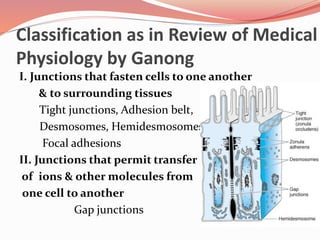
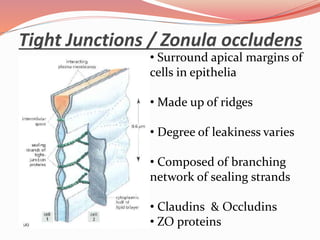
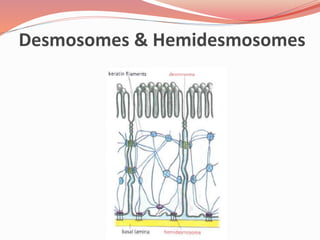
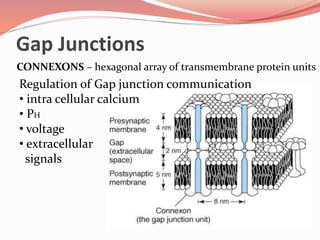
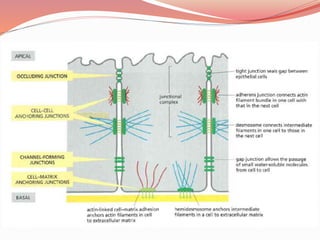
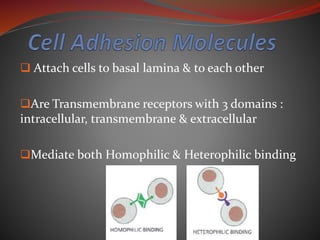
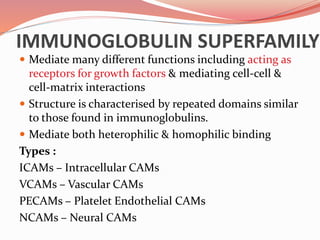
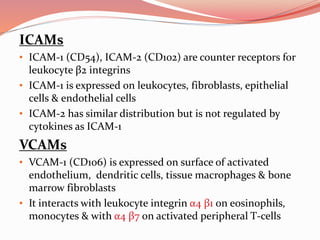
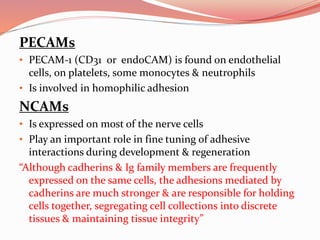
Cell junctions are specialized contact sites that hold cells together and attach cells to the extracellular matrix. They are classified into three main groups: tight junctions, gap junctions, and adherens junctions. Tight junctions form continuous seals around cells to control permeability and prevent diffusion between cells. Gap junctions allow small molecules and ions to pass directly between cells to facilitate cell-cell communication. Adherens junctions, such as desmosomes and hemidesmosomes, anchor cells to other cells or the extracellular matrix. Cell adhesion molecules like cadherins, integrins, and immunoglobulin superfamily proteins mediate cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion through homophilic or heterophilic binding interactions.