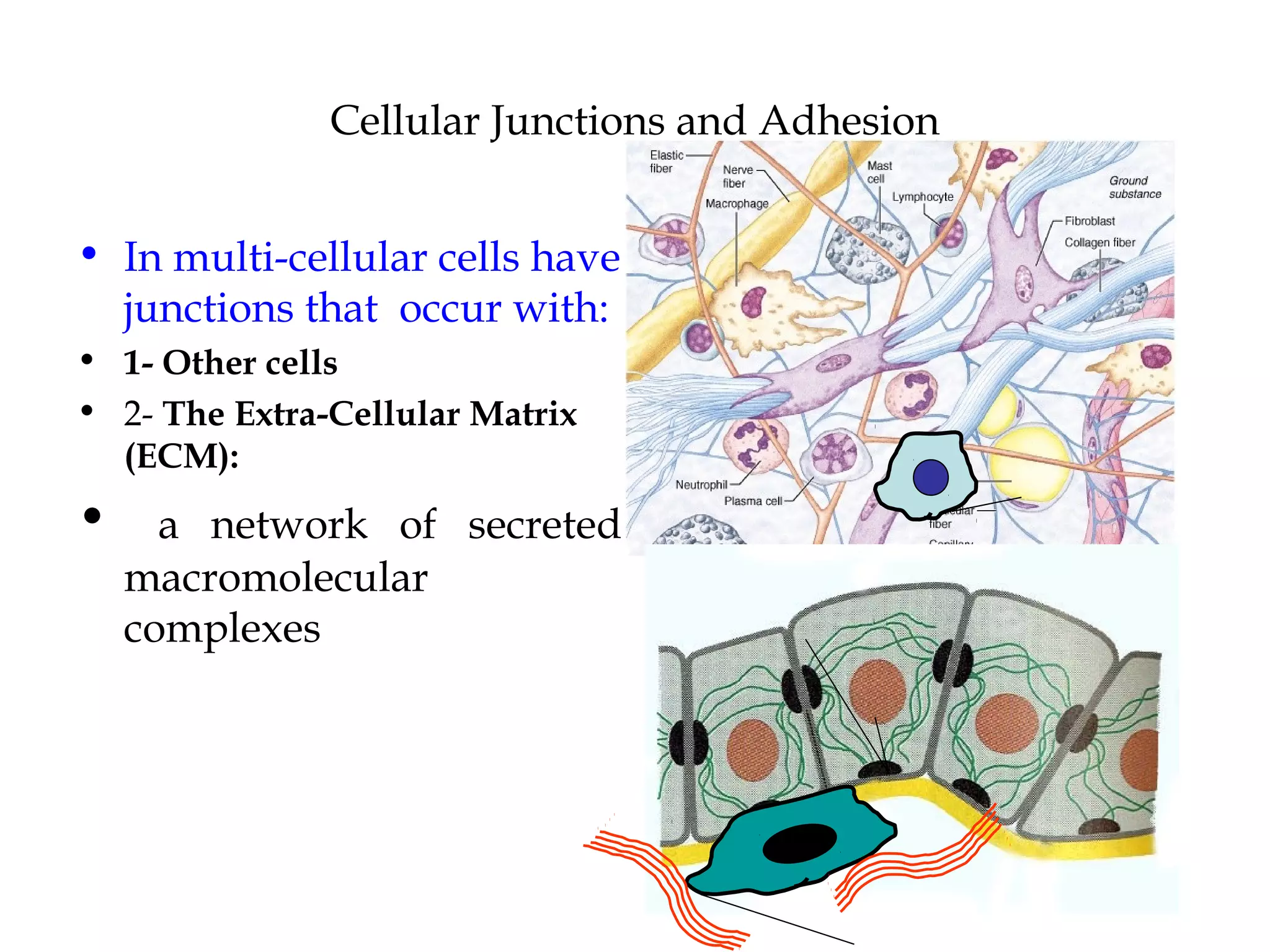
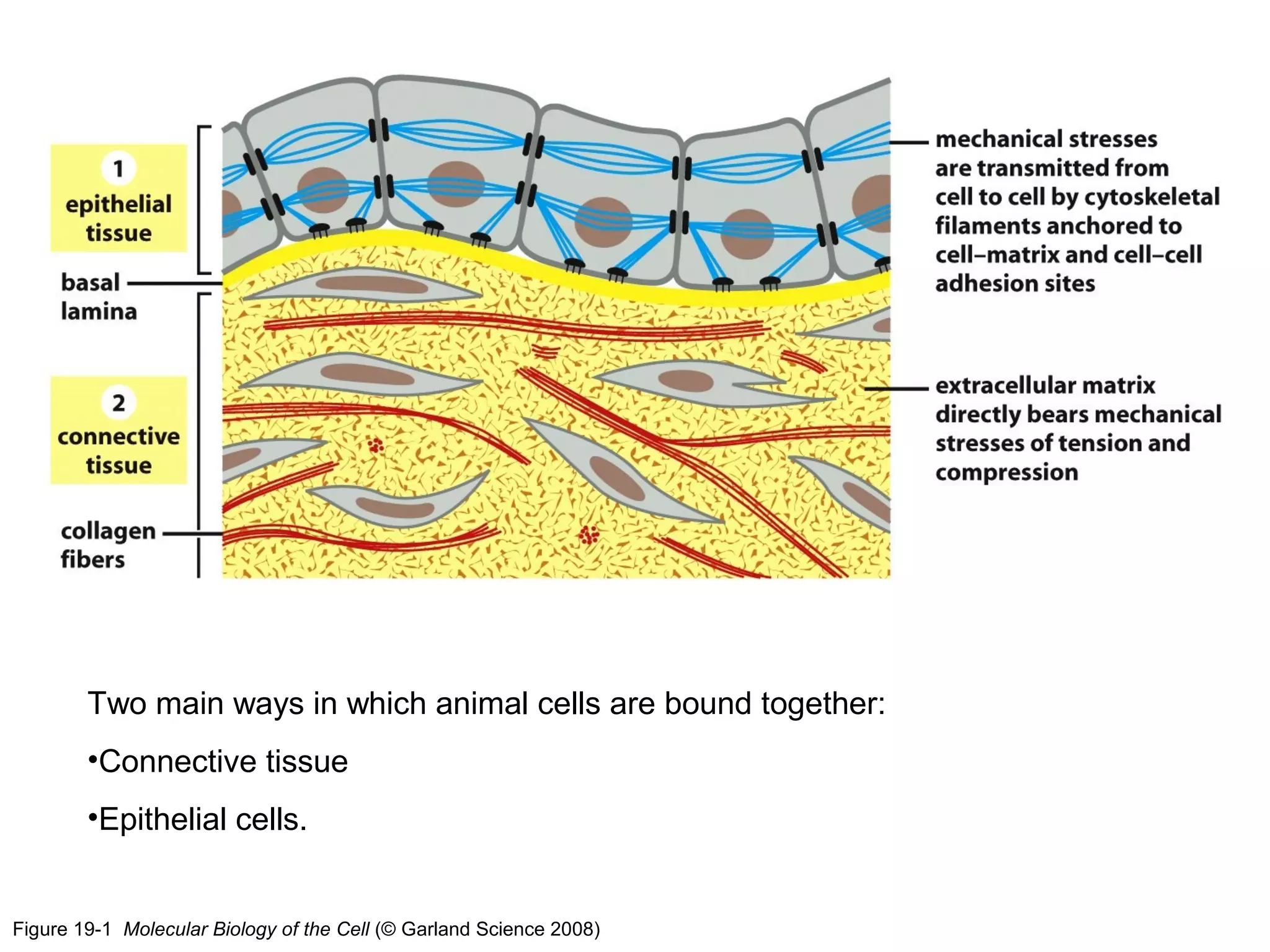
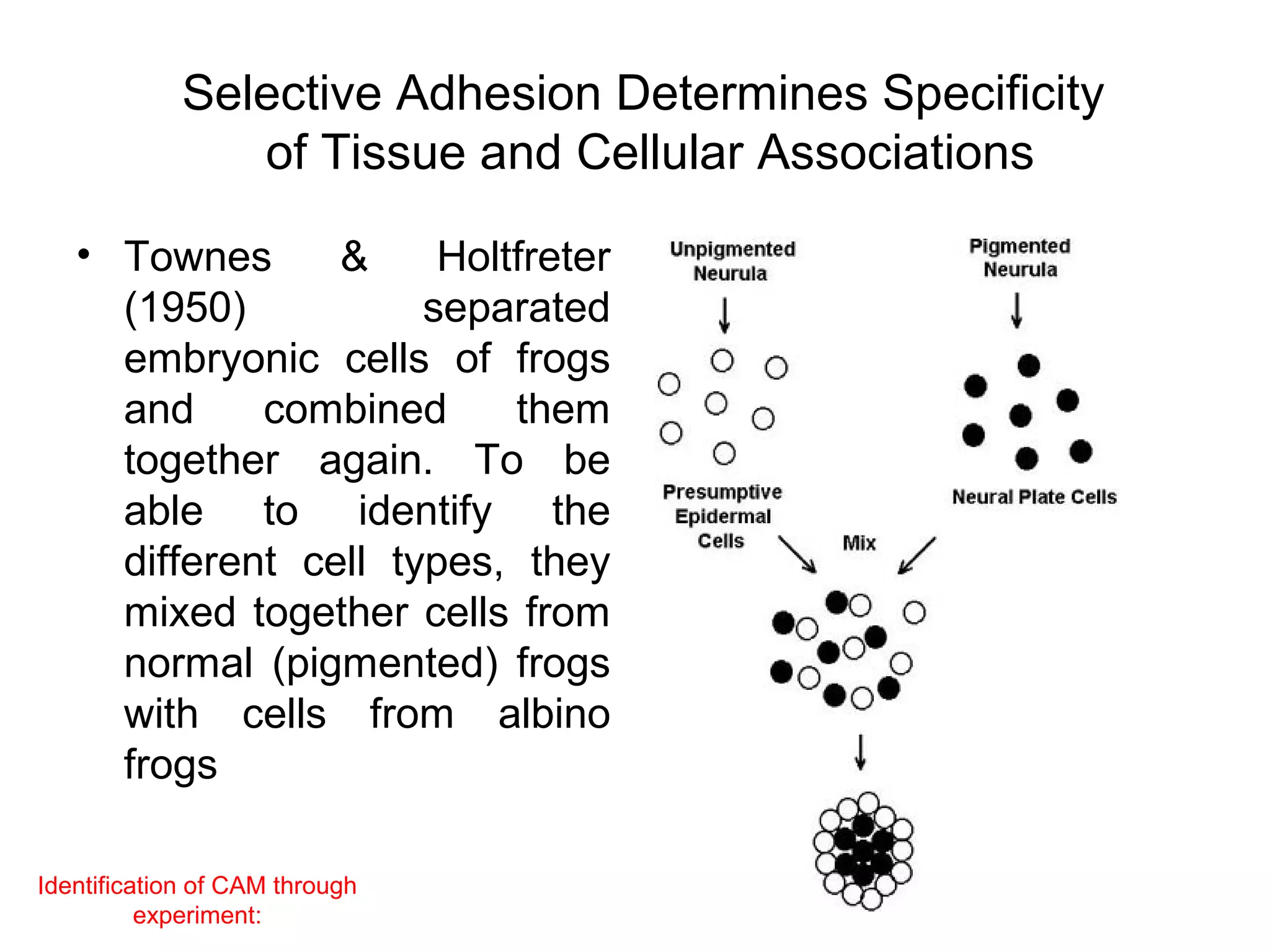
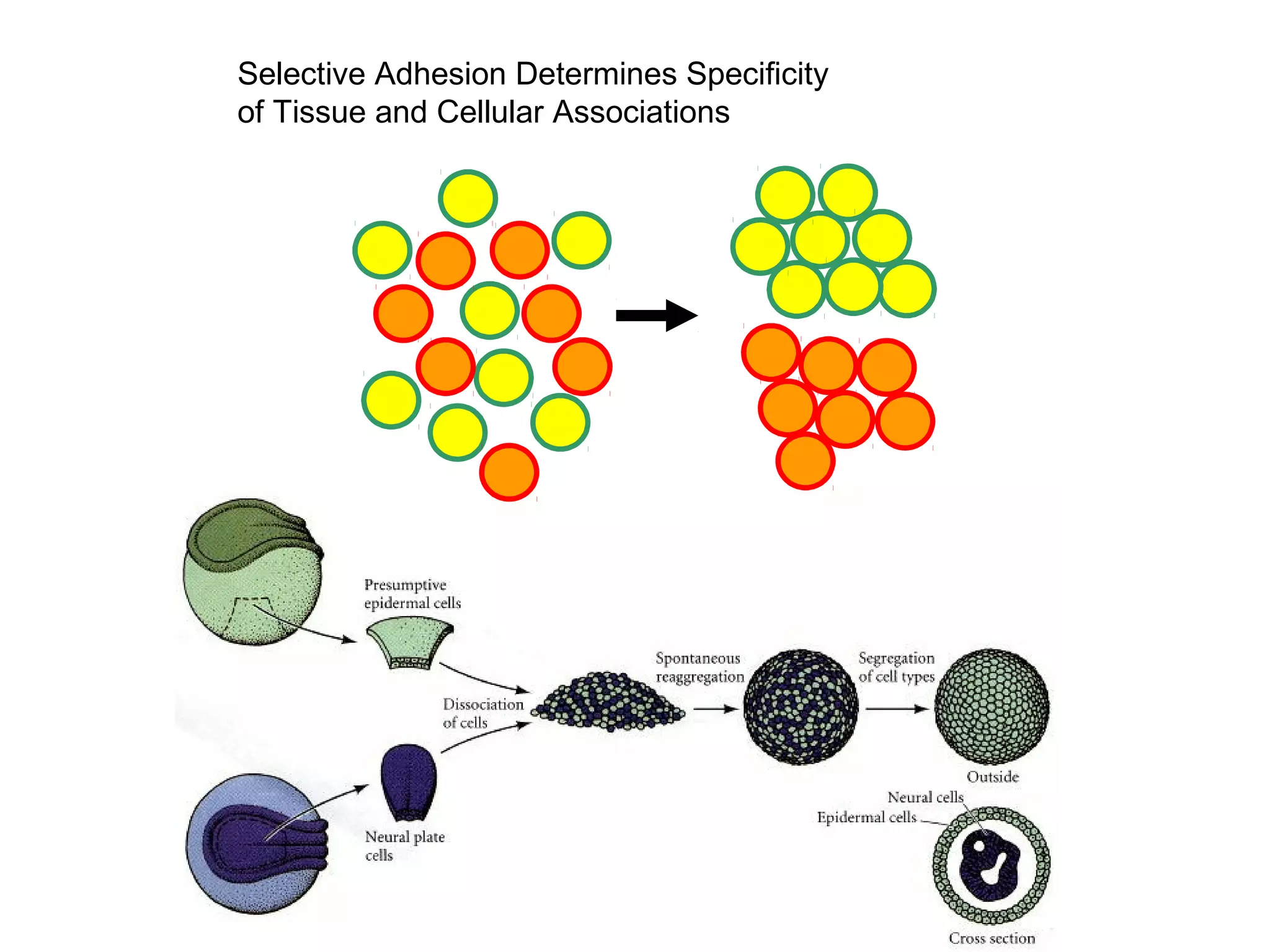
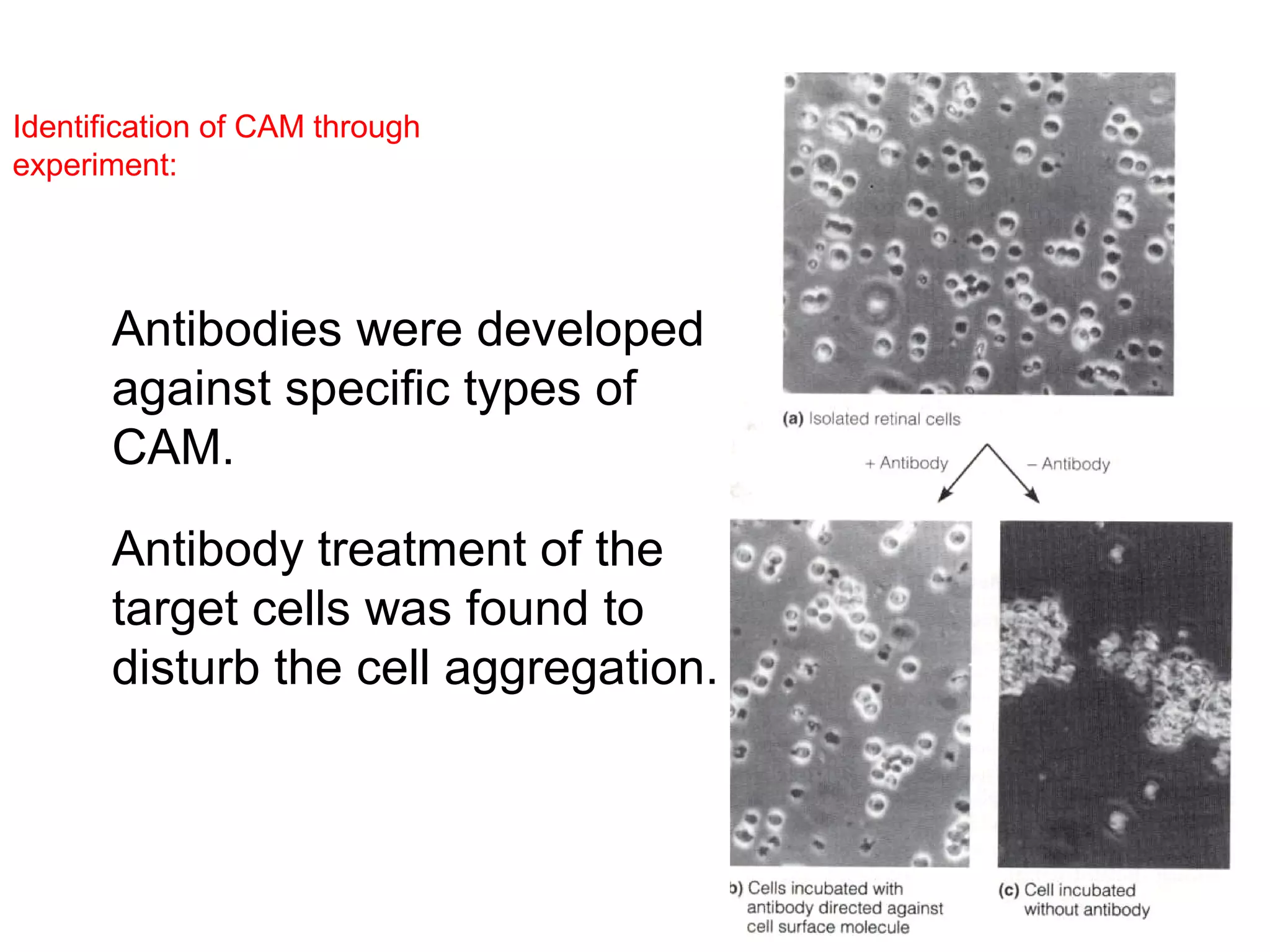
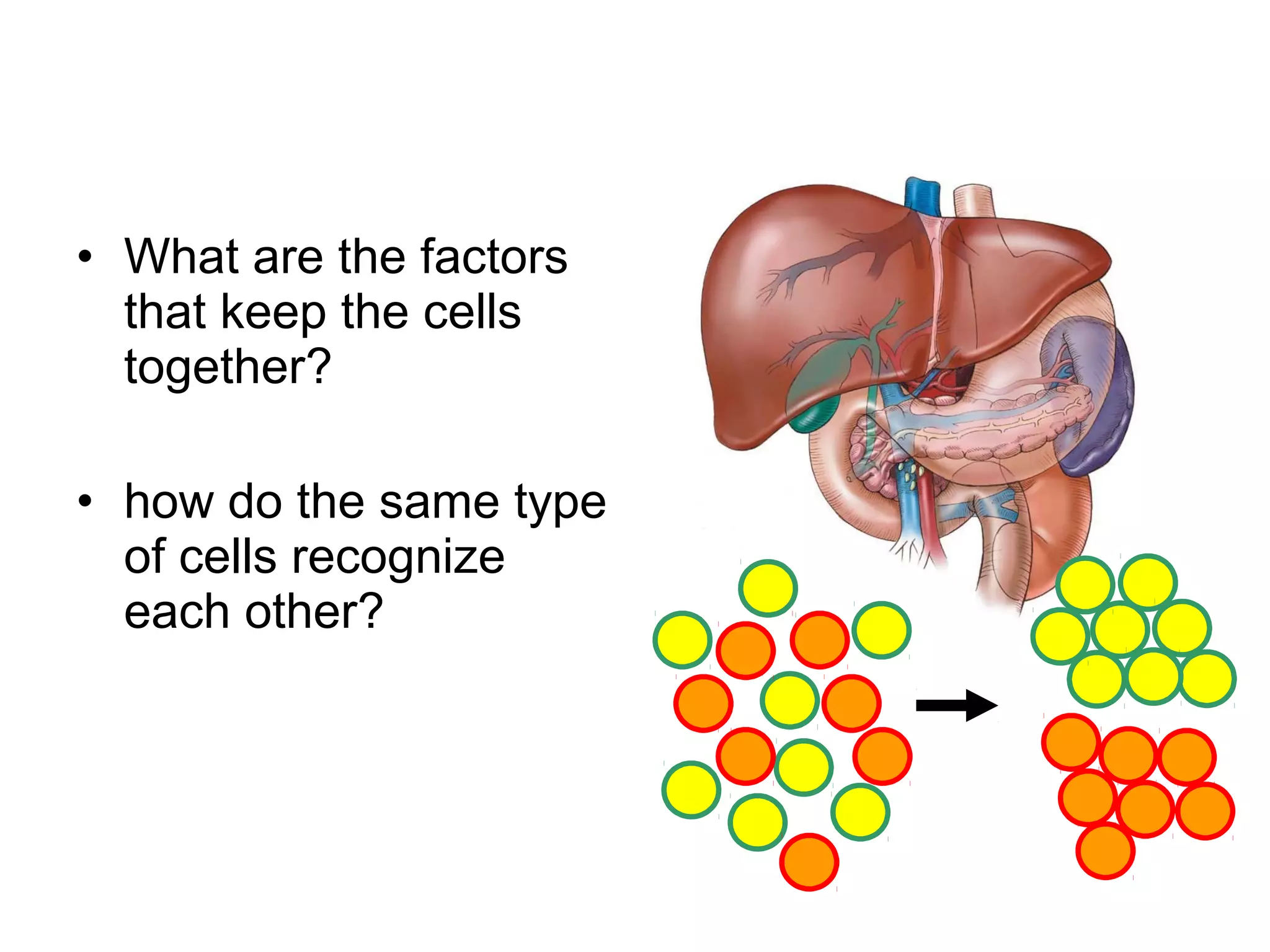
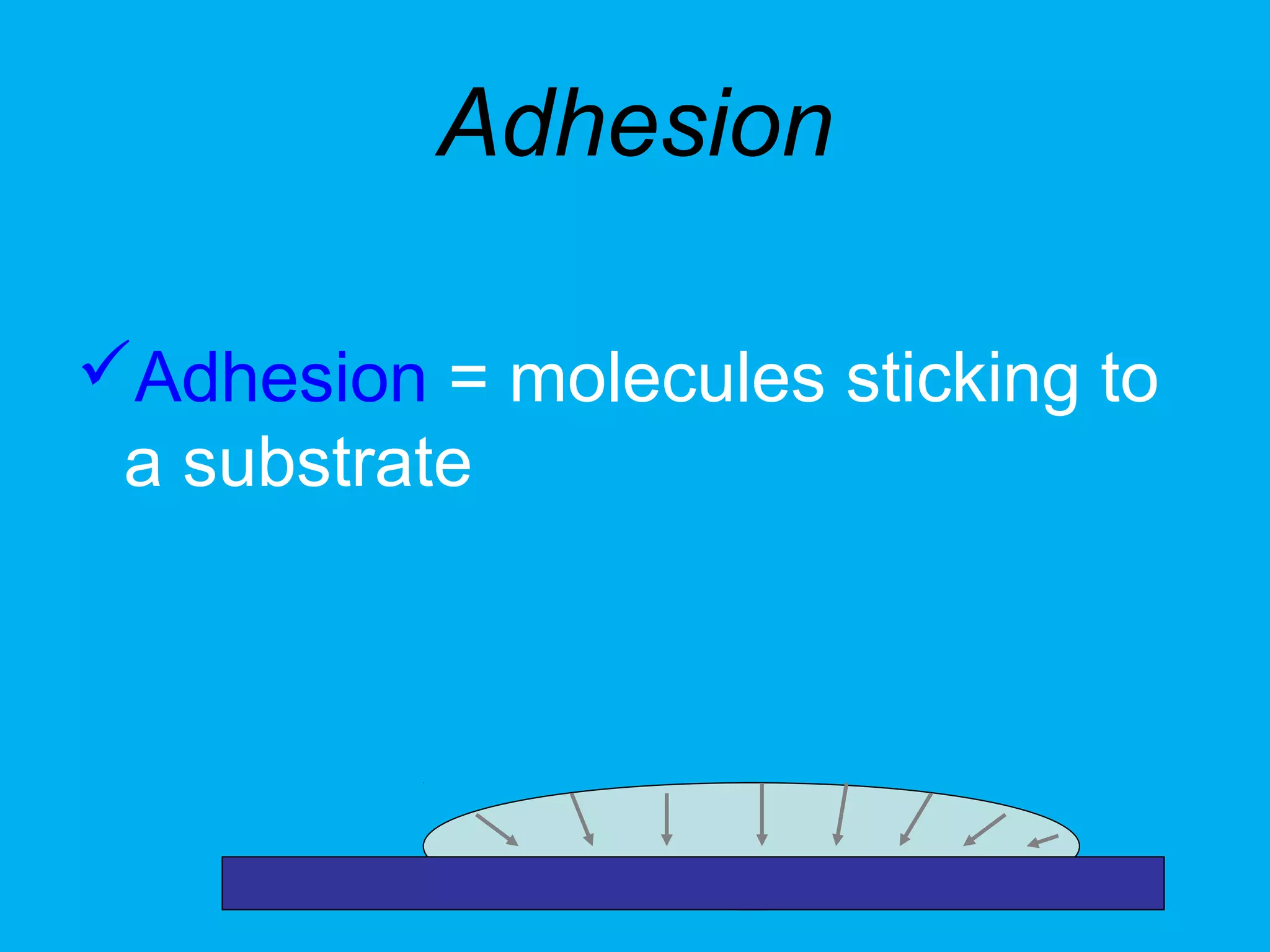
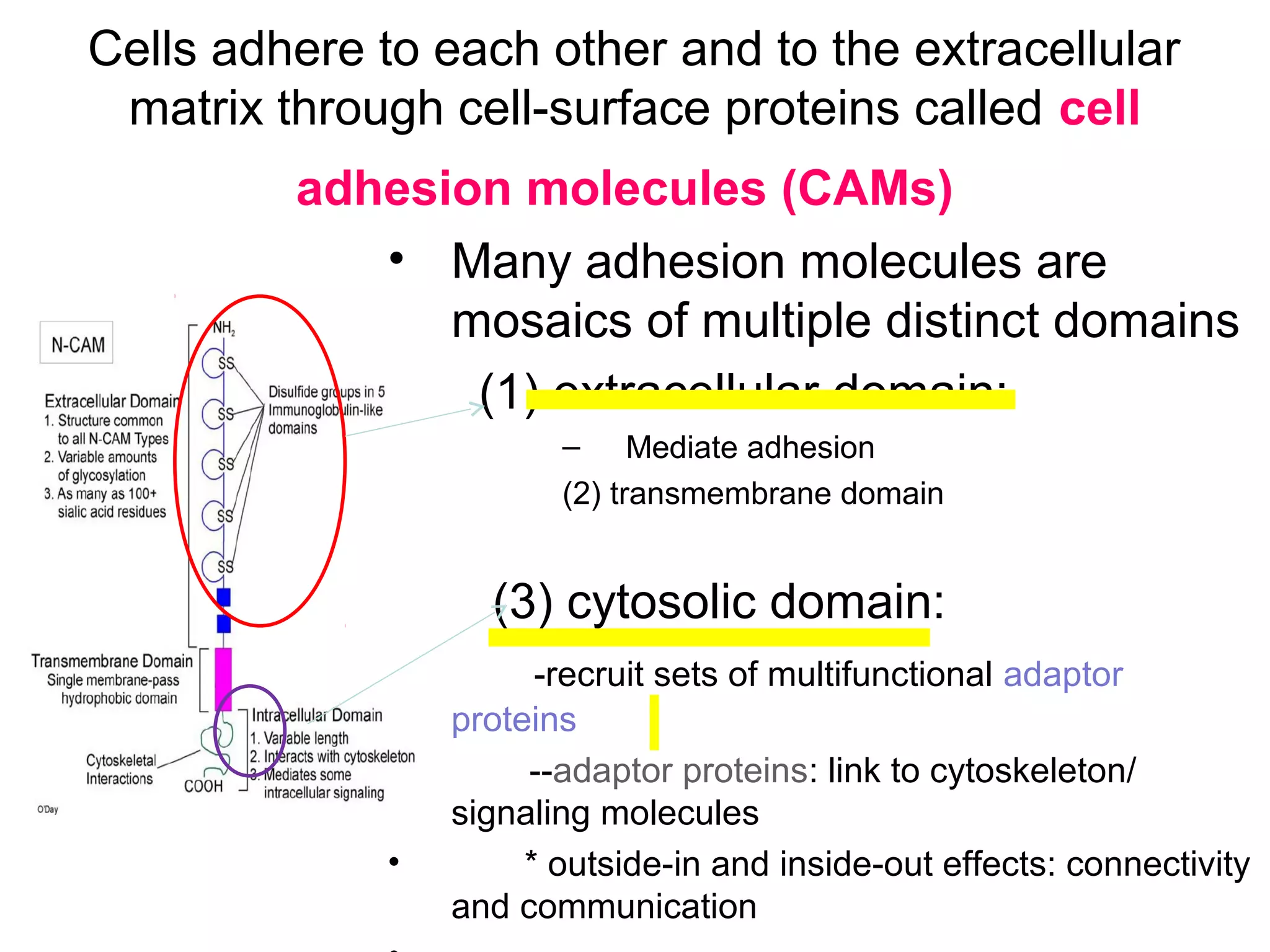
