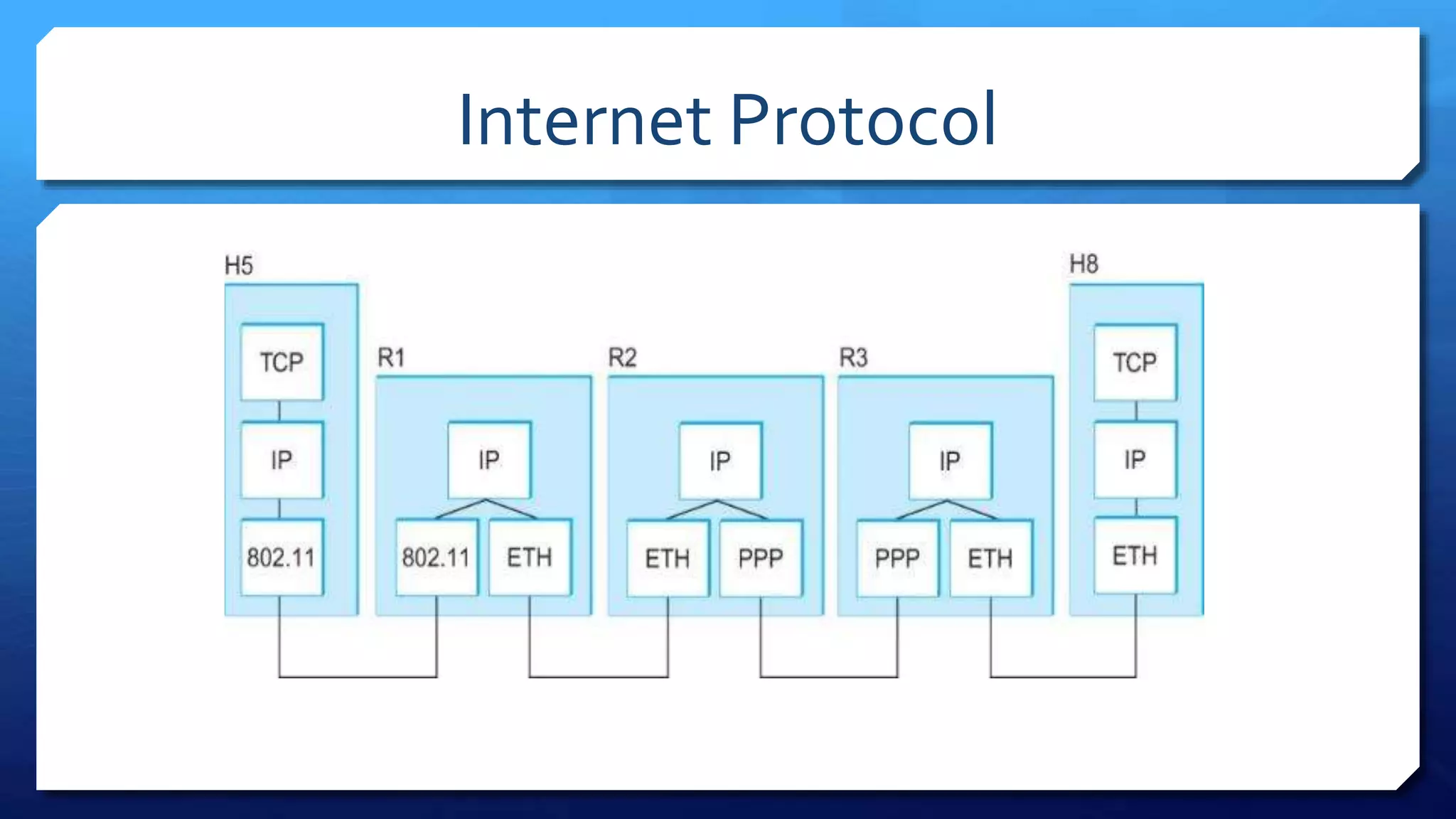
- The Internet Protocol (IP) is the key networking protocol that enables internetworking and provides host-to-host delivery of data packets across interconnected networks of varying technologies.
