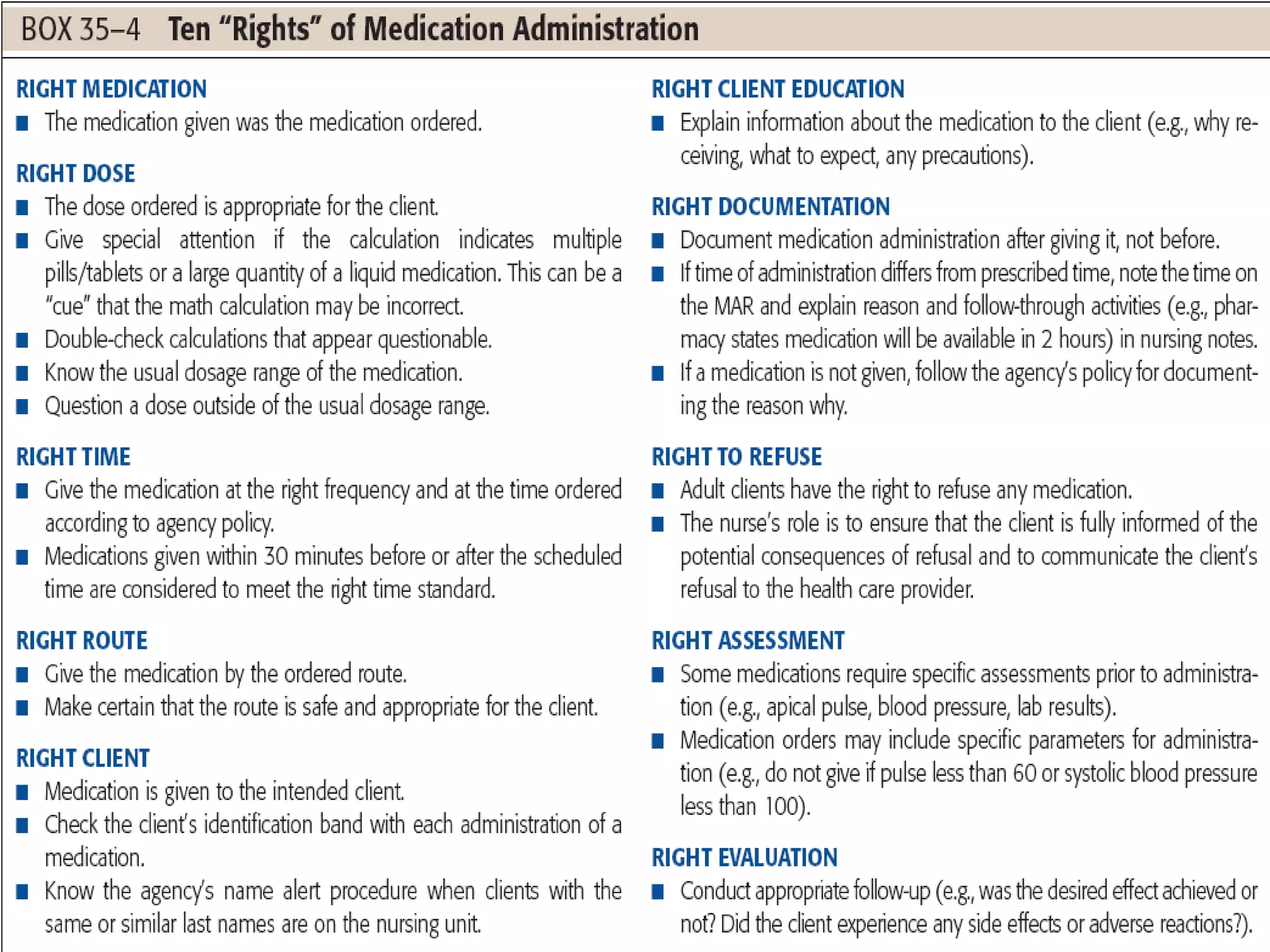
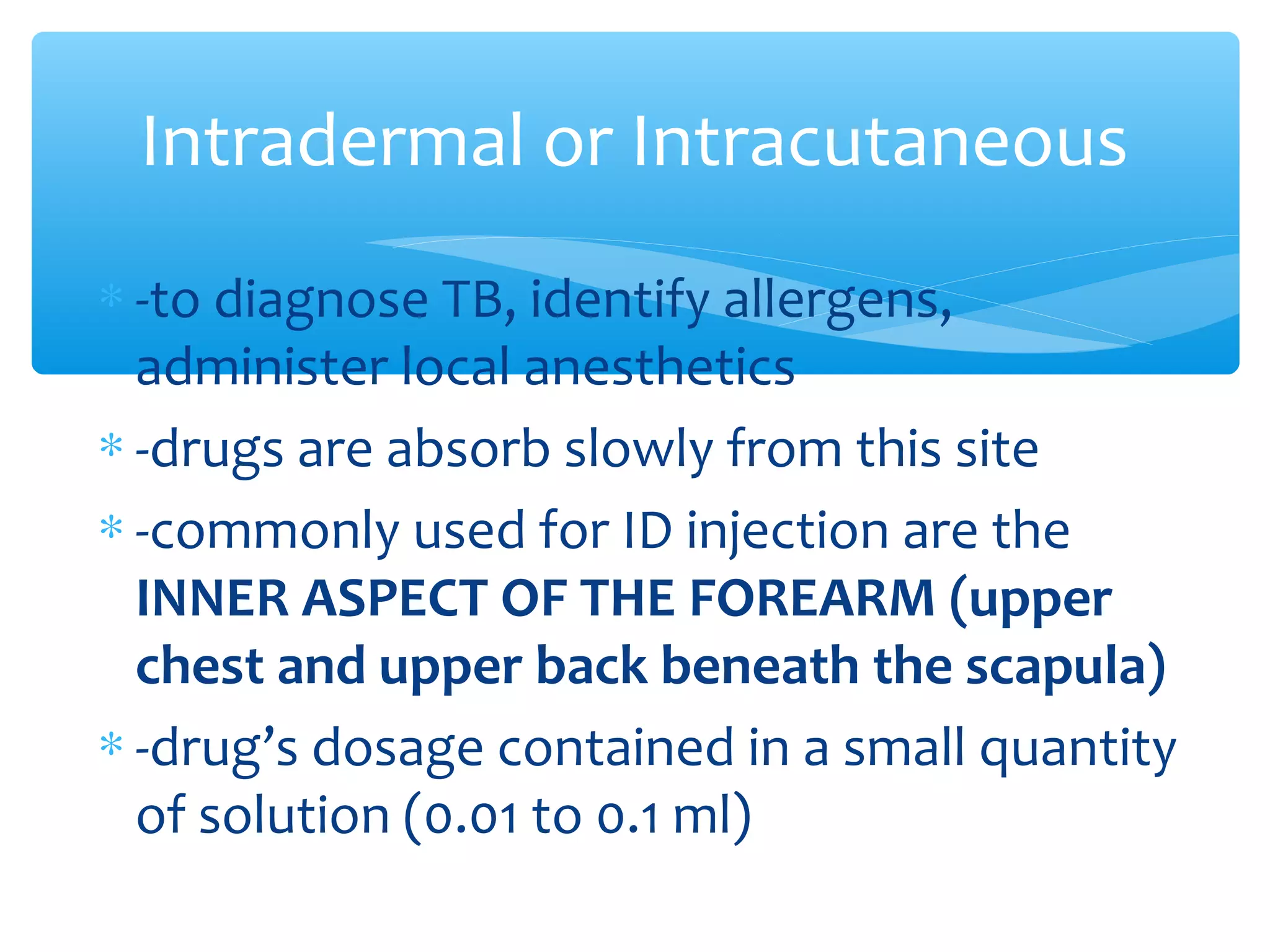
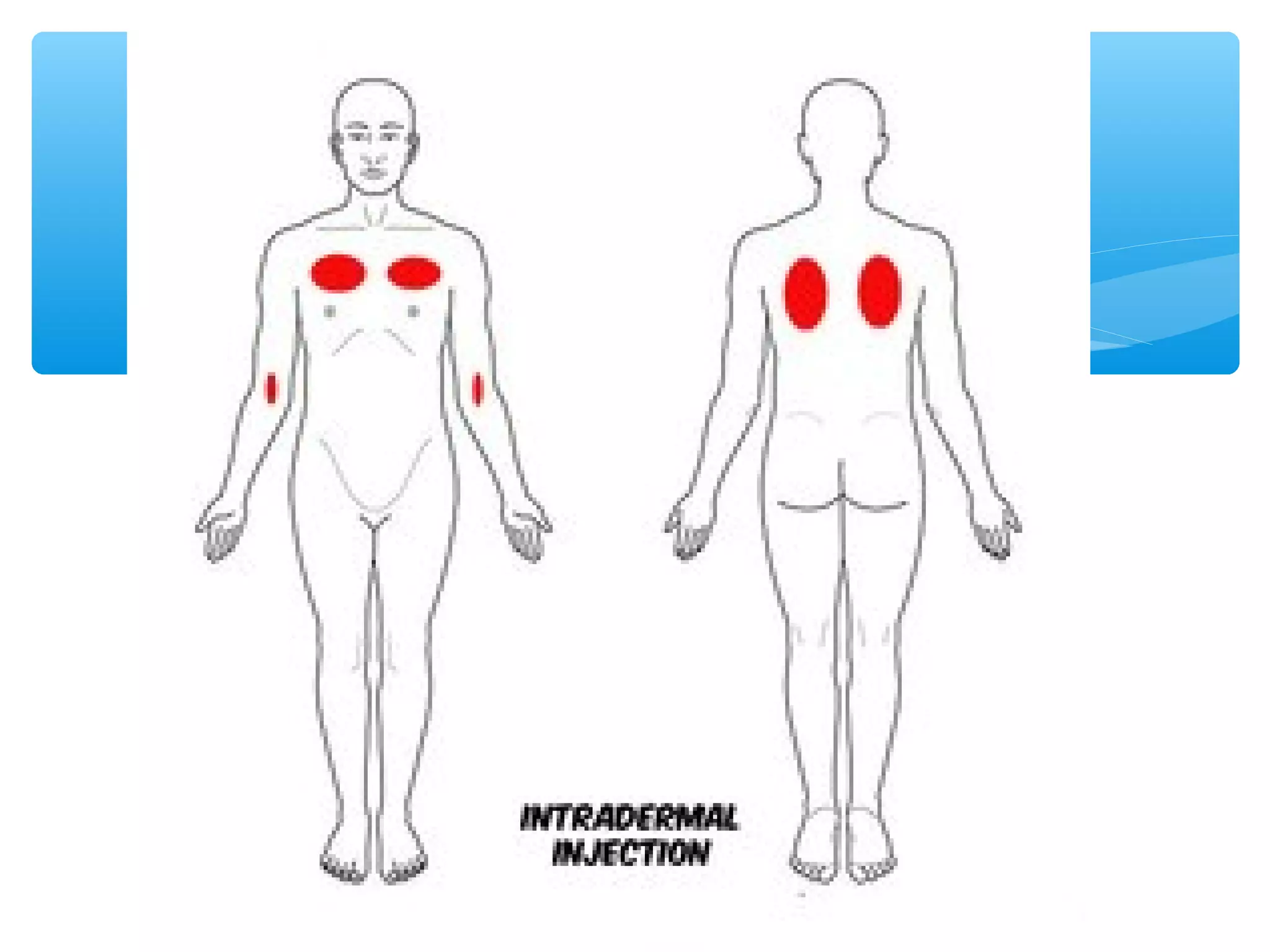
