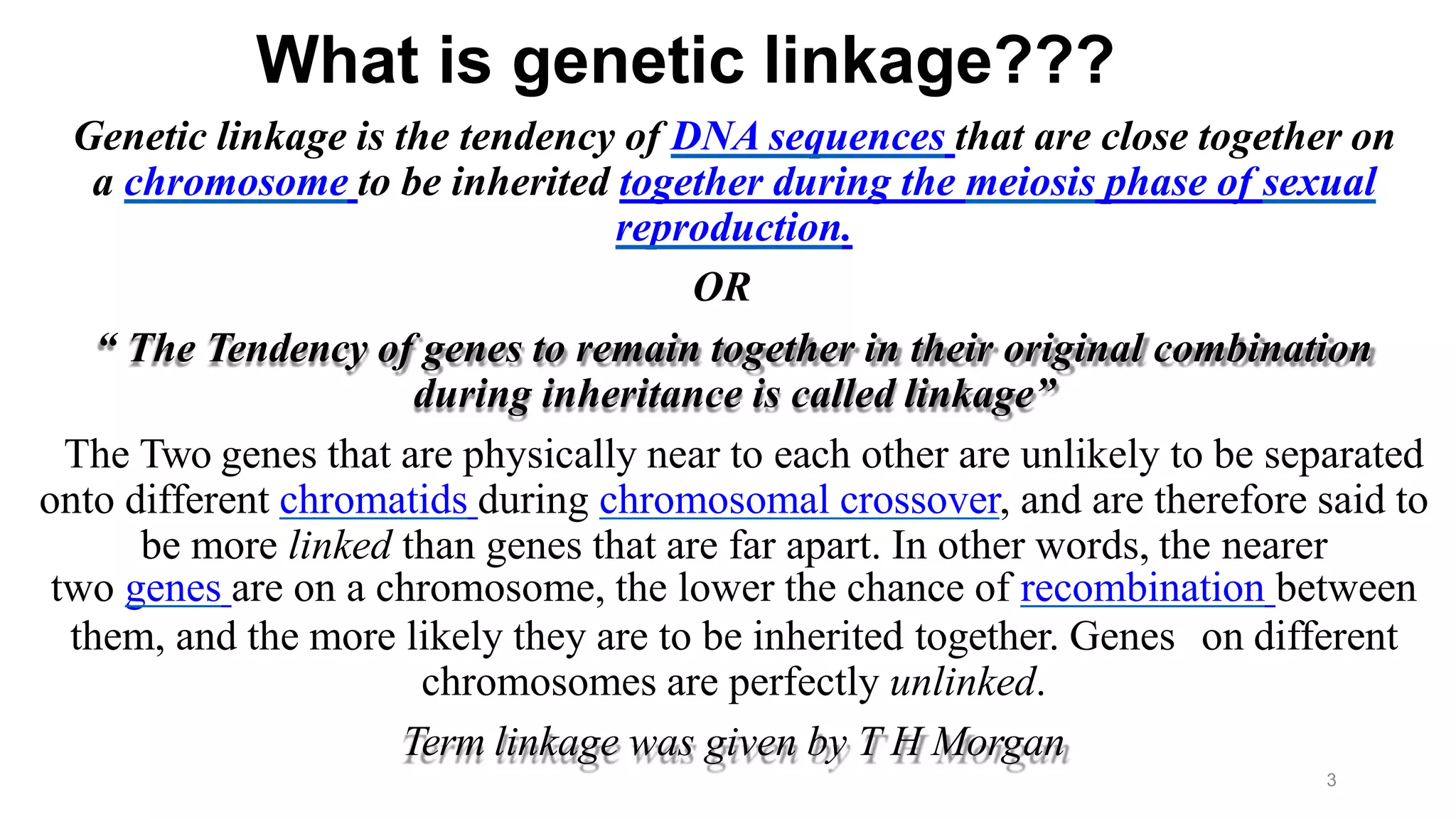
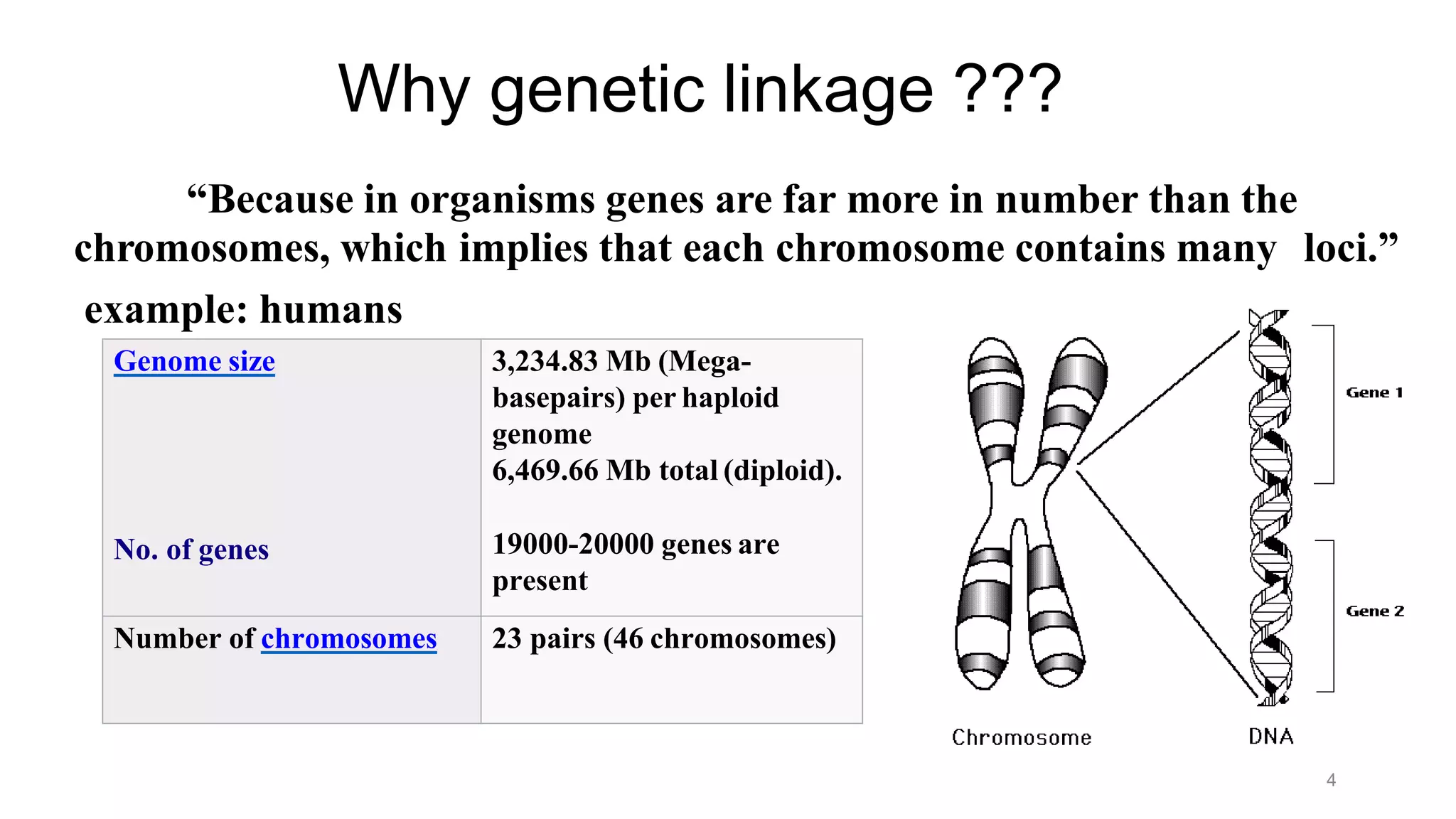
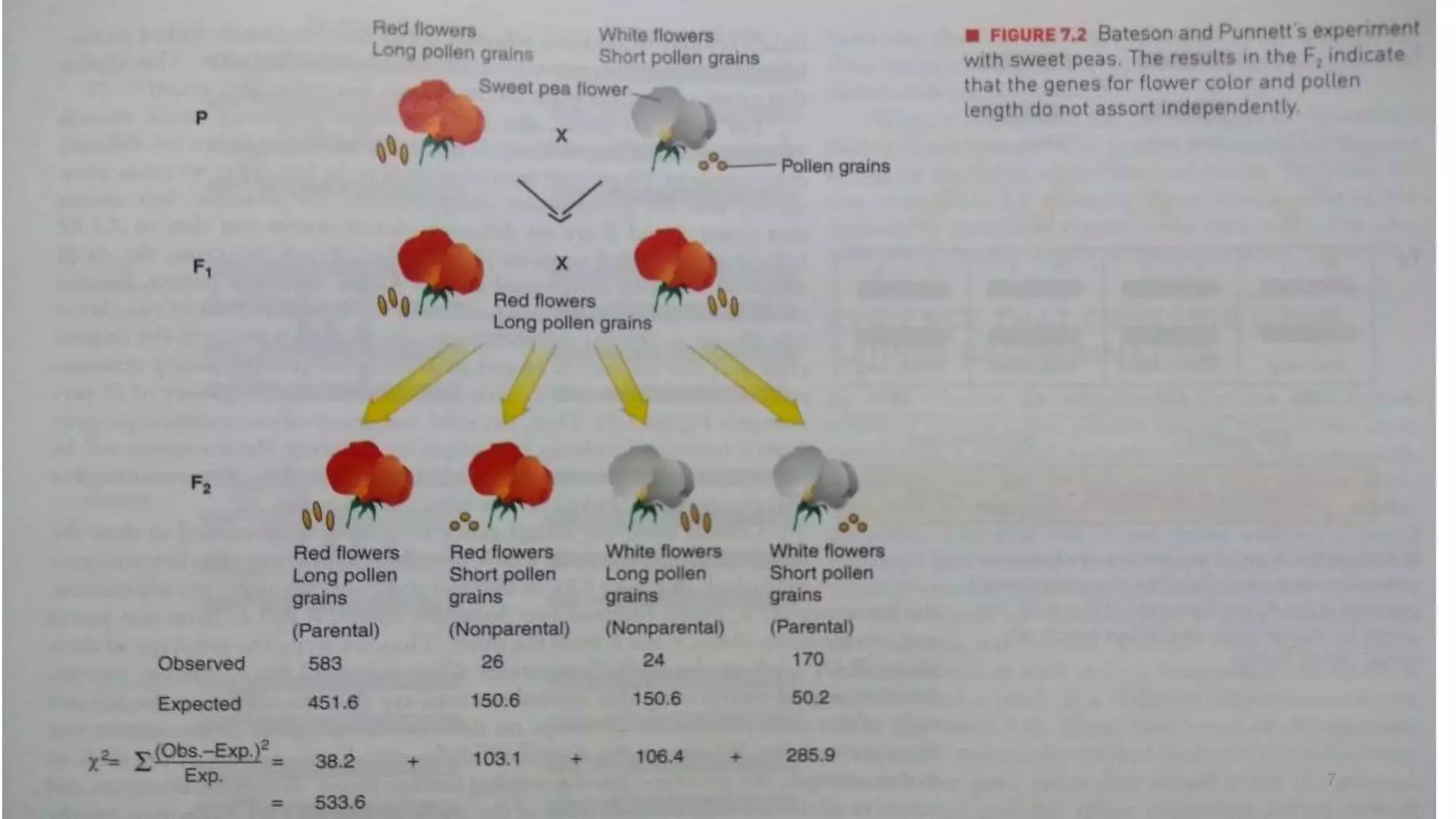
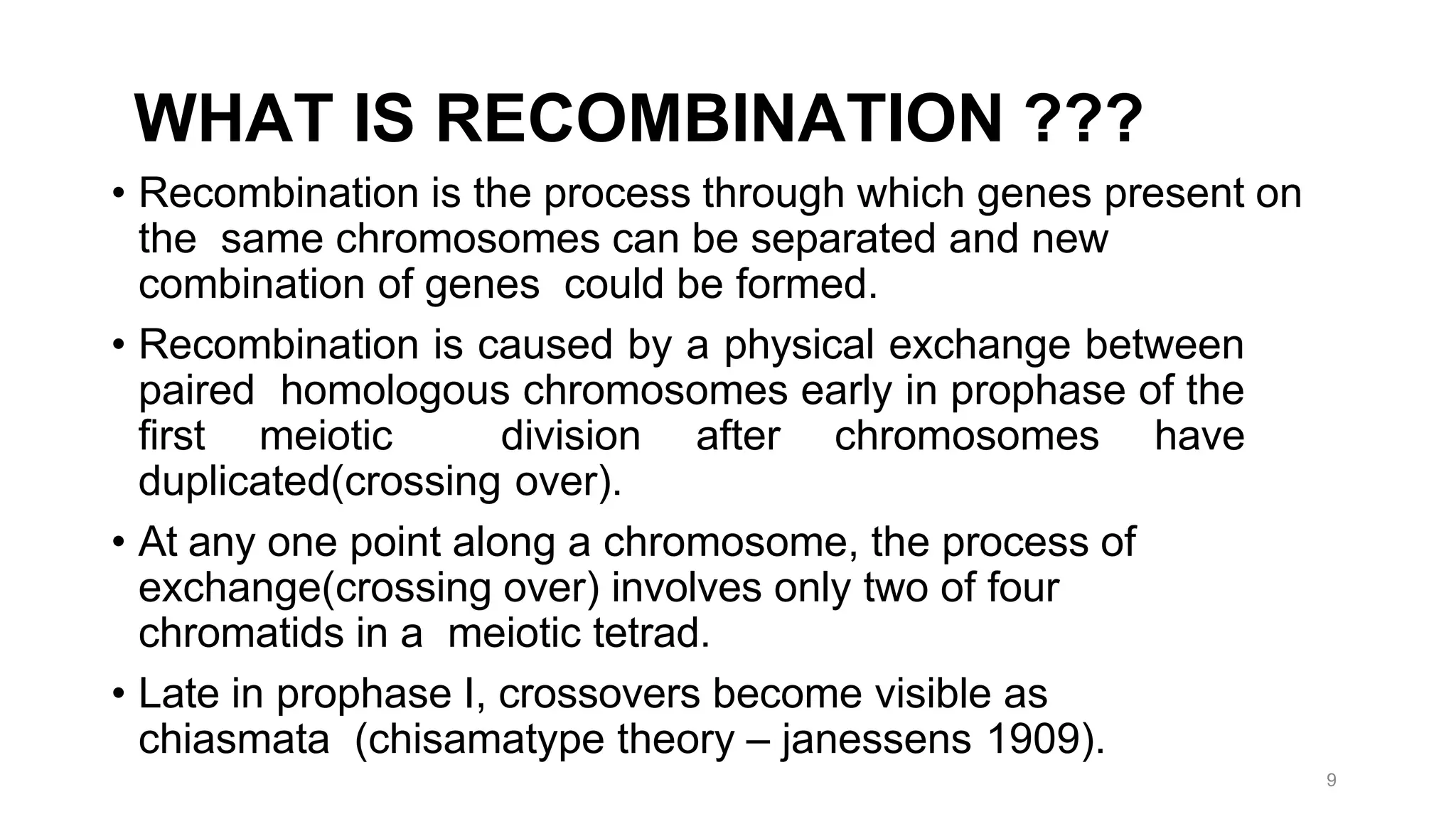
