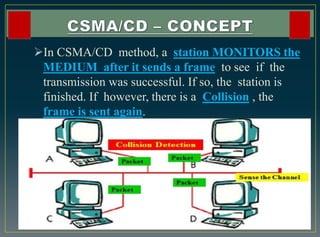
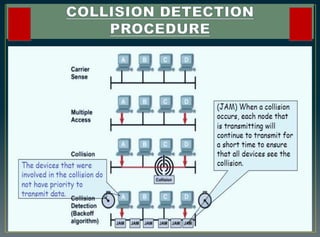
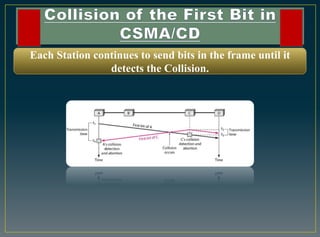
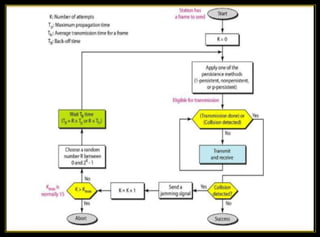
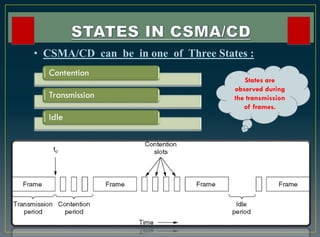
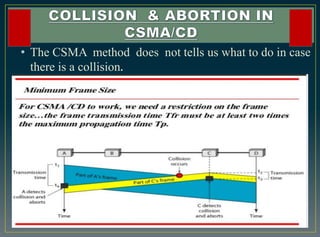
The CSMA/CD protocol enhances the basic CSMA method by incorporating collision detection for improved media access control, particularly in early Ethernet networks. It allows stations to sense the medium before transmitting and respond to collisions by transmitting a jam signal and retrying after a random delay. Despite its effectiveness in managing data collisions, CSMA/CD is limited by cable length and becomes less efficient in larger networks.