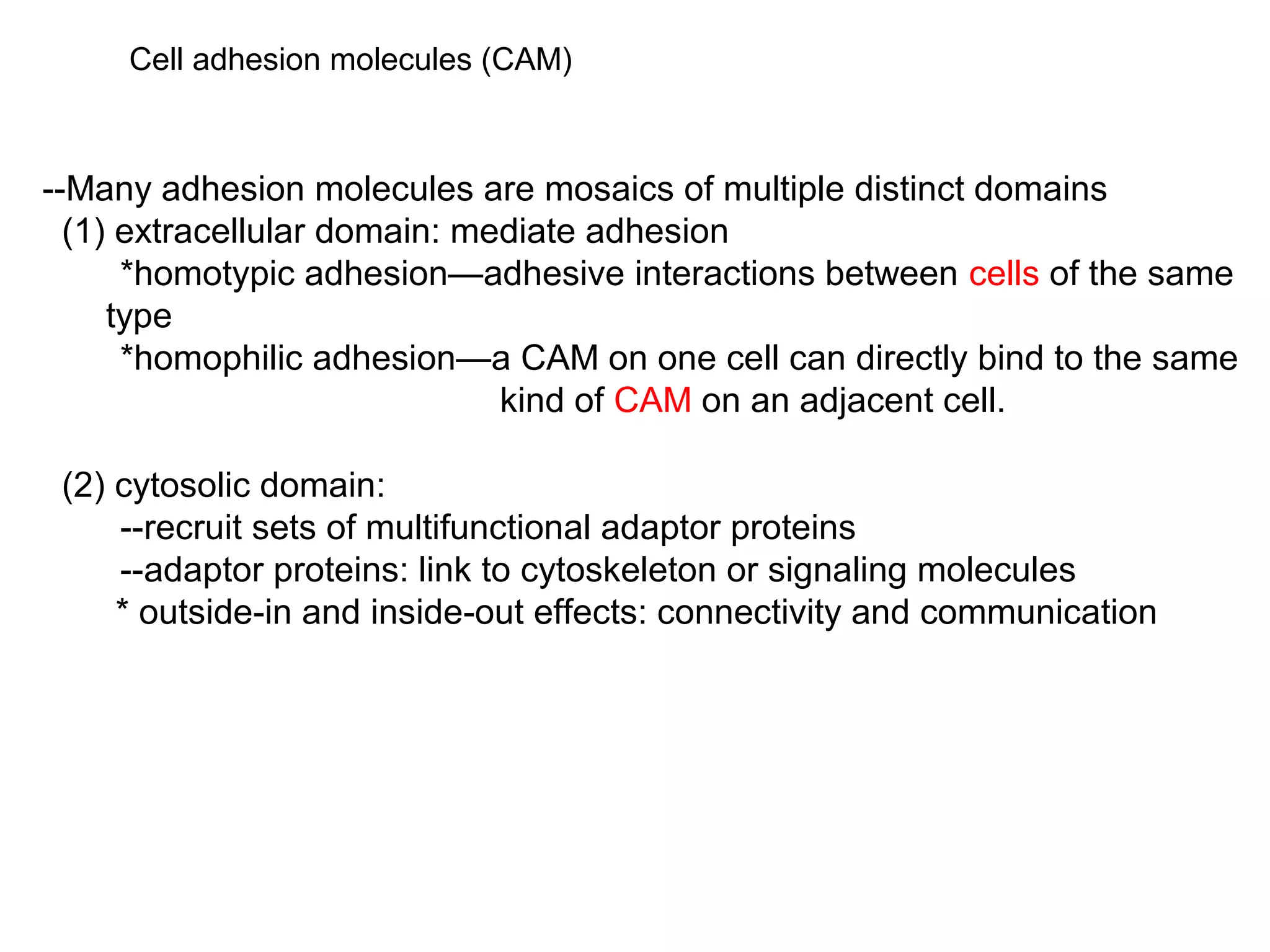
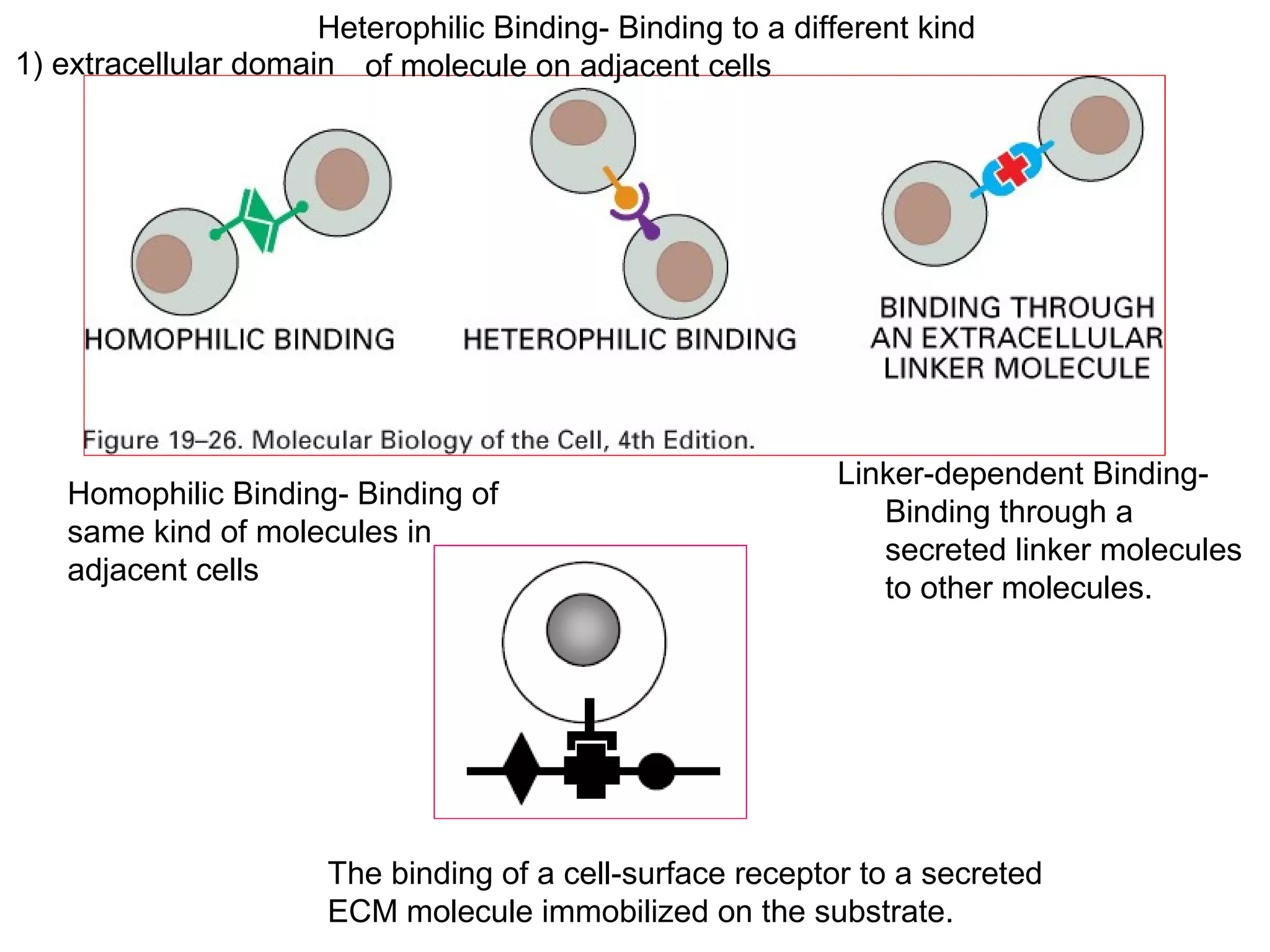
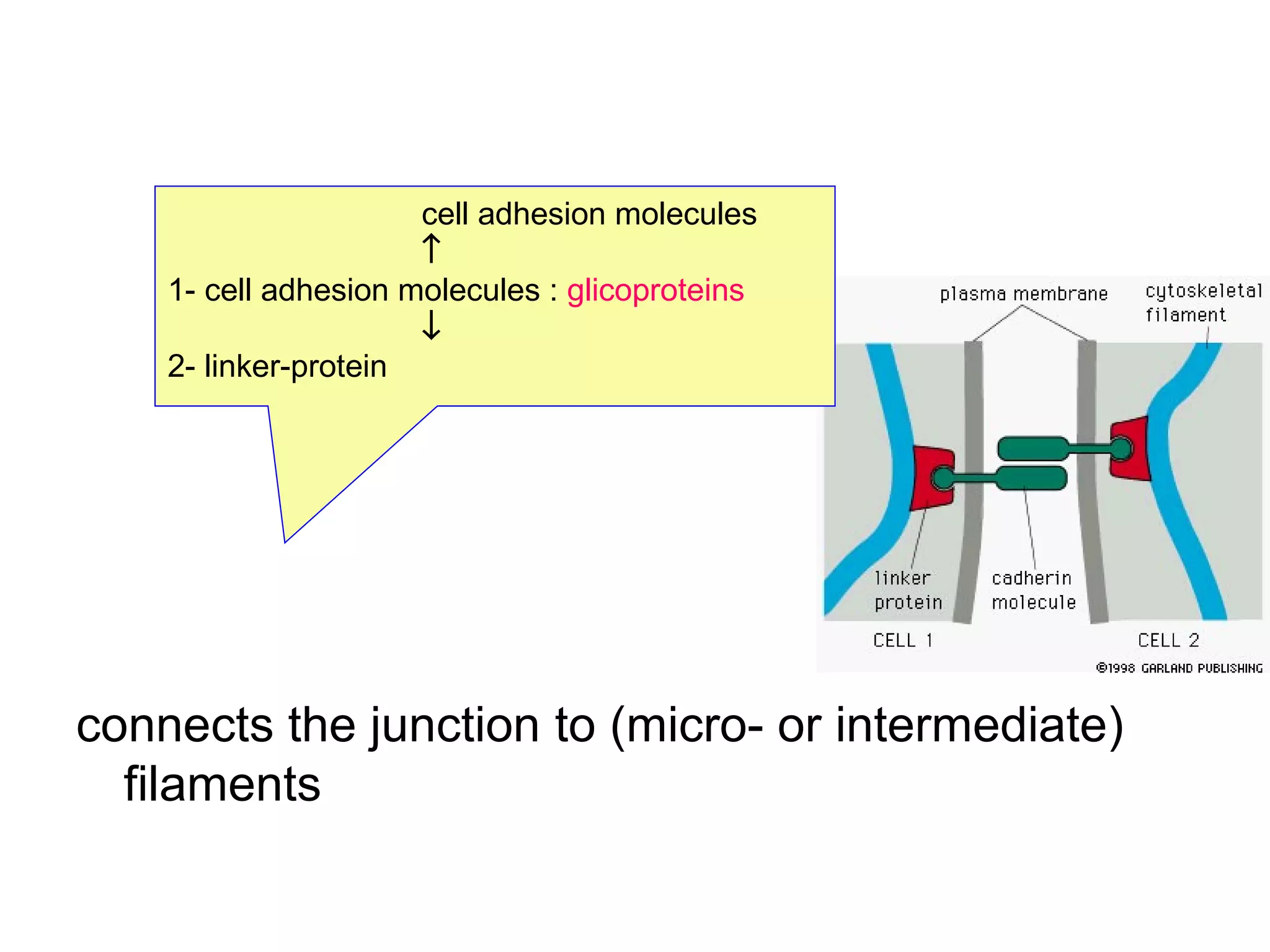
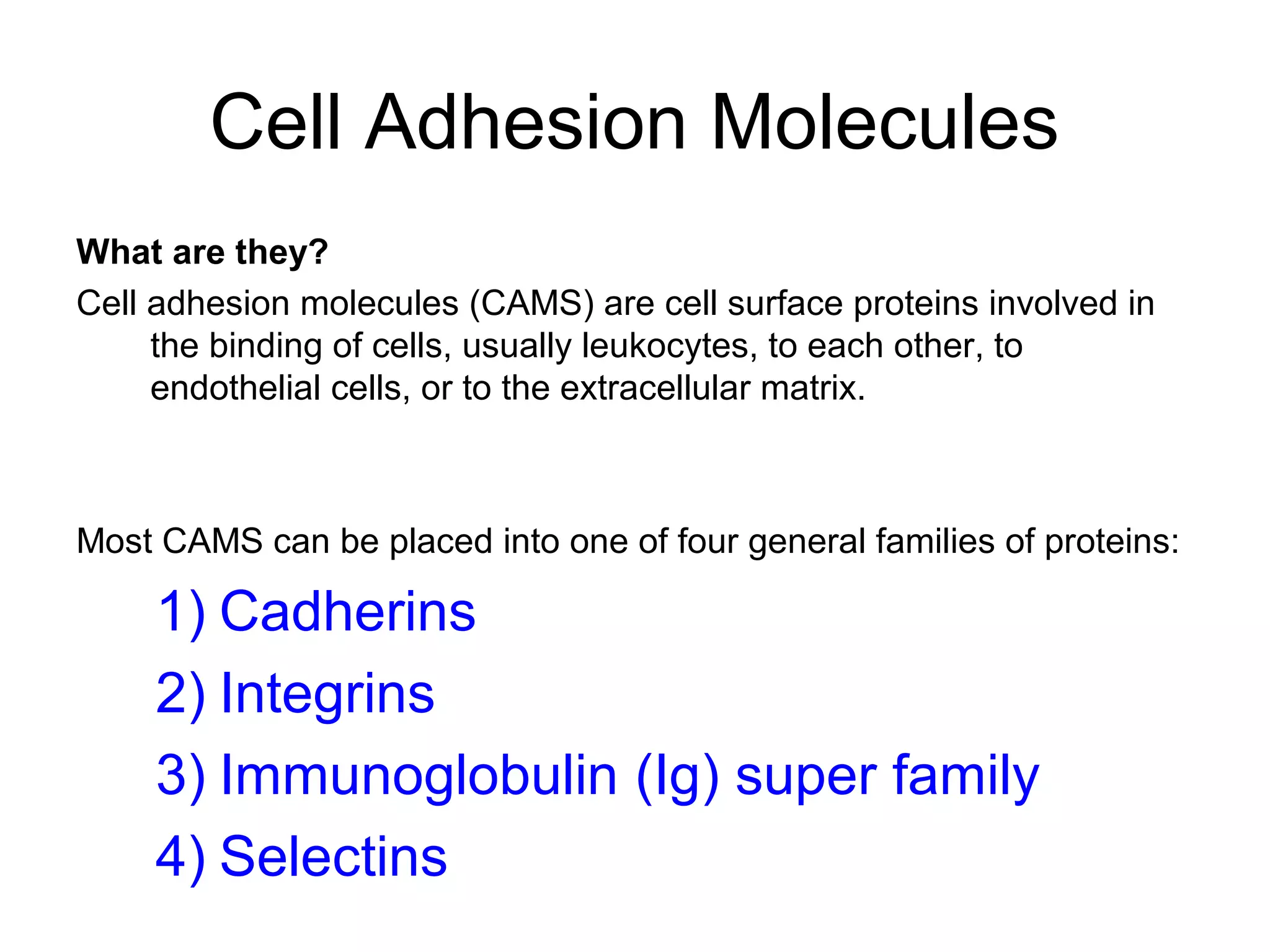
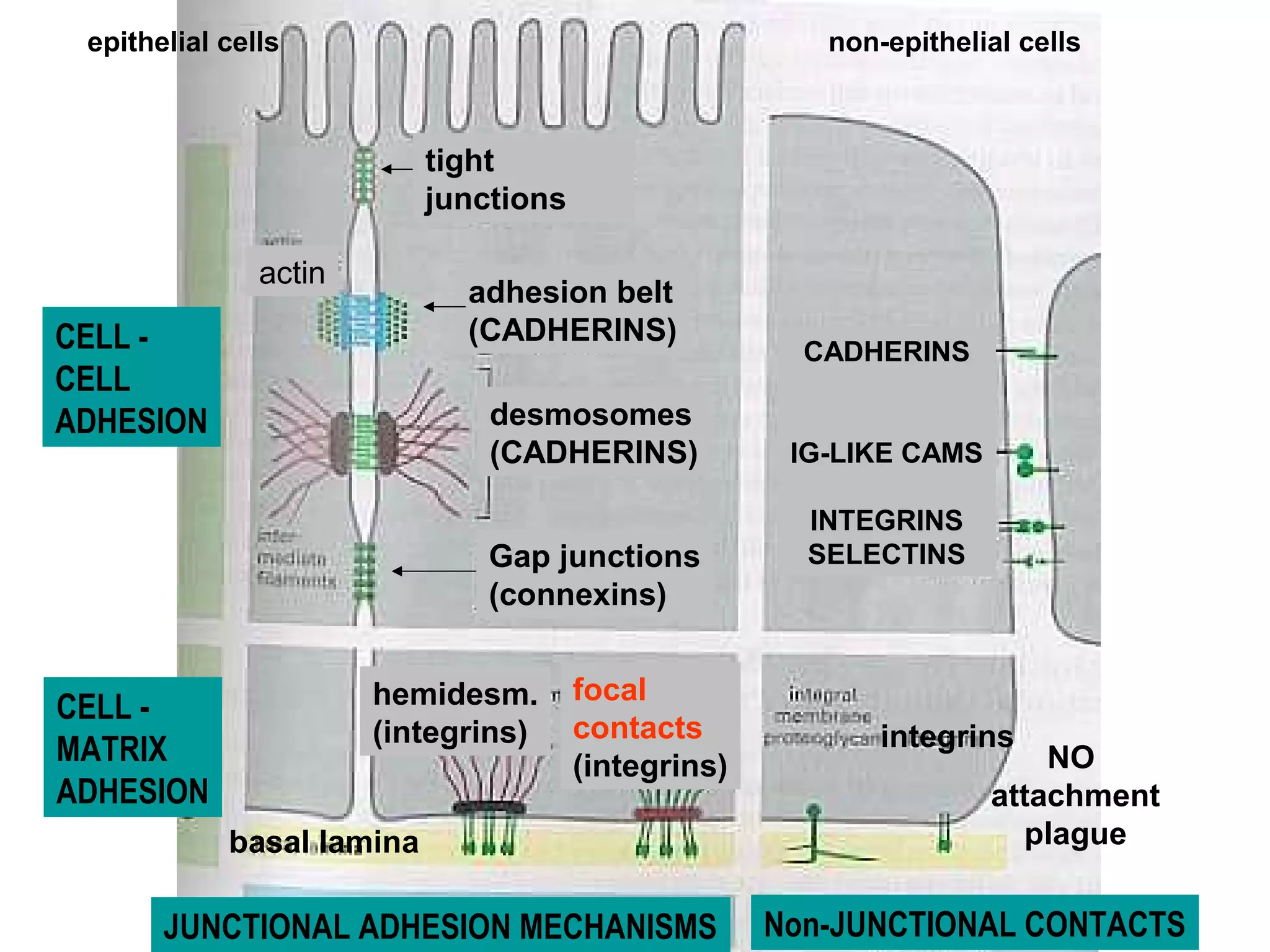
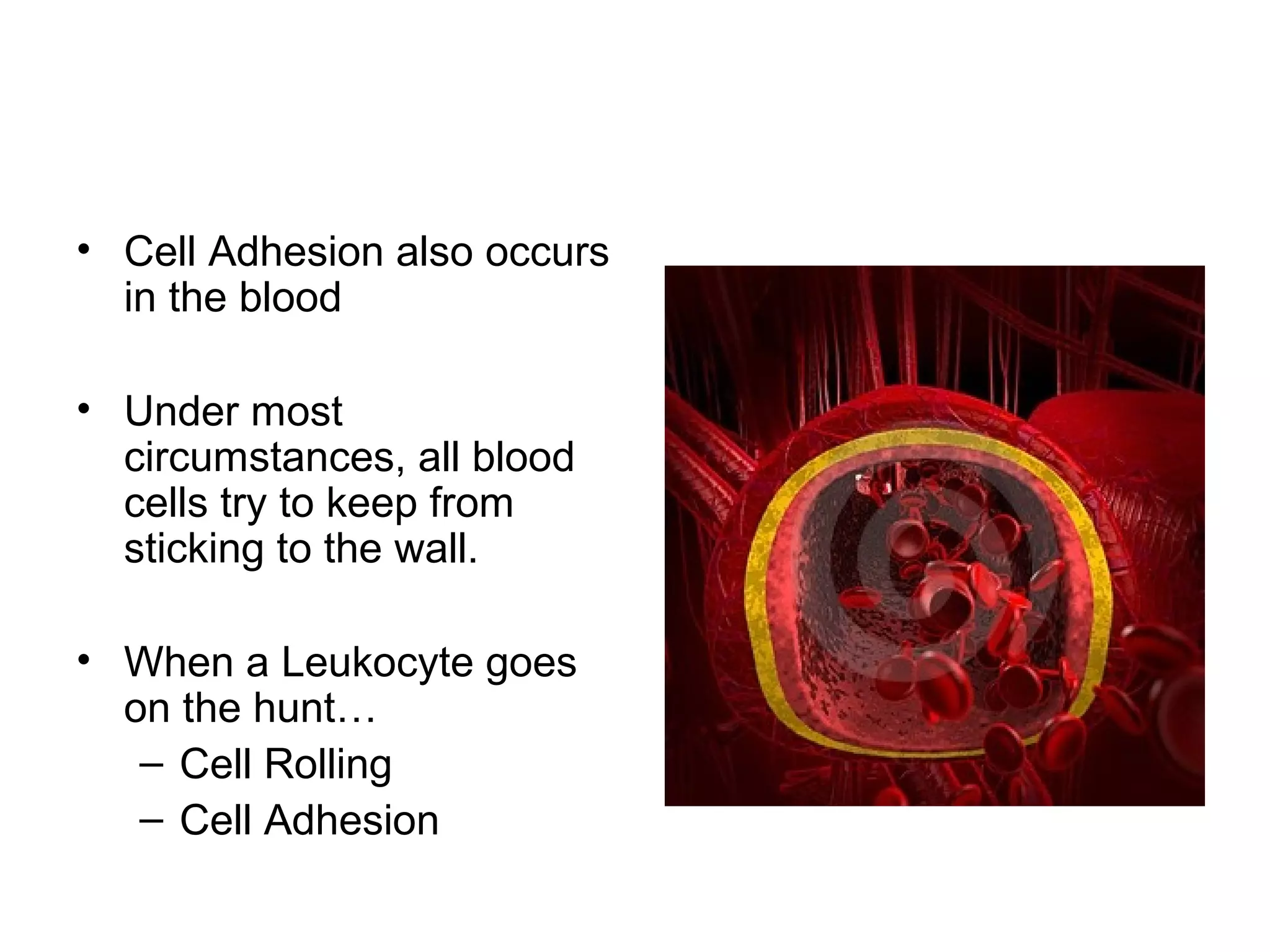
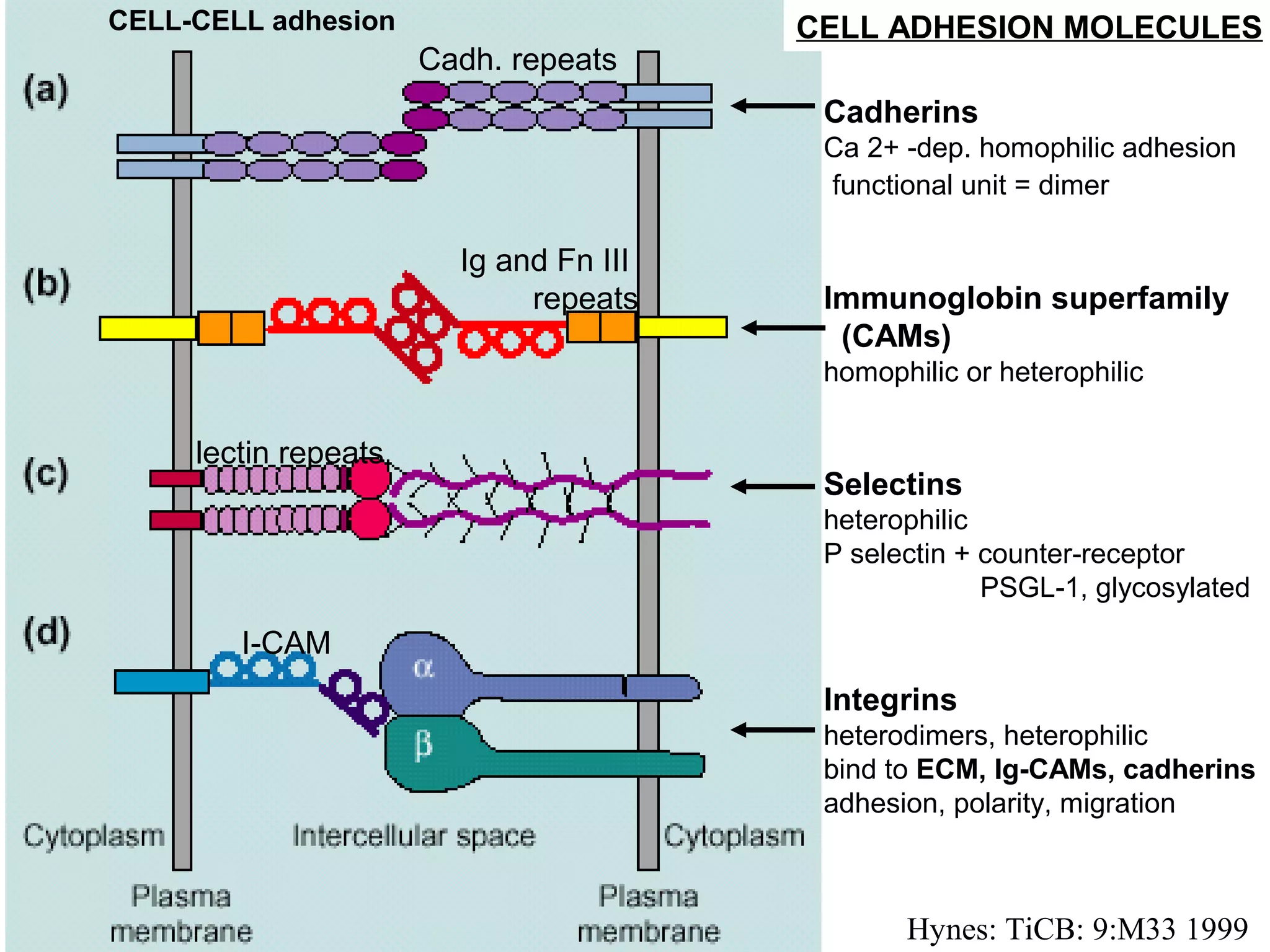
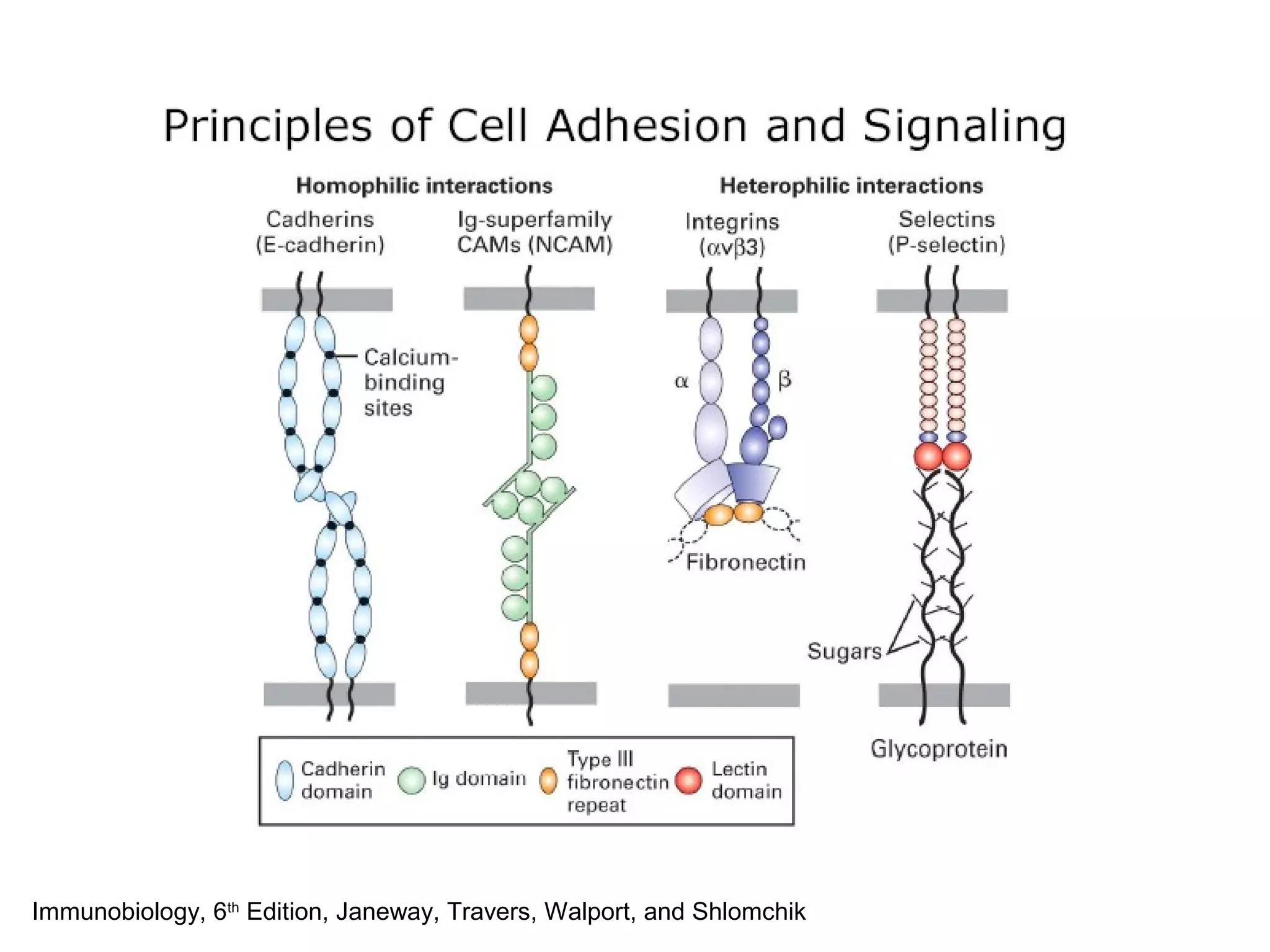
