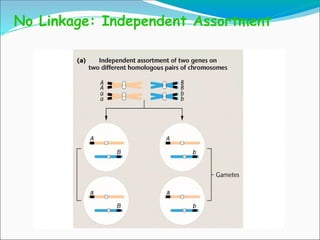
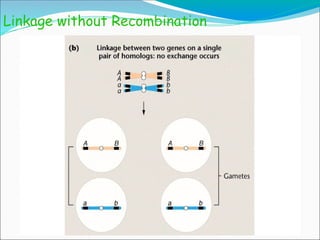
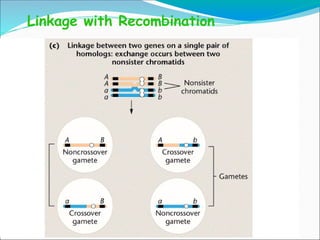
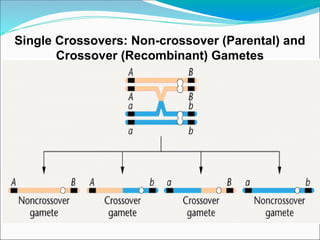
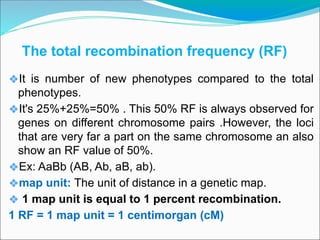
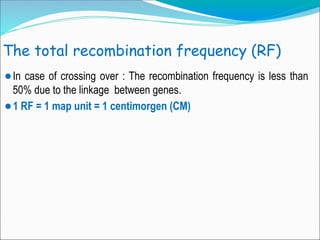
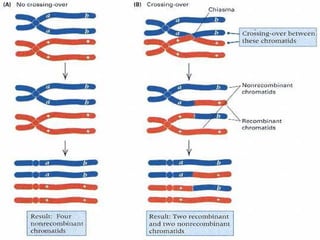
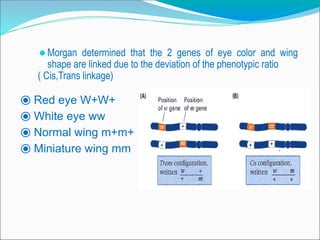
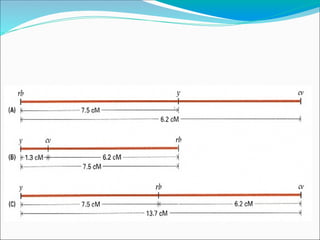
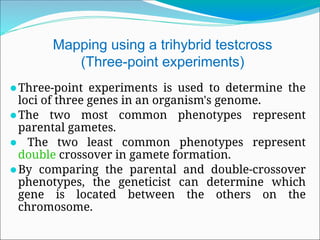
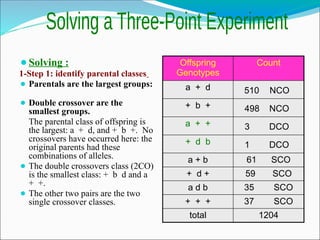
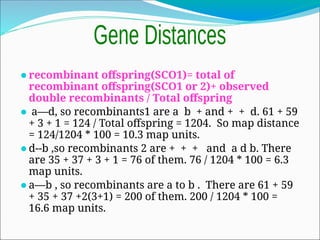
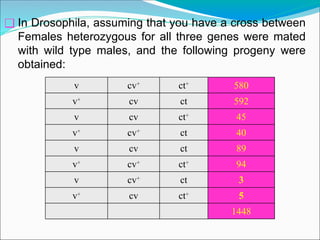
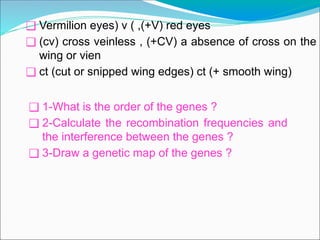
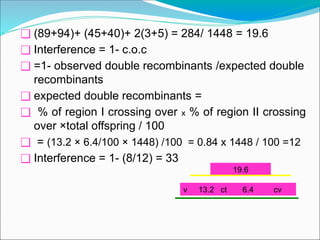
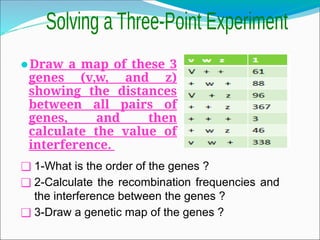
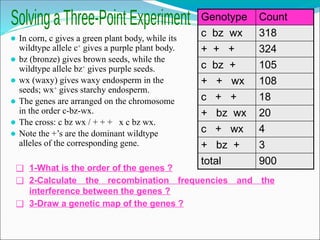
The document discusses recombination processes in meiosis, namely independent assortment and crossing over, and explains Mendel's law of independent assortment with examples. It covers genetic linkage, types of linkage (cis and trans), recombination frequency, genetic mapping, and includes methods for calculating distances between genes on chromosomes. It also outlines steps for conducting three-point experiments and calculating interference in genetic mapping.