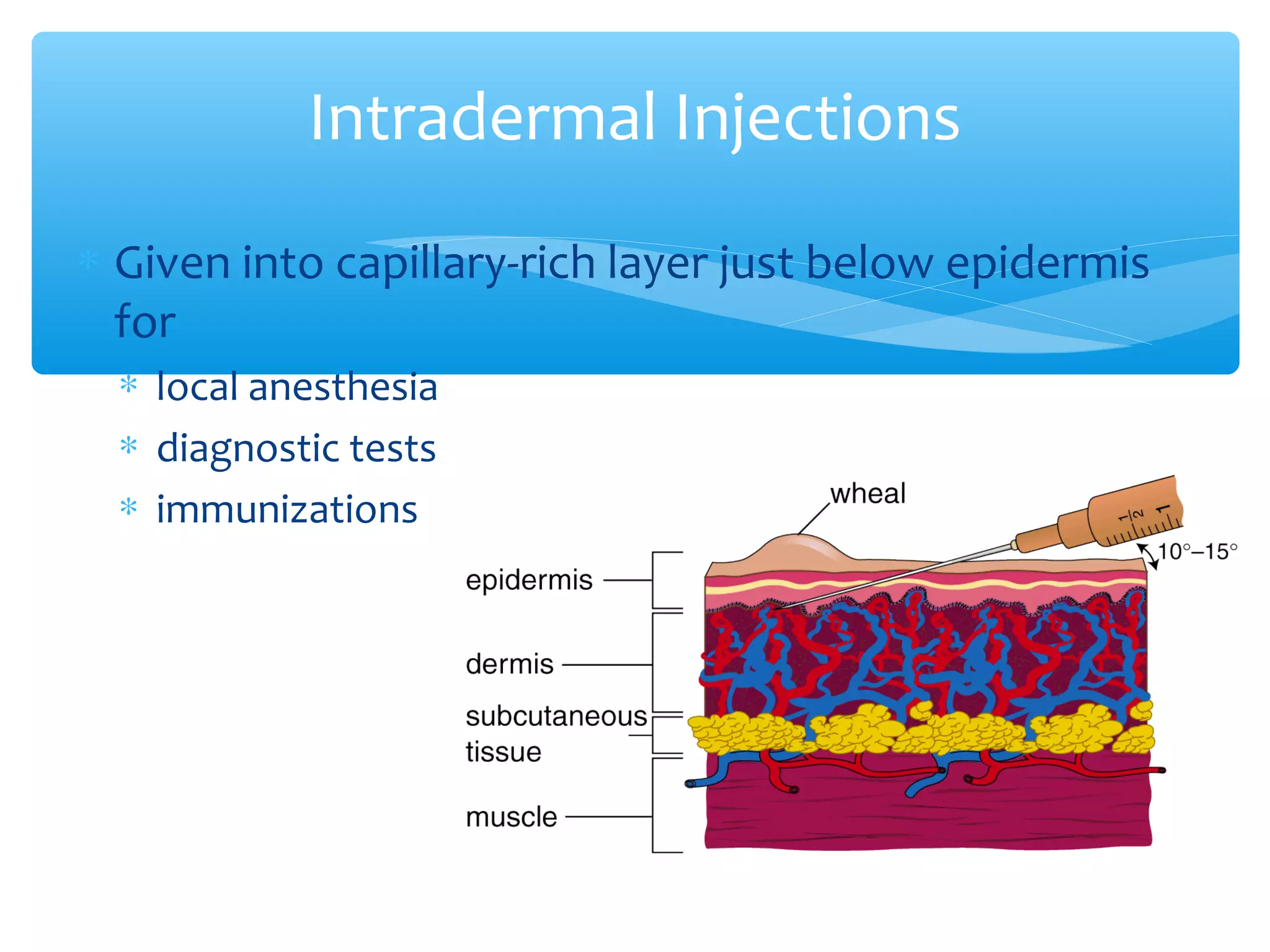
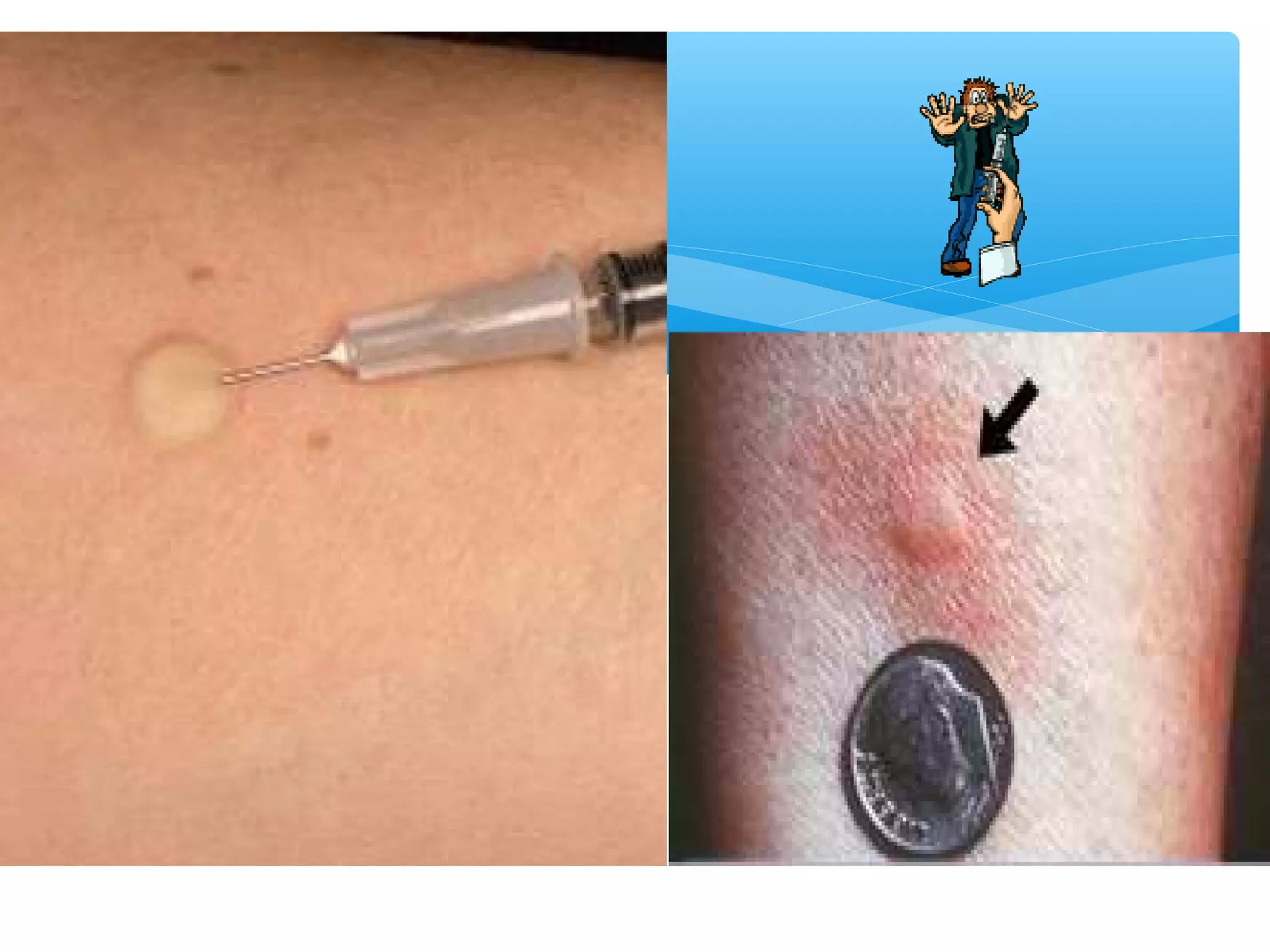
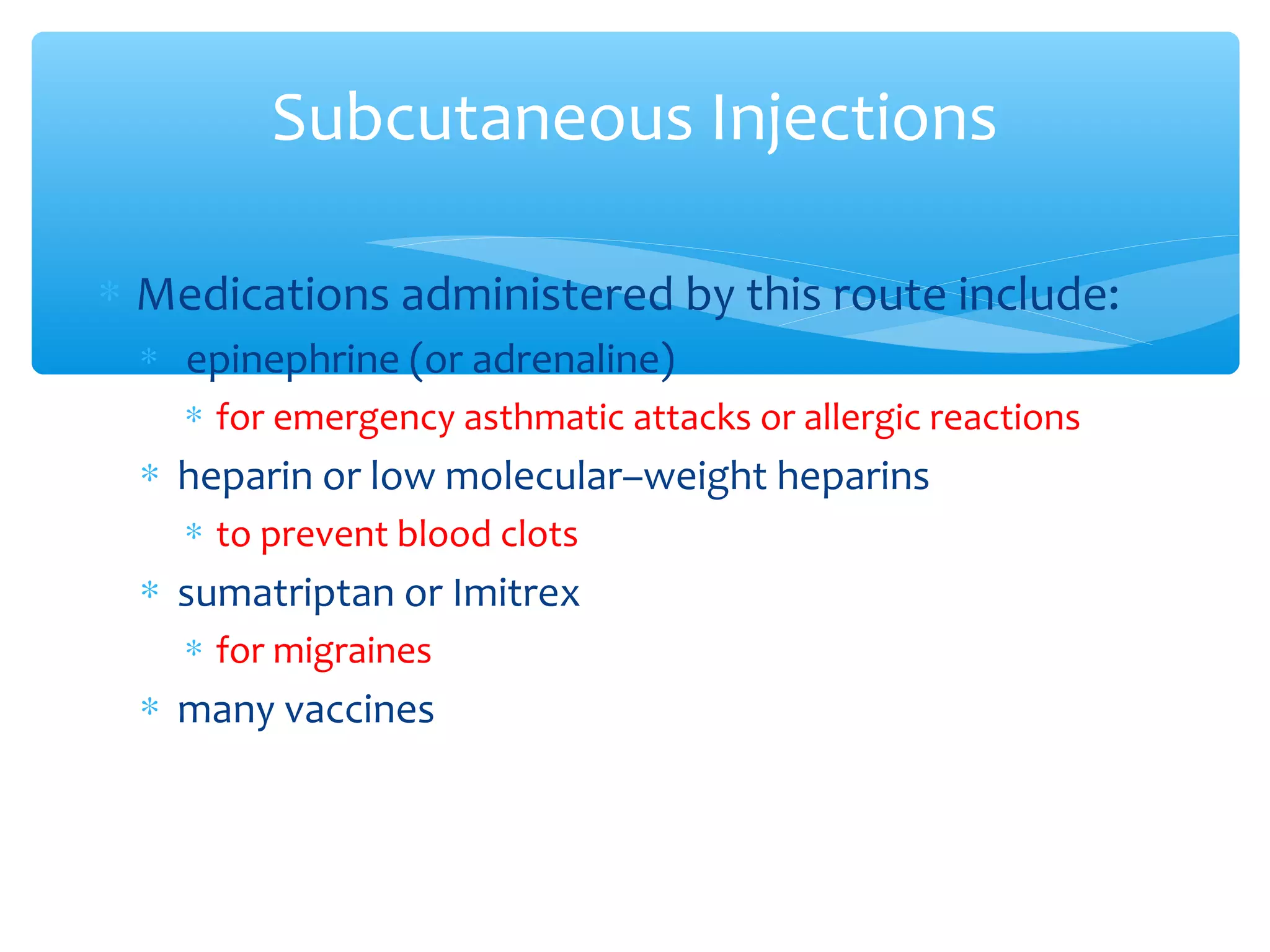