- IP uses a best-effort delivery model, meaning it does not guarantee delivery of data packets and does not remedy lost, corrupted, misdelivered, or undelivered packets.
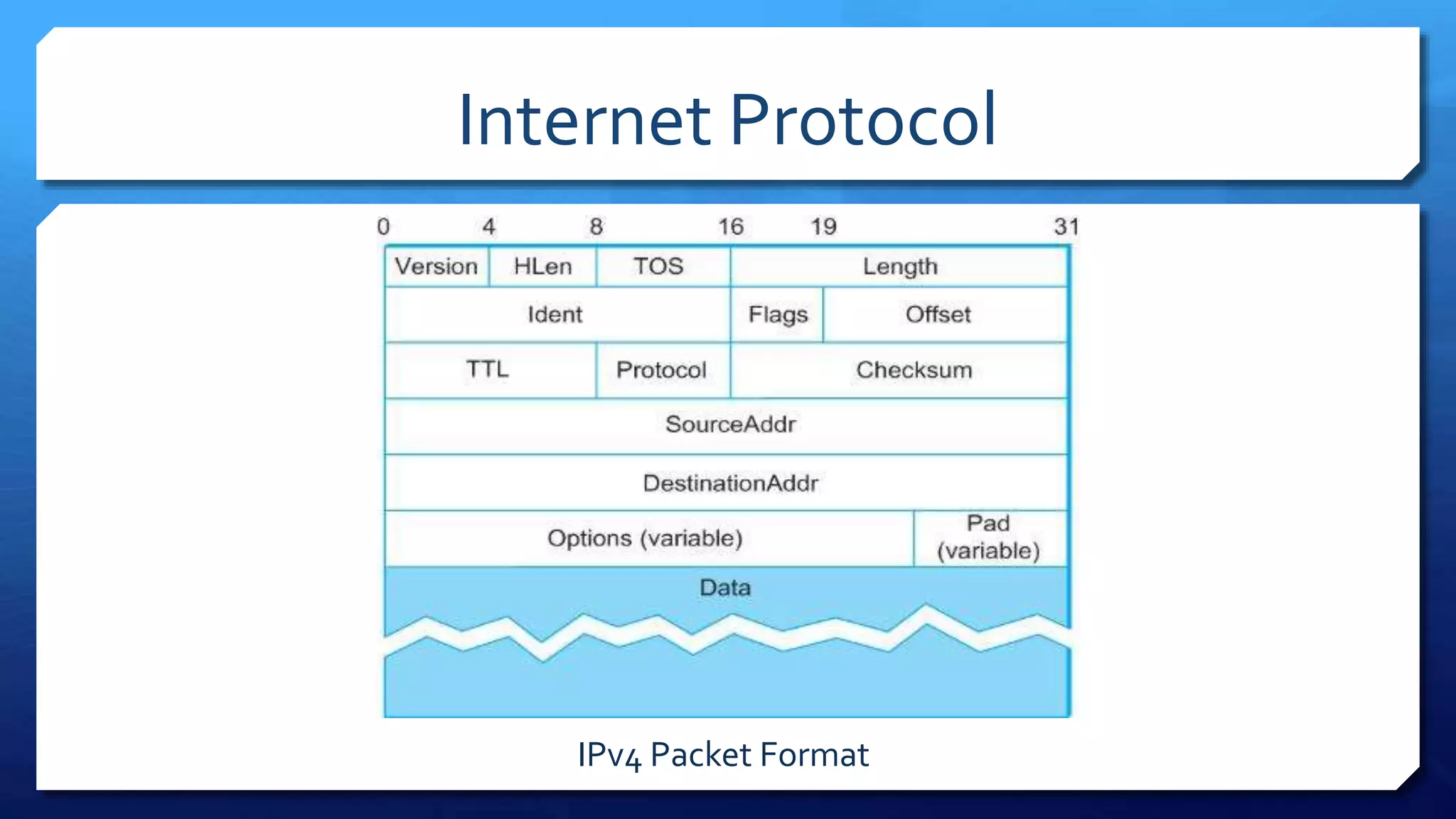