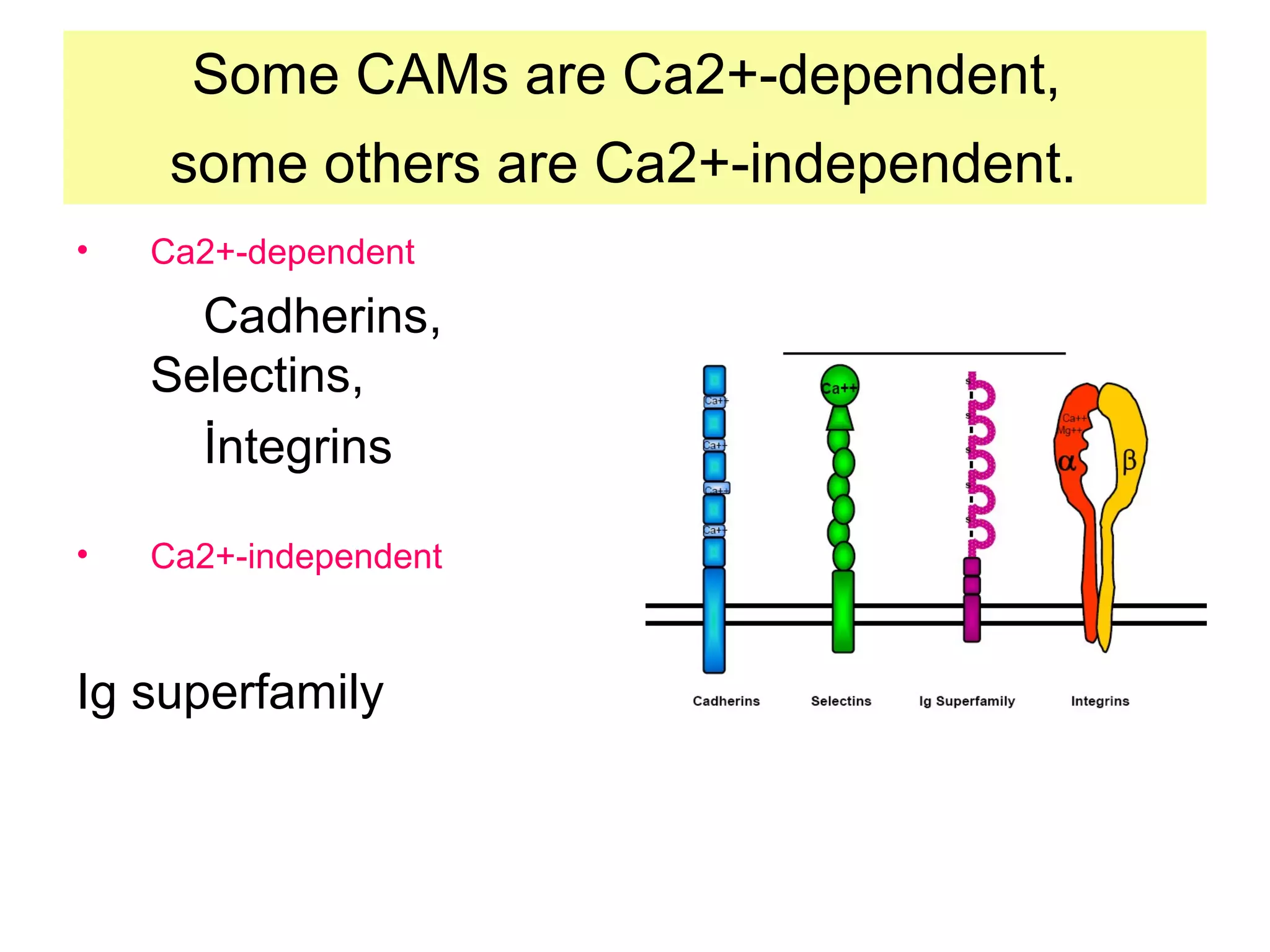
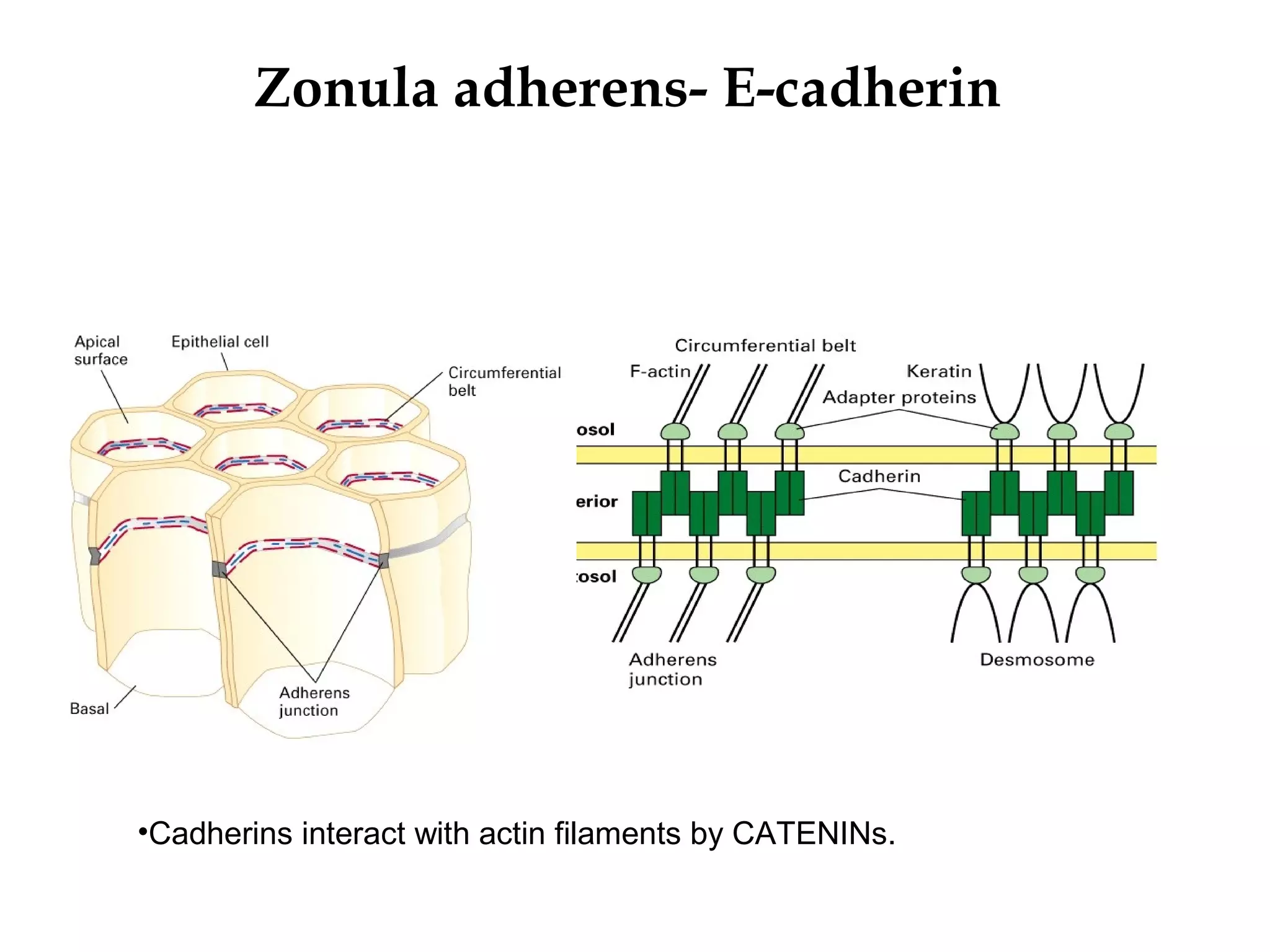
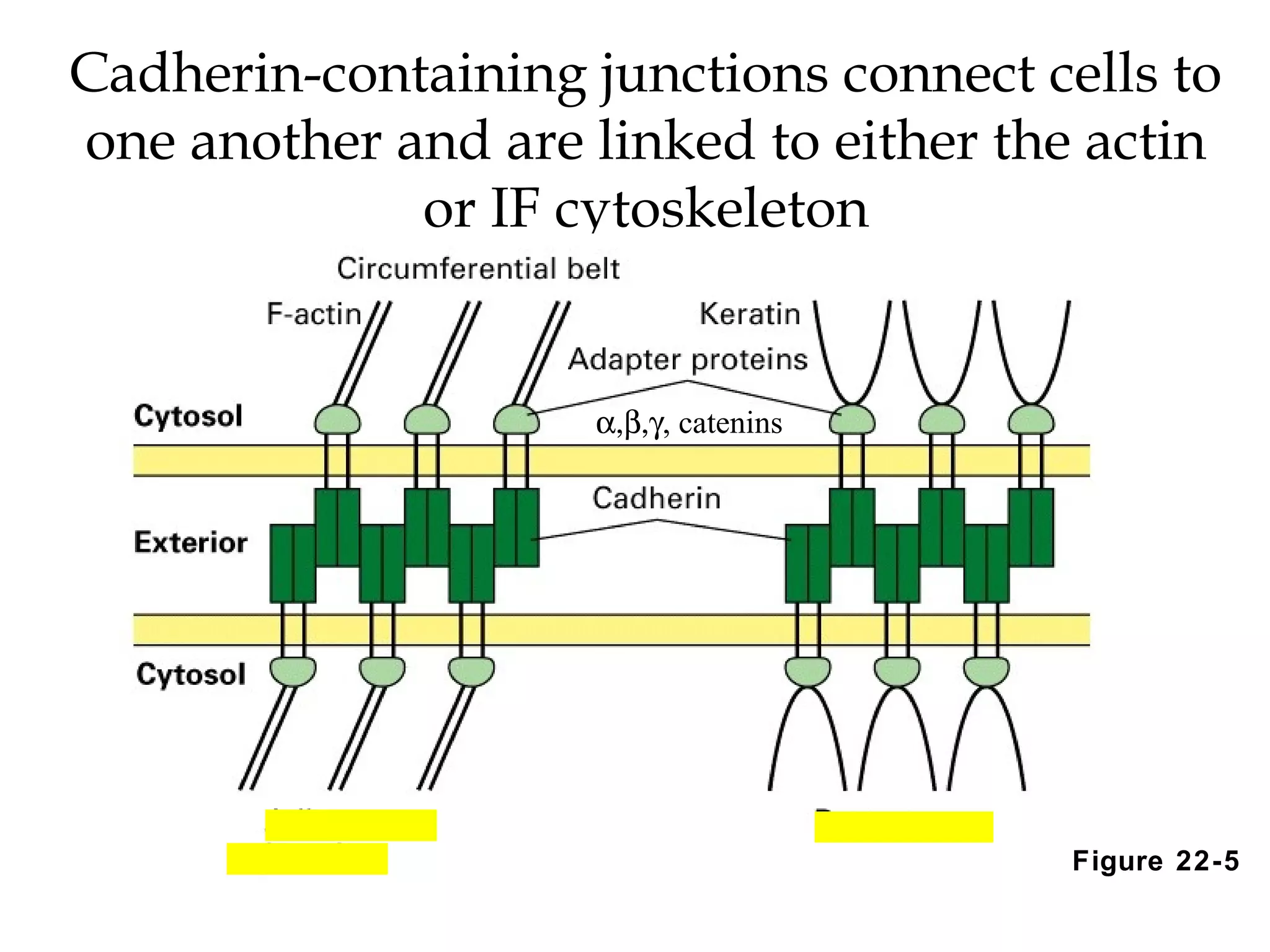
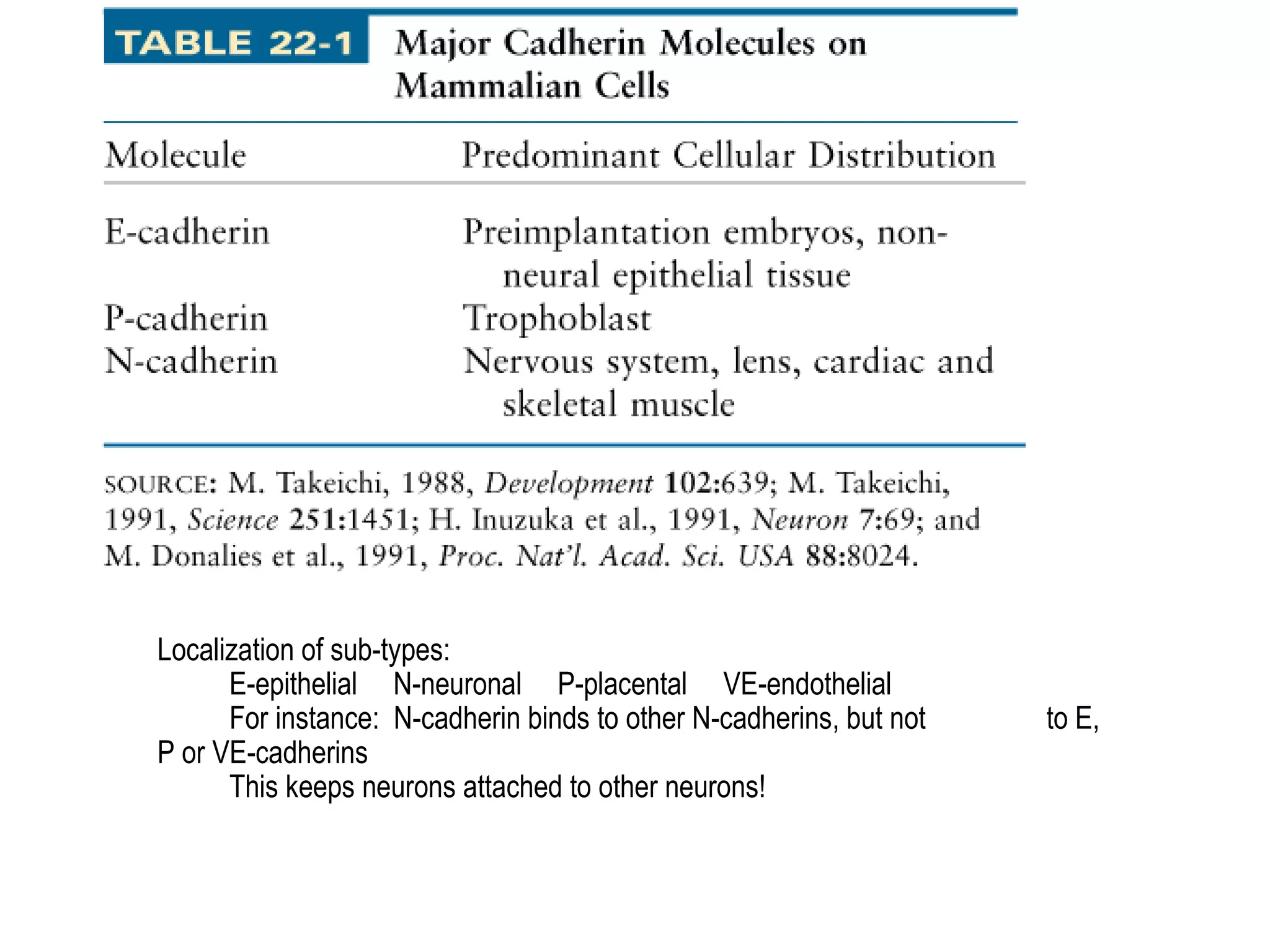
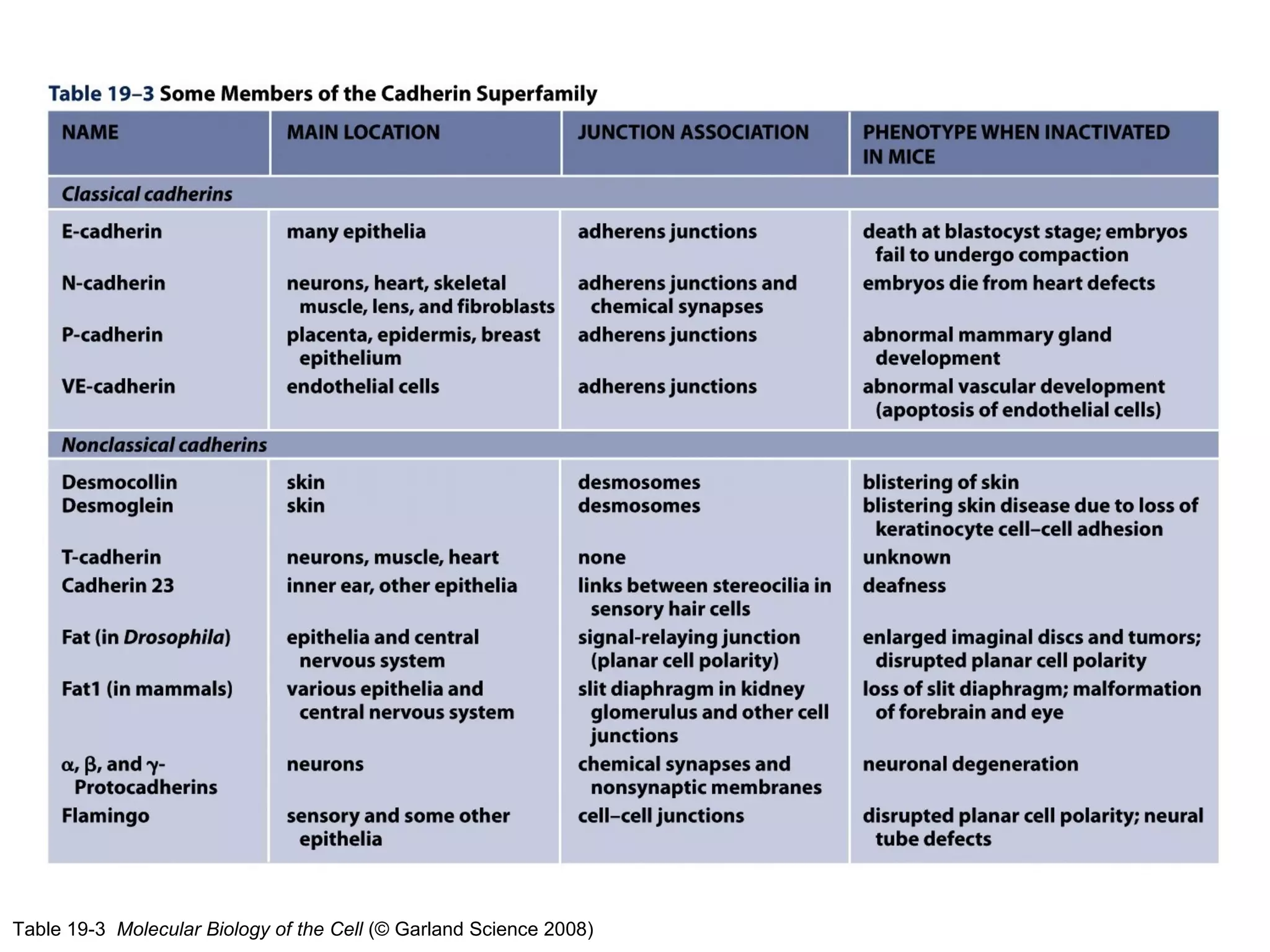
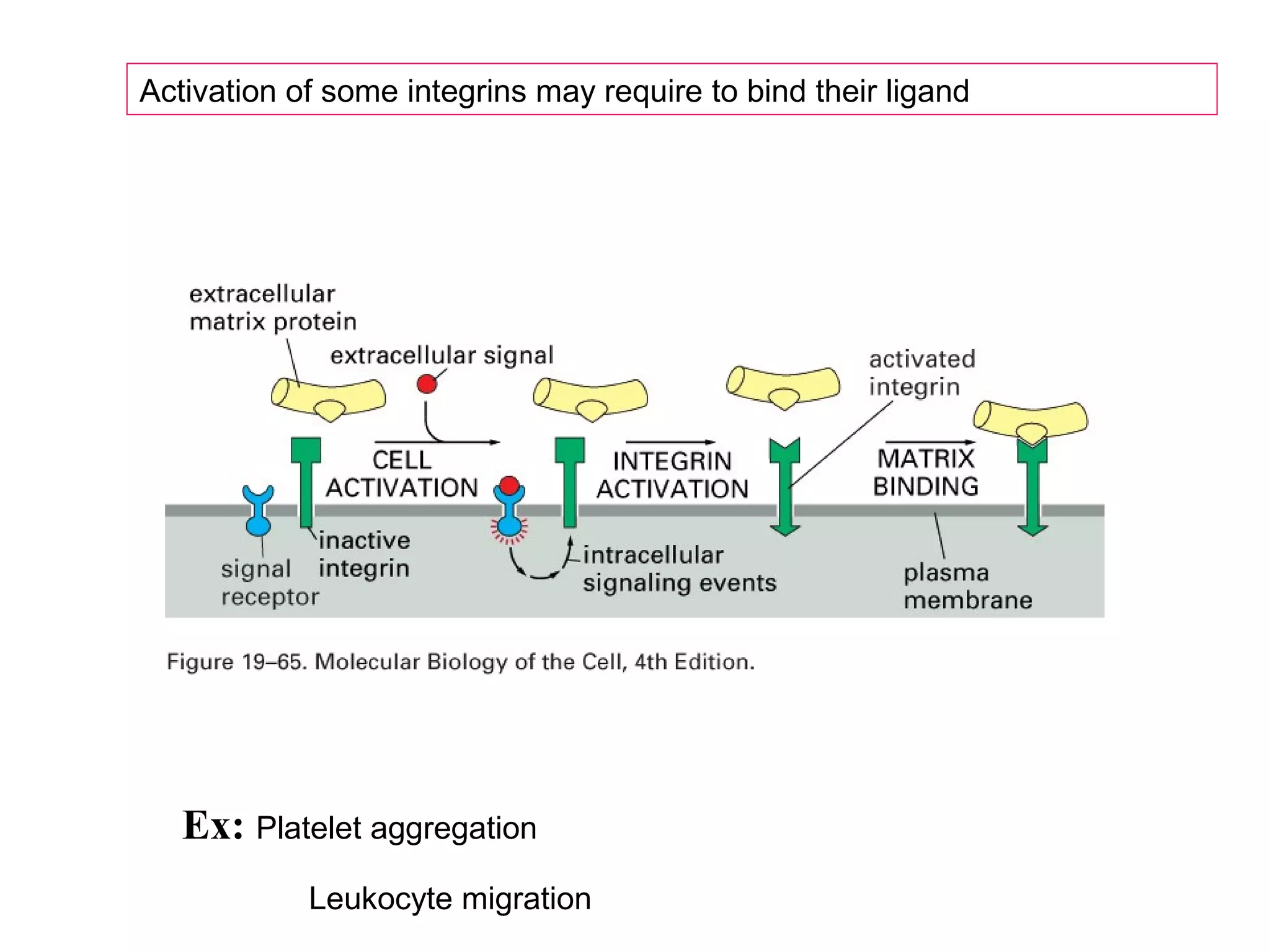
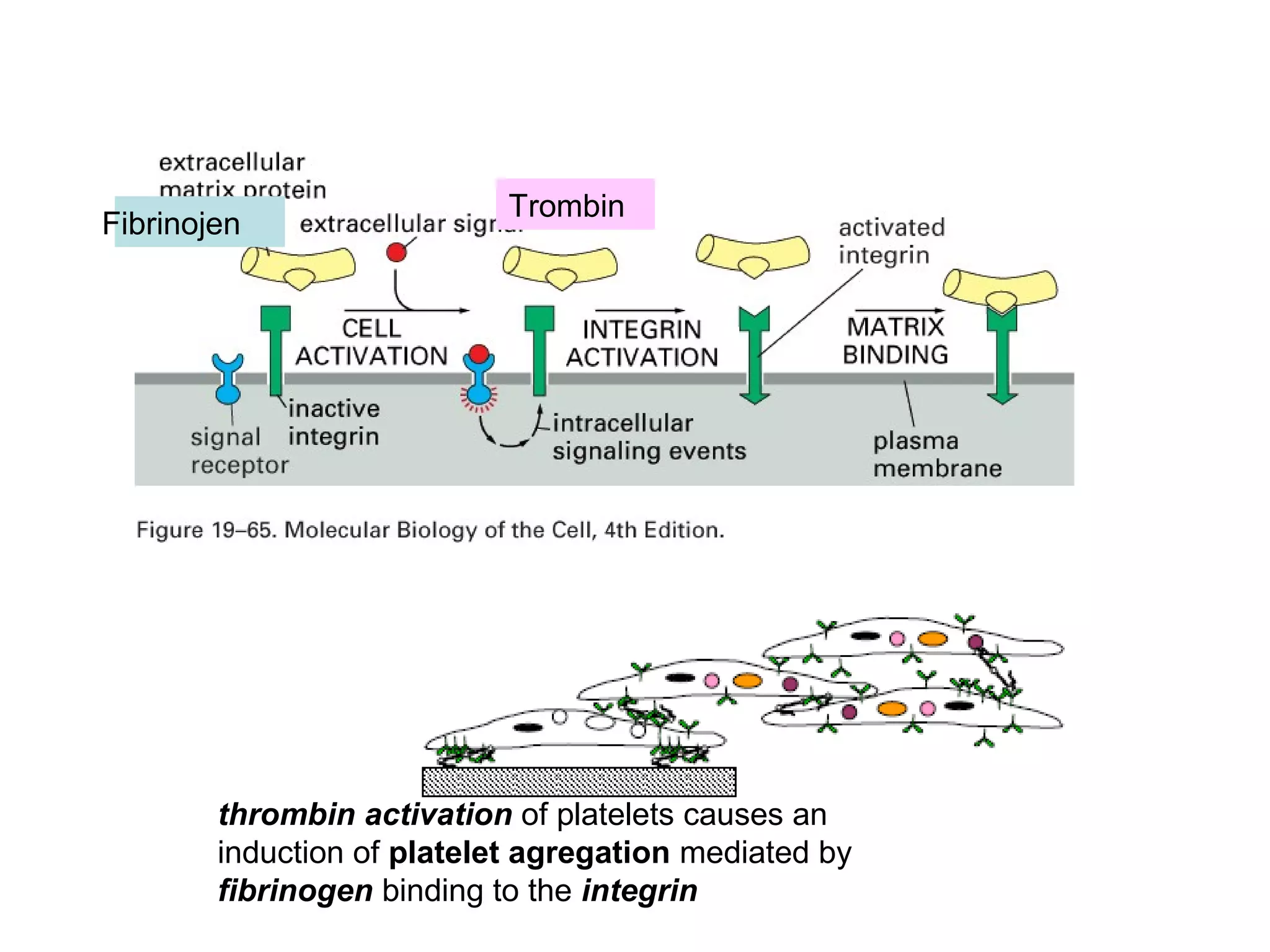
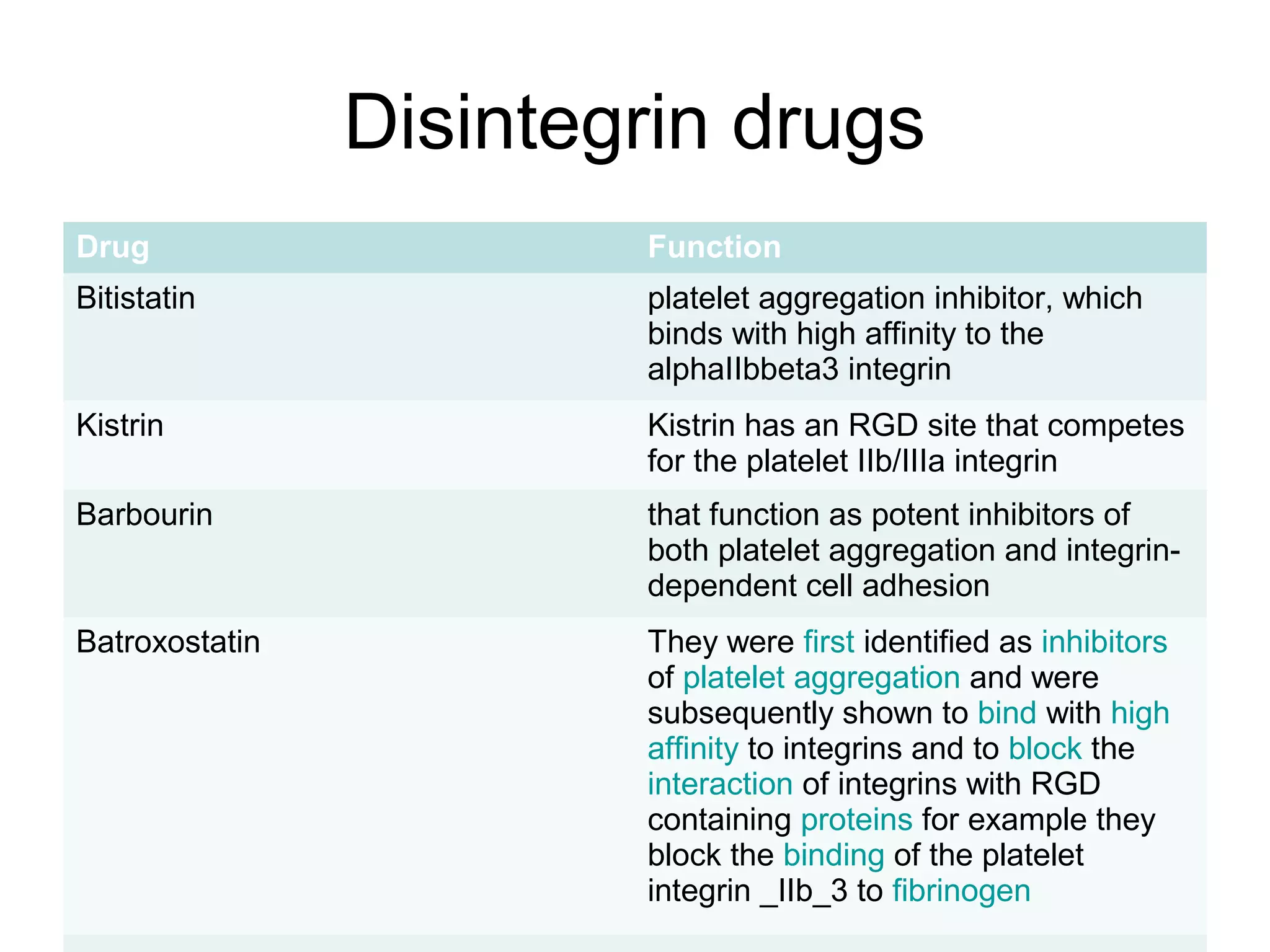