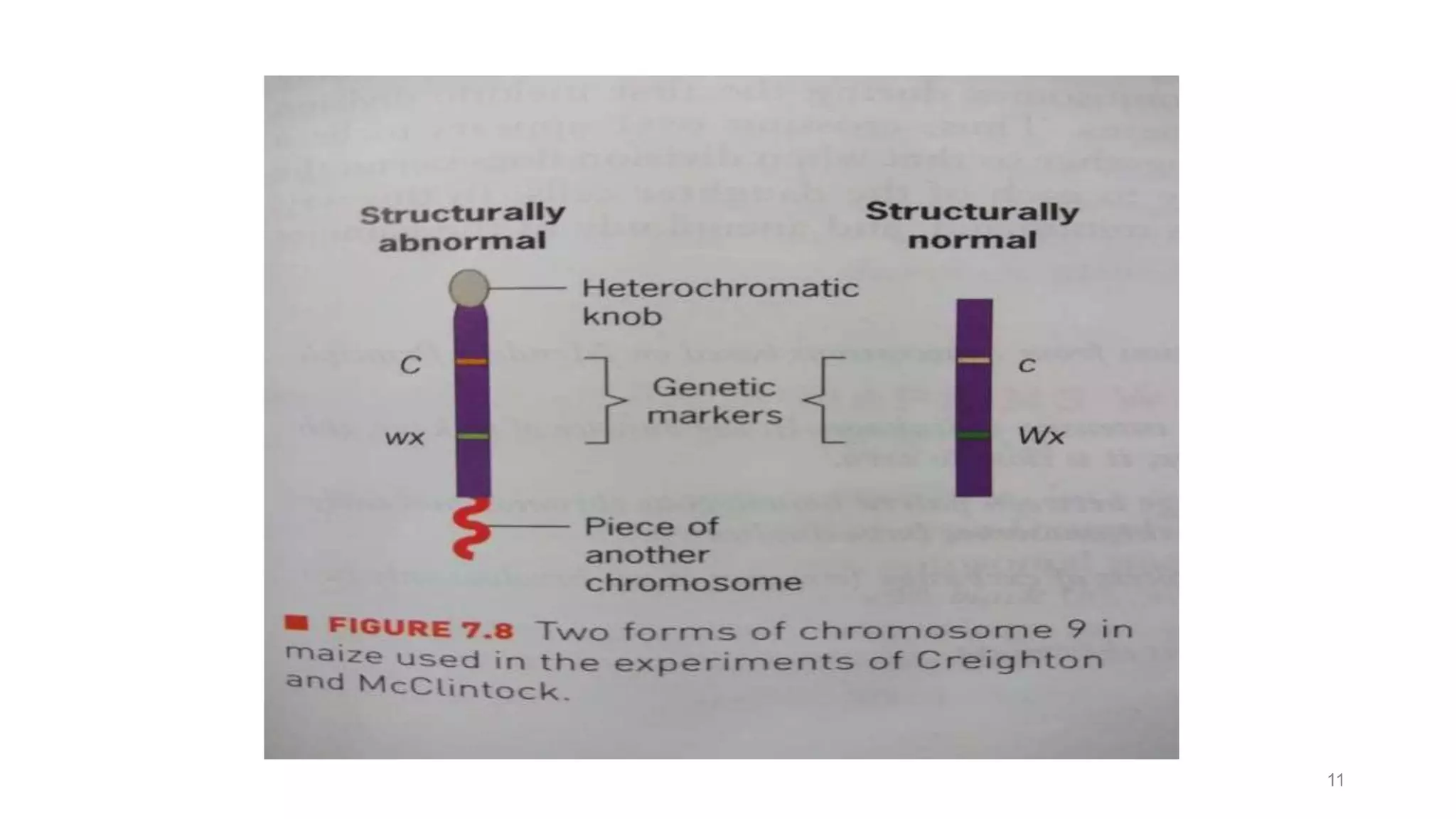
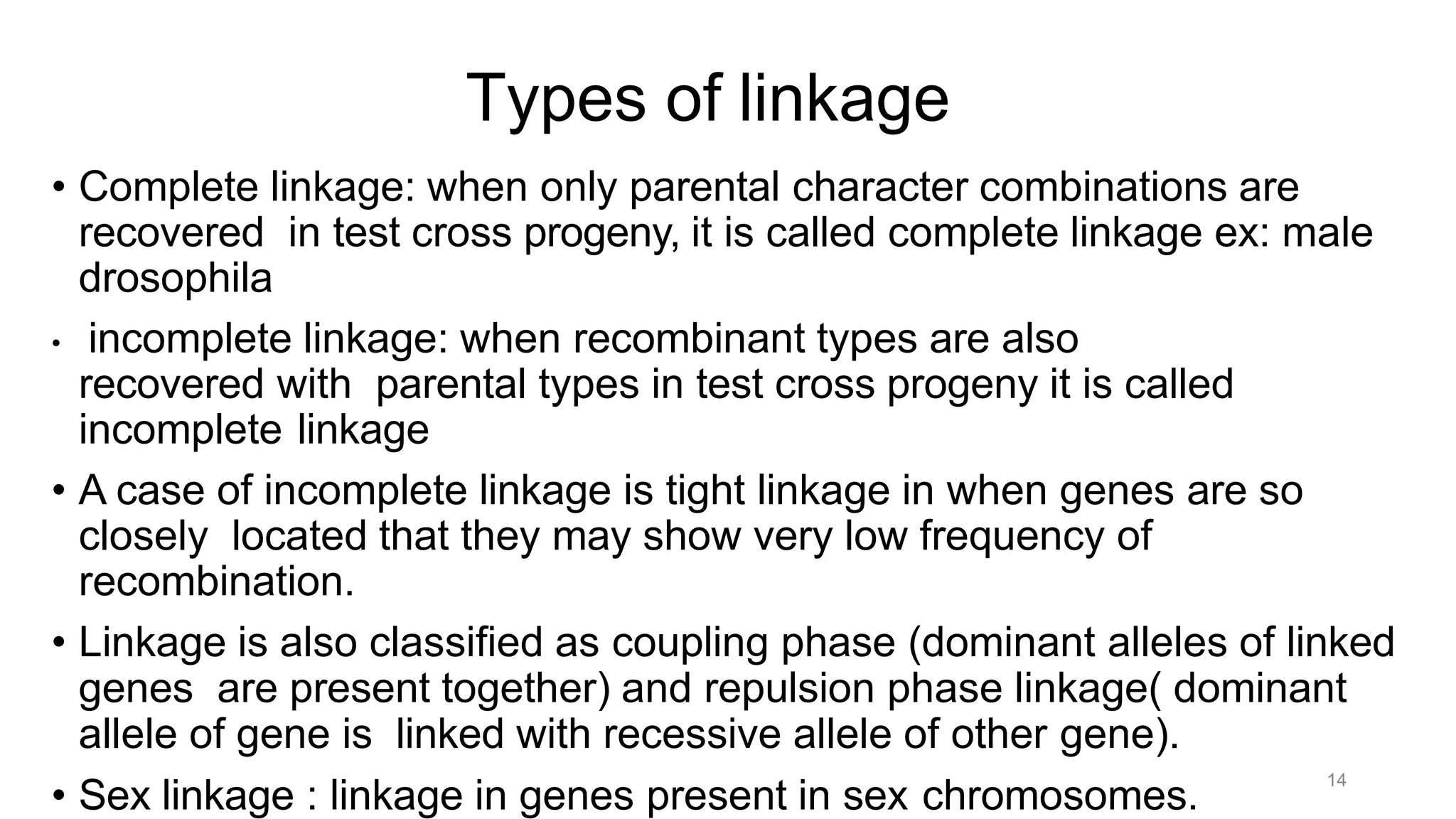
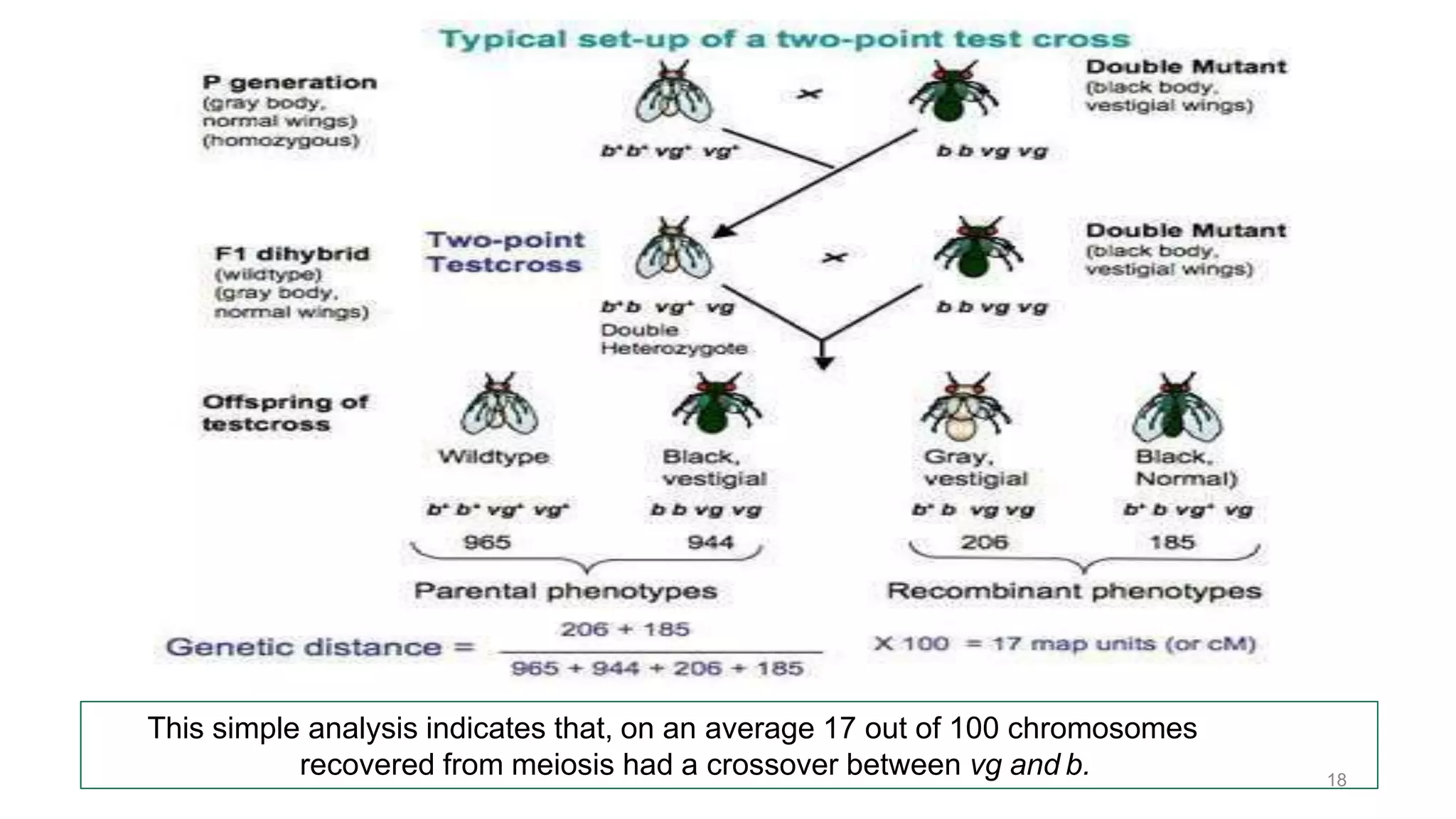
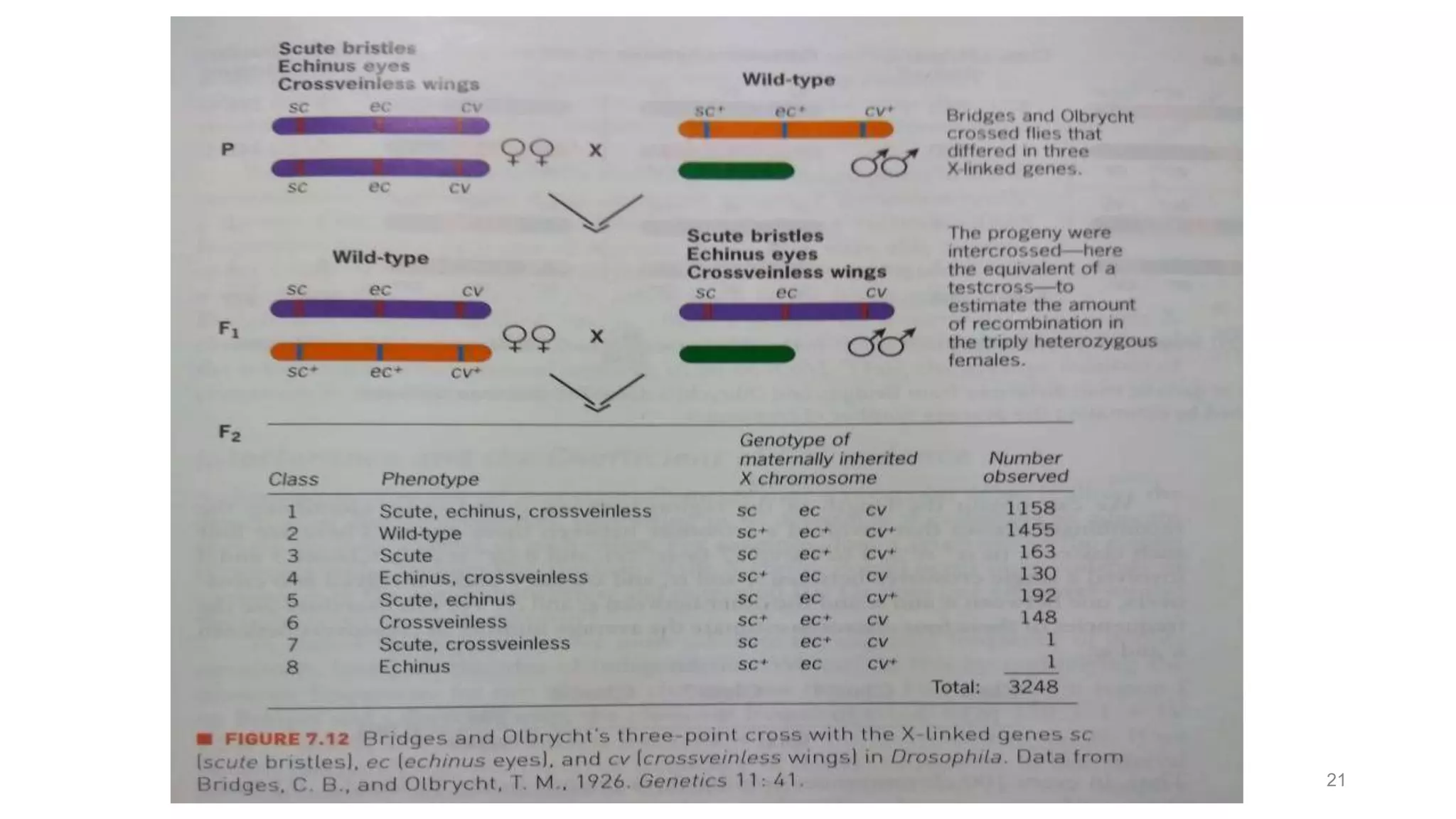