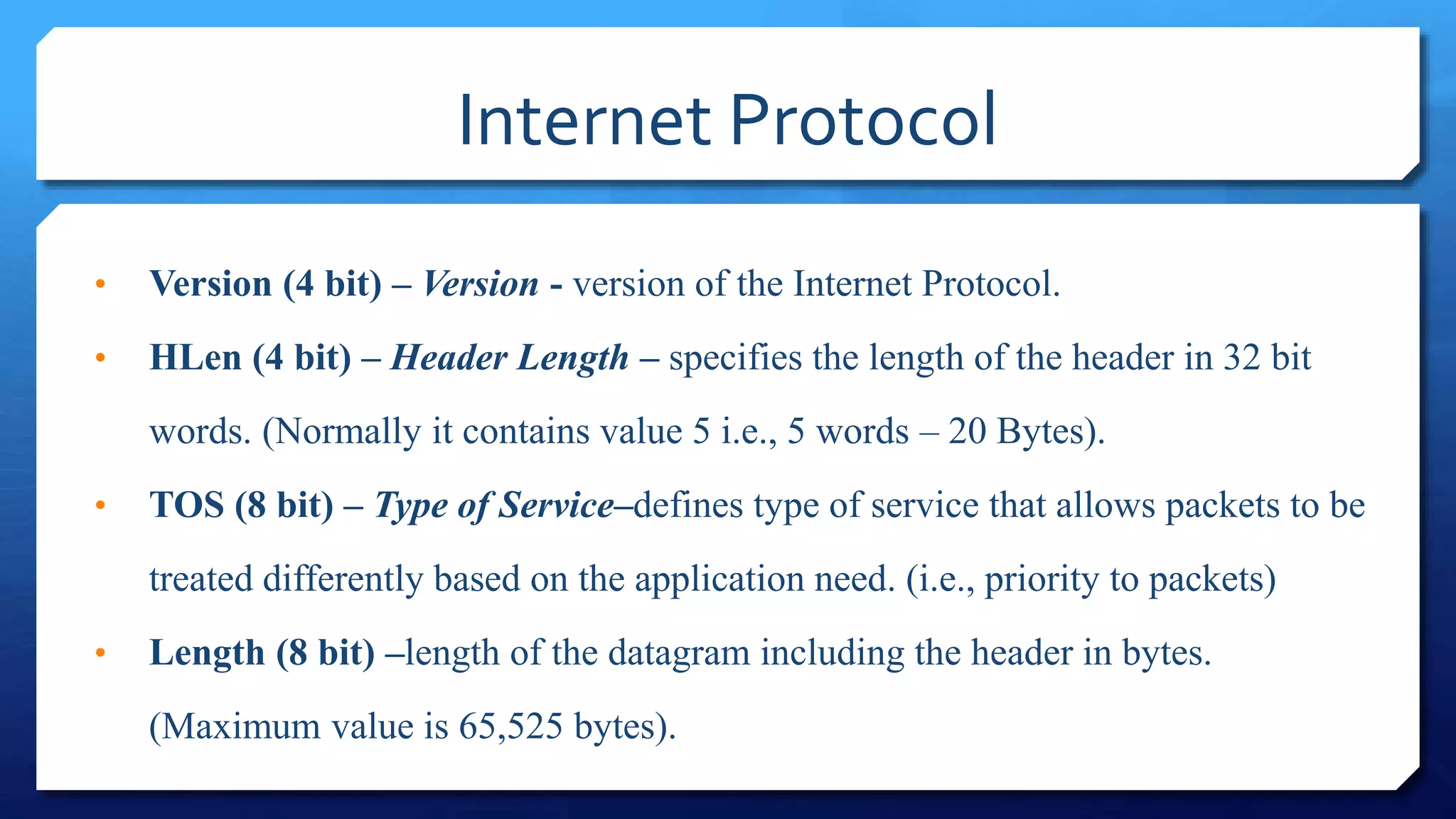
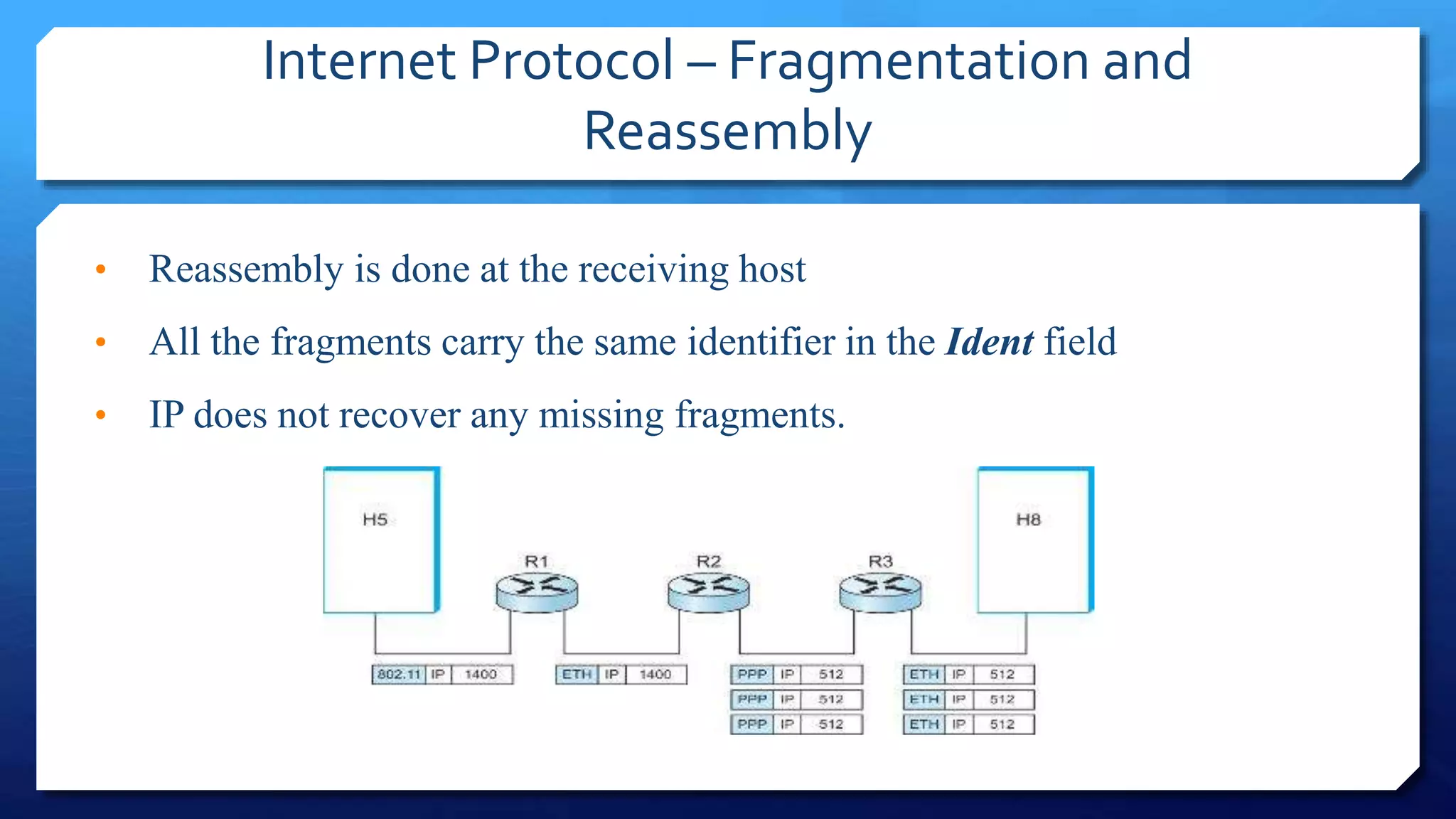
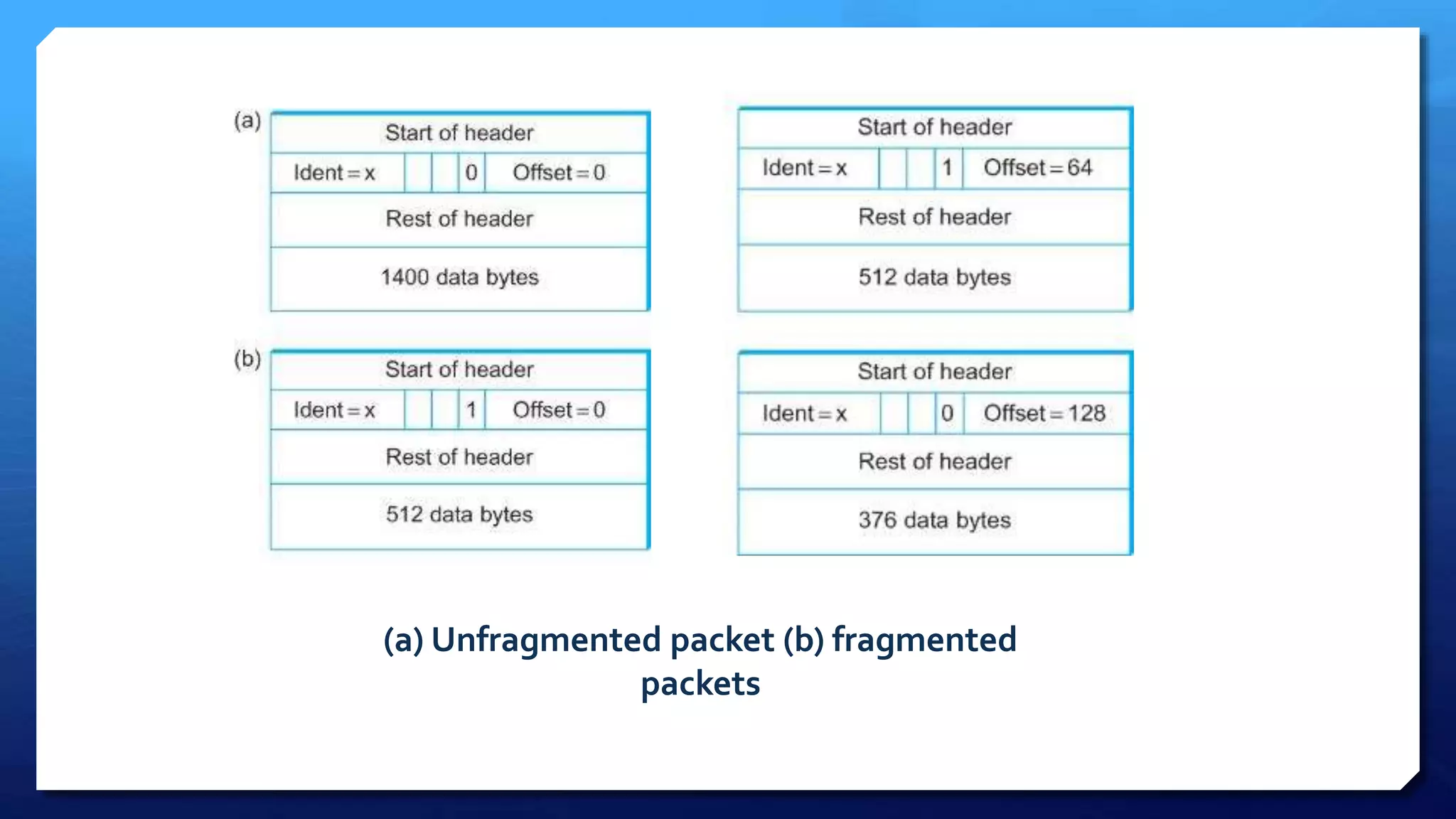
