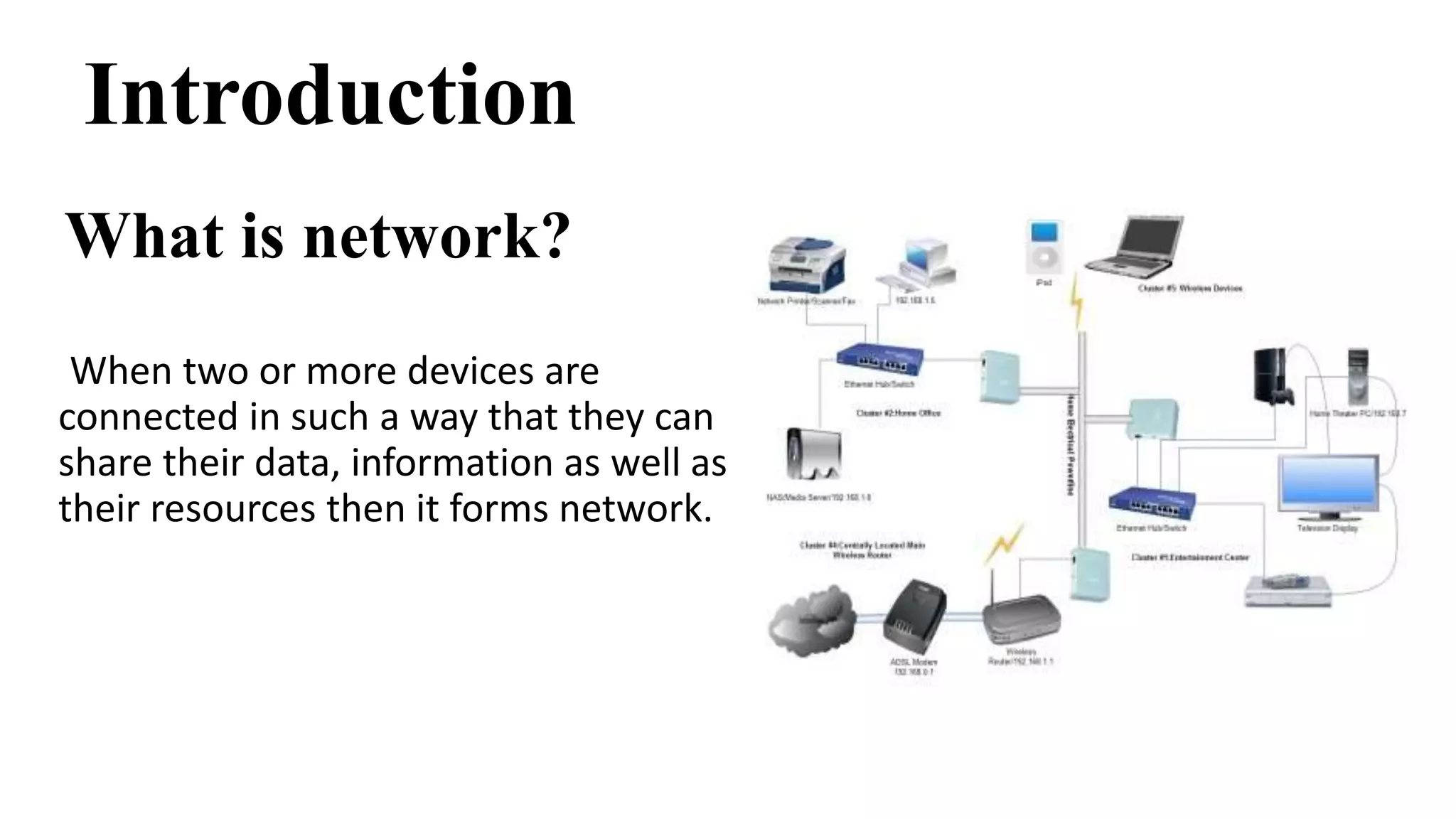
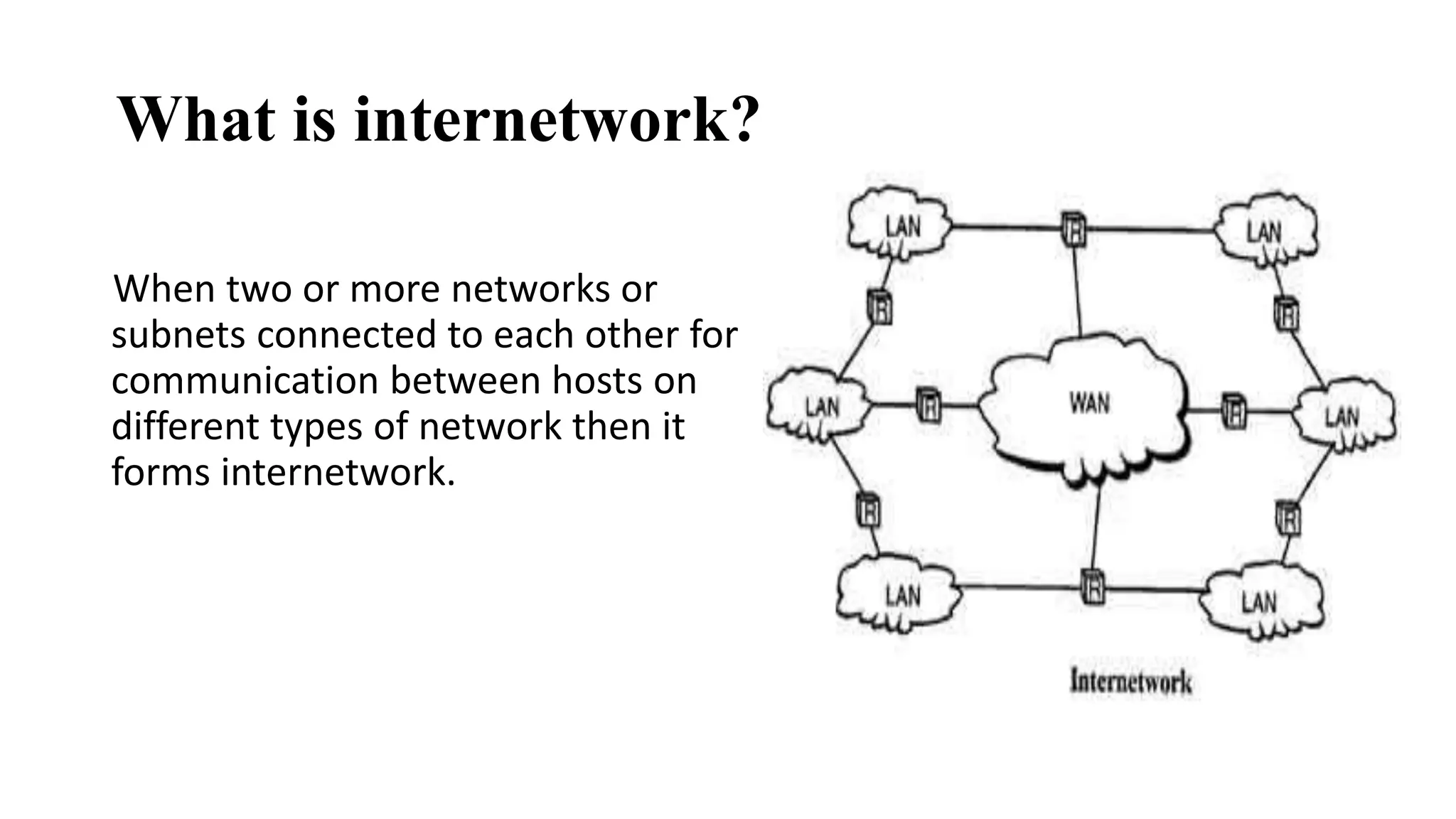
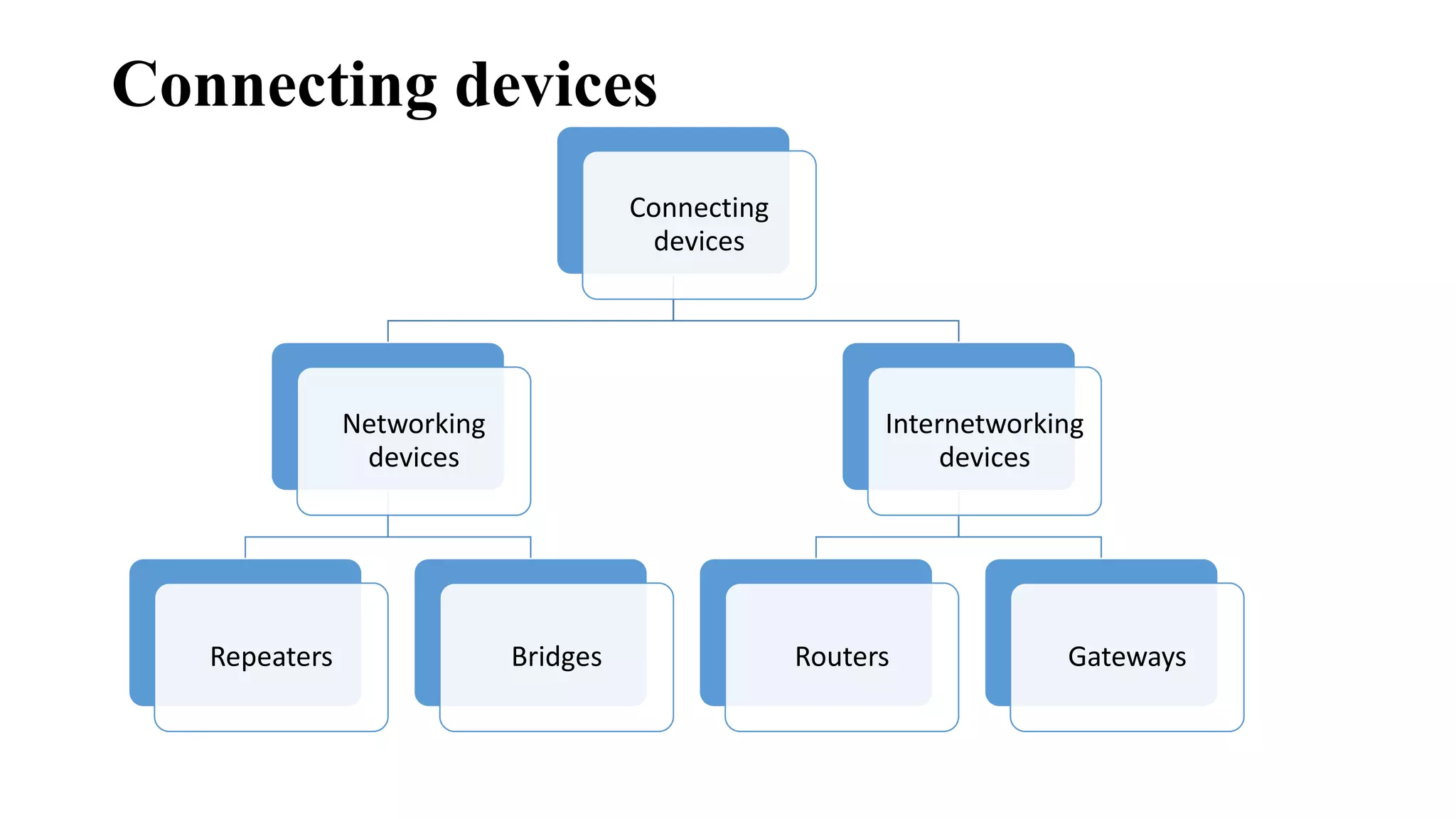
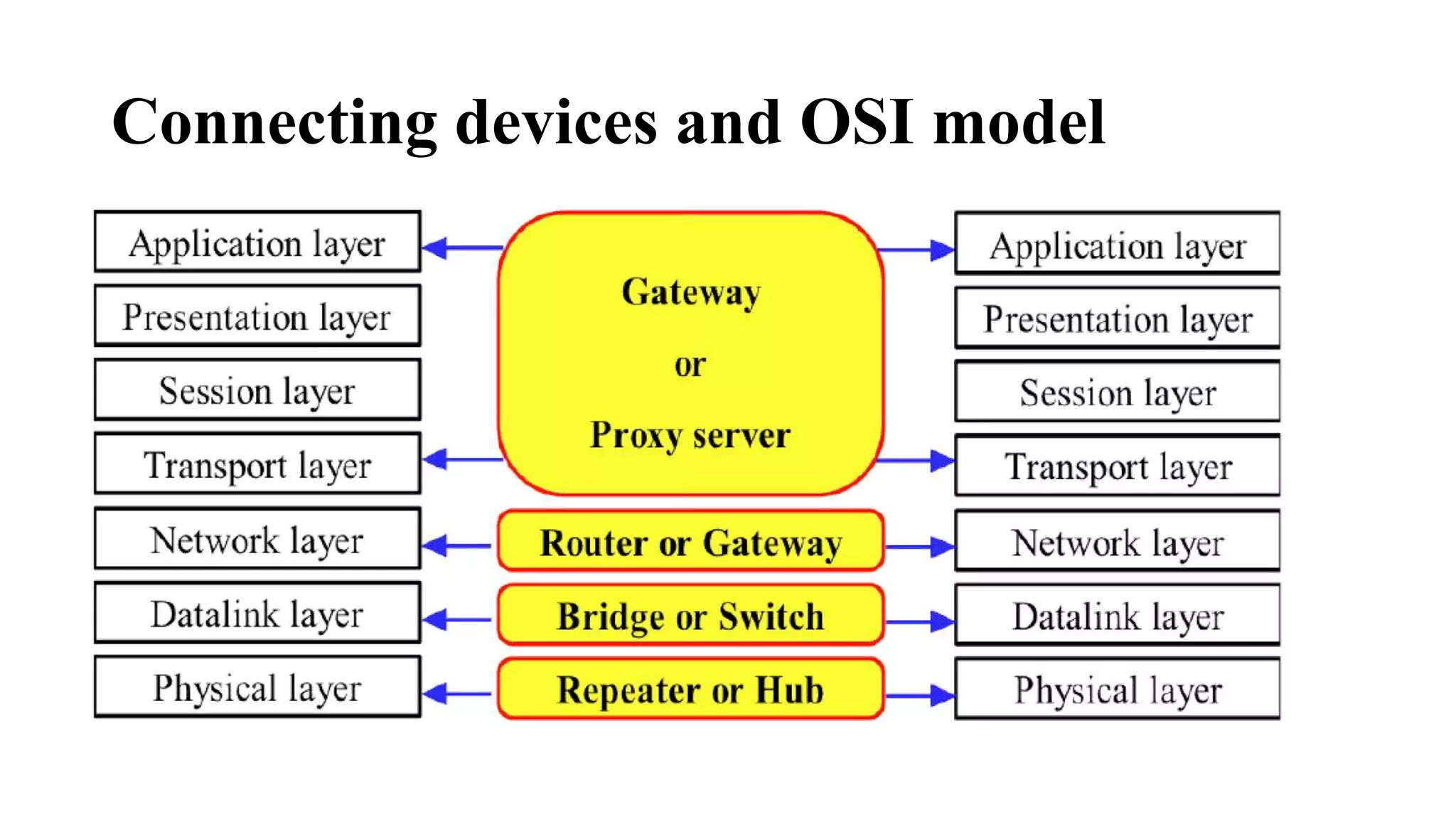