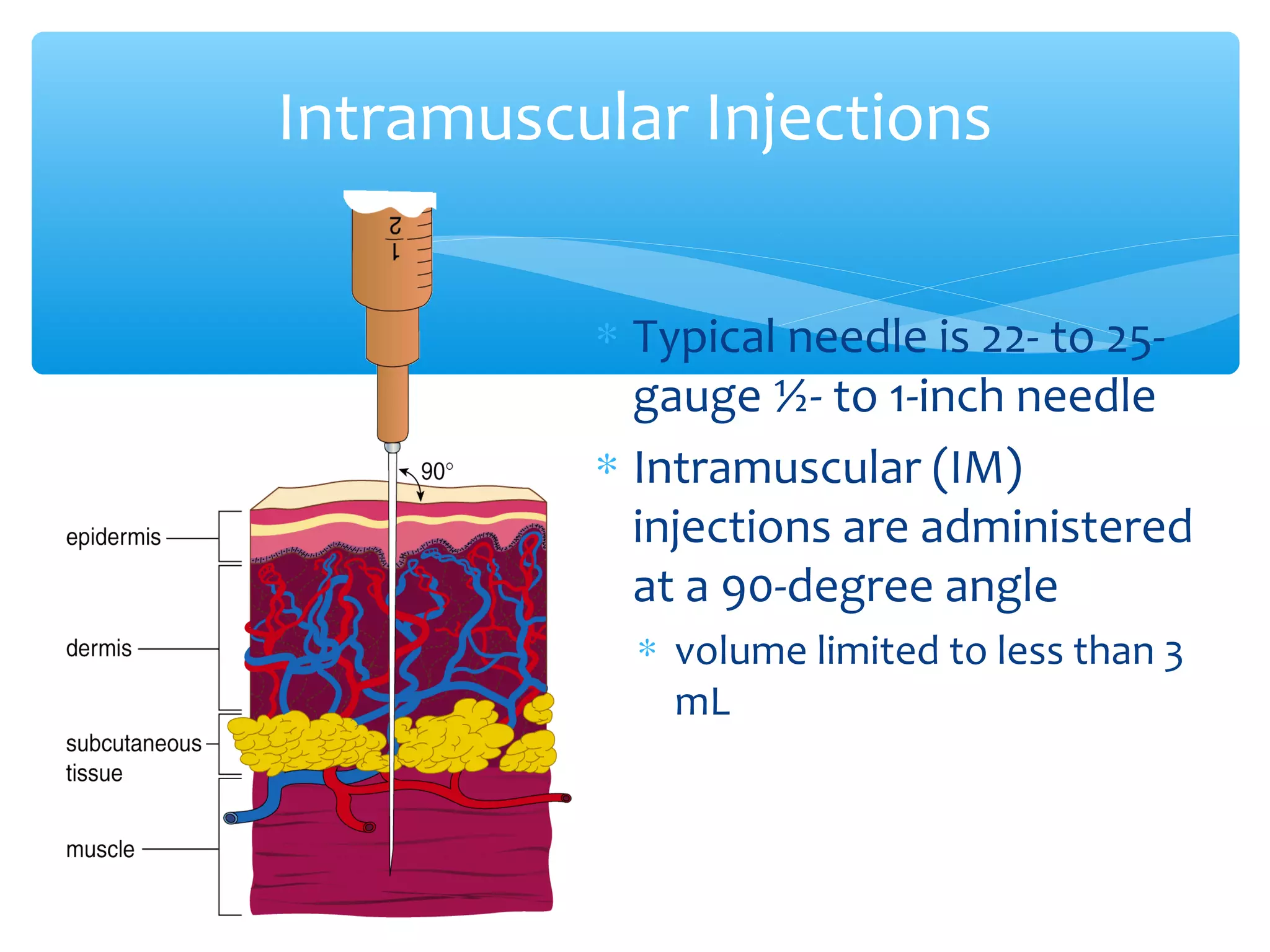
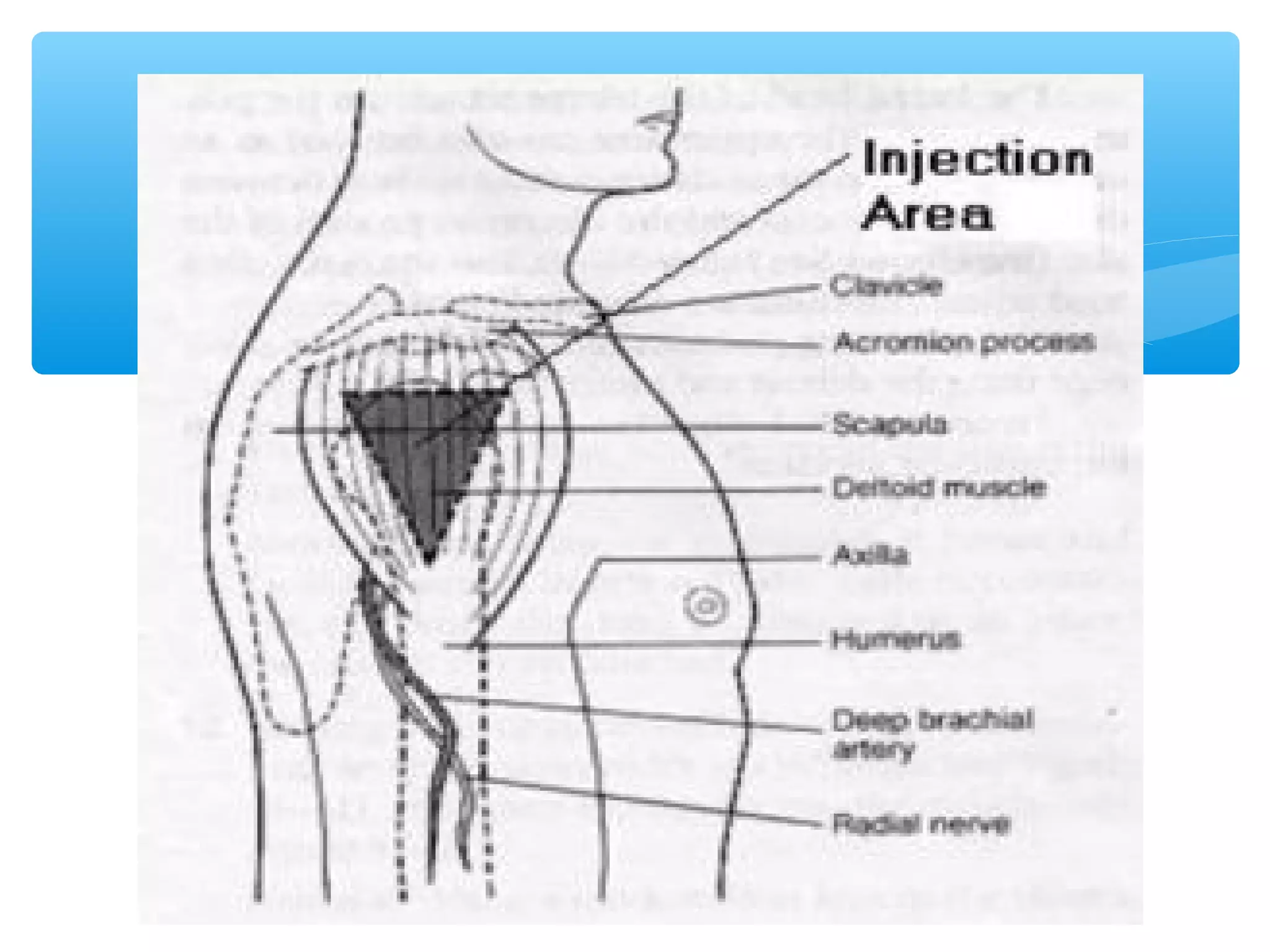