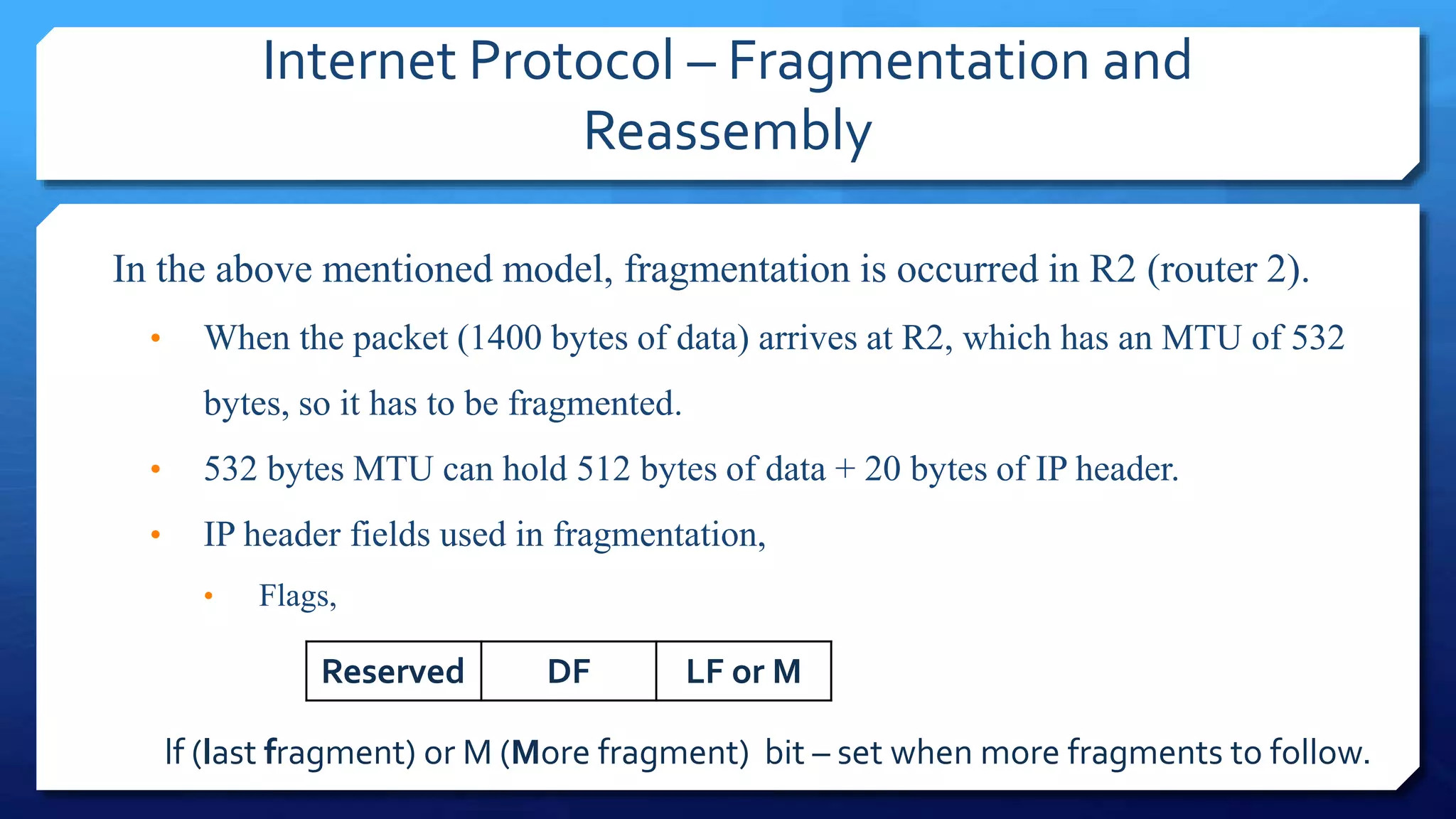
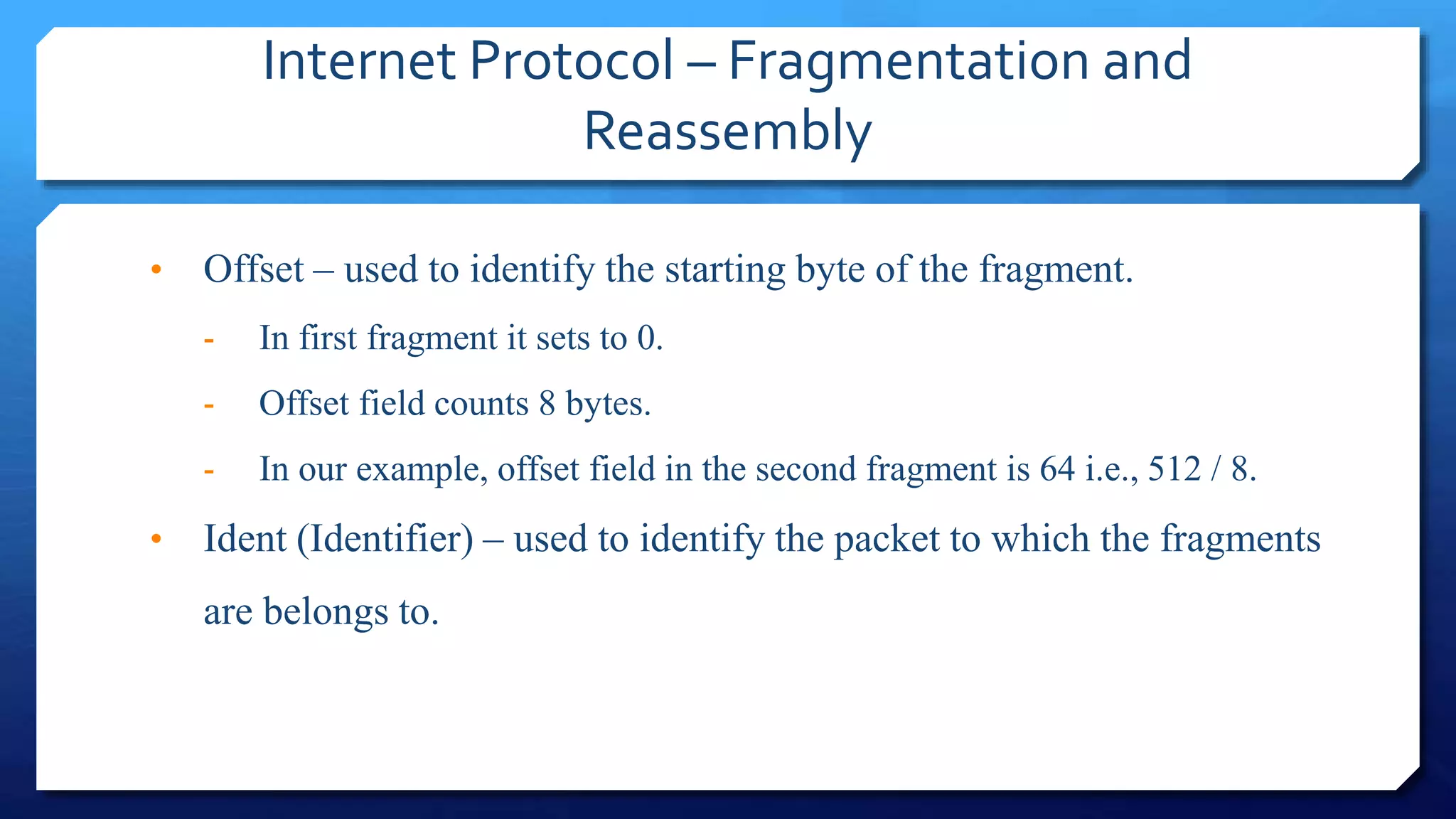
- IP packet headers contain fields for source and destination addresses, protocol type, fragmentation information, and more. IP packets can be fragmented into smaller pieces to accommodate networks with smaller maximum transmission unit sizes.