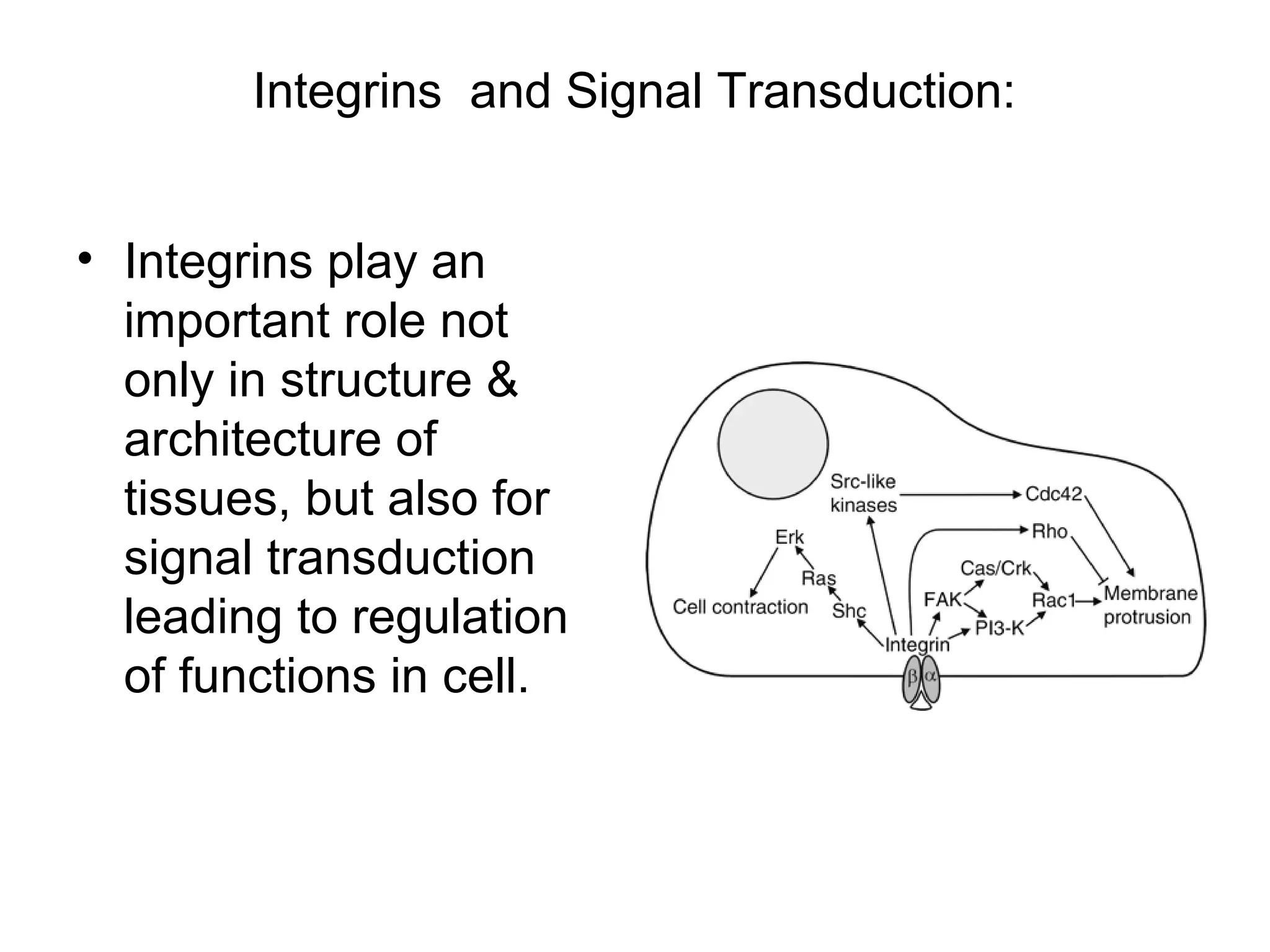
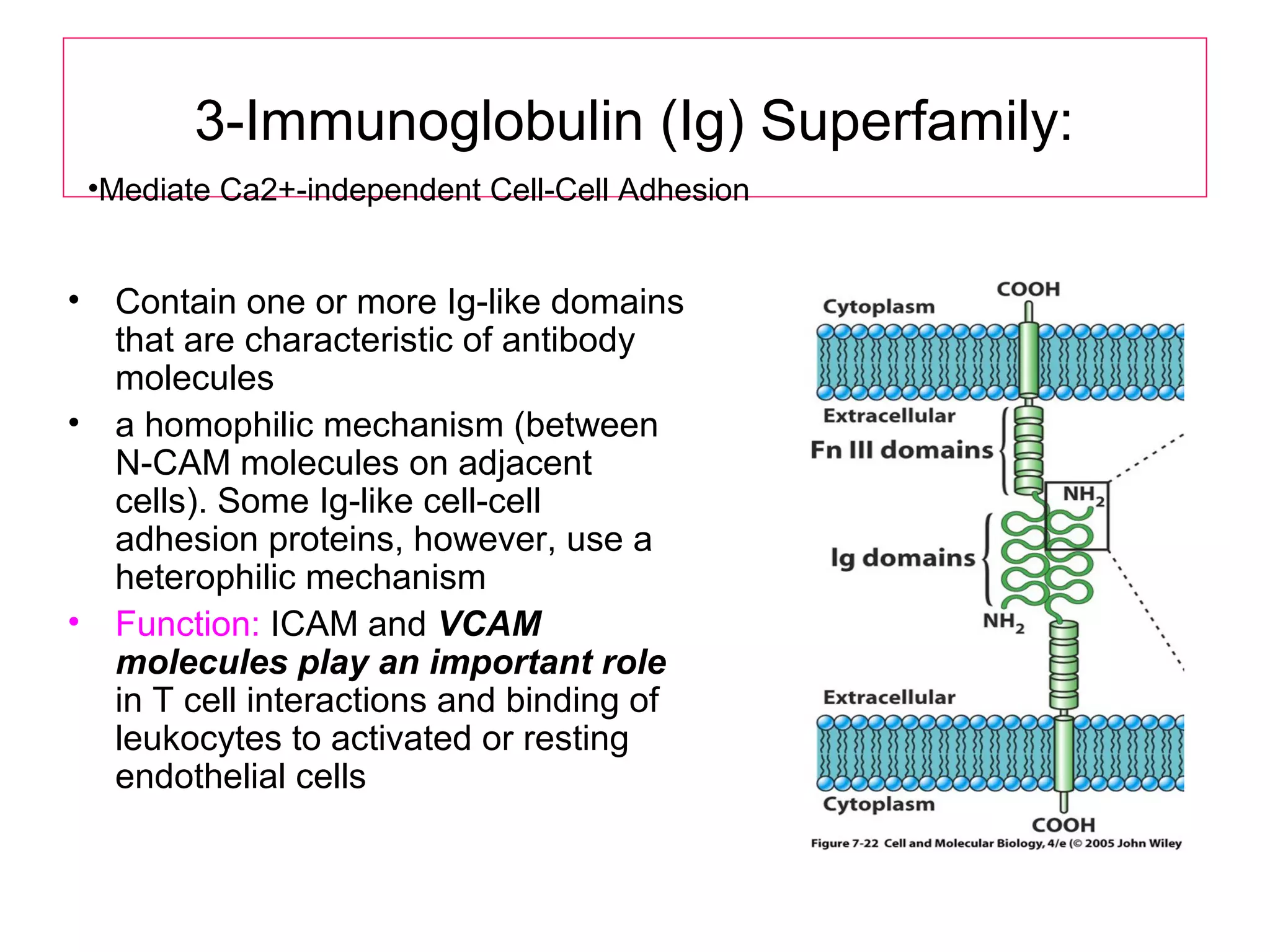
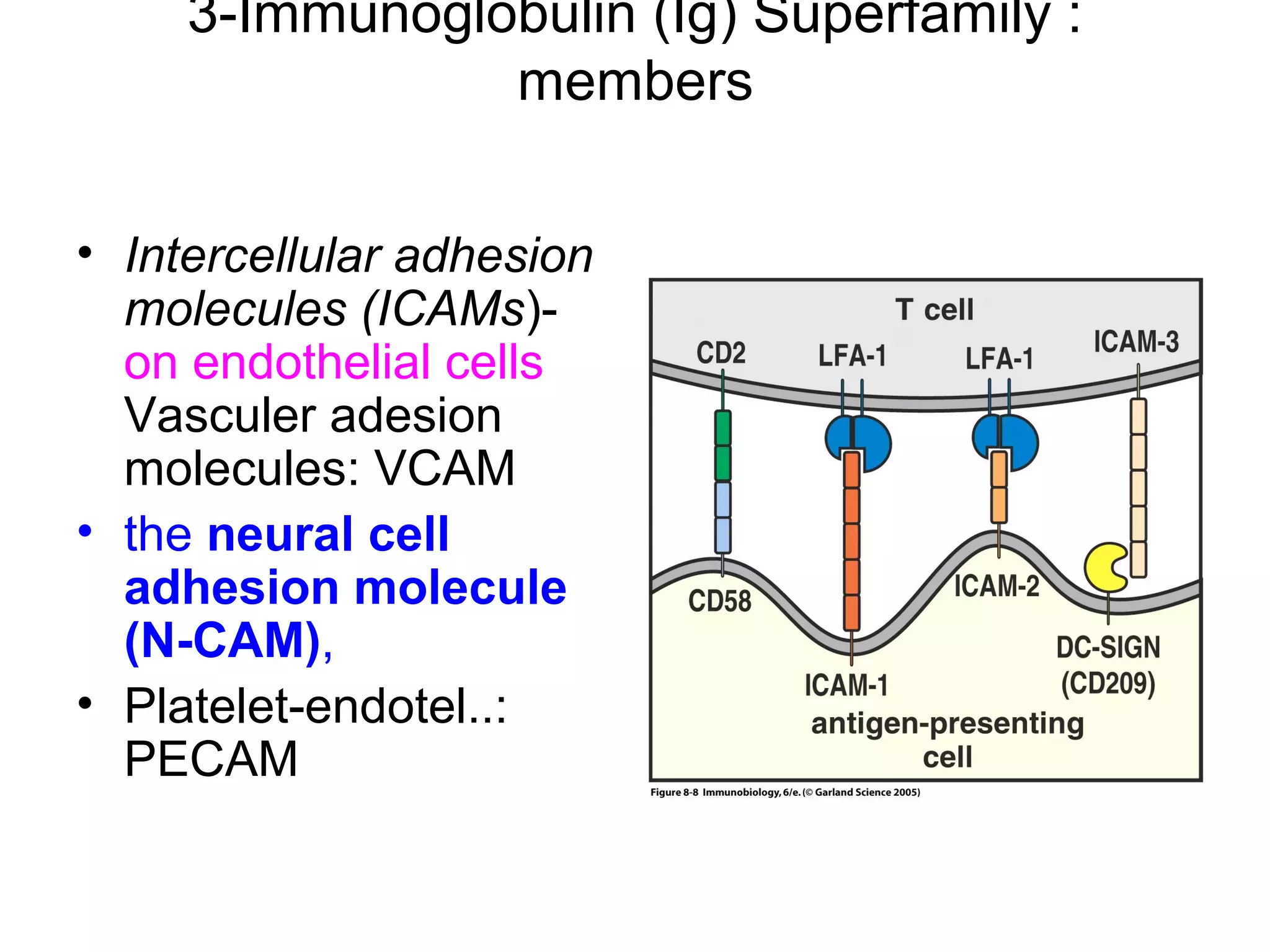
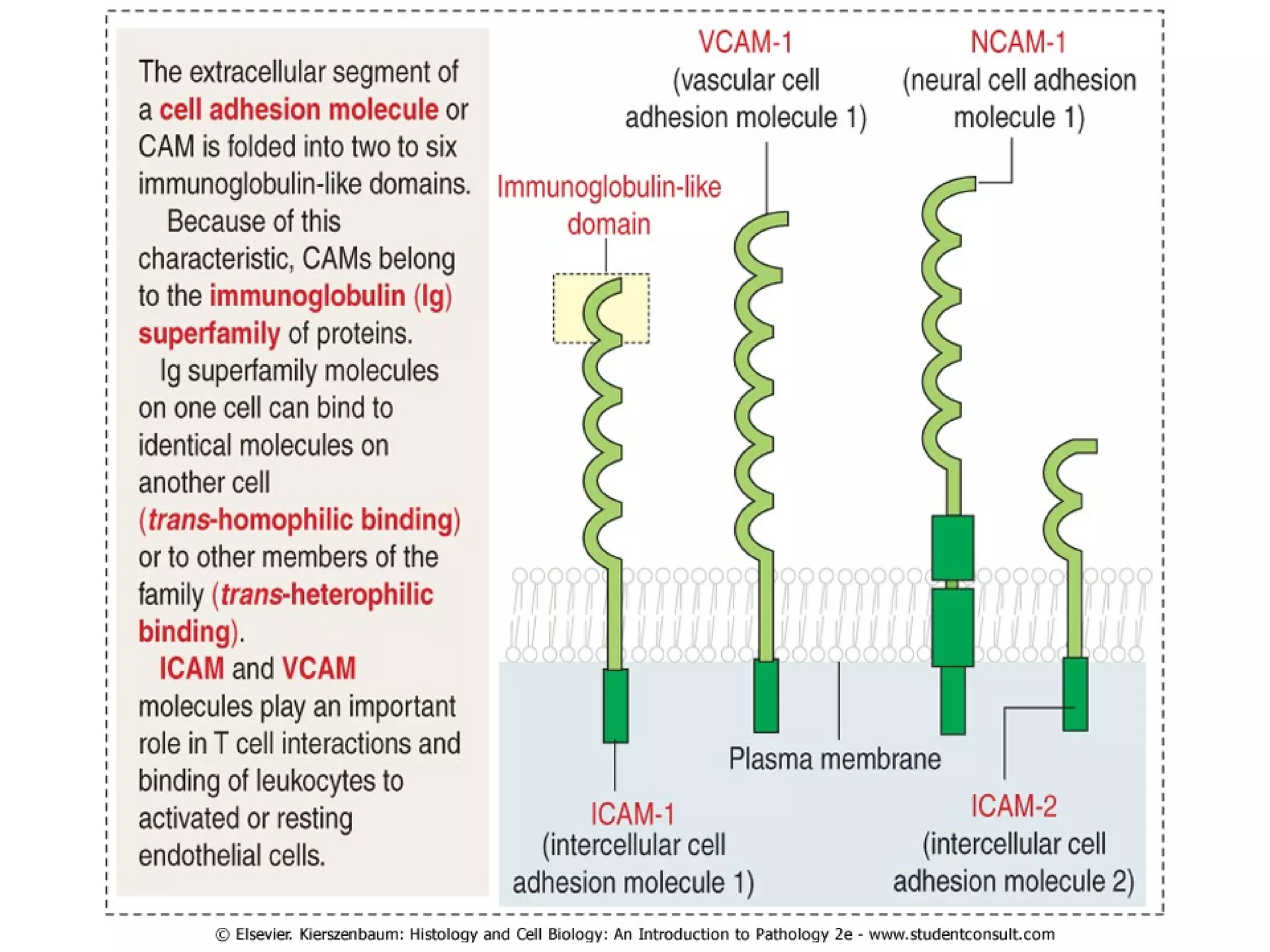
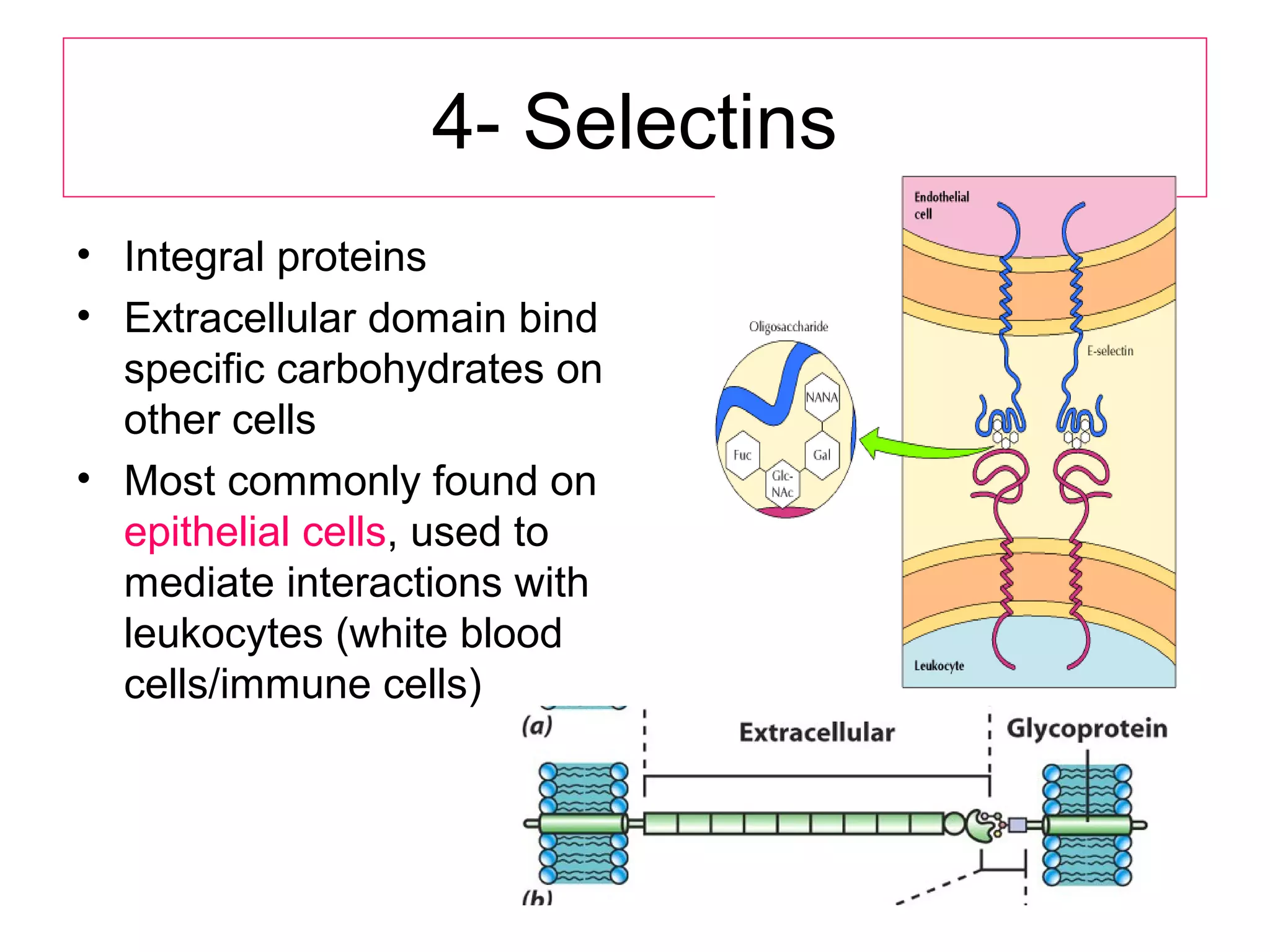
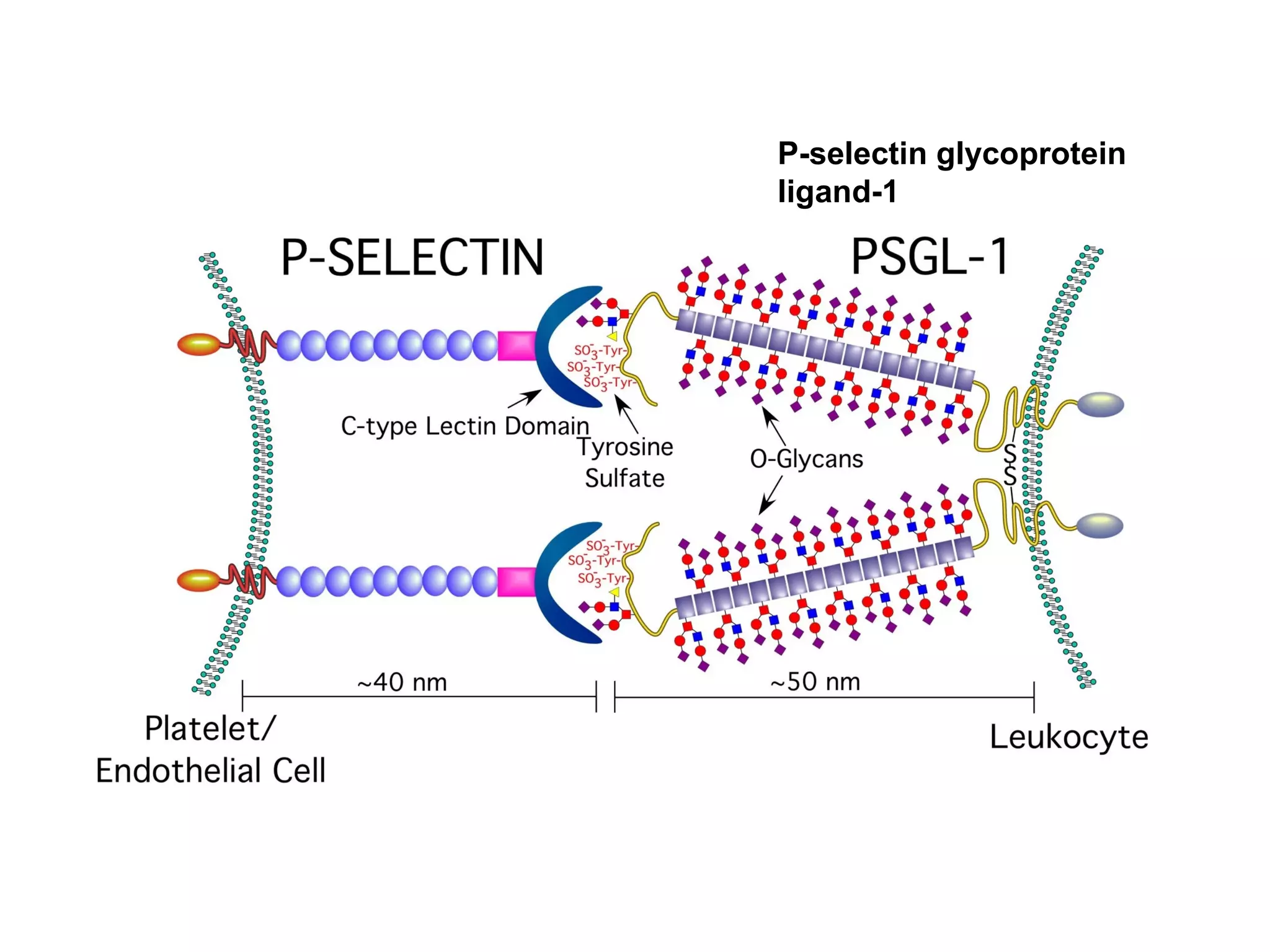
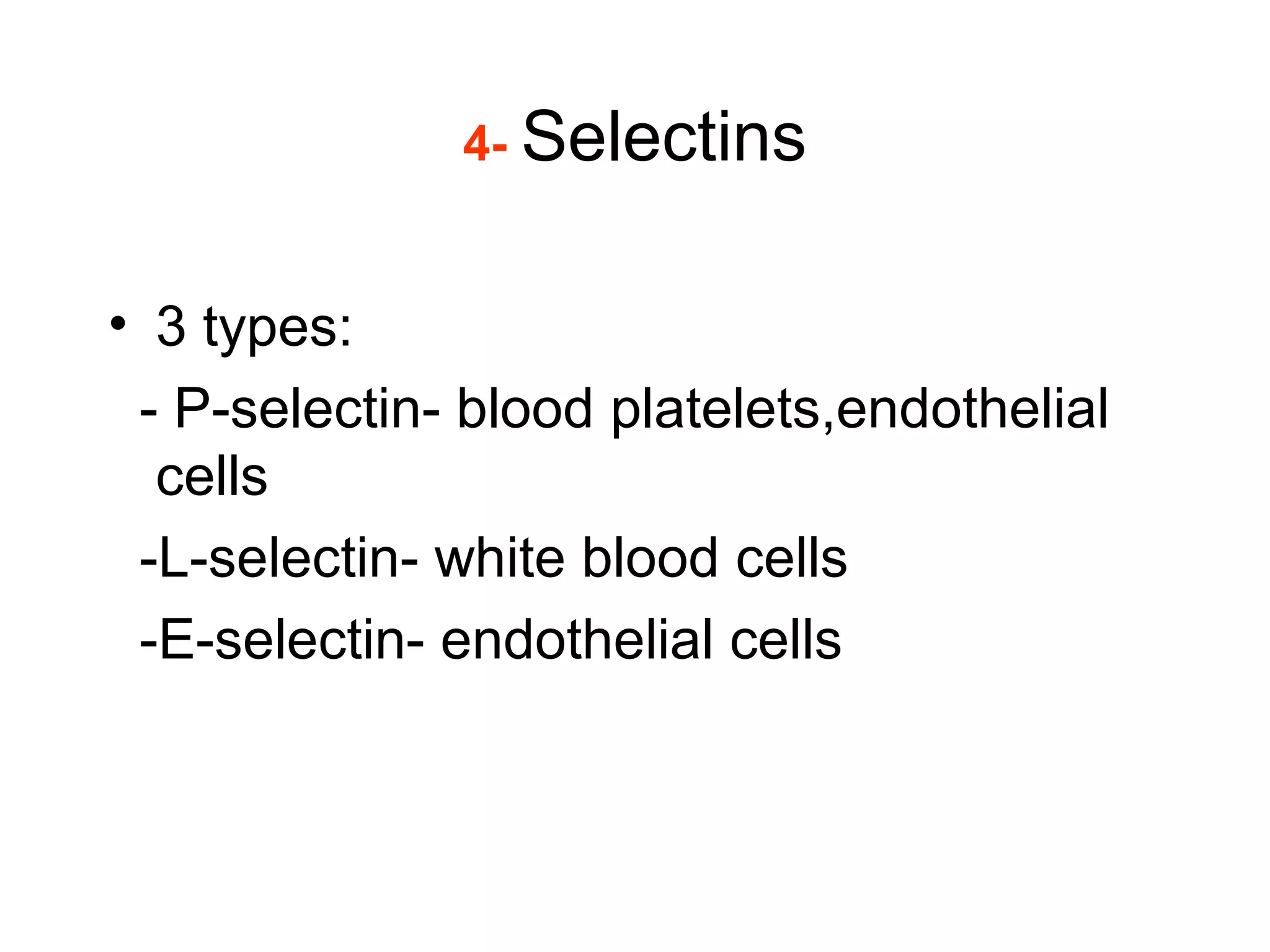
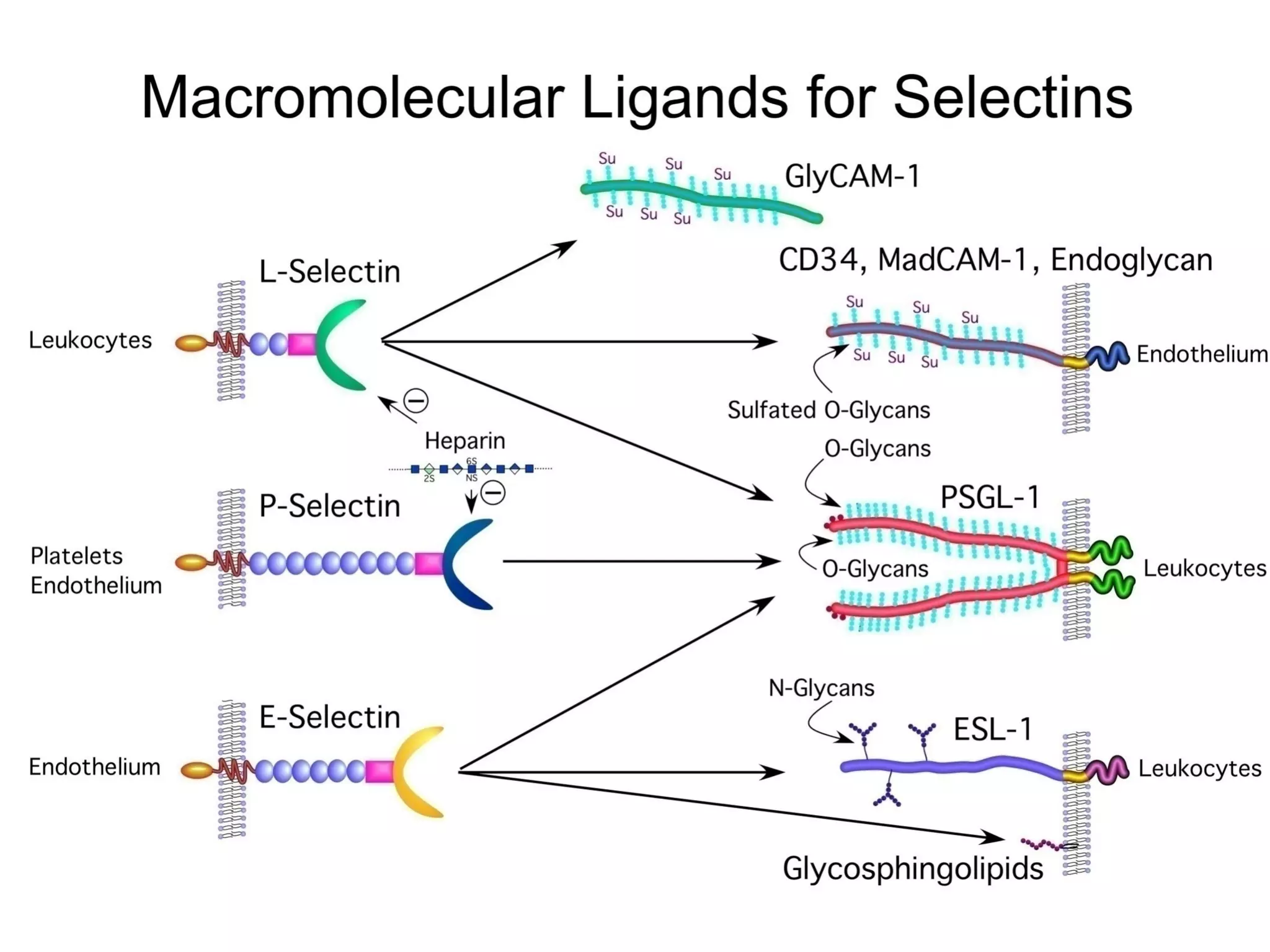
