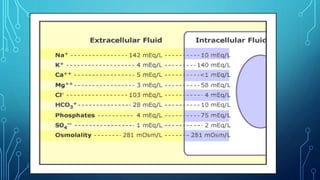
This document contains a student's questions about electrolytes and the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, along with responses providing information about these topics. It defines intracellular and extracellular electrolytes and gives examples. It also explains the history, theory, and application of the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. Finally, it discusses buffer solutions, buffer capacity, and how the body maintains acid-base balance through buffers in blood and other fluids.