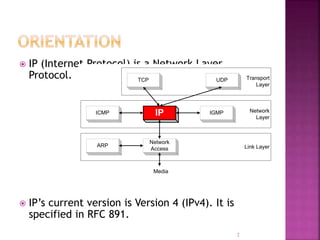
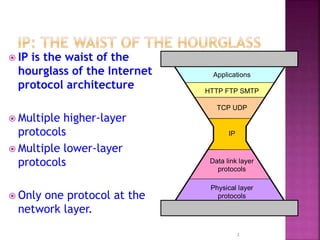
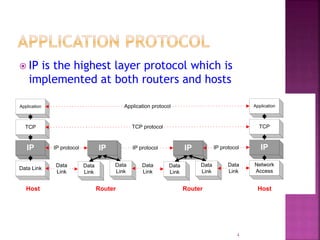
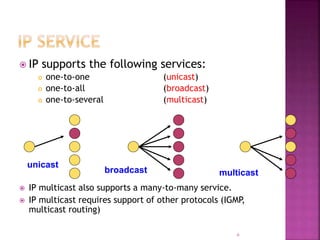
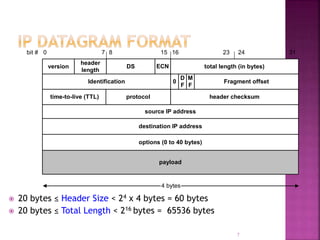
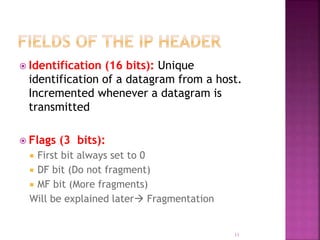
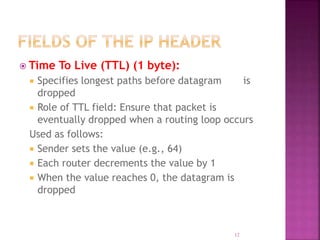
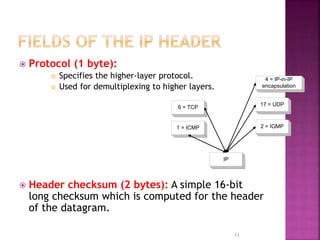
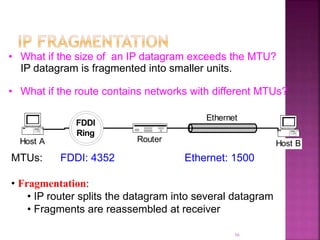
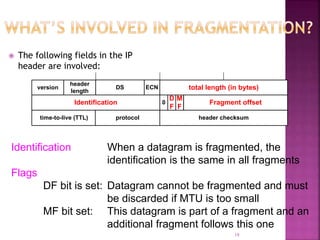
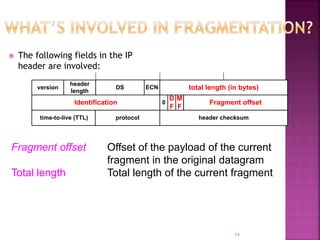
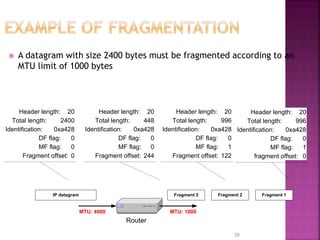
IP is the network layer protocol that provides an unreliable, connectionless, best-effort delivery service for transmitting data packets across networks. It operates by fragmenting large data packets into smaller fragments if needed to meet the maximum transmission unit size of the underlying data link layer. Key fields in the IP header include the identification field to identify fragments of the same packet, the fragment offset field to indicate the position of data in the original packet, and flags to indicate if a packet is a fragment or the last fragment.