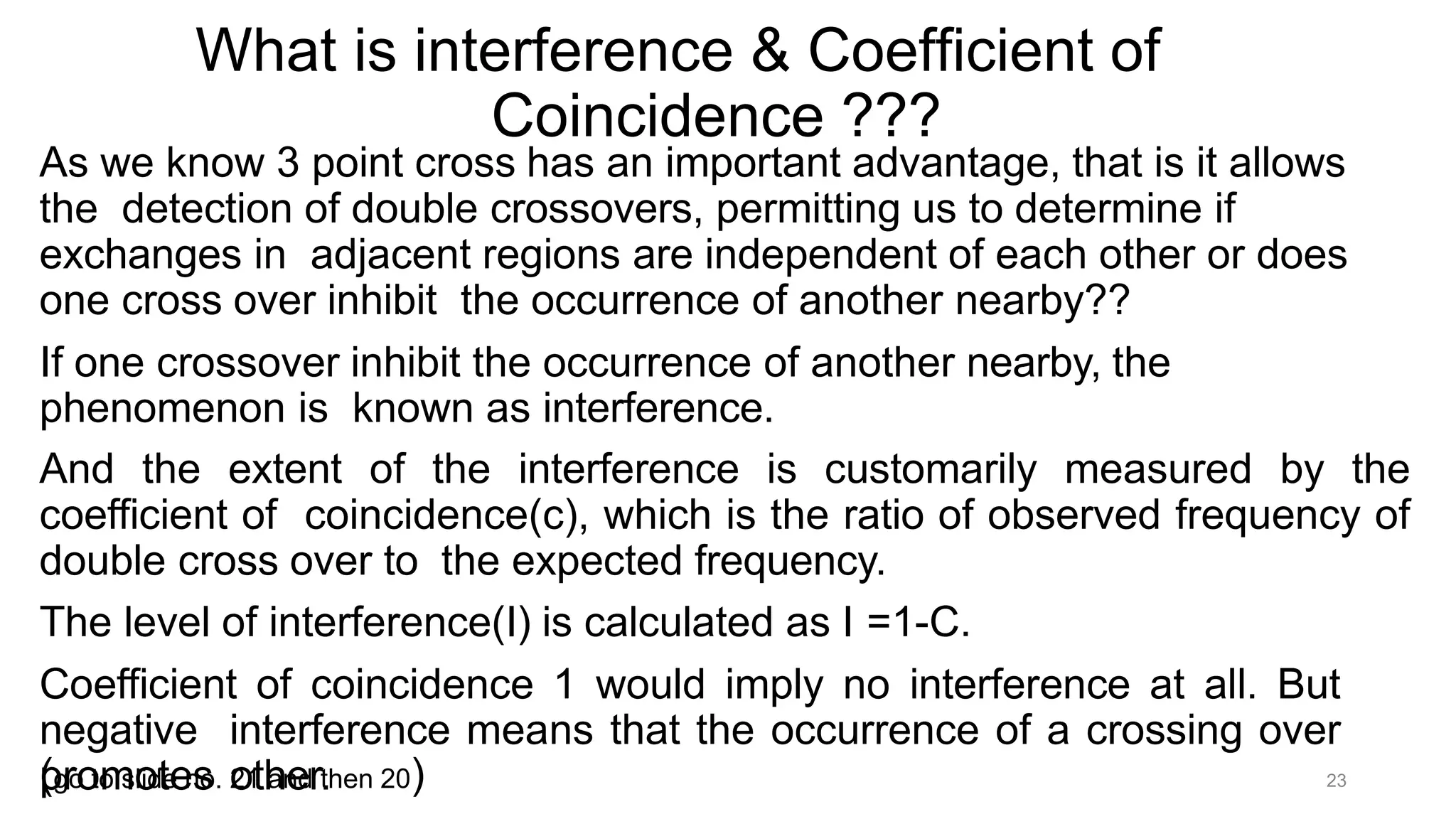
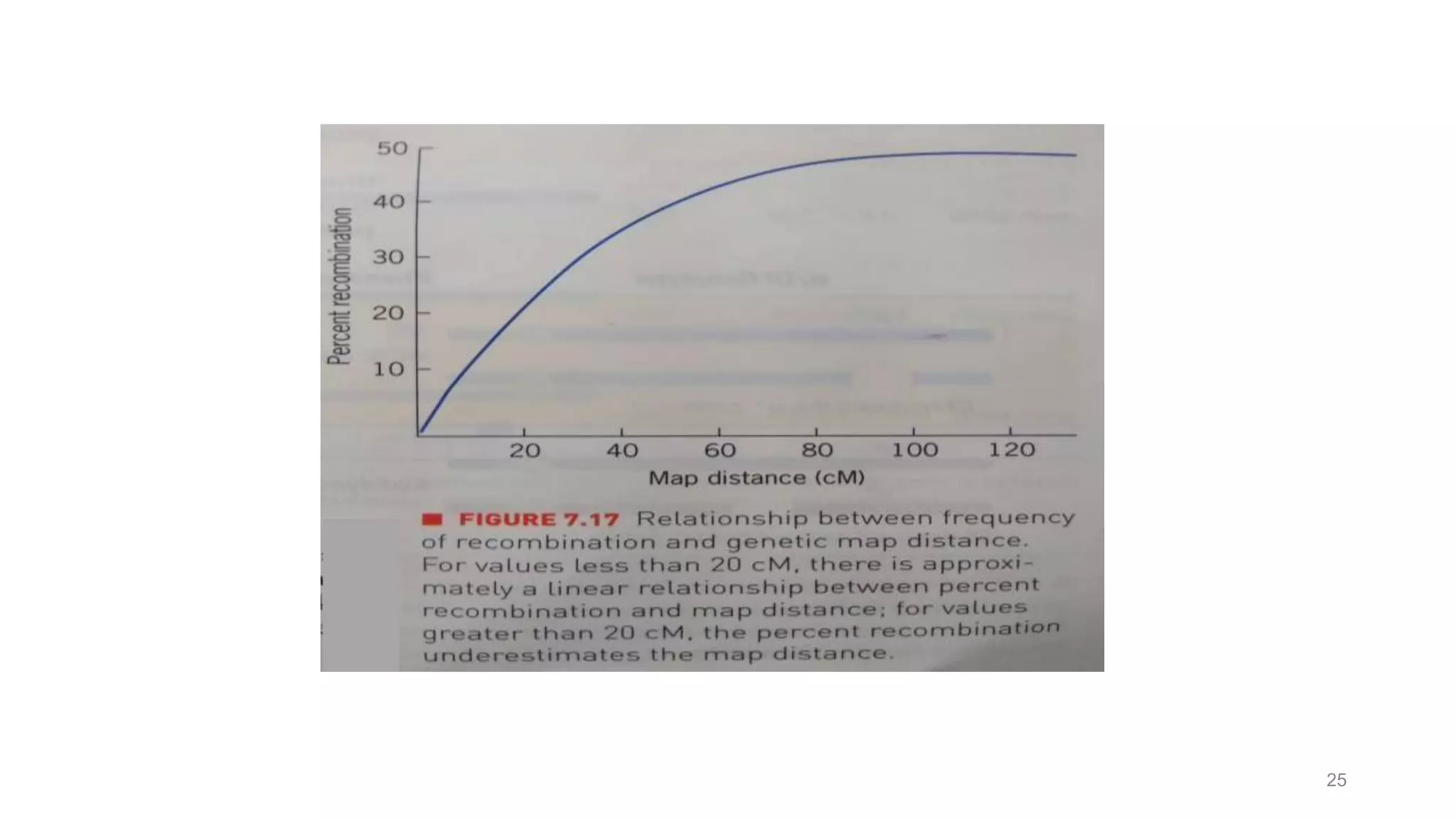
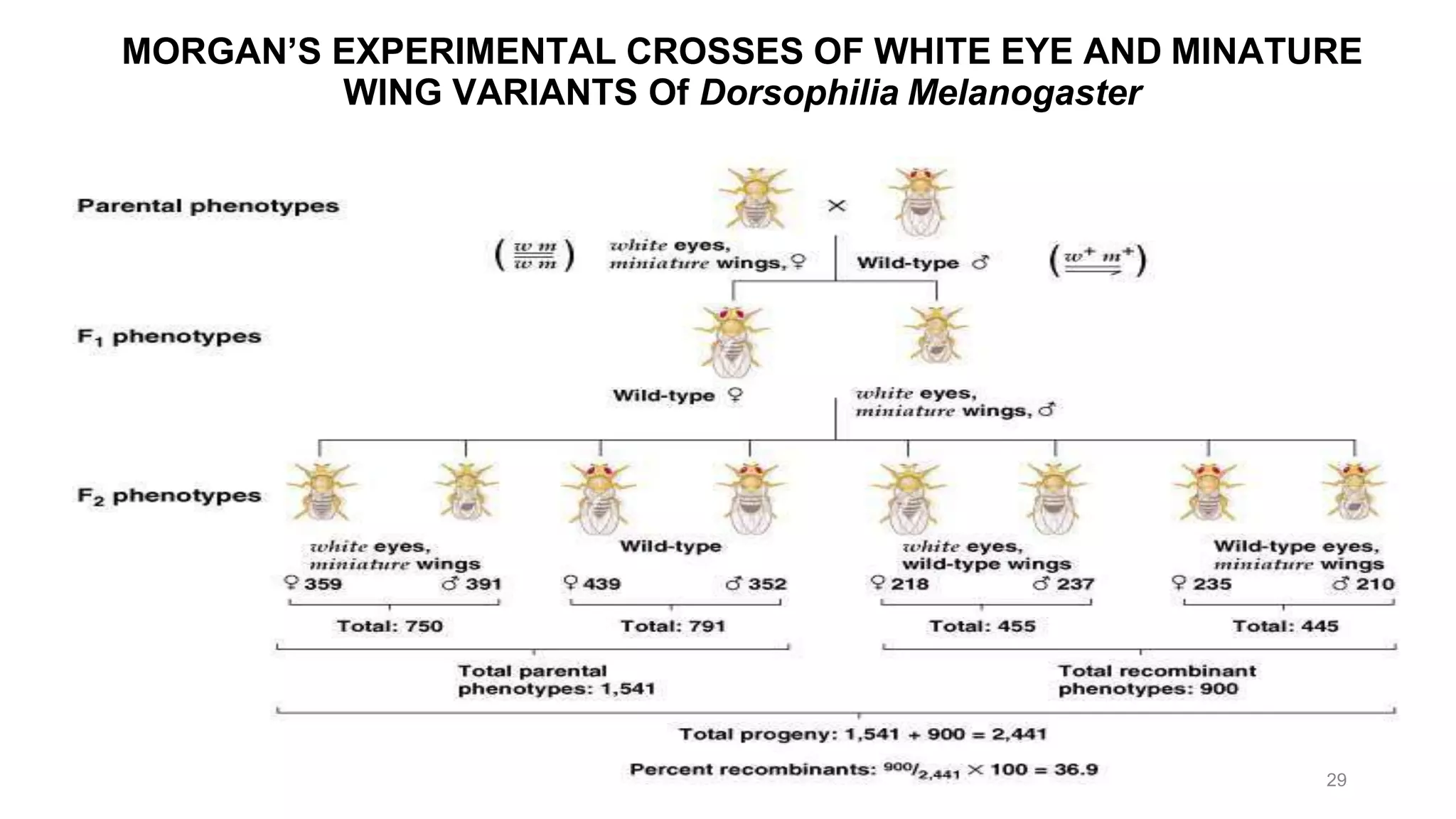
Genetic linkage refers to the tendency of genes that are located physically close together on the same chromosome to be inherited together during meiosis. This occurs because closely linked genes are unlikely to be separated during chromosomal crossover. Genetic linkage was discovered in 1906 by Bateson and Punnett while studying inheritance of flower color and pollen length in peas. They observed offspring ratios that deviated from the expected independent assortment ratio, providing evidence that the genes were linked. Linked genes can sometimes separate through the process of recombination during meiosis, where chromosomes exchange DNA segments through crossover. The frequency of recombination between two genes is used to estimate the distance between them on the chromosome map.