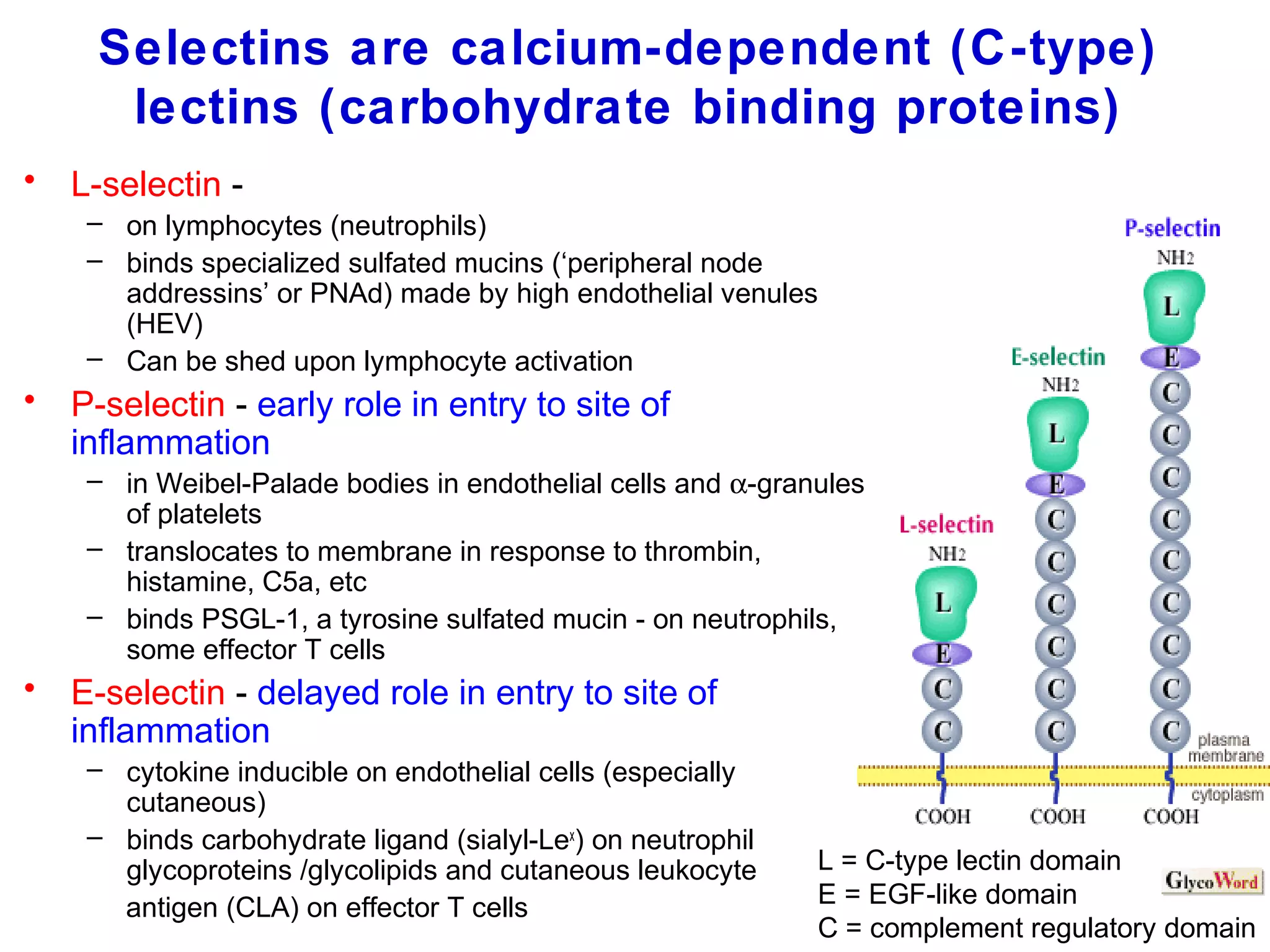
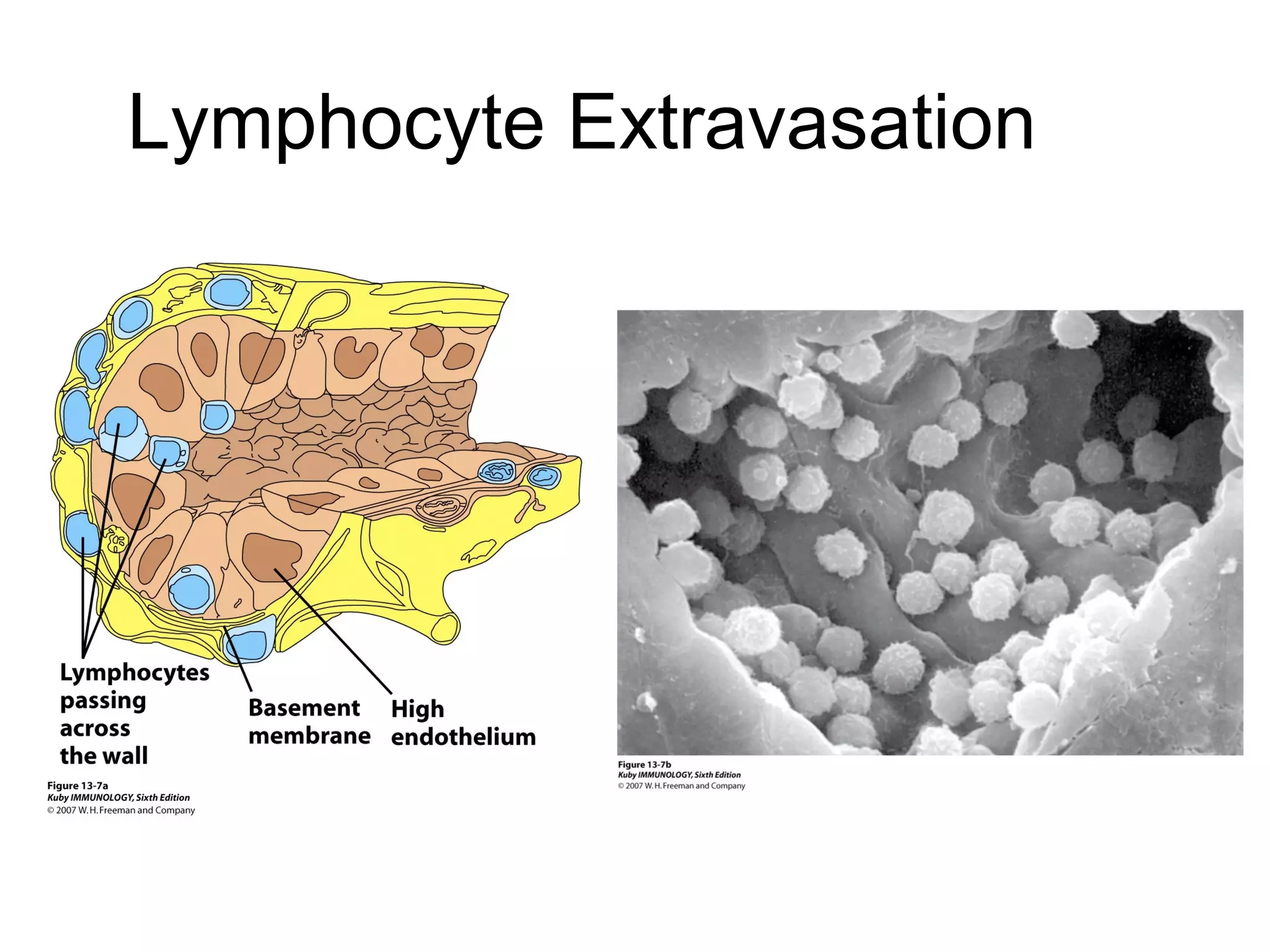
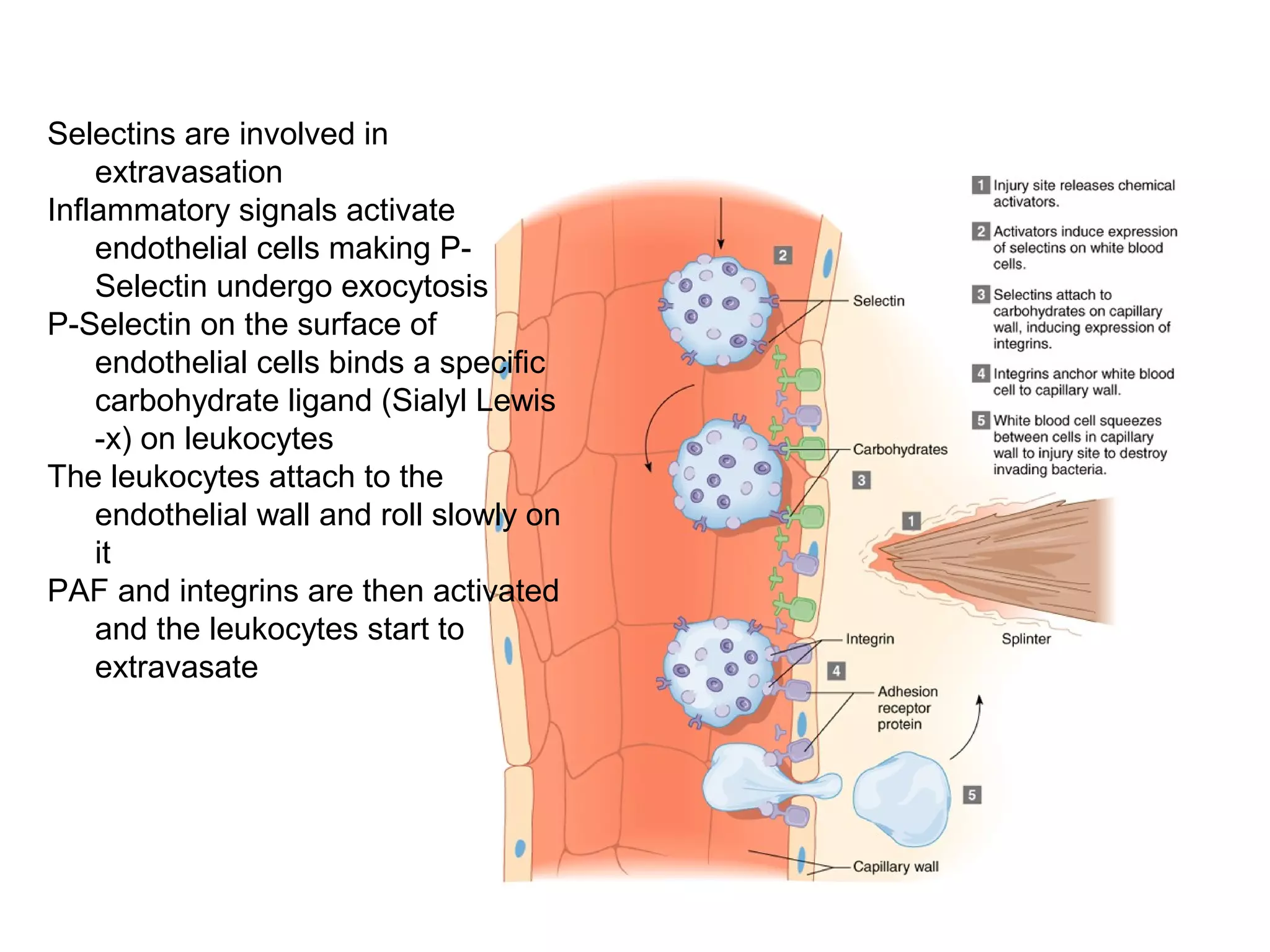
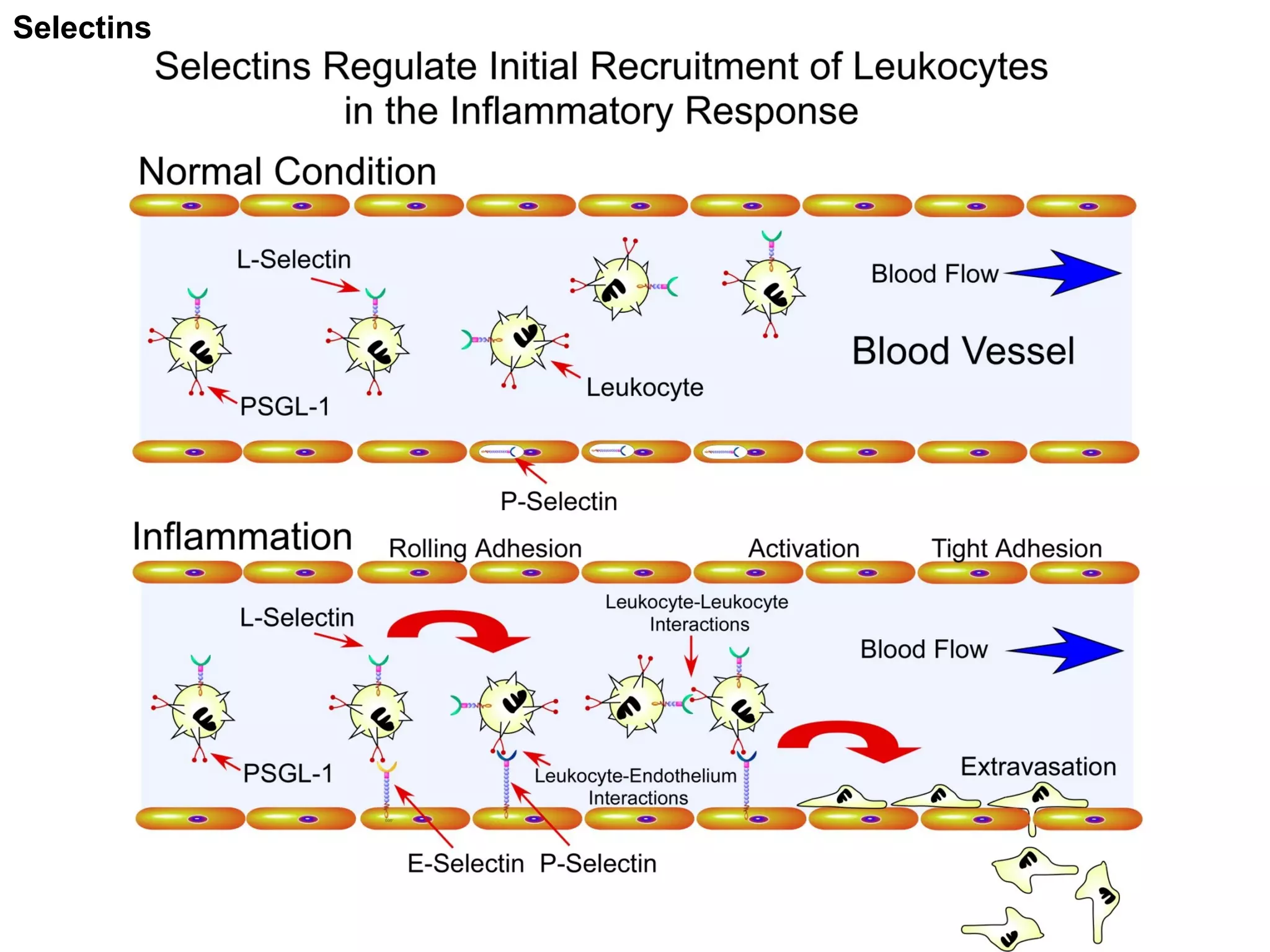
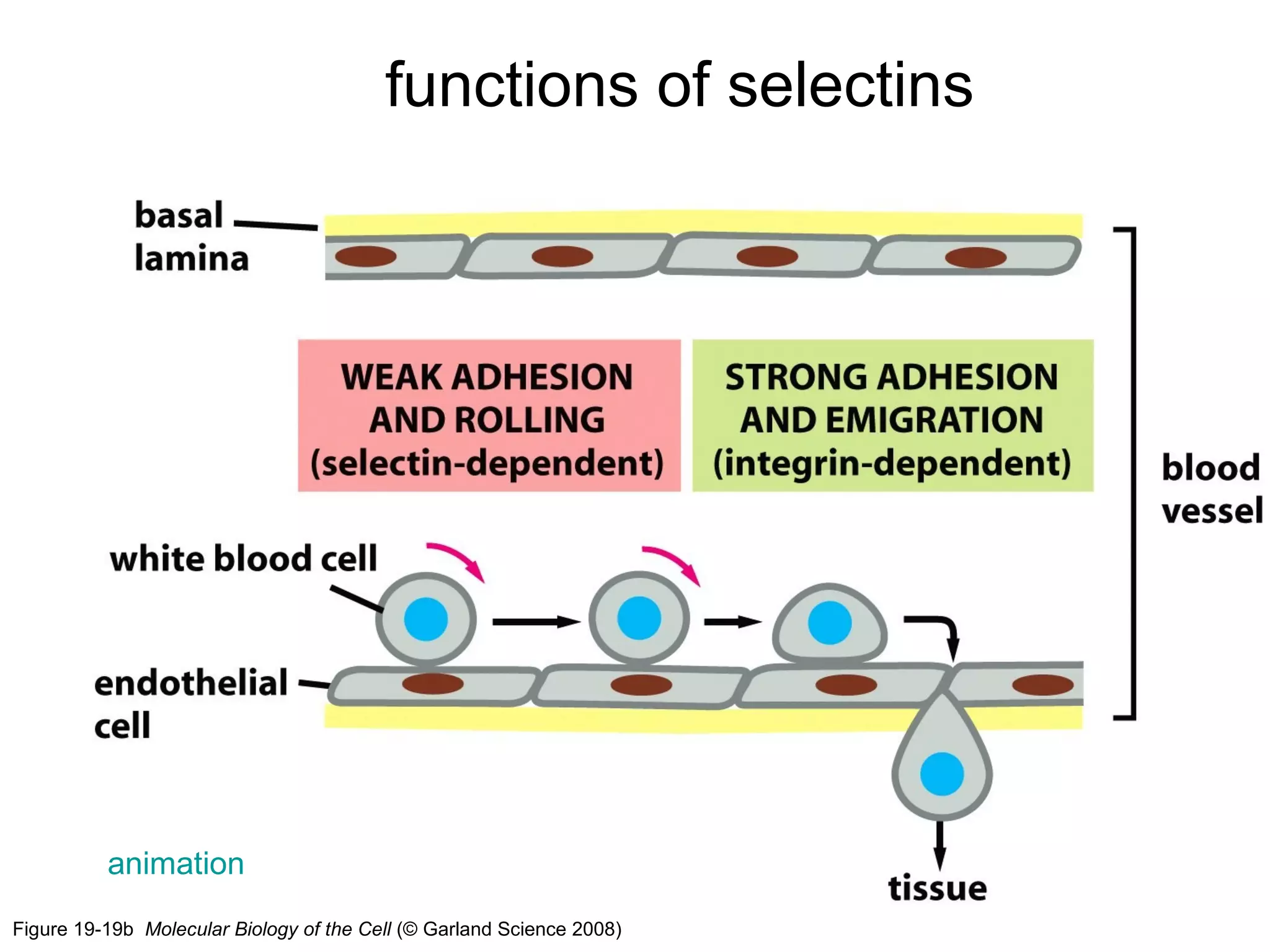
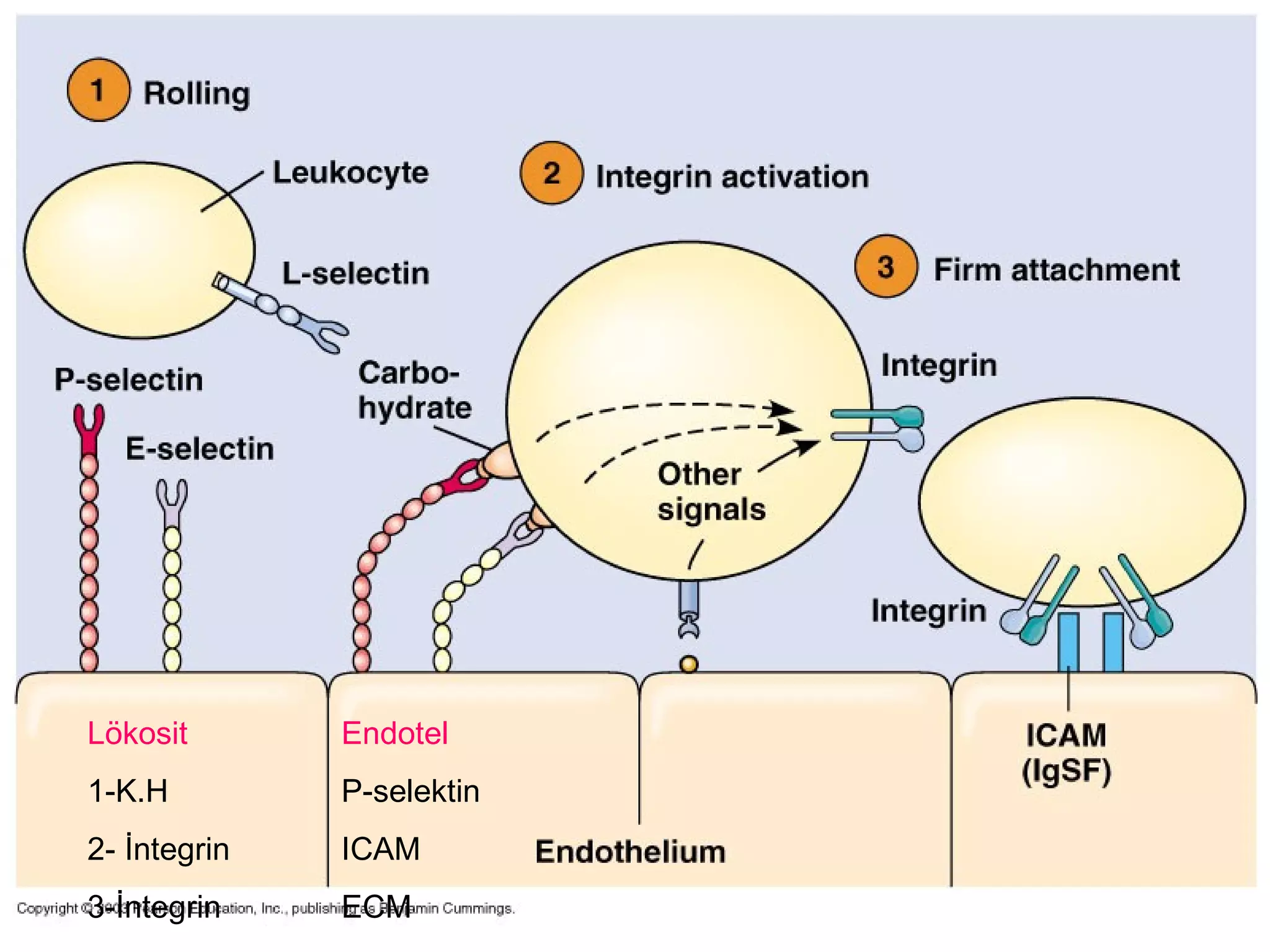
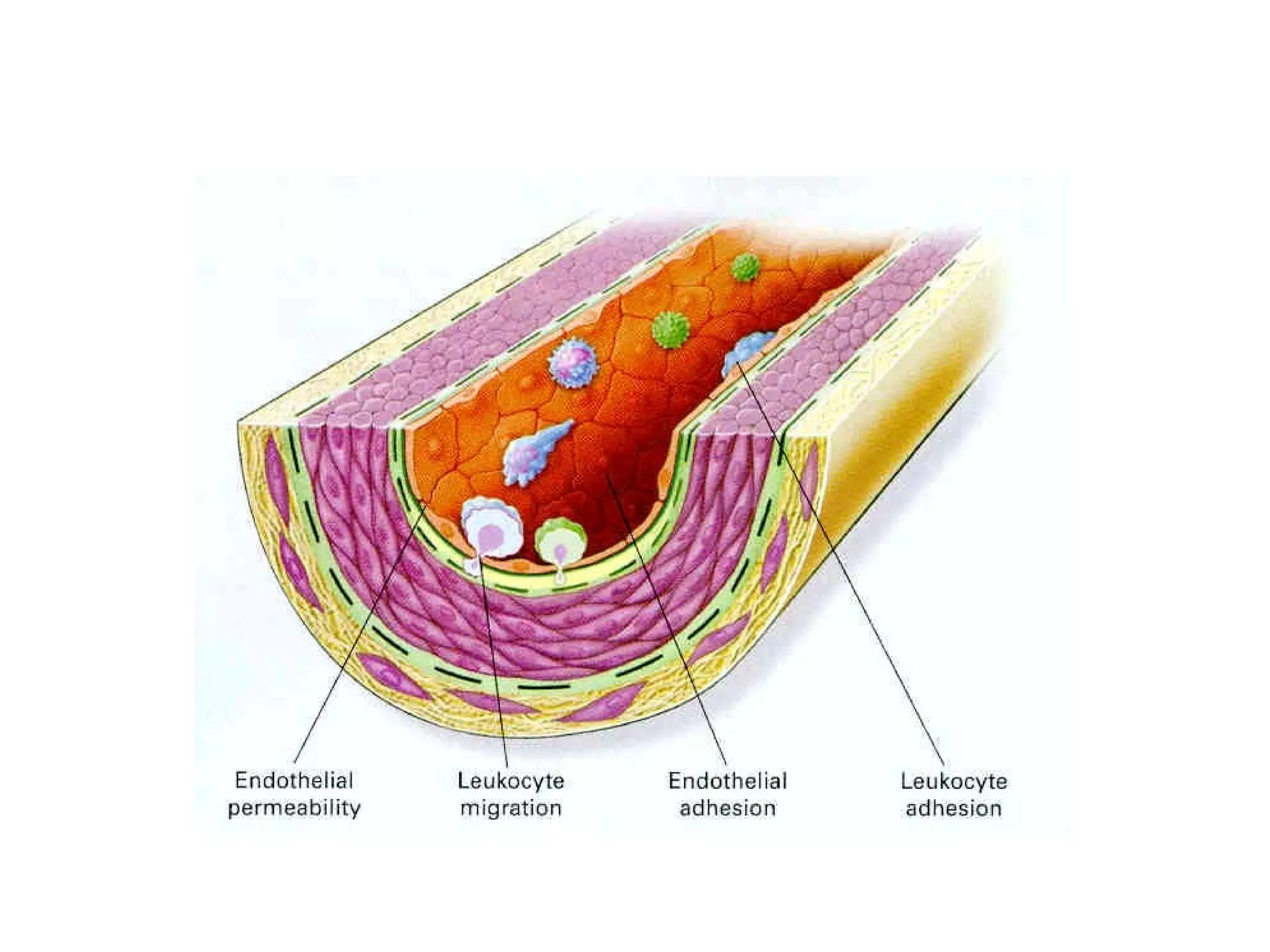
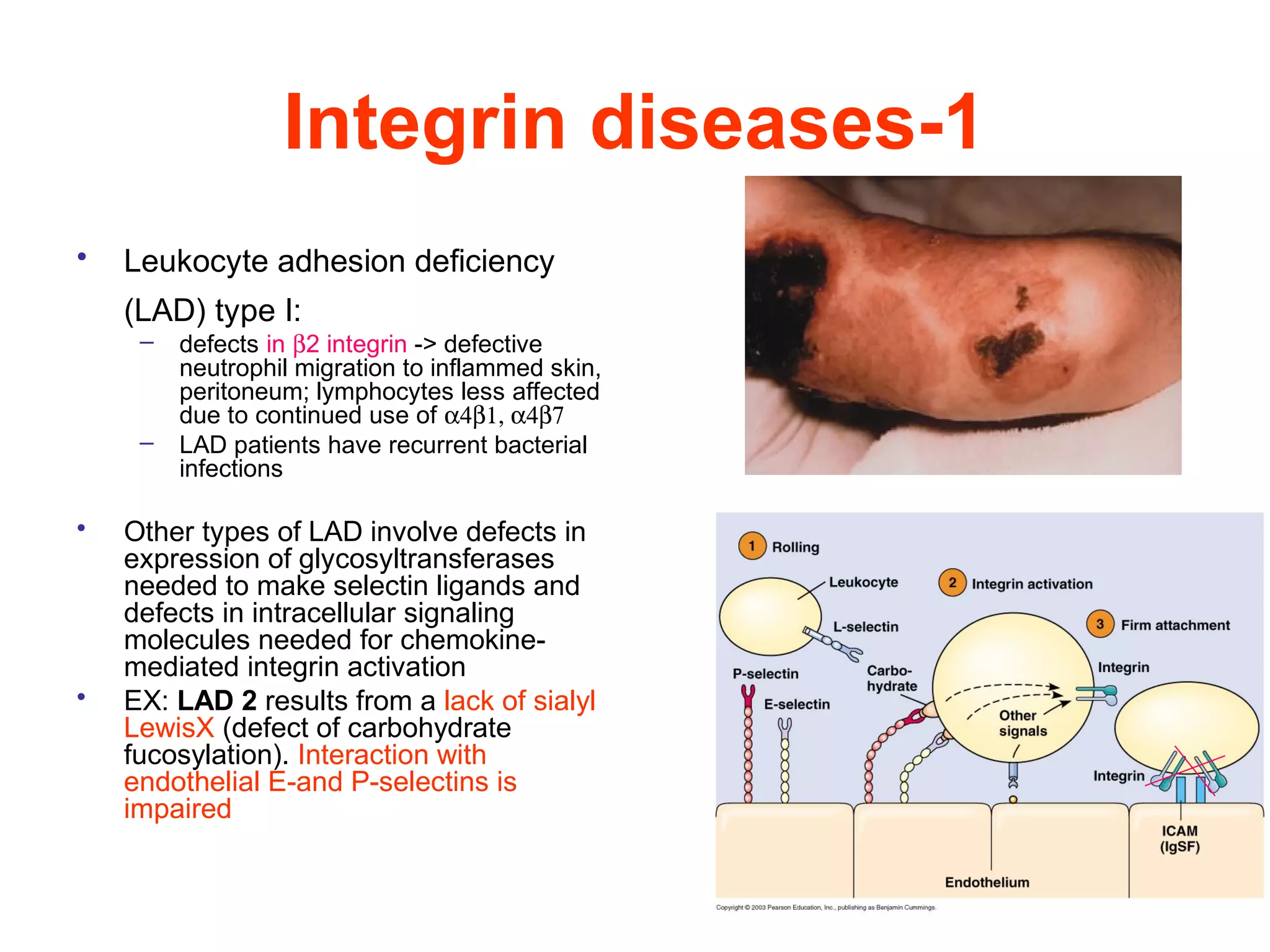