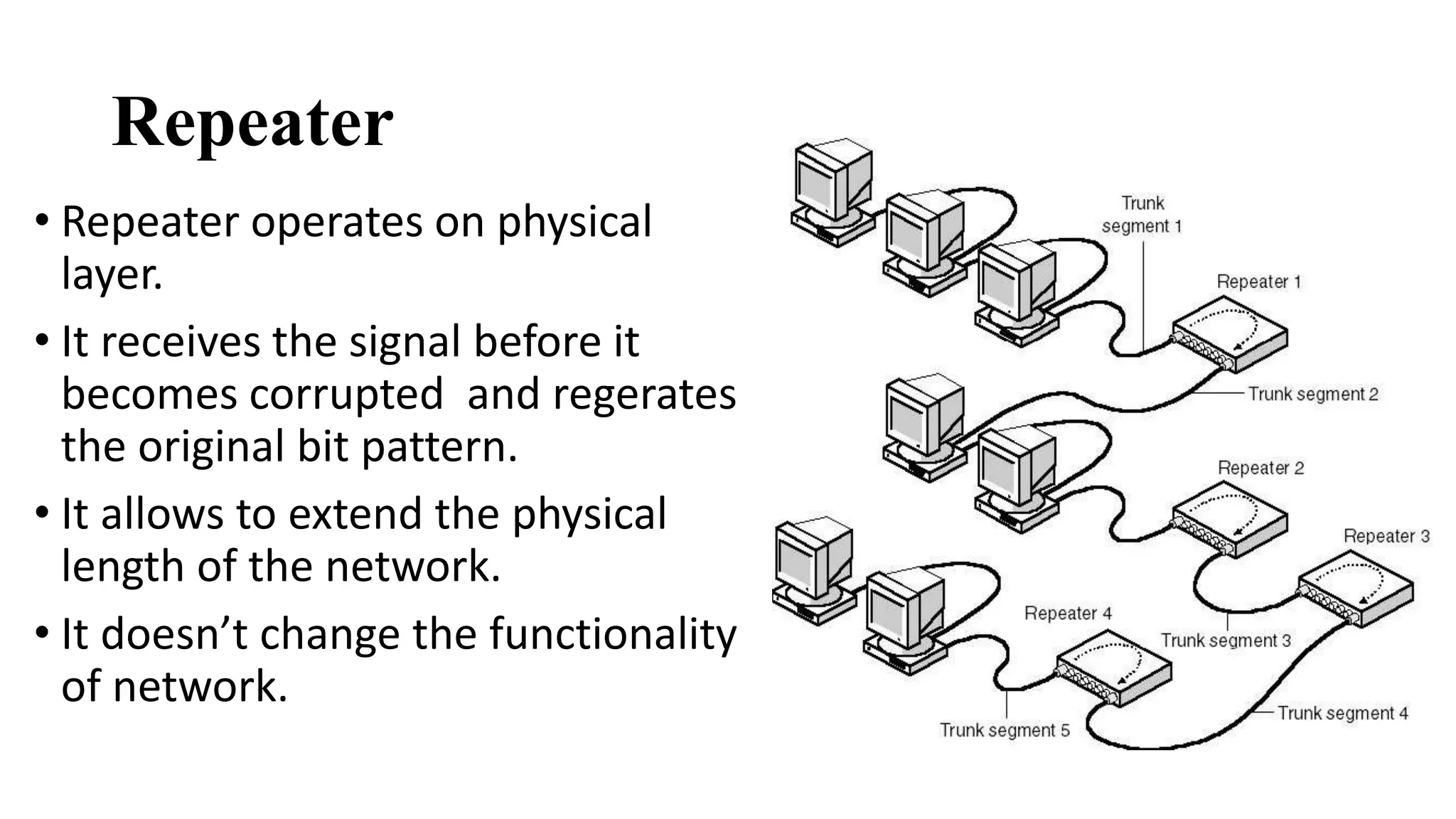
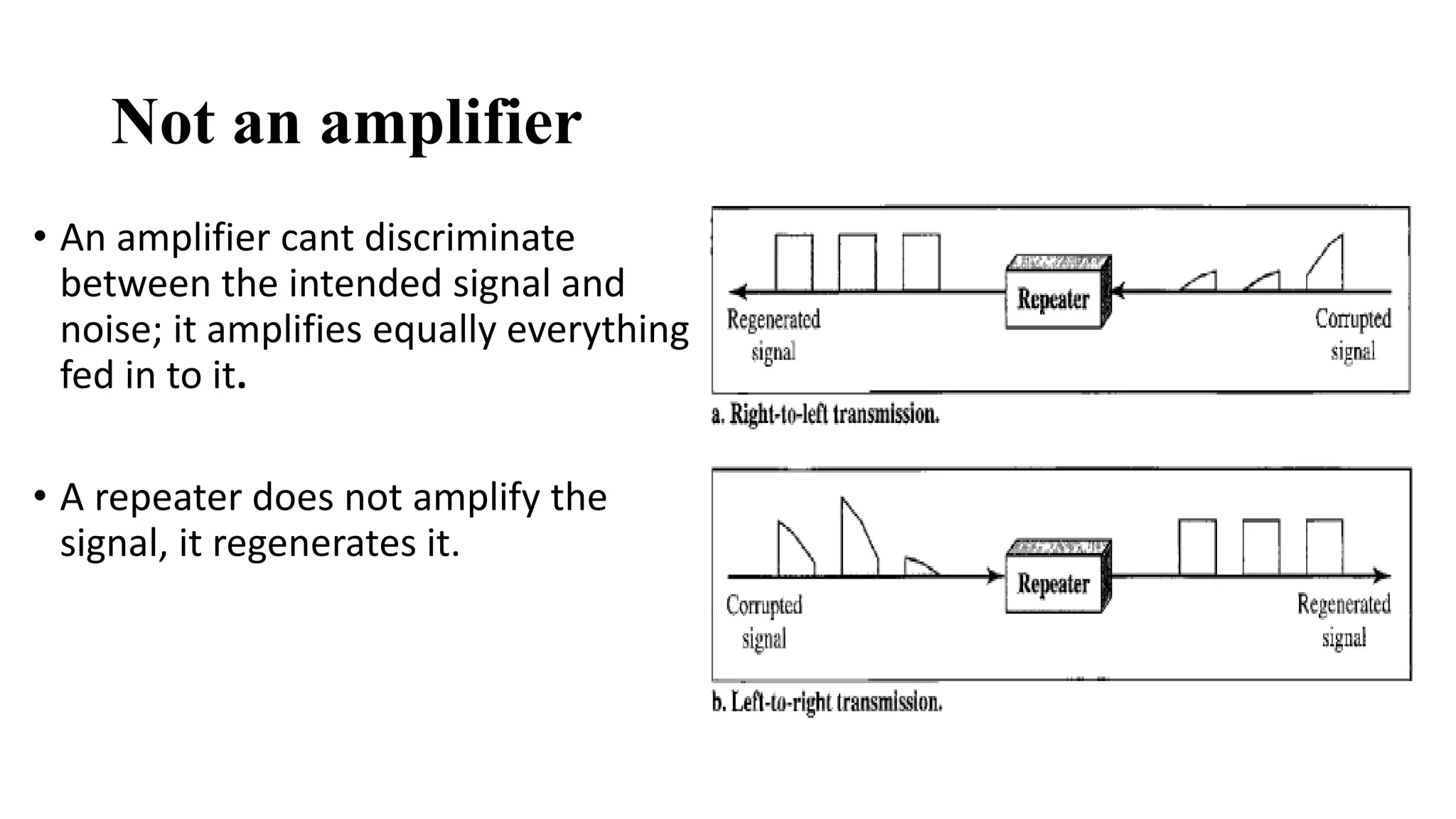
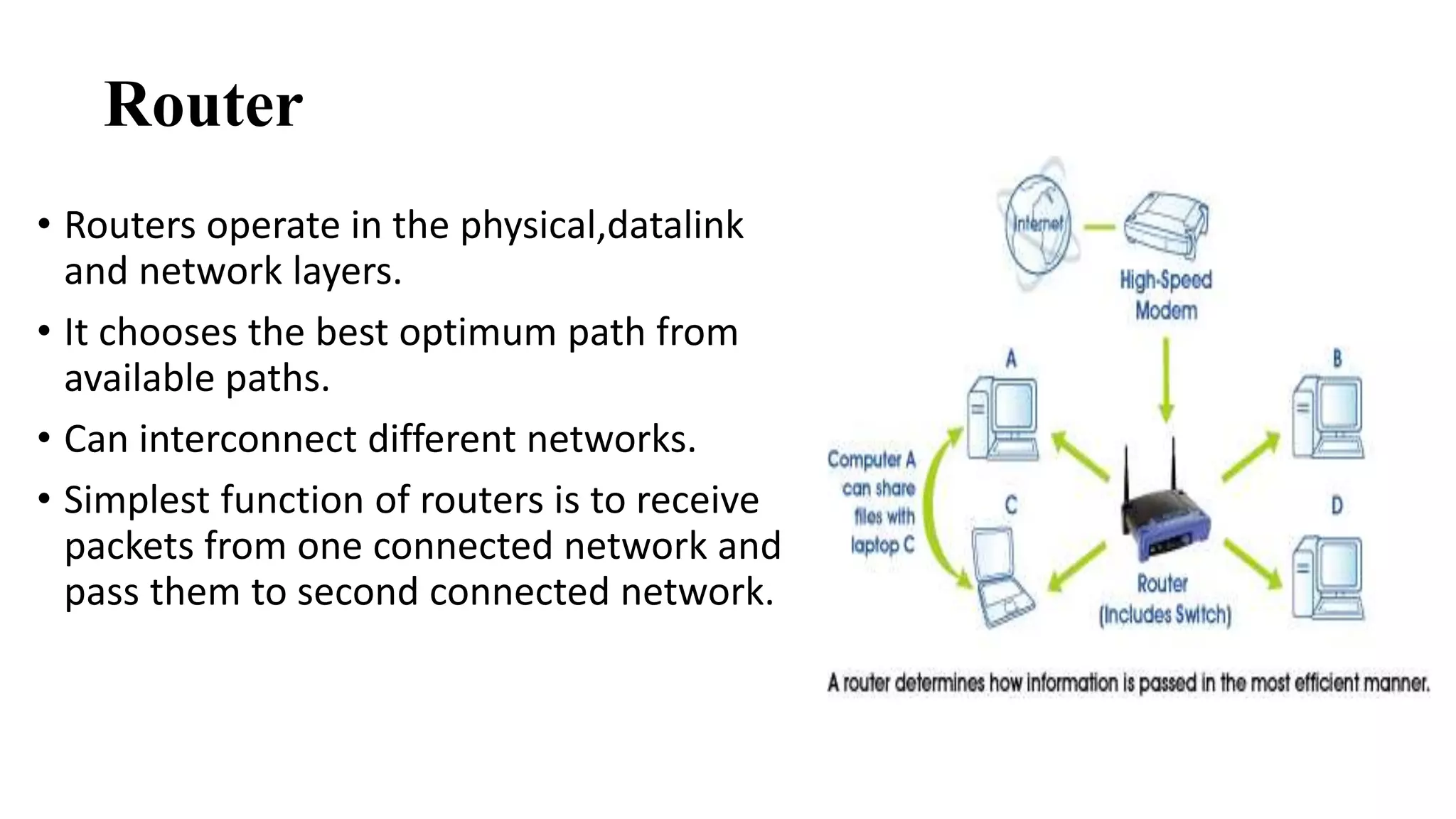
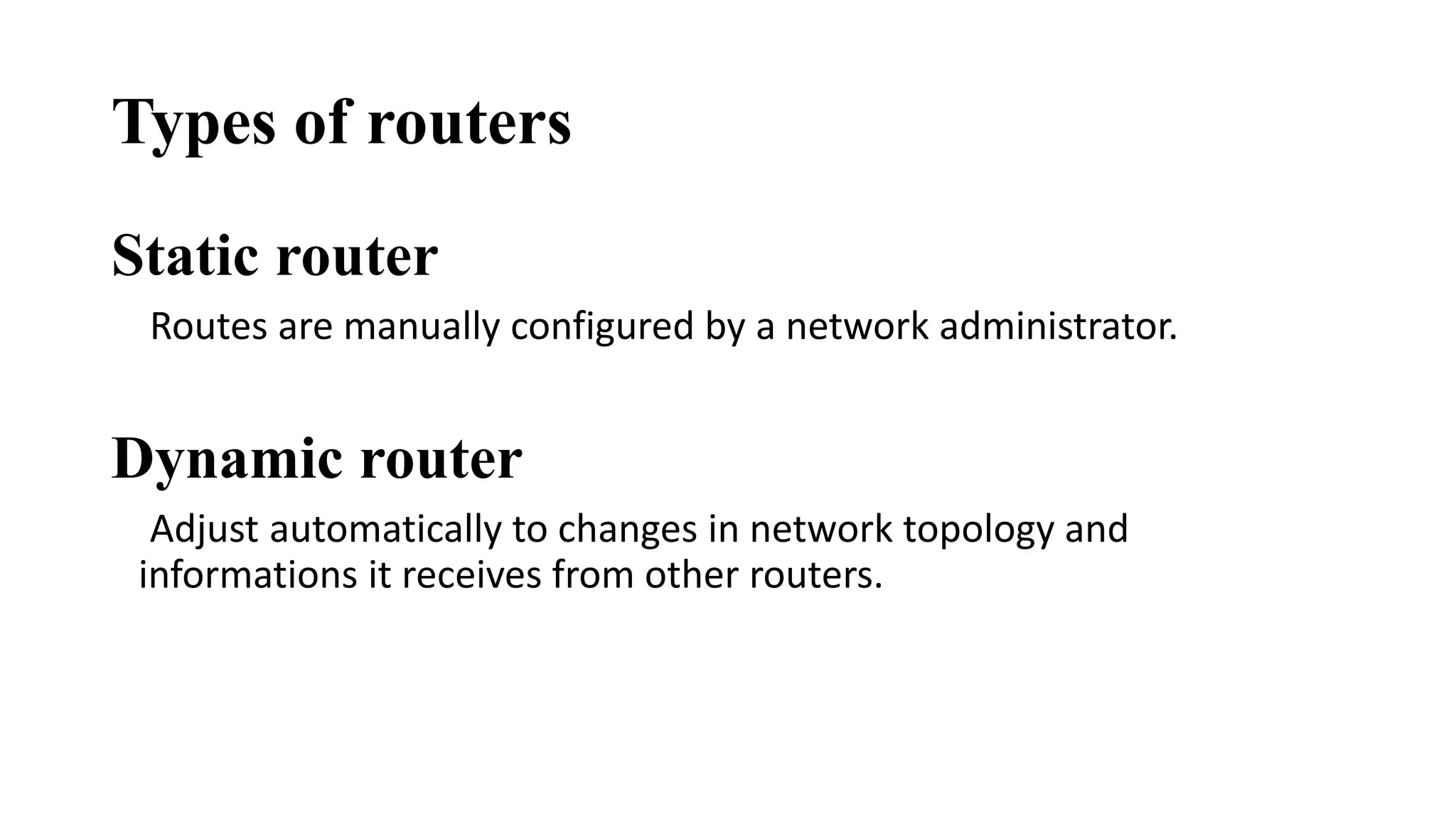
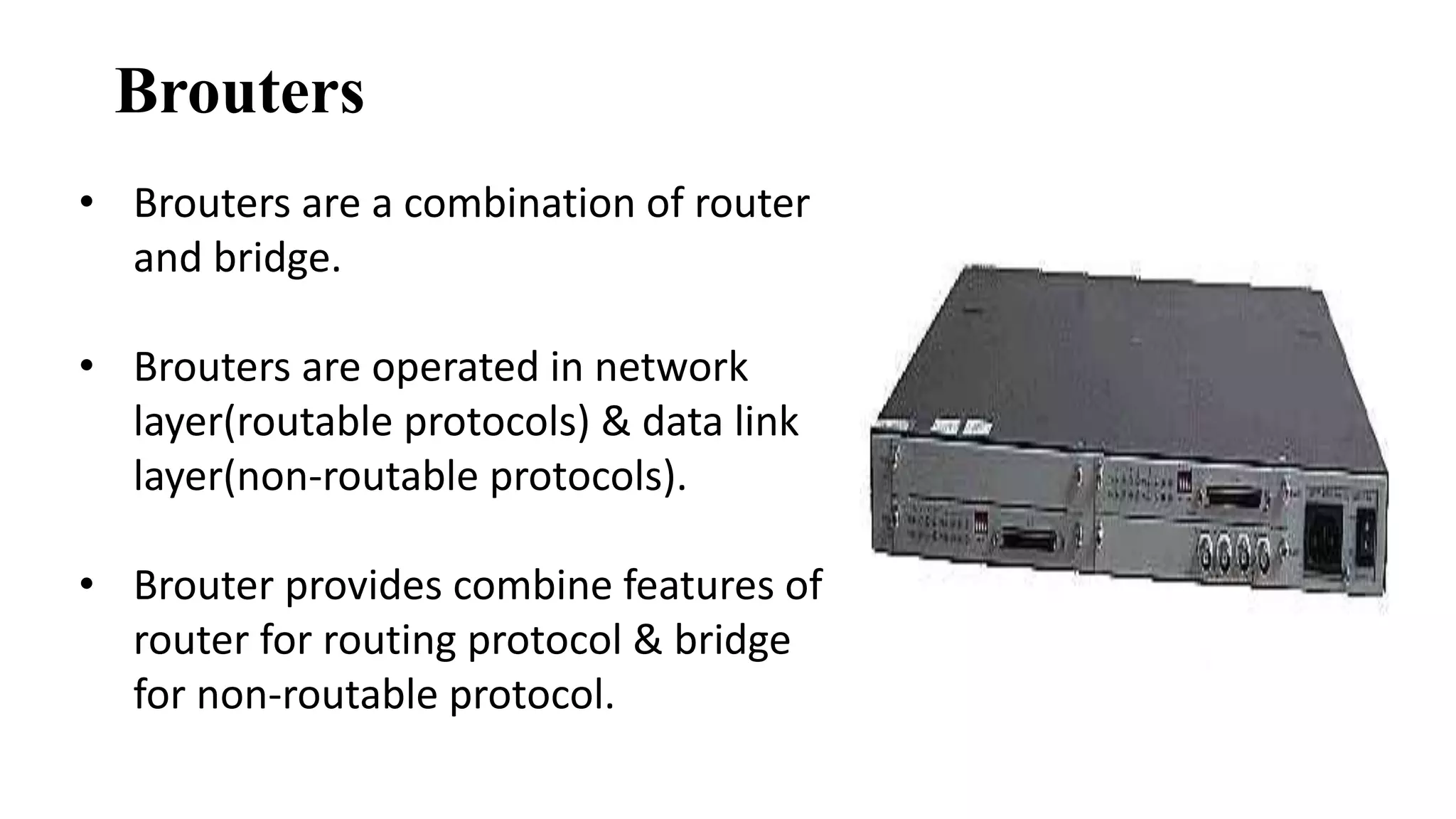