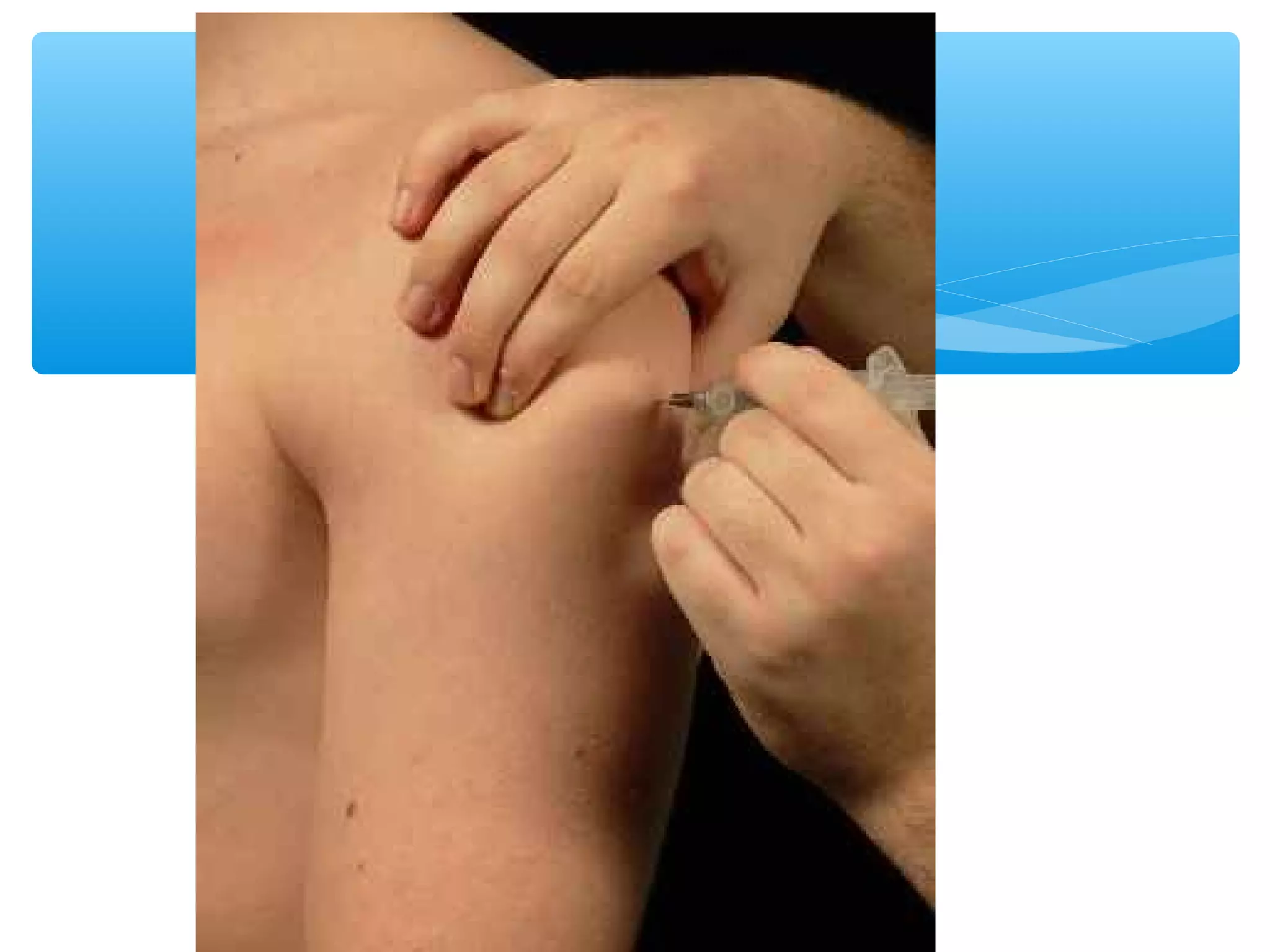
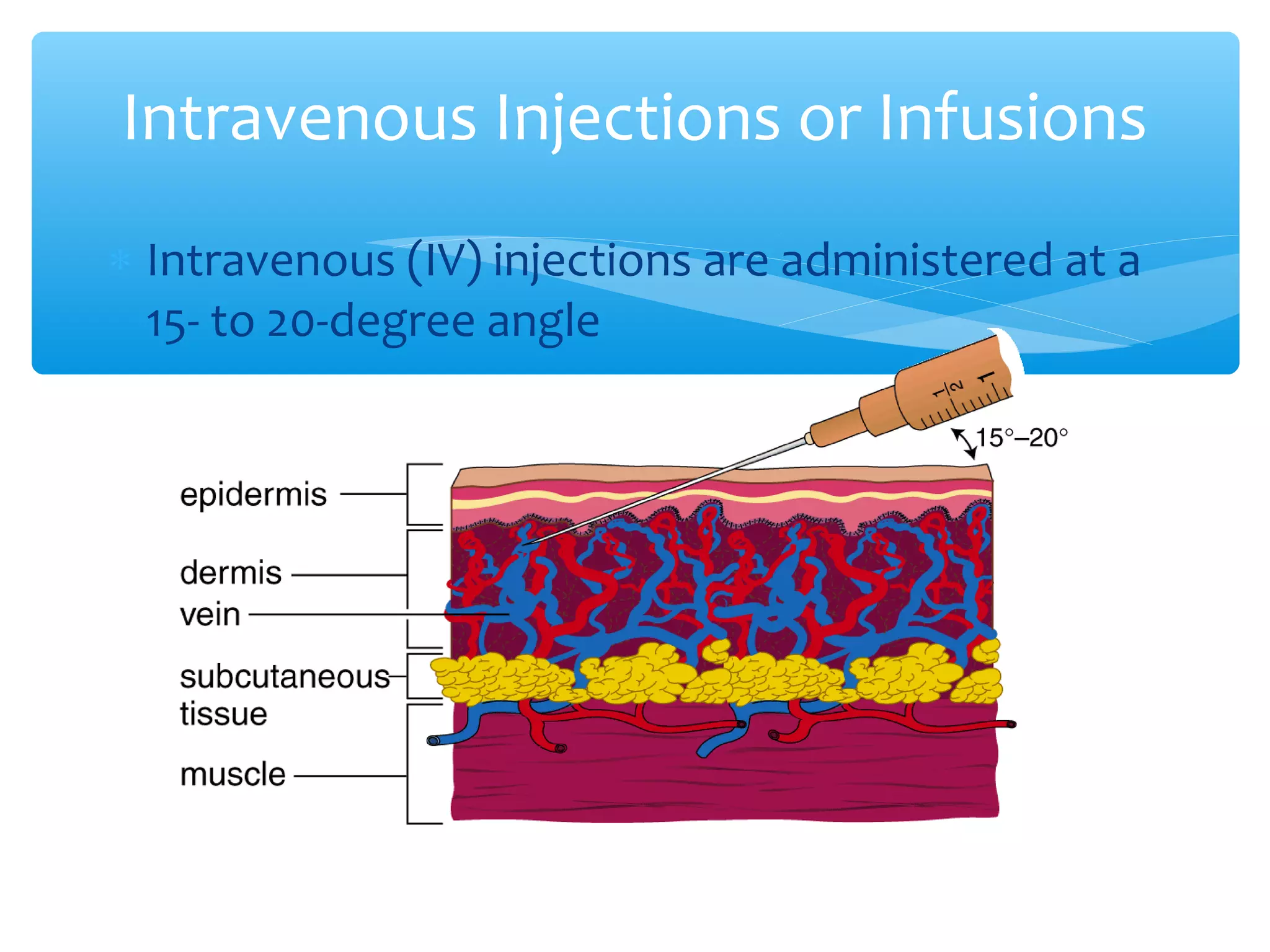
Parenteral administration involves injecting medications through routes other than the digestive tract, including intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous. Proper parenteral techniques require assessing the patient, using the correct equipment like needles and syringes, administering the right drug dose via the appropriate route, and documenting properly. While parenteral routes can deliver medications faster than oral administration, they also carry risks if not performed correctly.