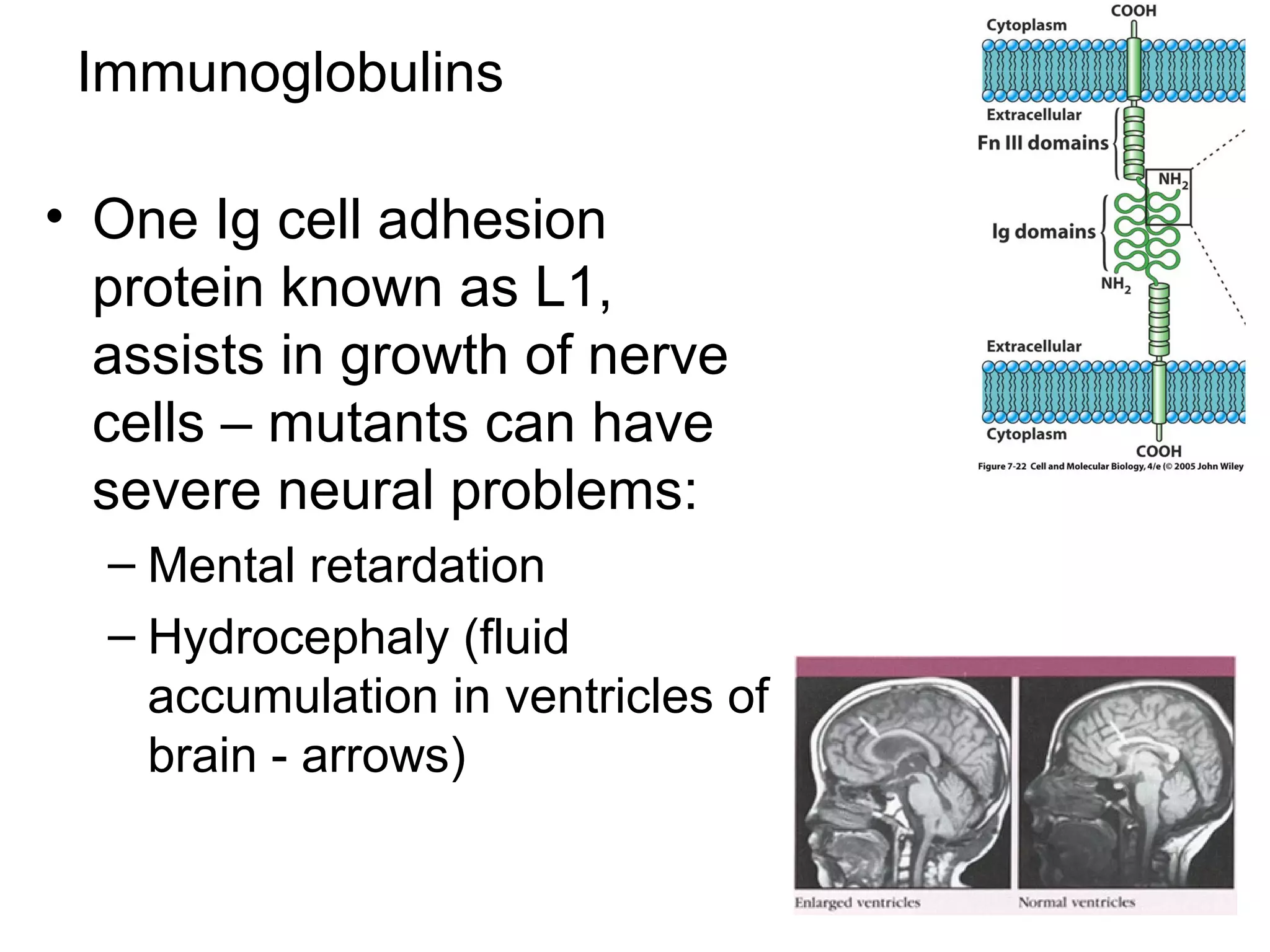
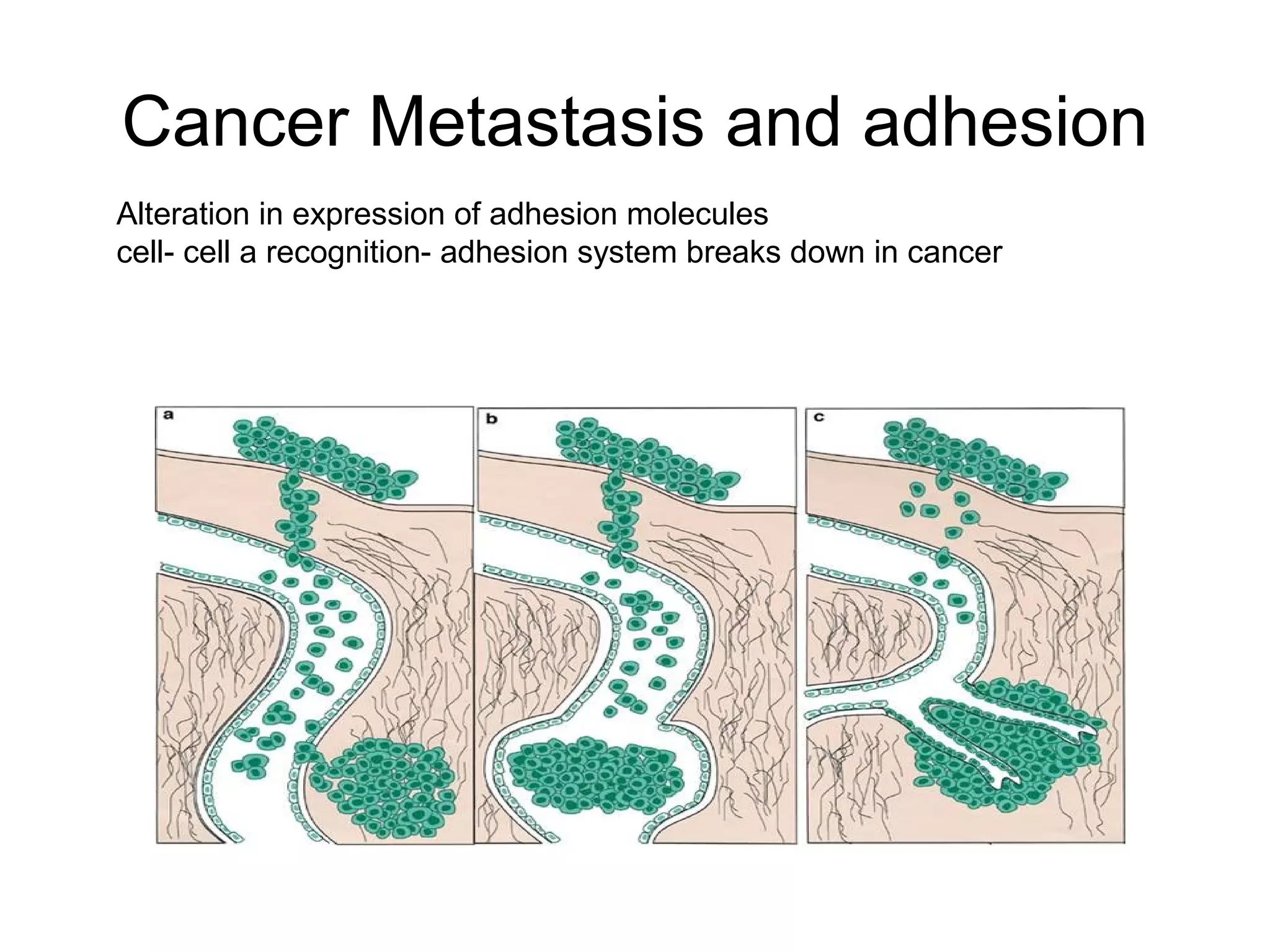
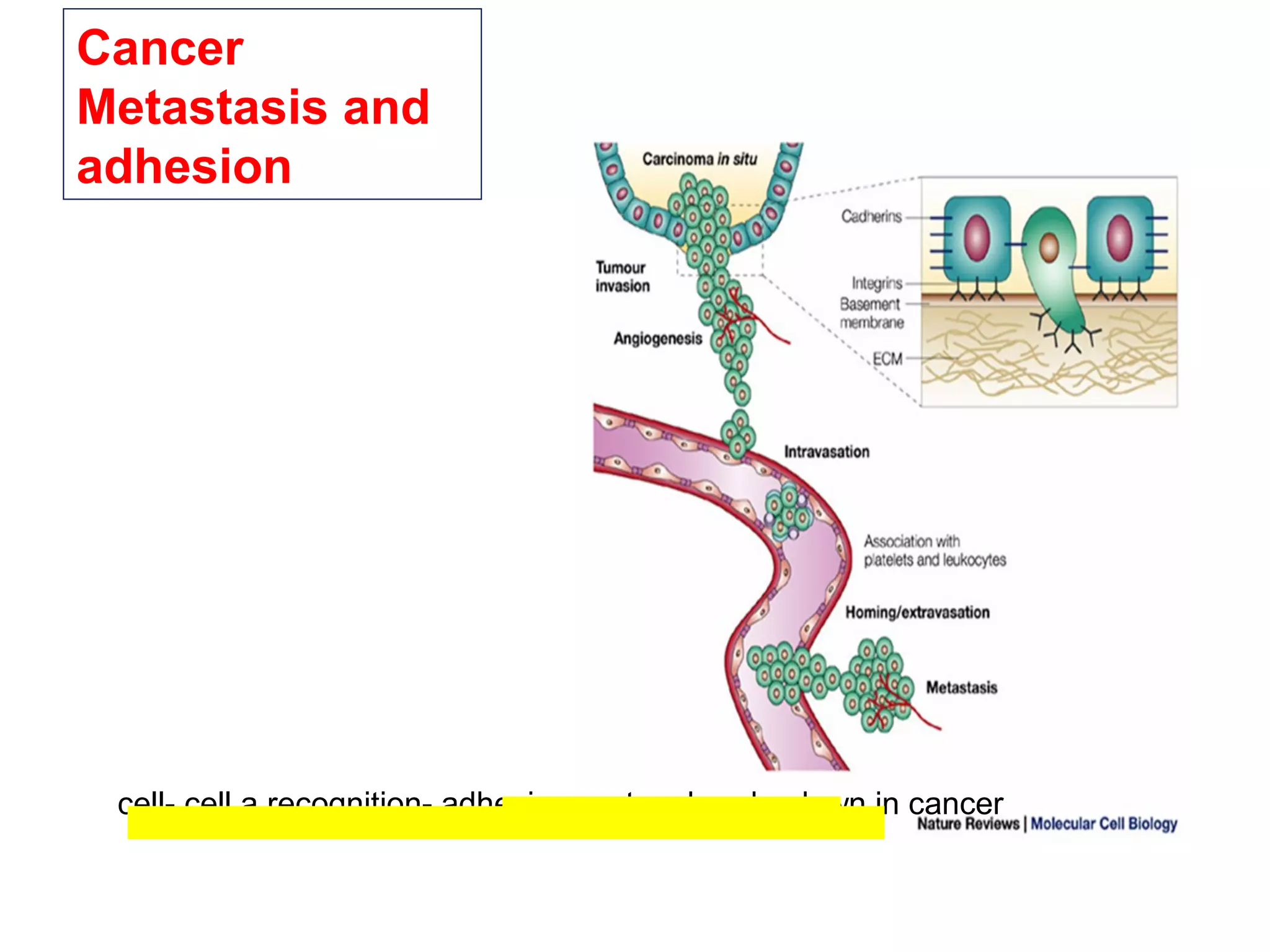
1) Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) allow cells to adhere to other cells and to the extracellular matrix. The main CAM families are cadherins, integrins, the immunoglobulin superfamily, and selectins.