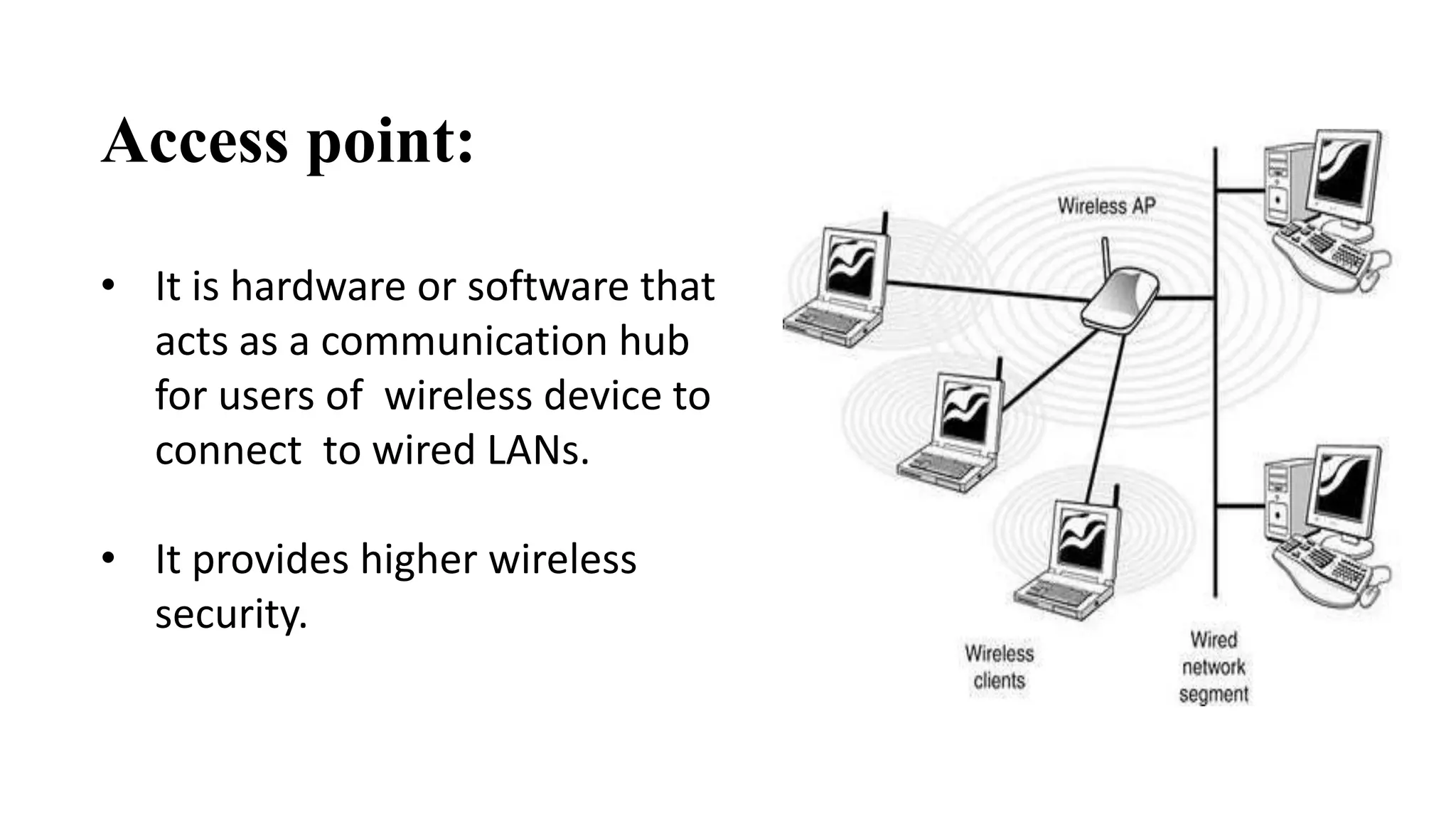
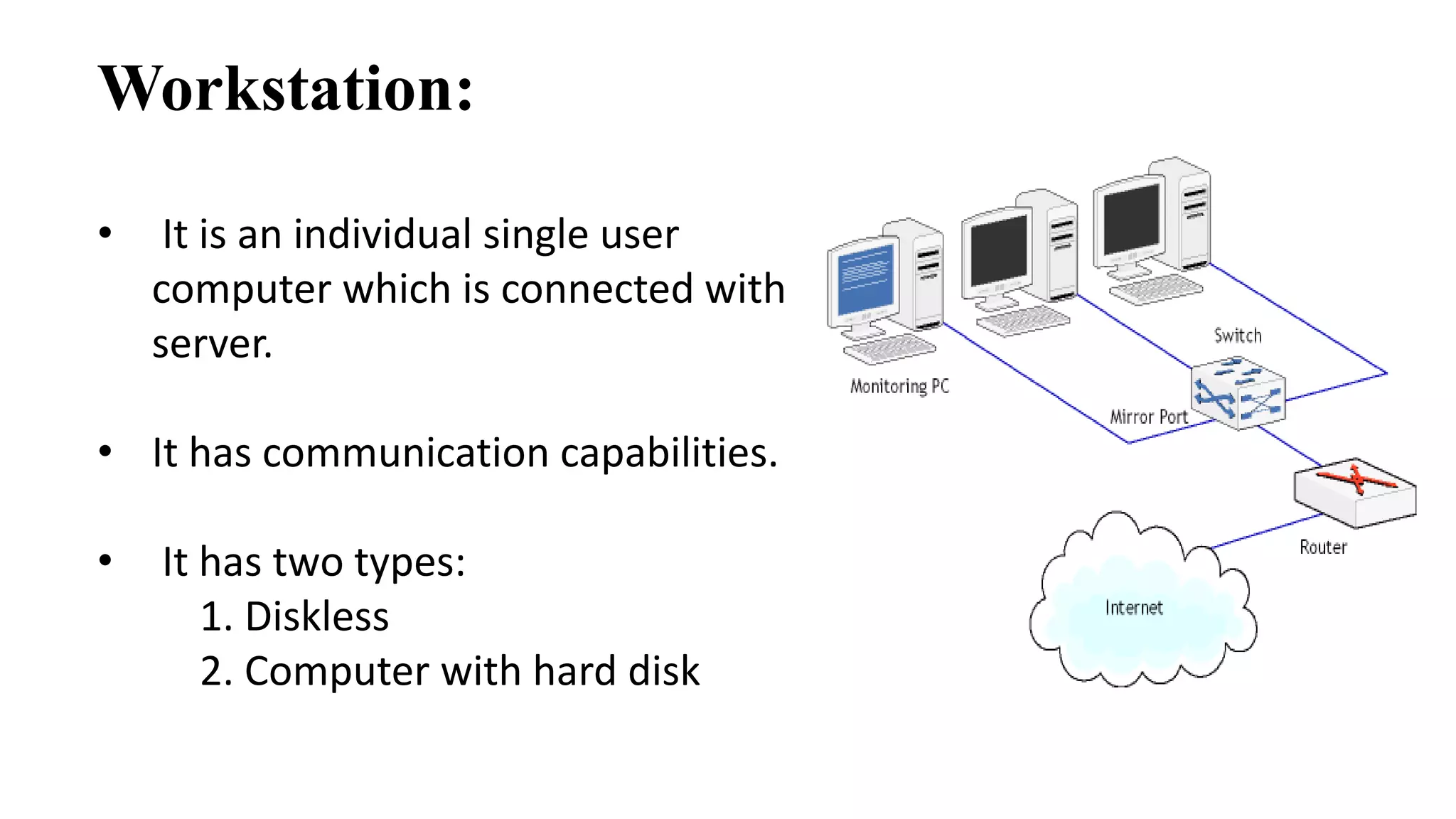
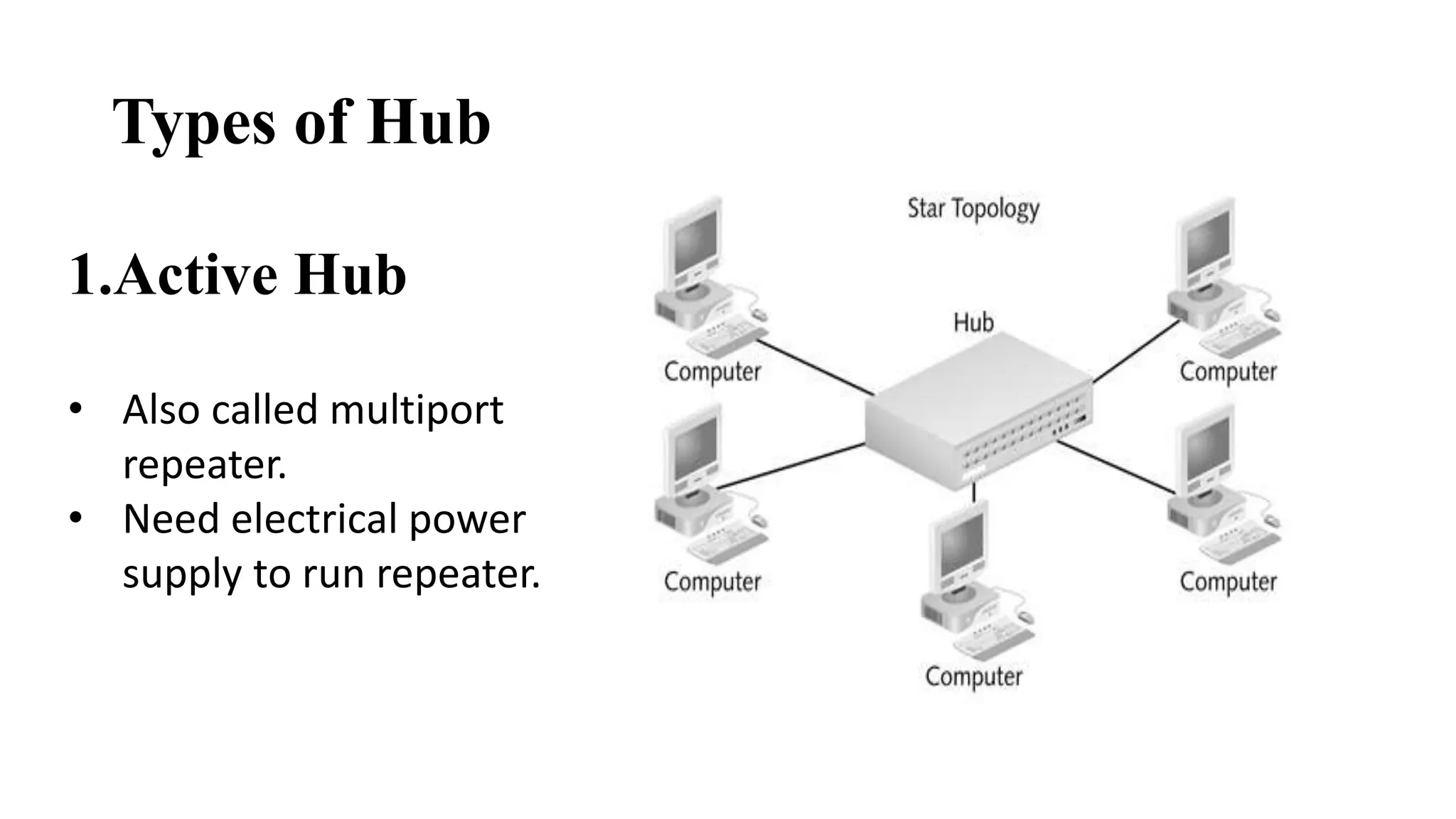
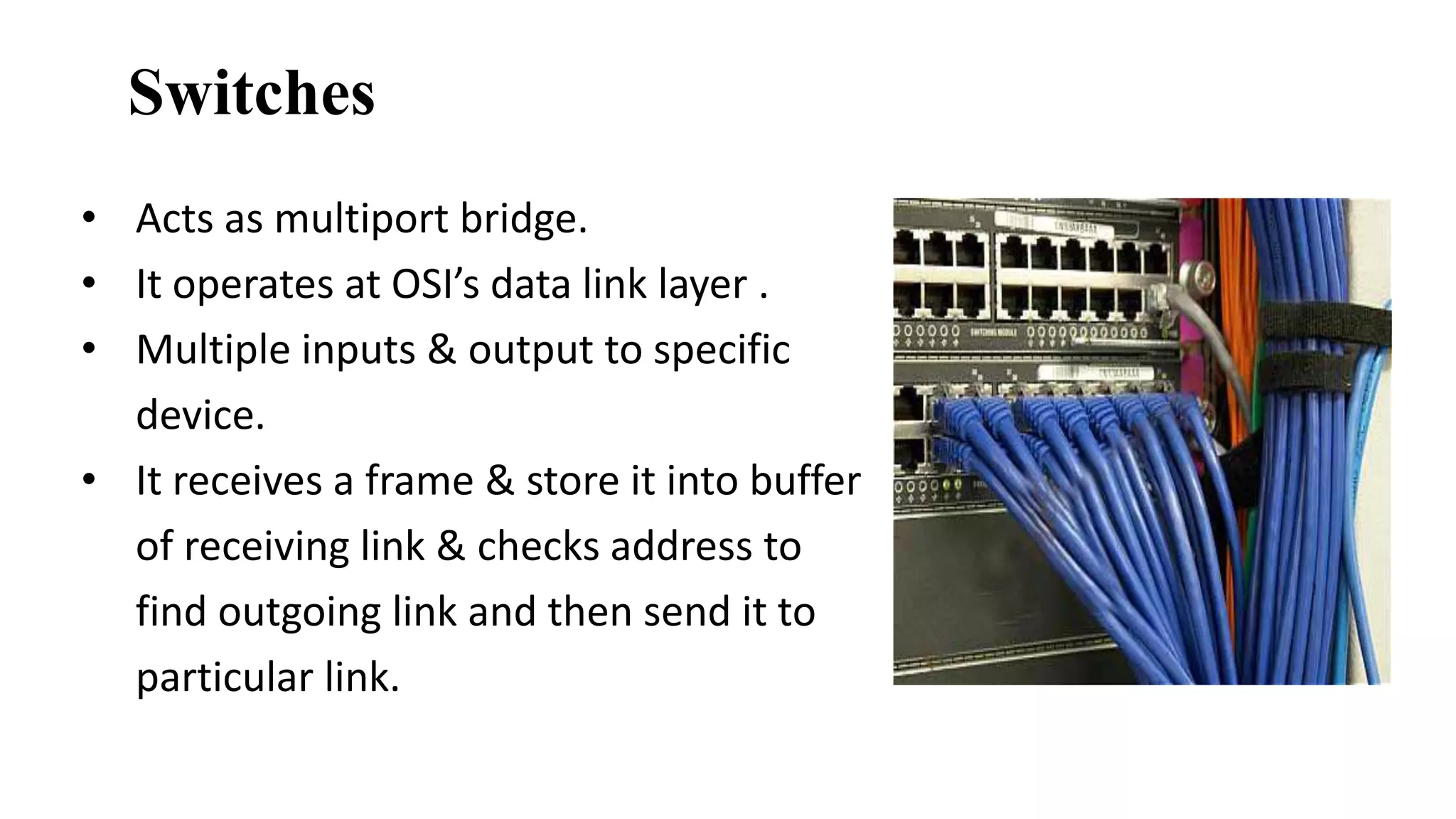
