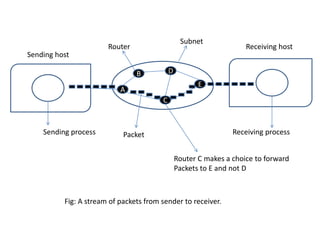
A wide area network (WAN) connects multiple local area networks (LANs) over a large geographical area like a country or continent. The hosts on the LANs are connected through communication lines and routers that make up the WAN subnet. The subnet carries messages between hosts, allowing computers in different locations to communicate. The objectives of building a WAN include consolidating data, voice and video services, reducing network costs, and improving performance through optimization. However, WANs are difficult for businesses to manage as traffic increases with cloud computing and emerging technologies. Cost effectiveness and reliability can also be challenges with WAN upgrades.