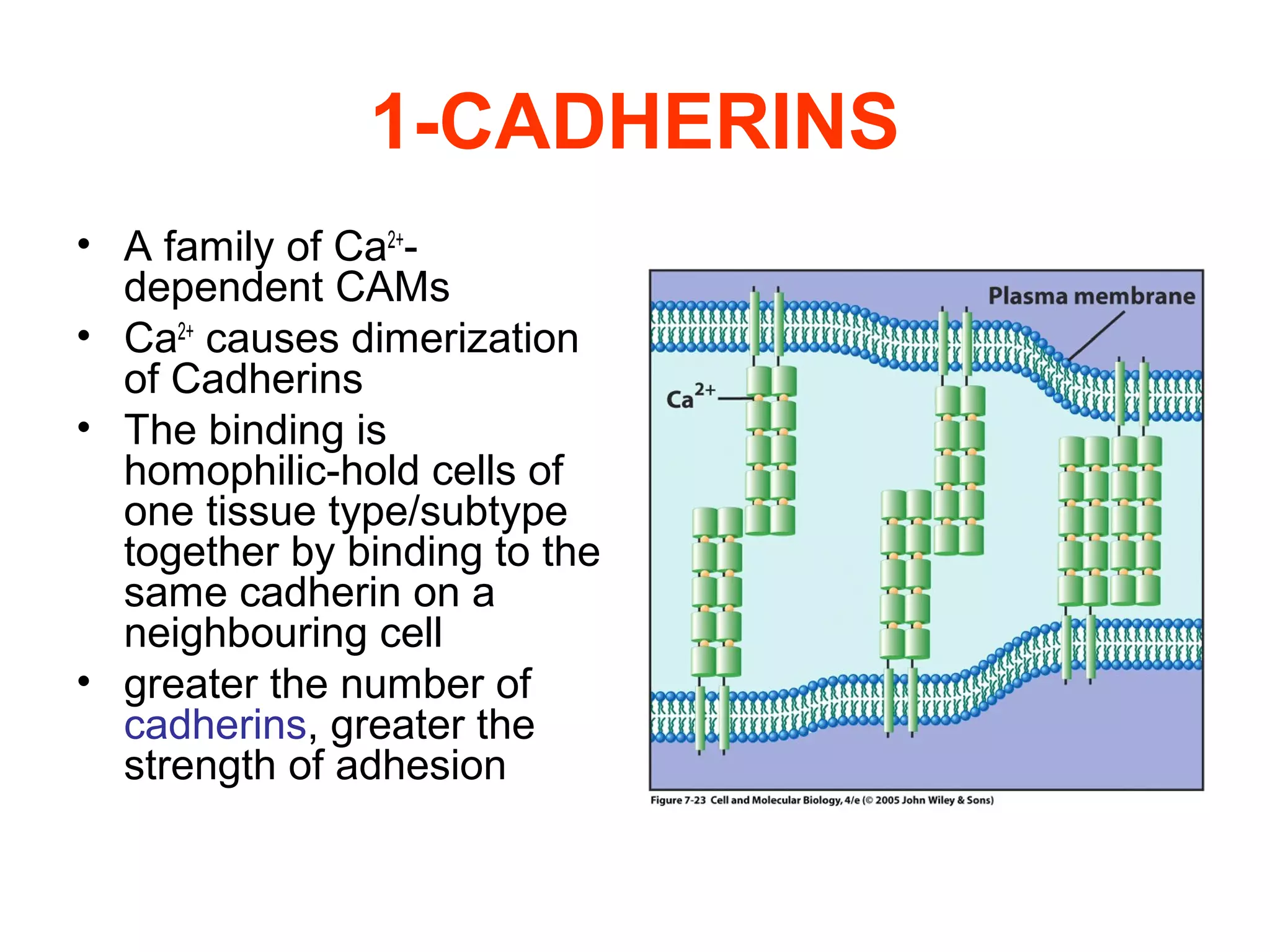
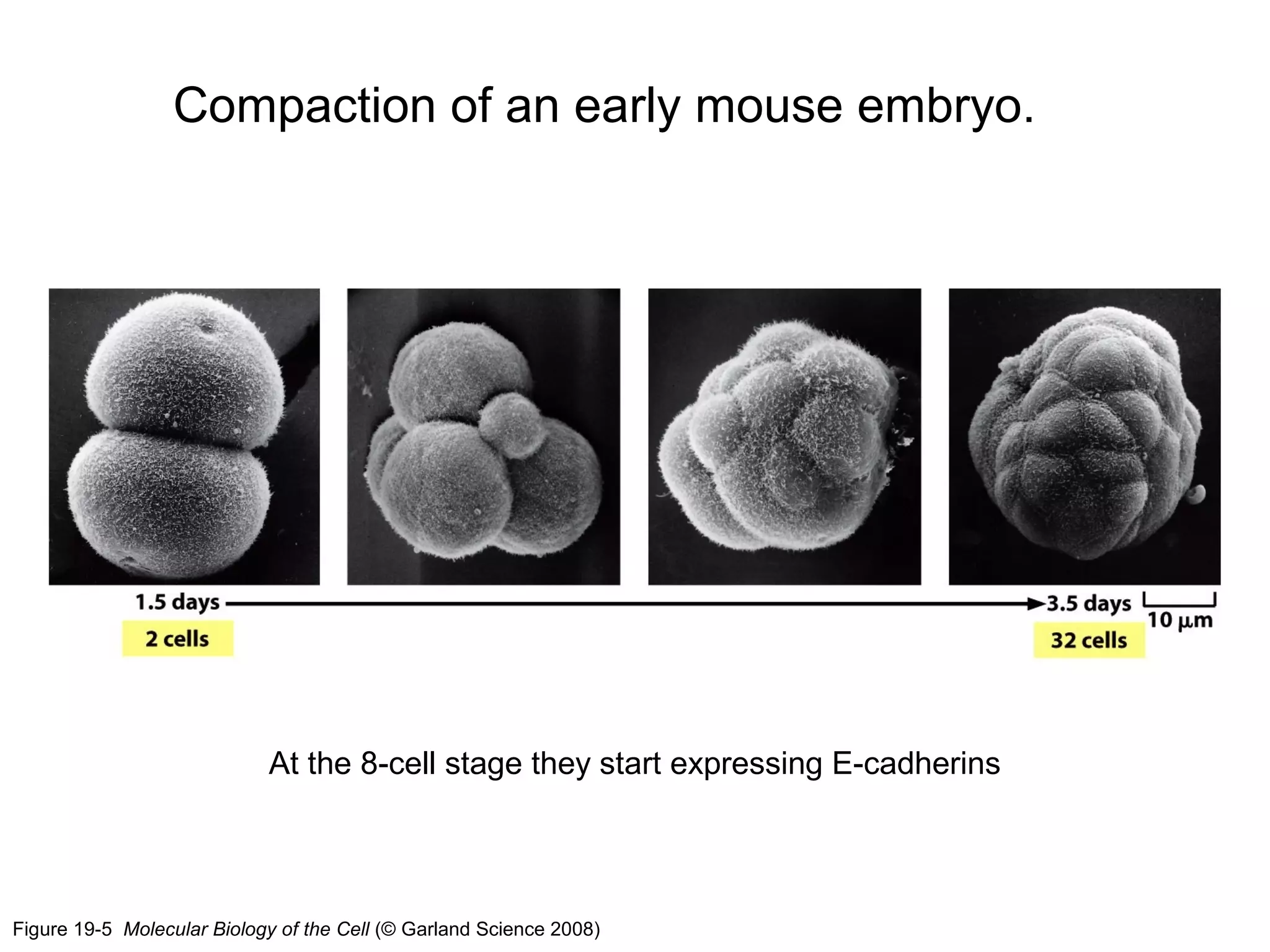
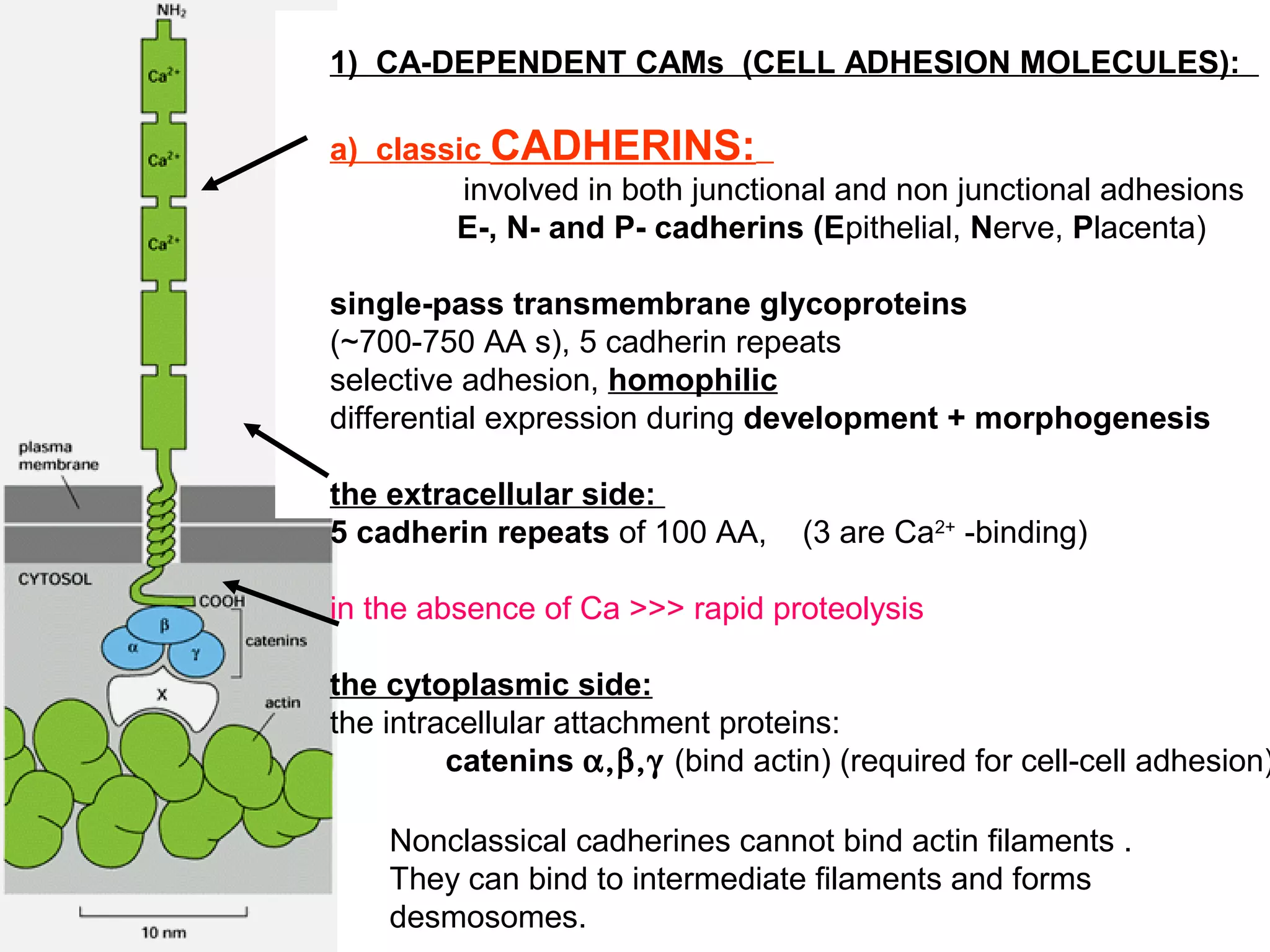
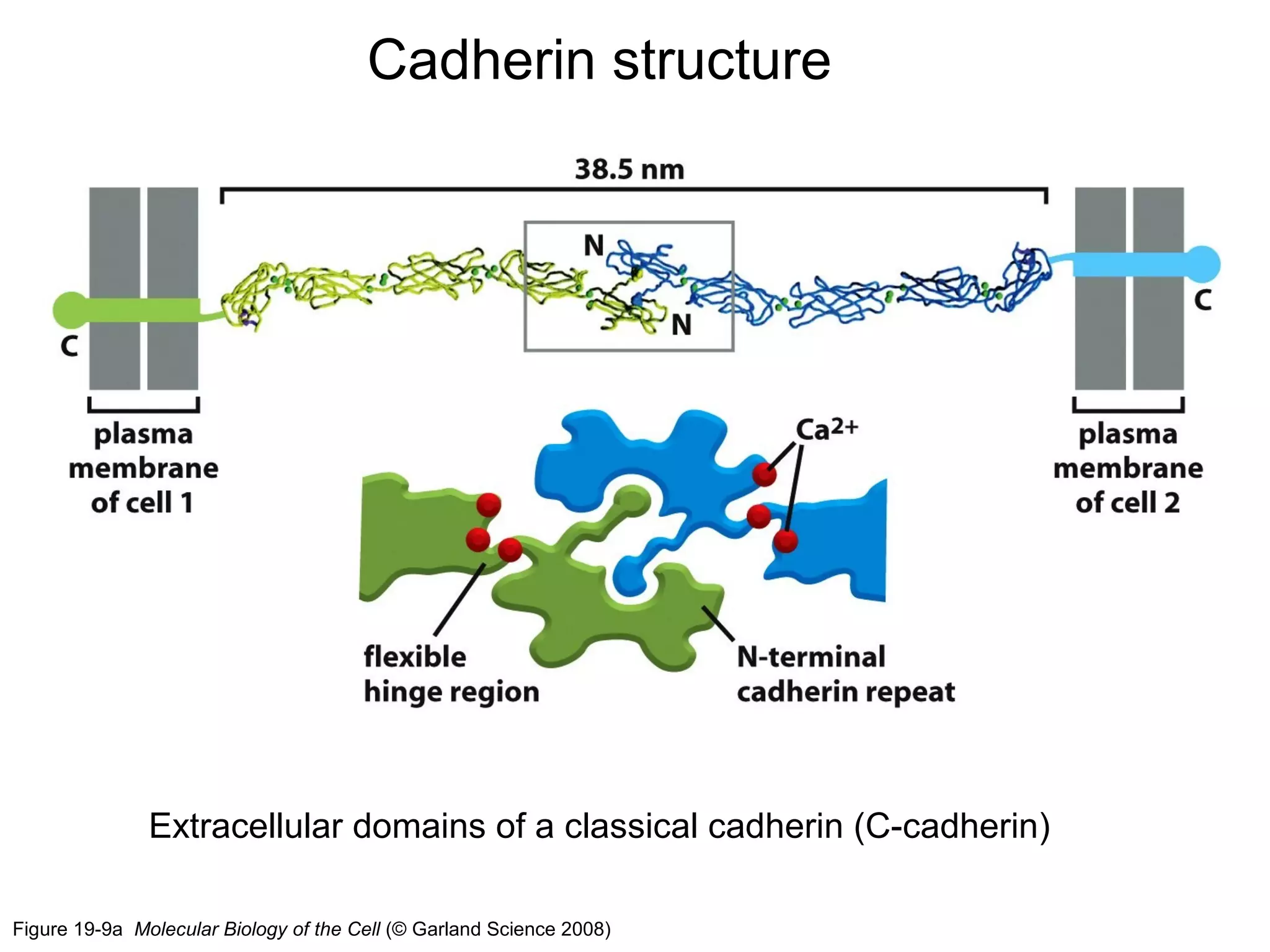
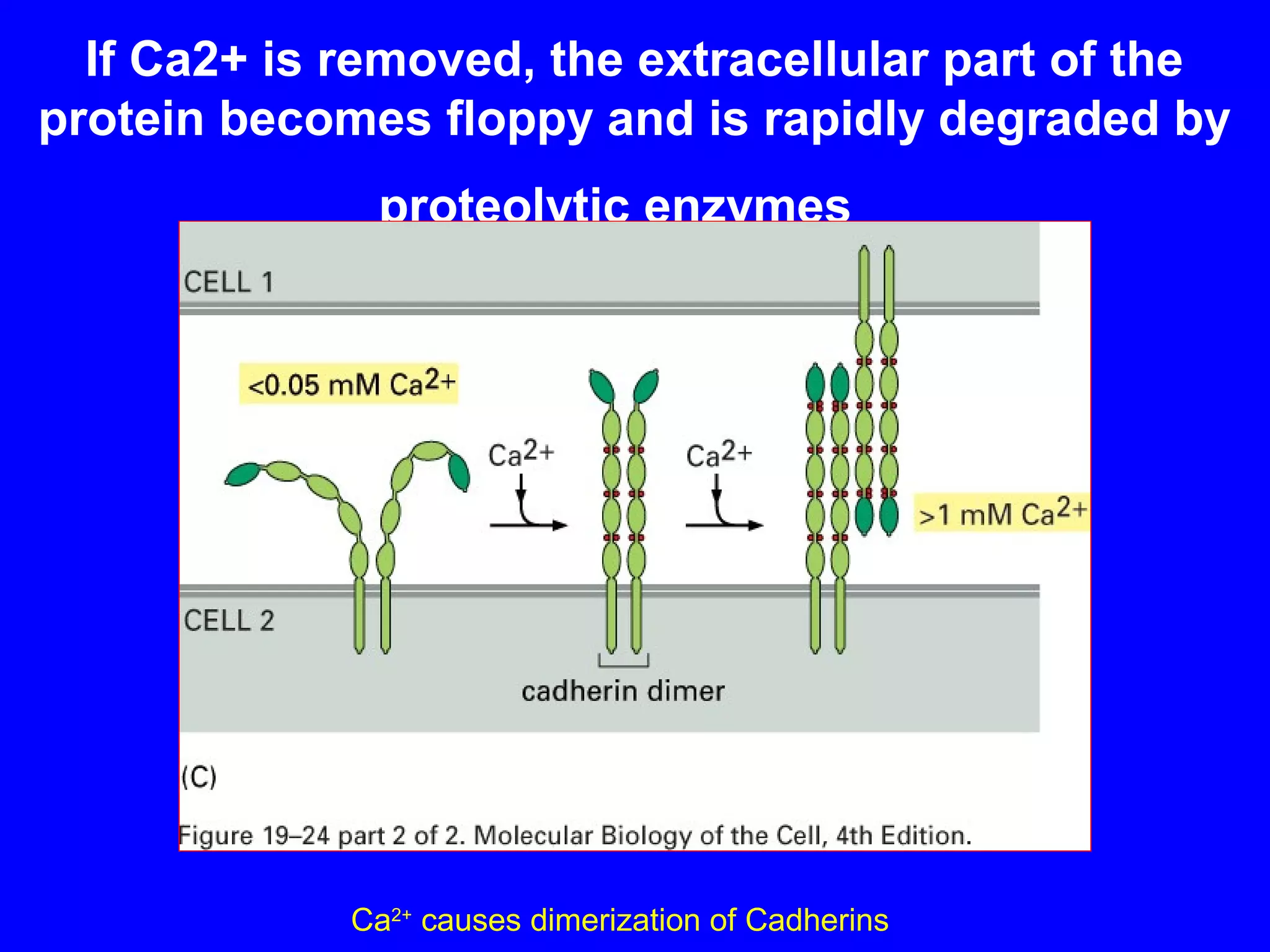
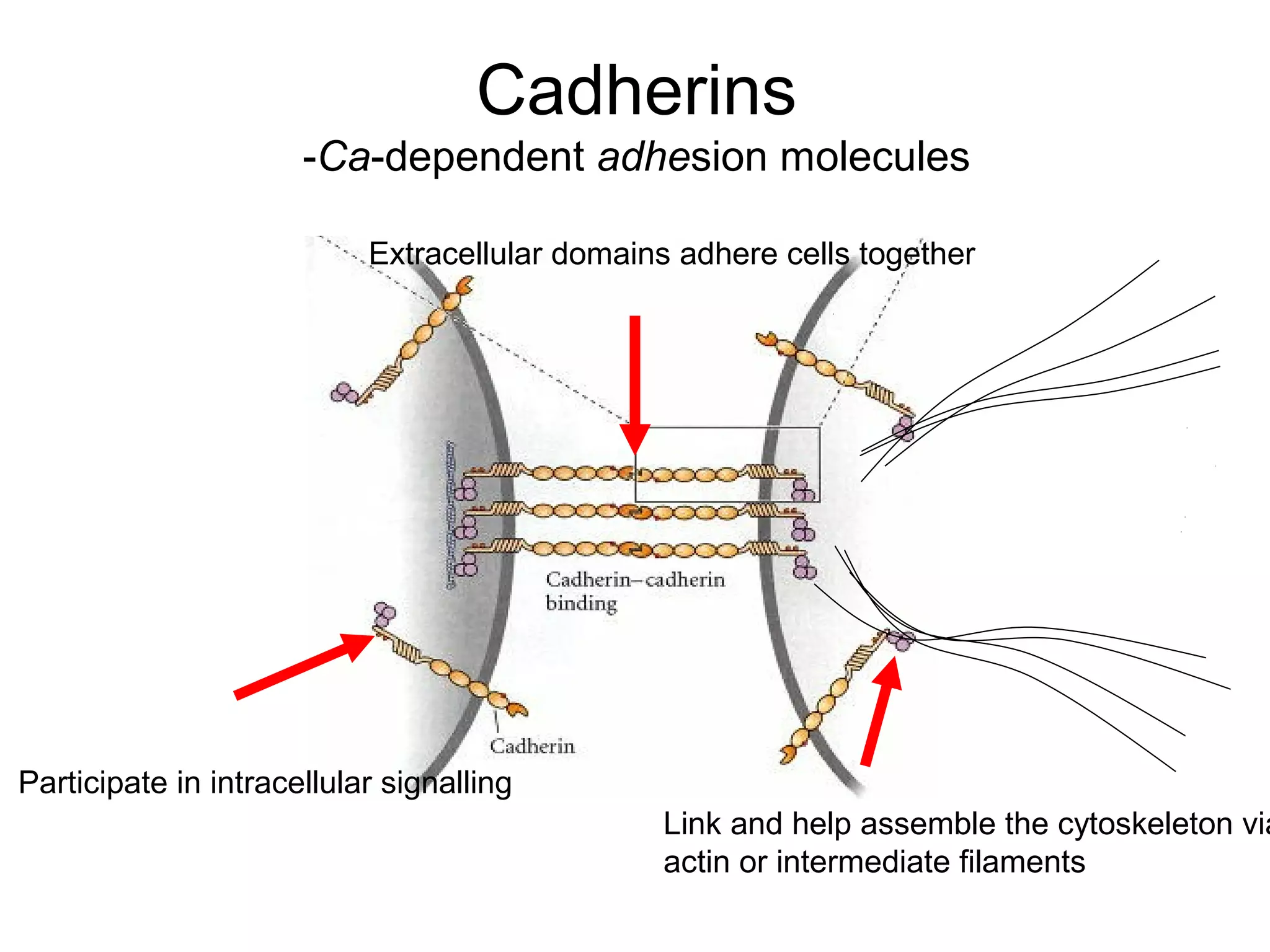
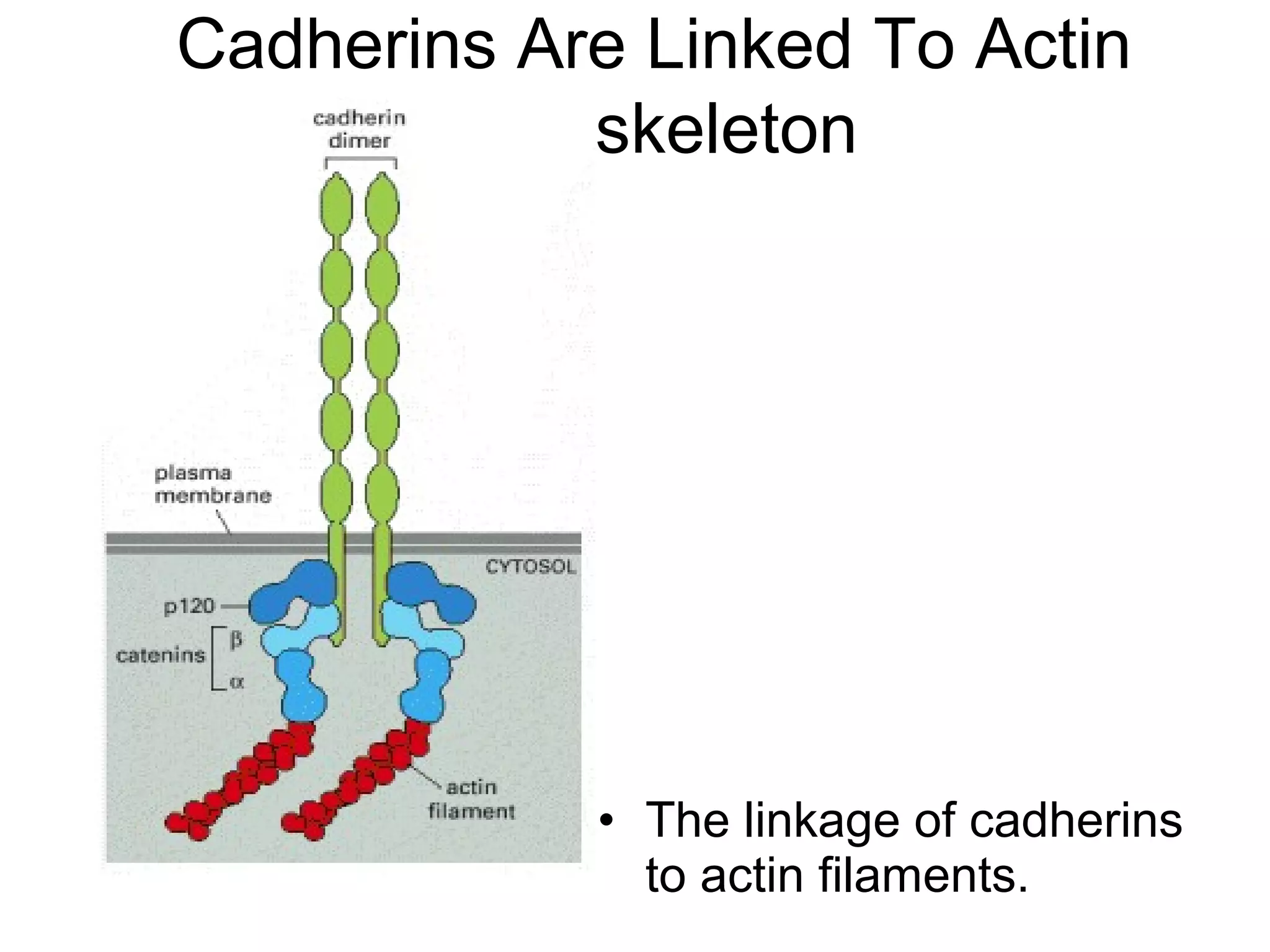
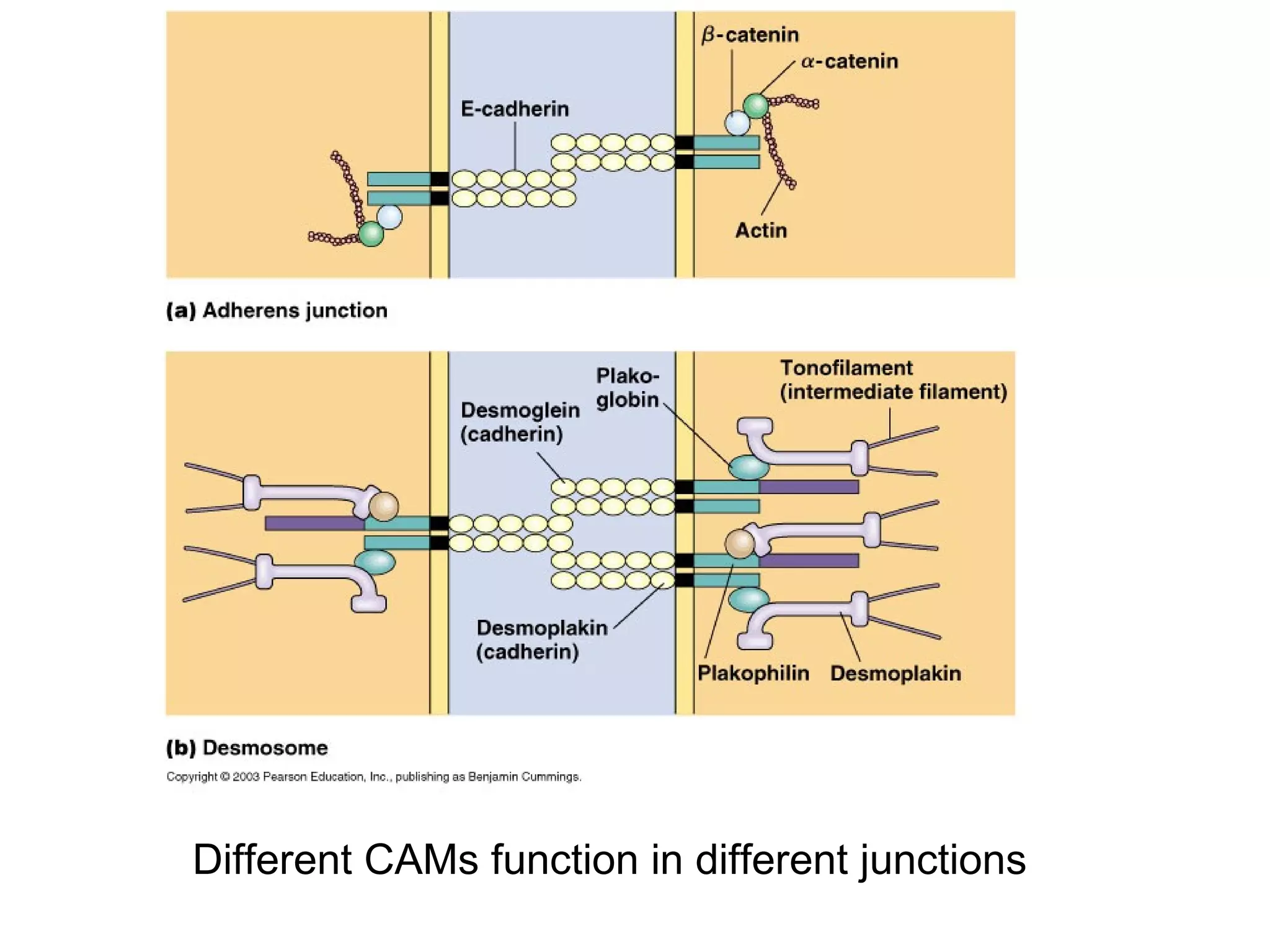
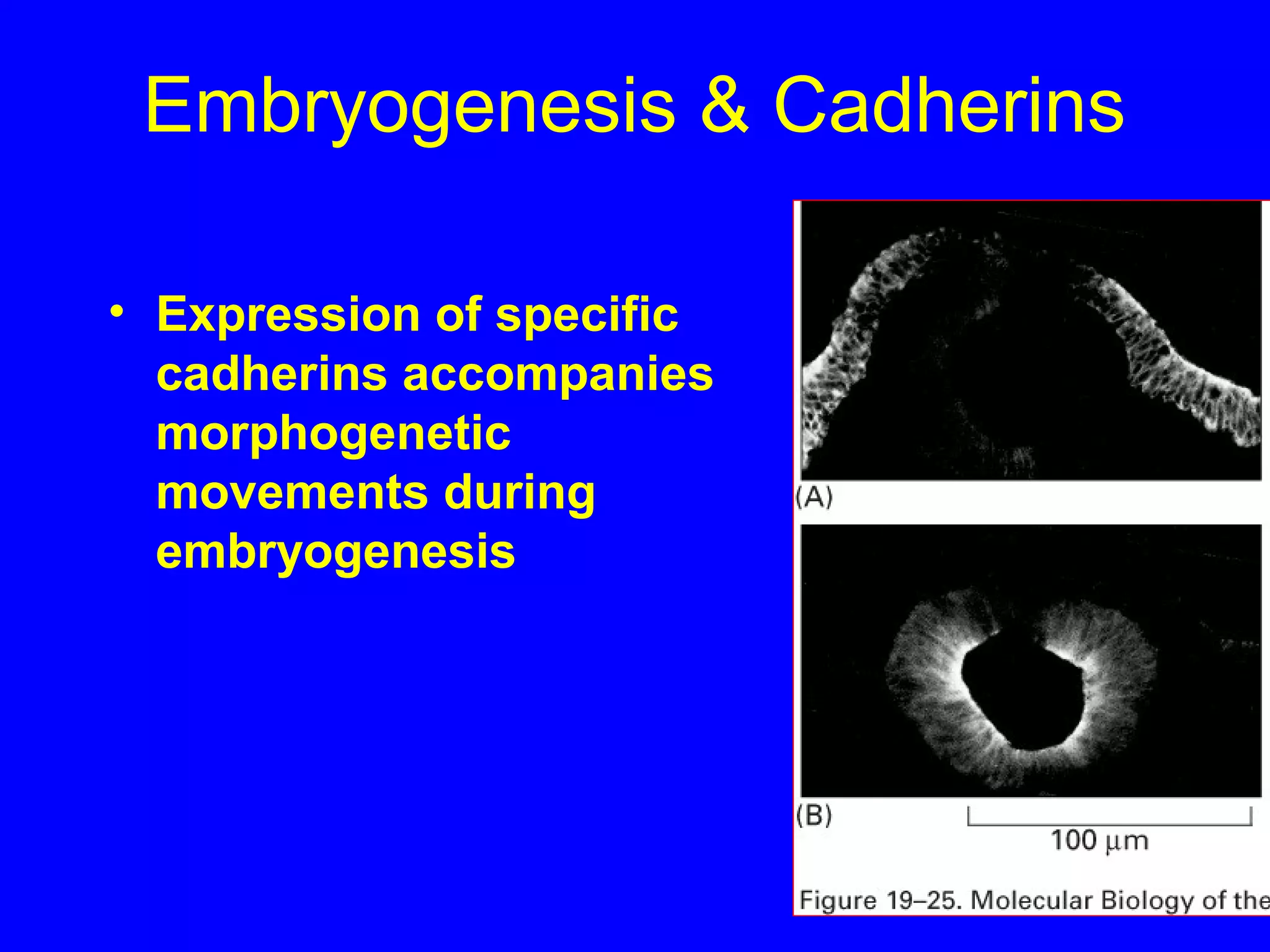
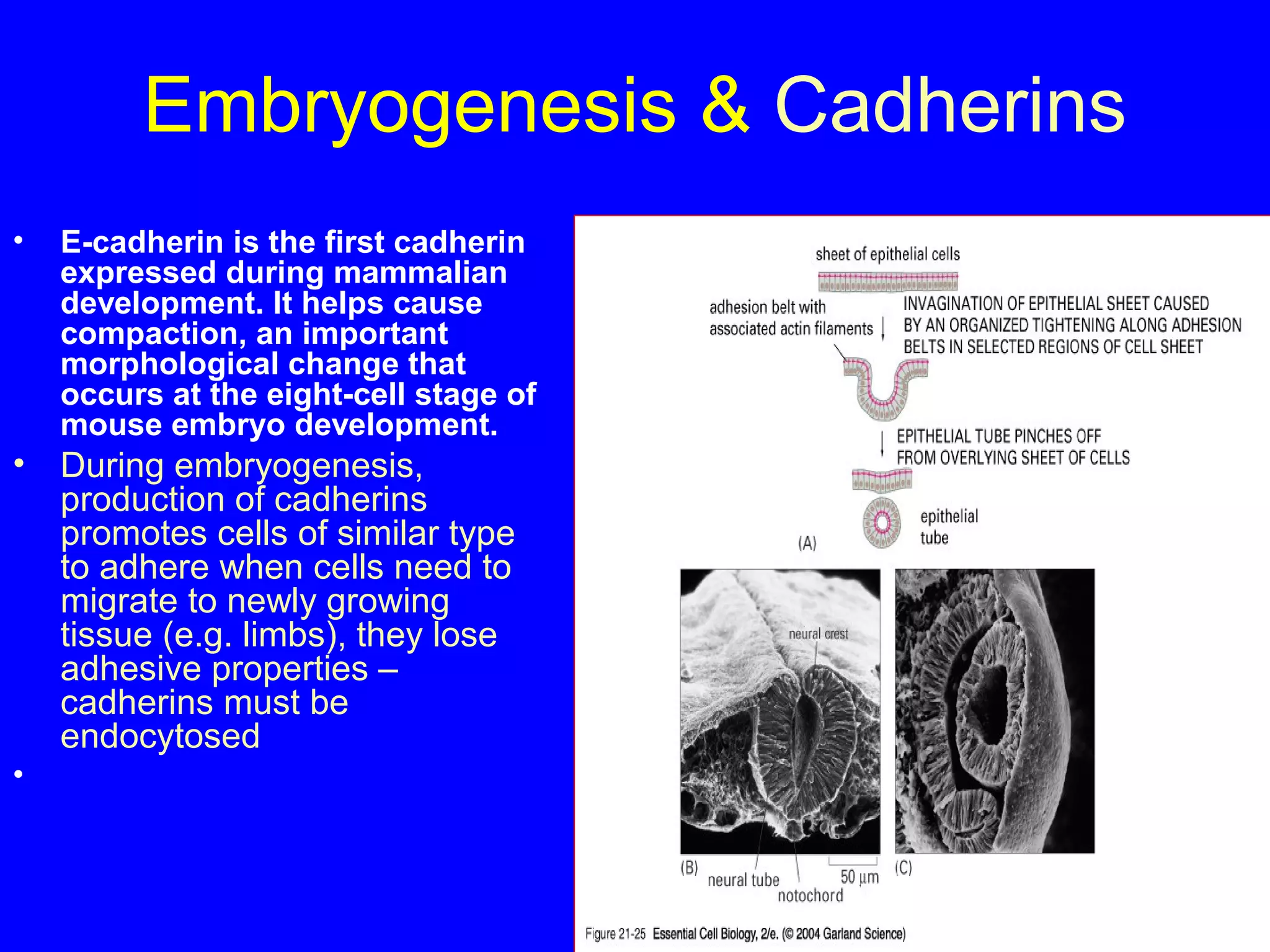
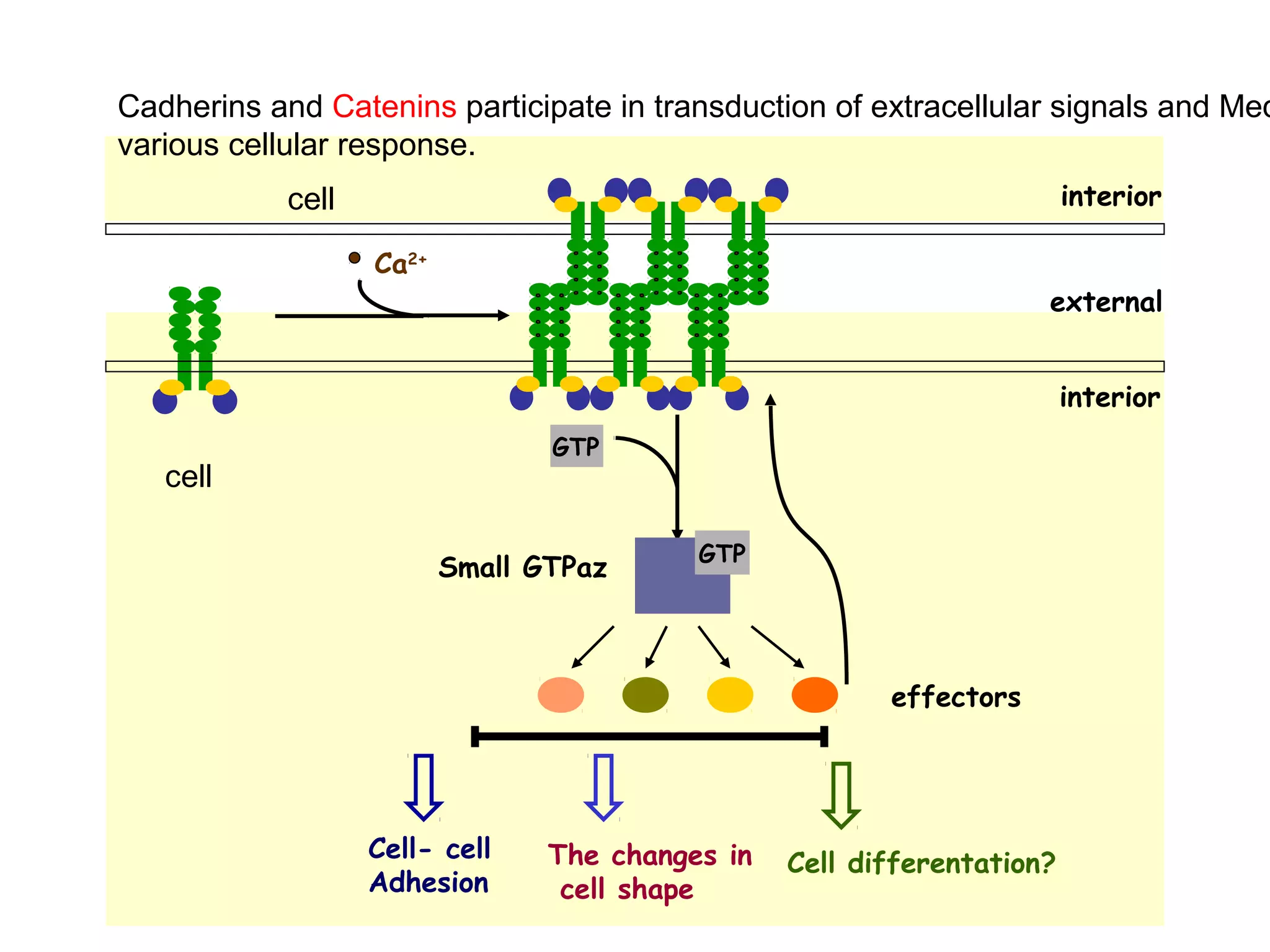