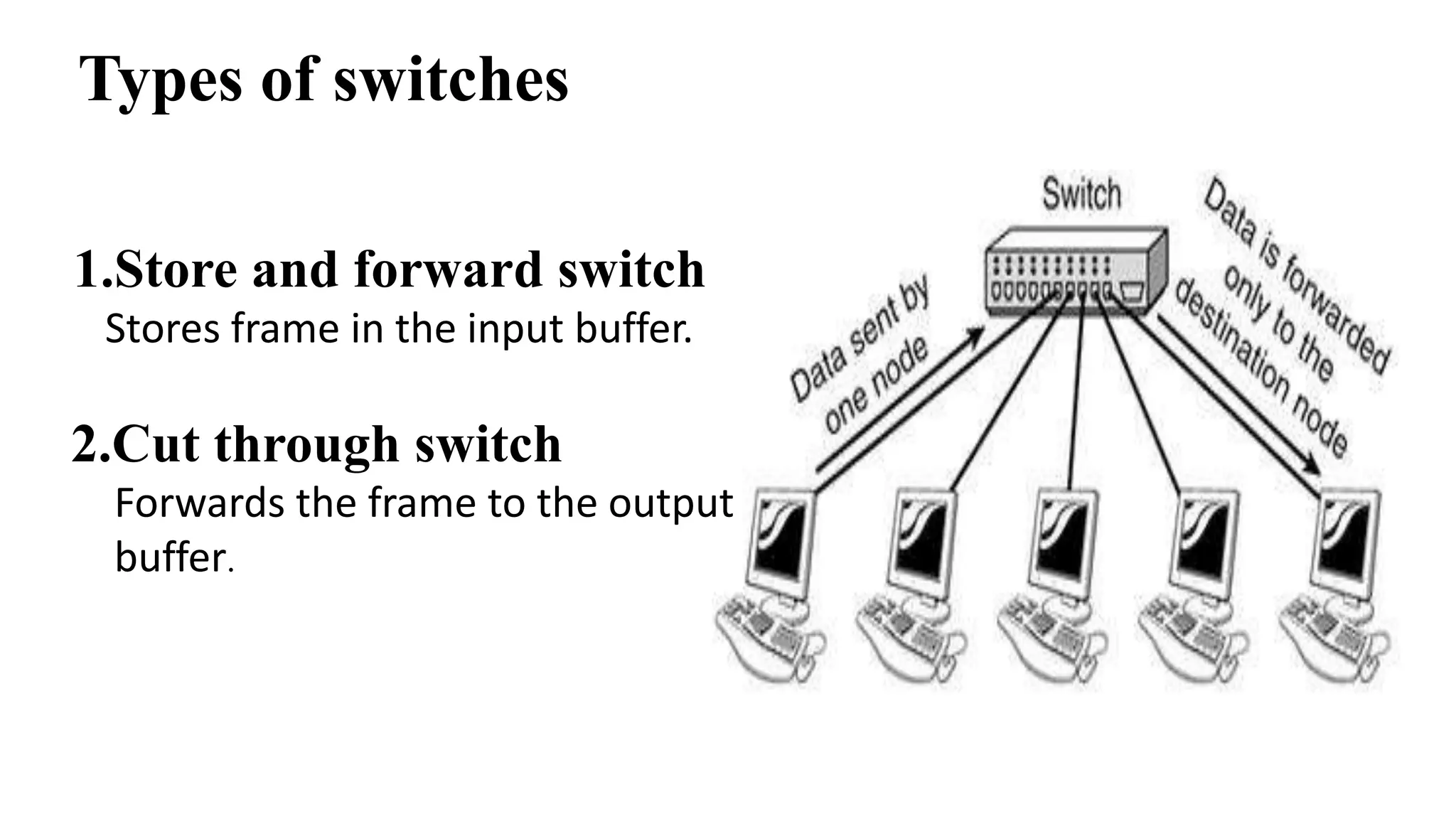
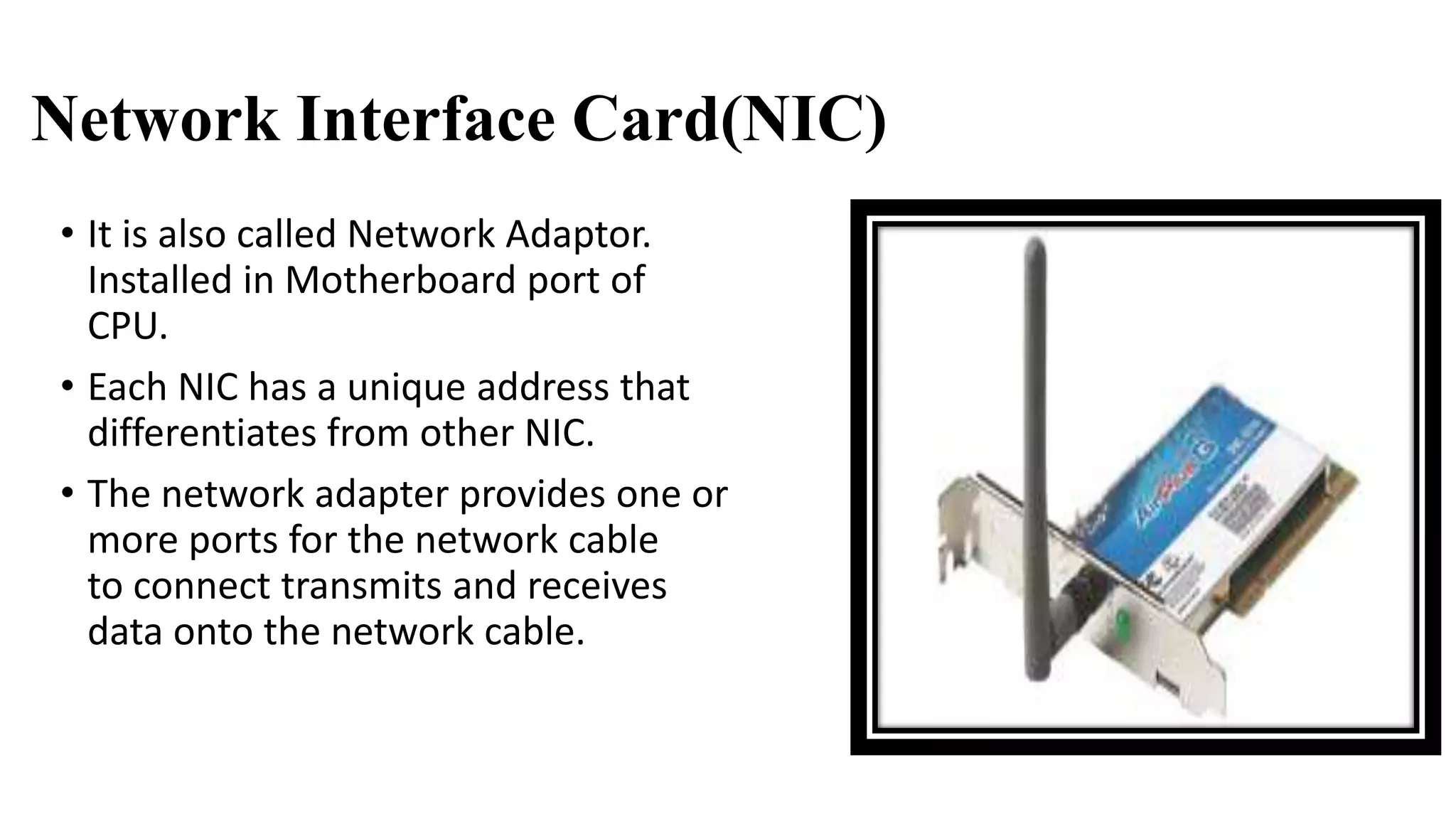
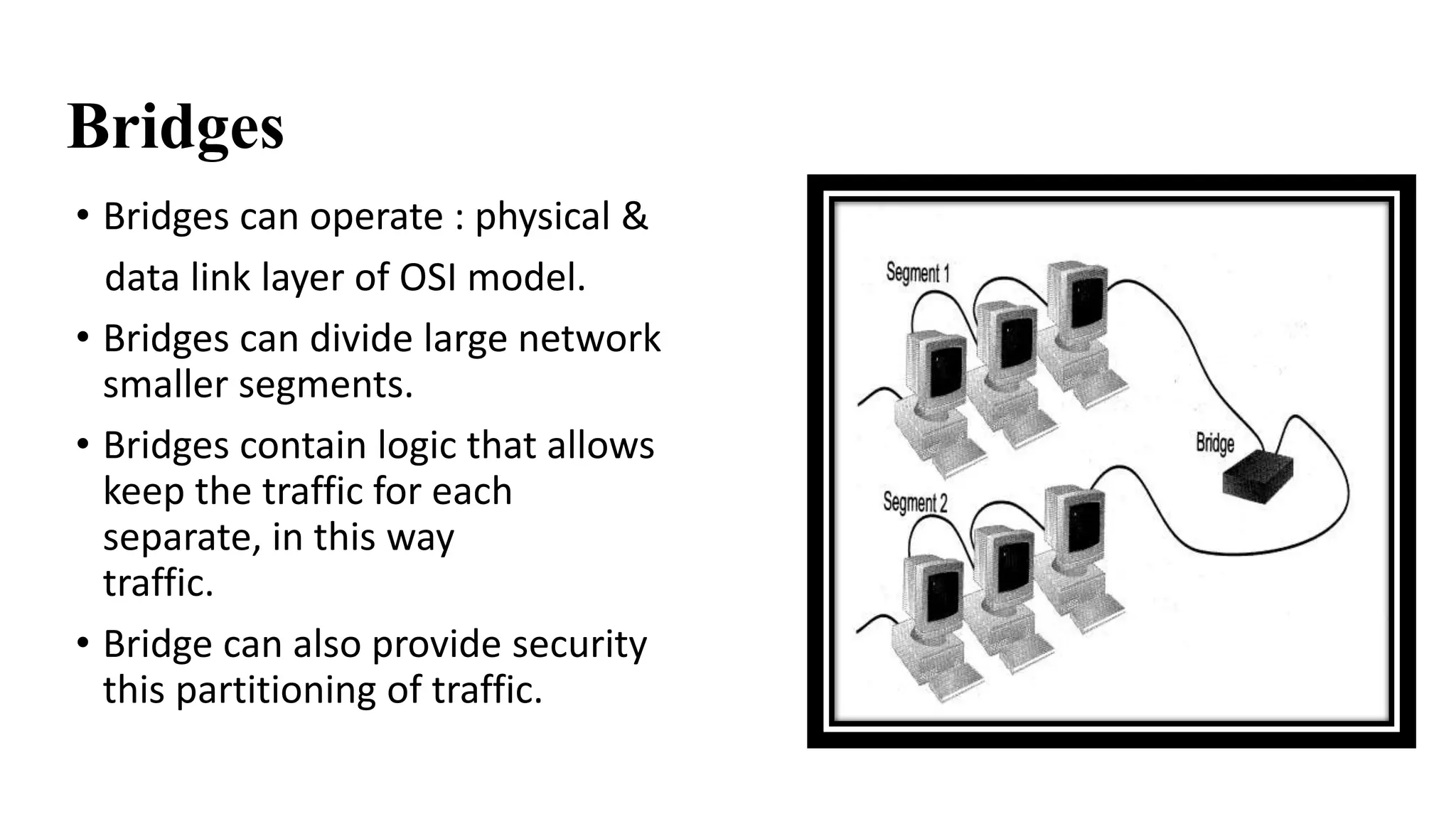
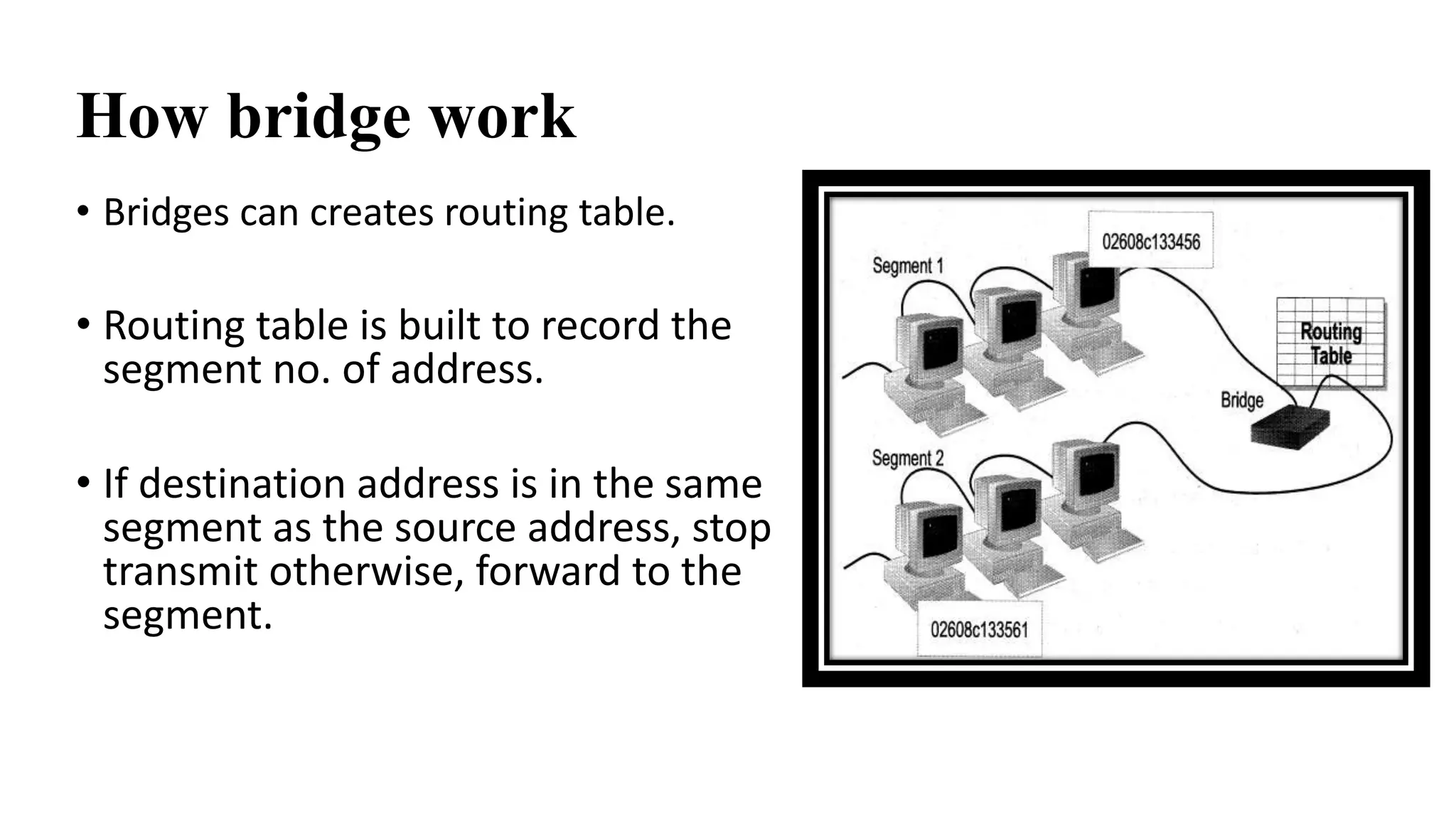
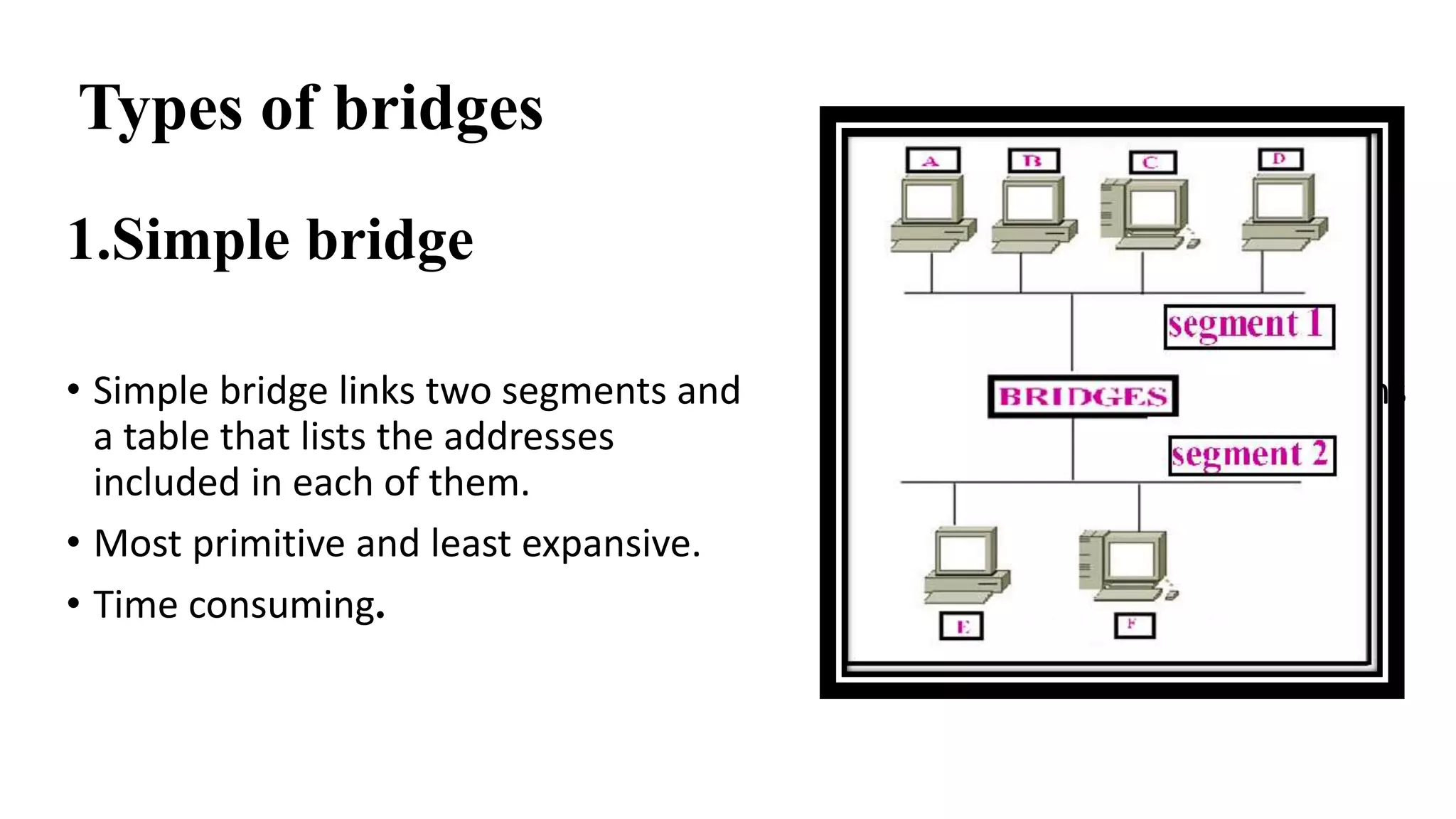
