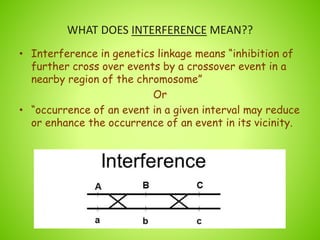
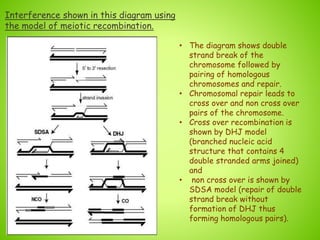
1. Interference in genetics means that one crossover event on a chromosome can reduce the likelihood of another crossover event occurring near the same location.
2. The document defines interference and provides examples of positive and negative interference. Positive interference occurs when the first crossover reduces the chances of a second nearby crossover, while negative interference enhances the chances of a second nearby crossover.
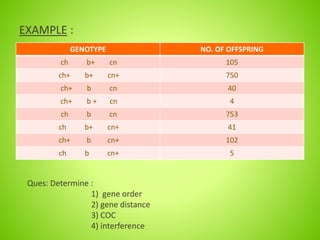
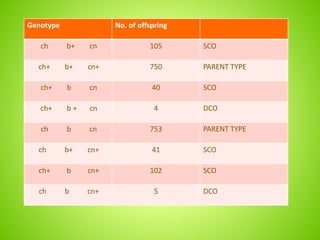
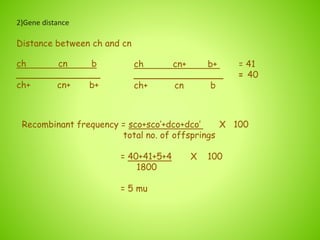
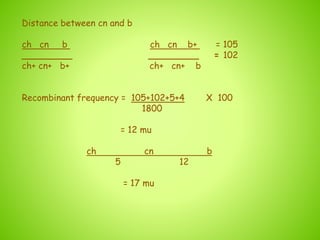
3. An example calculation is shown to determine gene order, distance, and coefficient of coincidence from offspring genotypes, leading to a value of 0.17 for interference, indicating that crossover events are not independent and one reduces the chances of another nearby.