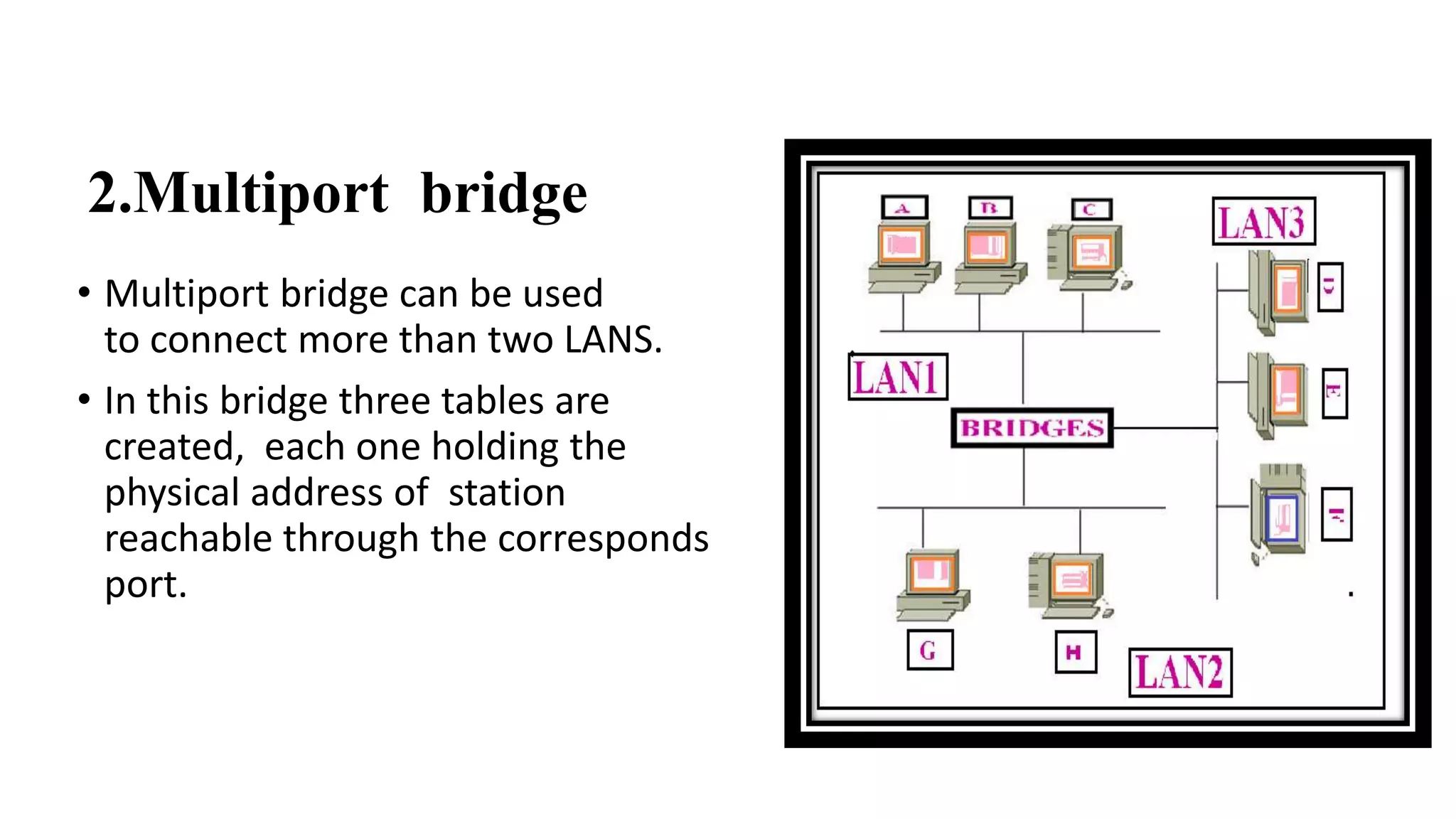
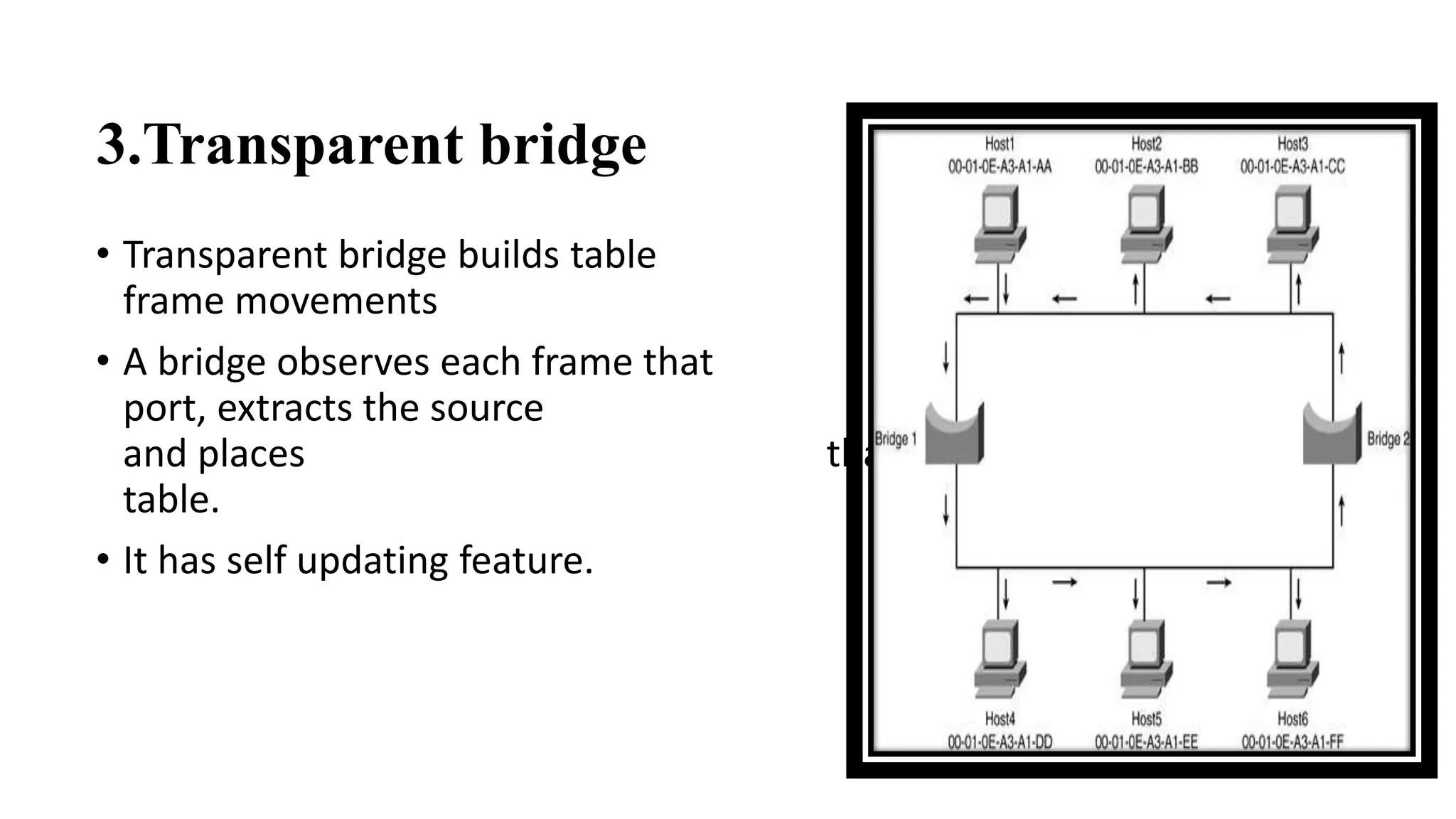
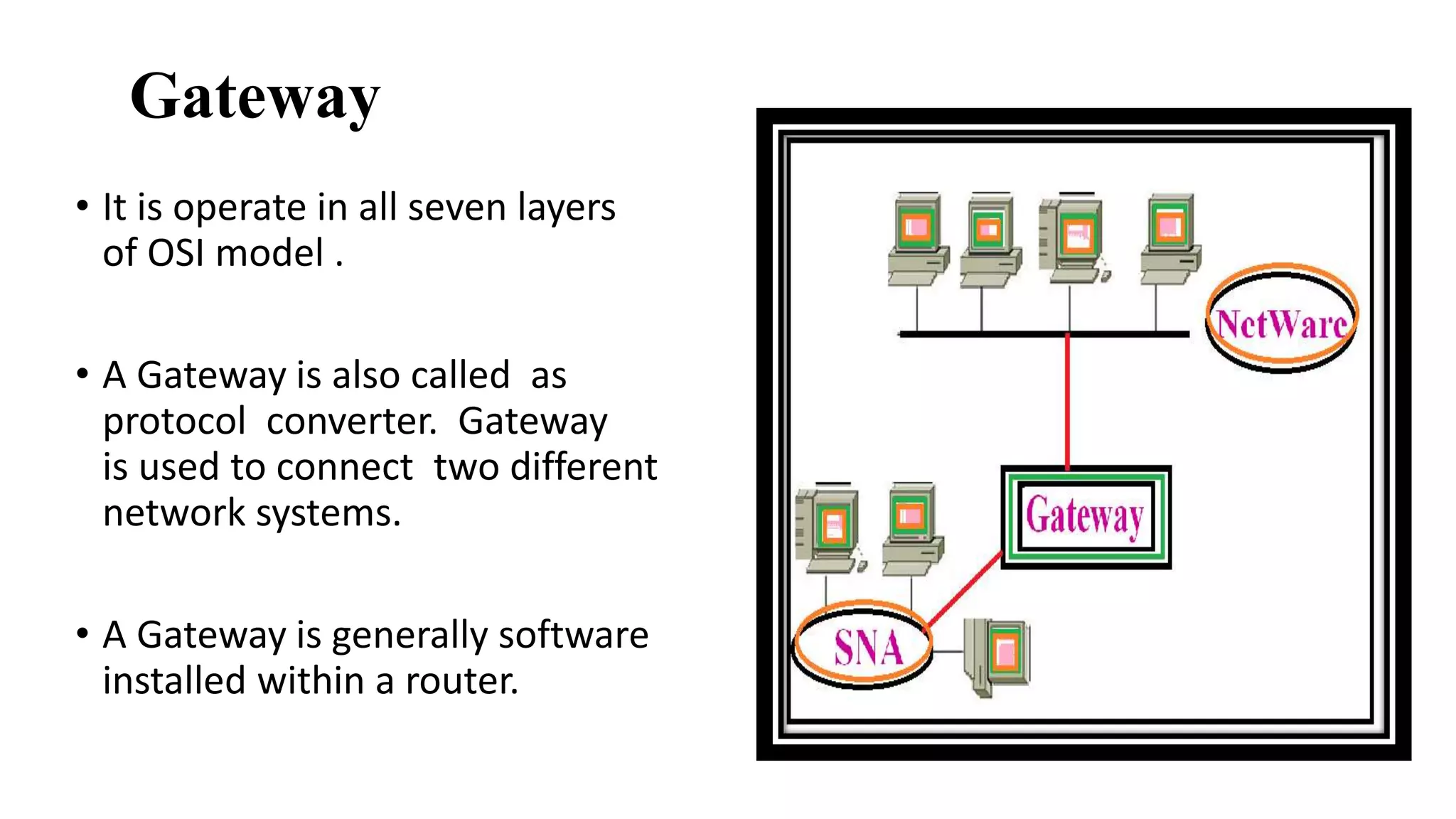
This document discusses various network devices and their functions. It describes repeaters, routers, brouters, hubs, switches, bridges, network interface cards (NICs), and gateways. Repeaters operate at the physical layer and regenerate signals to extend network distance. Routers operate at multiple layers and direct traffic between networks by maintaining routing tables. Bridges separate networks into segments to reduce congestion. Switches operate at the data link layer to limit collision domains. NICs connect devices to the network. Gateways connect different network types and protocols.