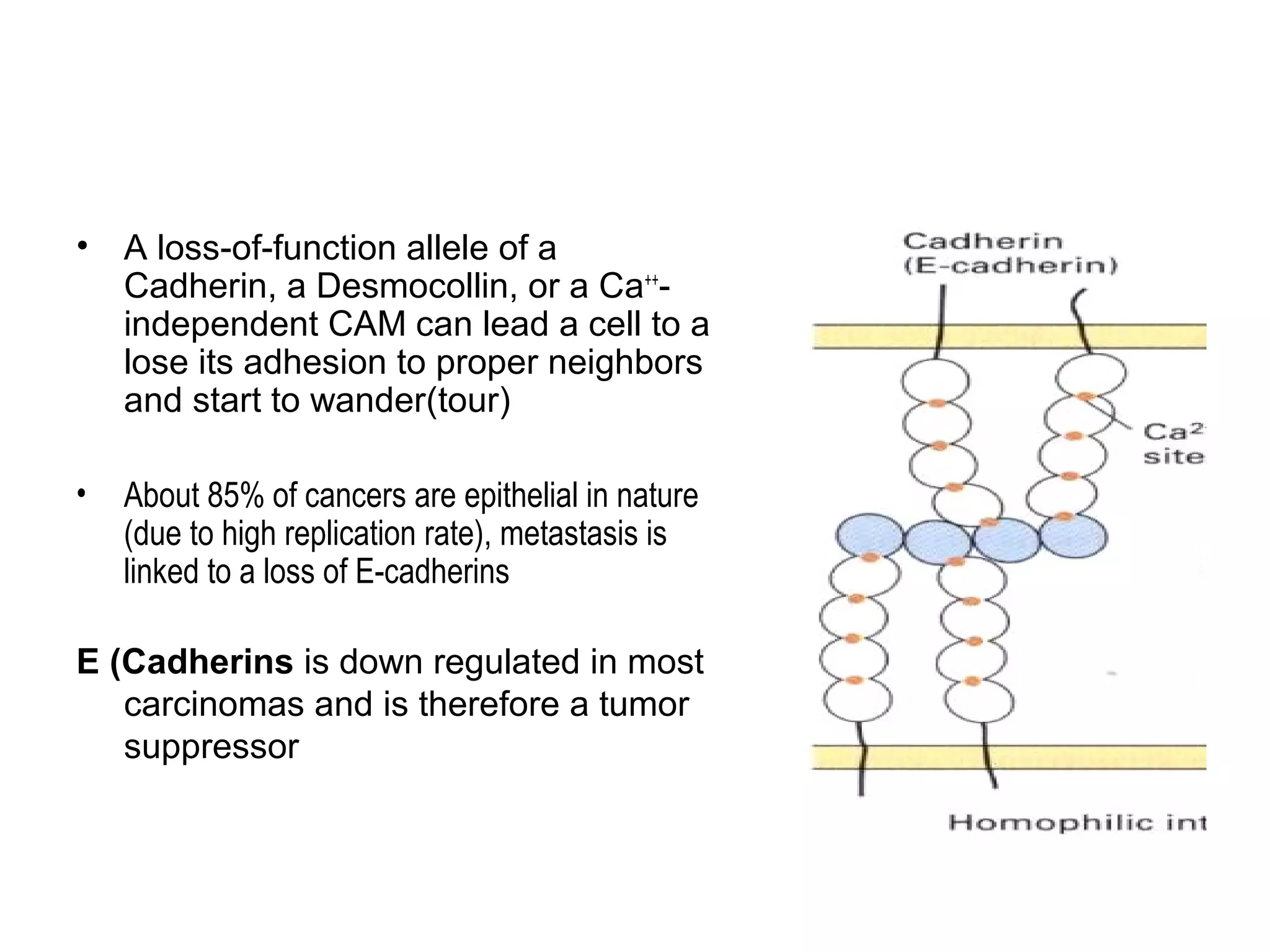
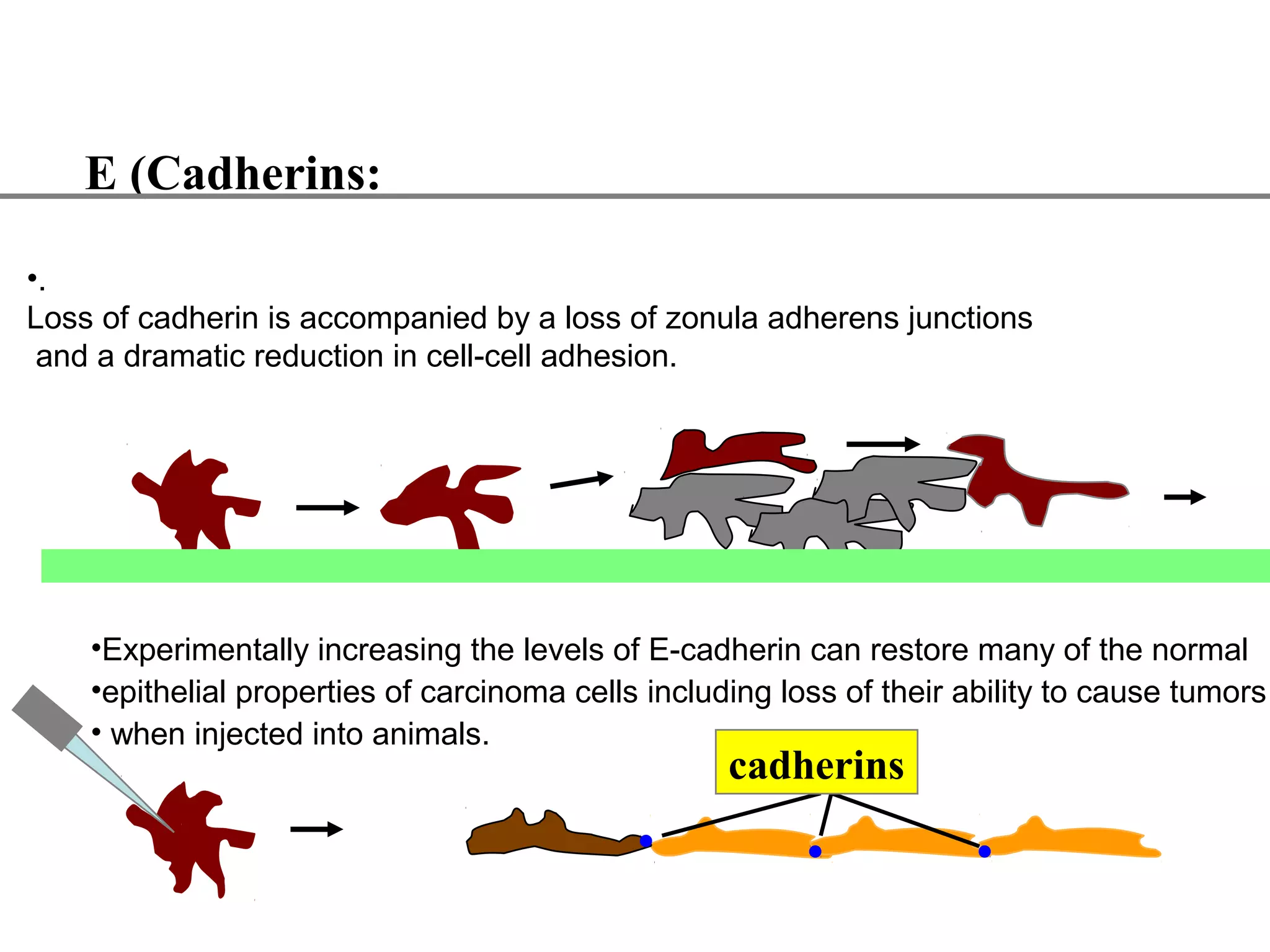
2) Cadherins are calcium-dependent CAMs that mediate homophilic adhesion between cells of the same type. They link to the actin cytoskeleton via catenins. Cadherins play important roles in tissue formation and embryogenesis.
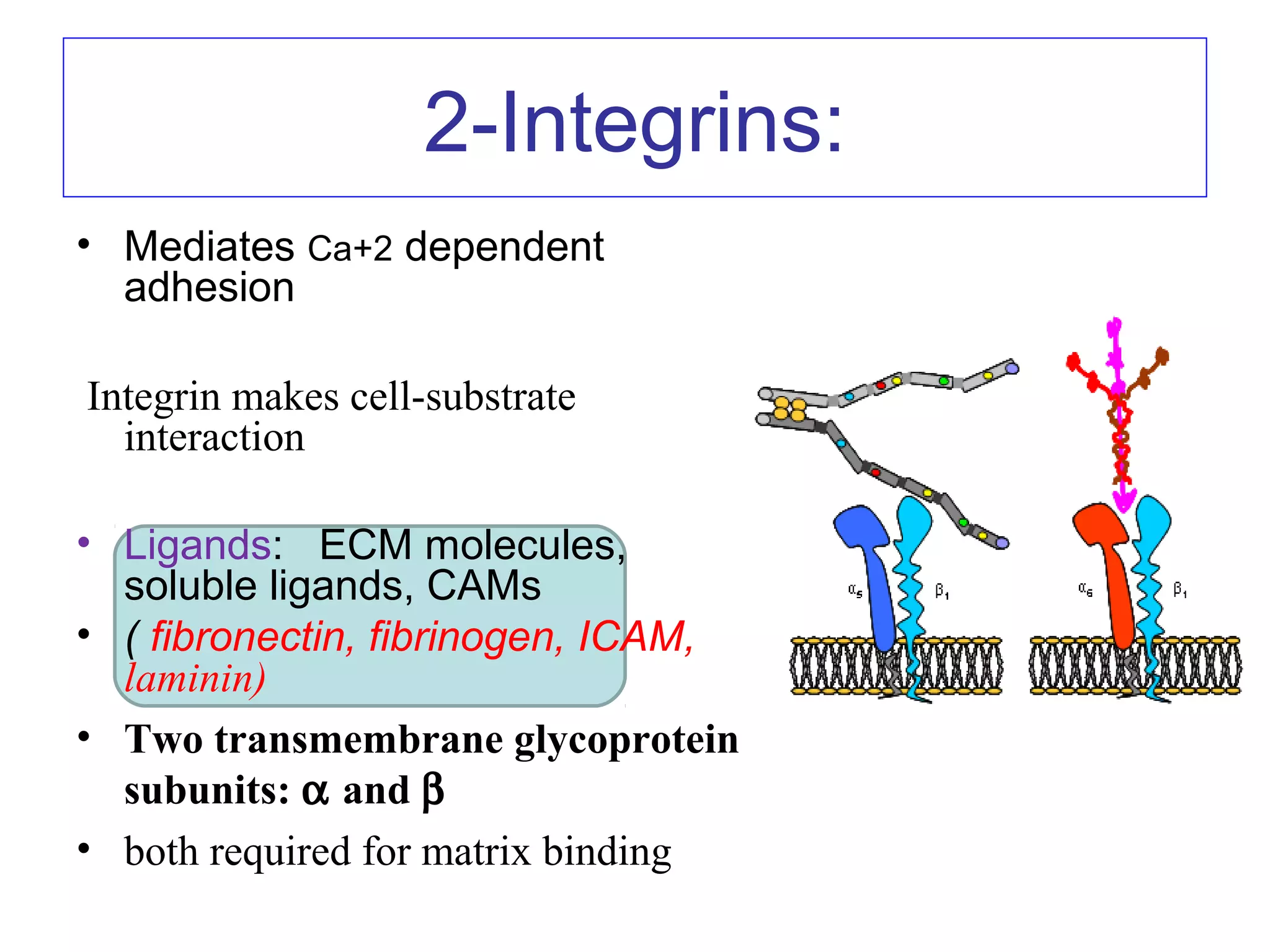
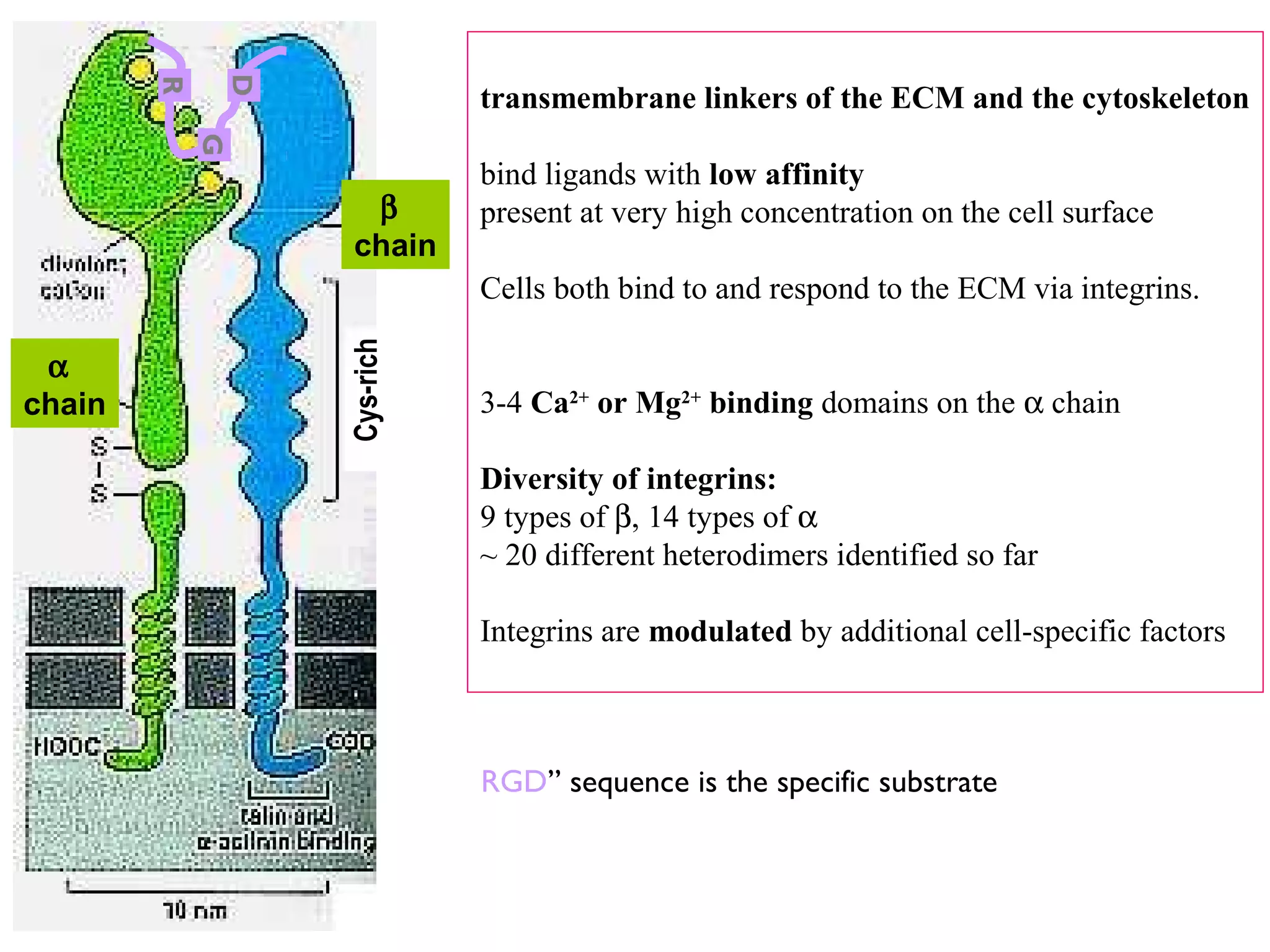
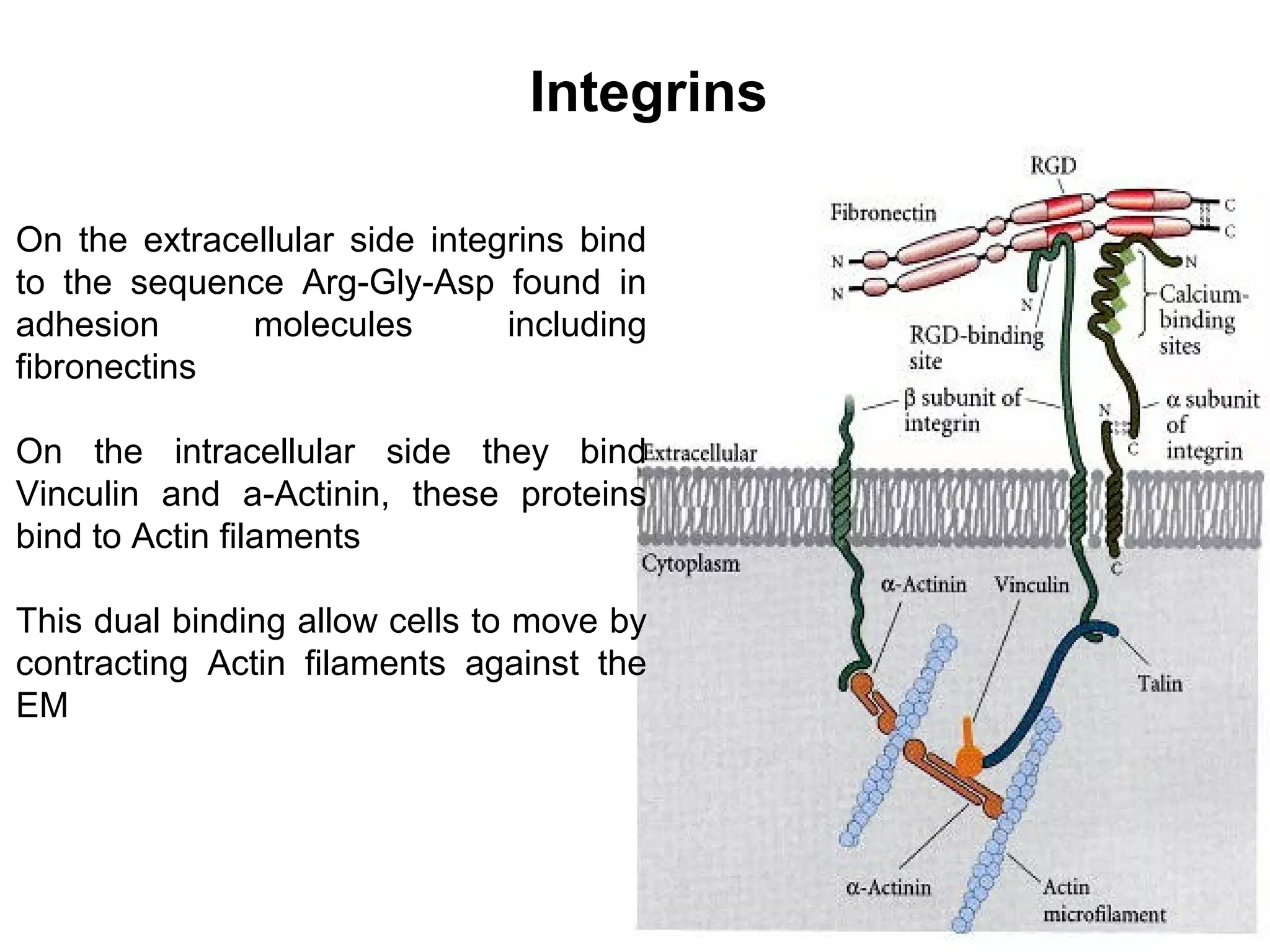
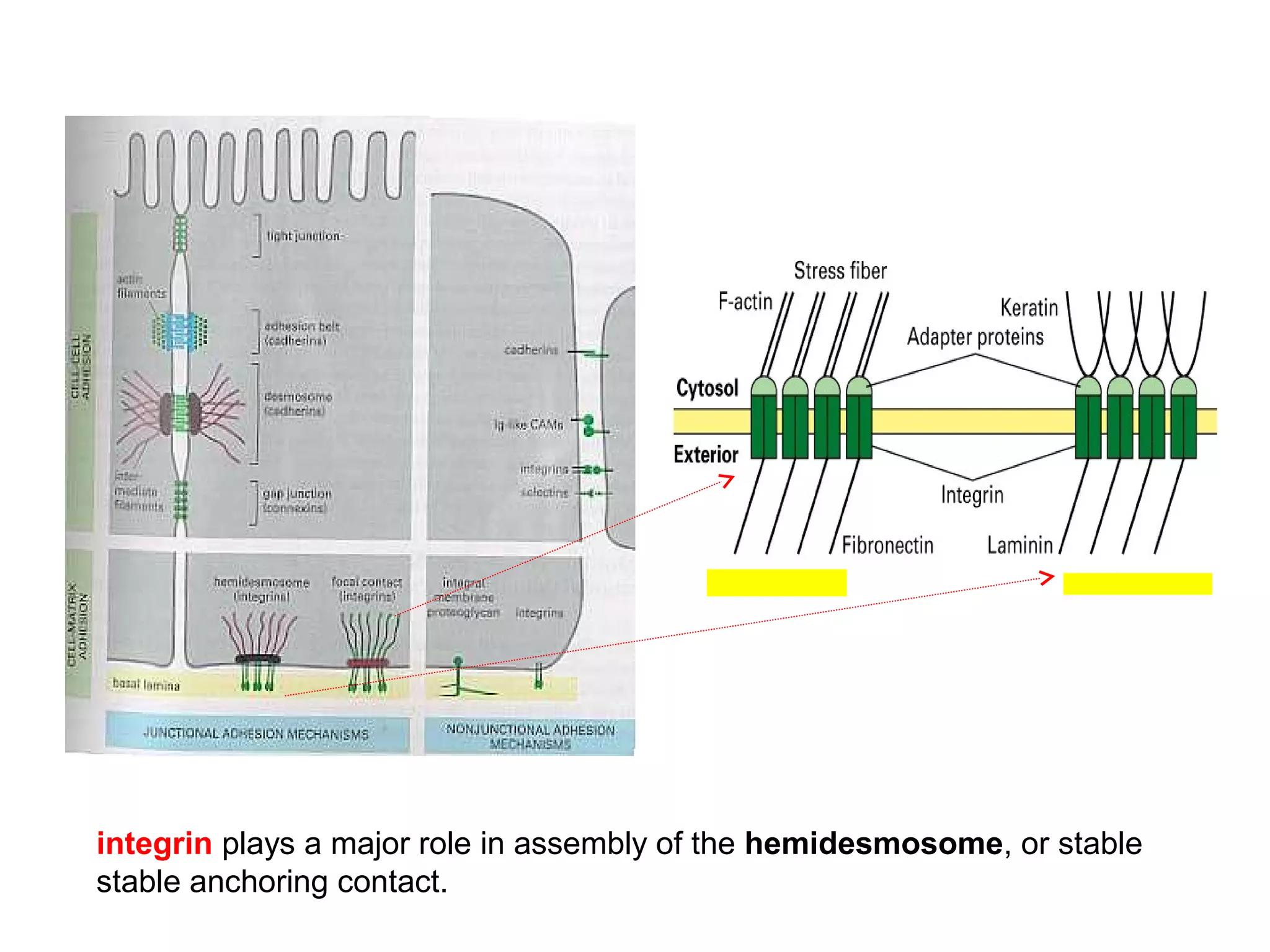
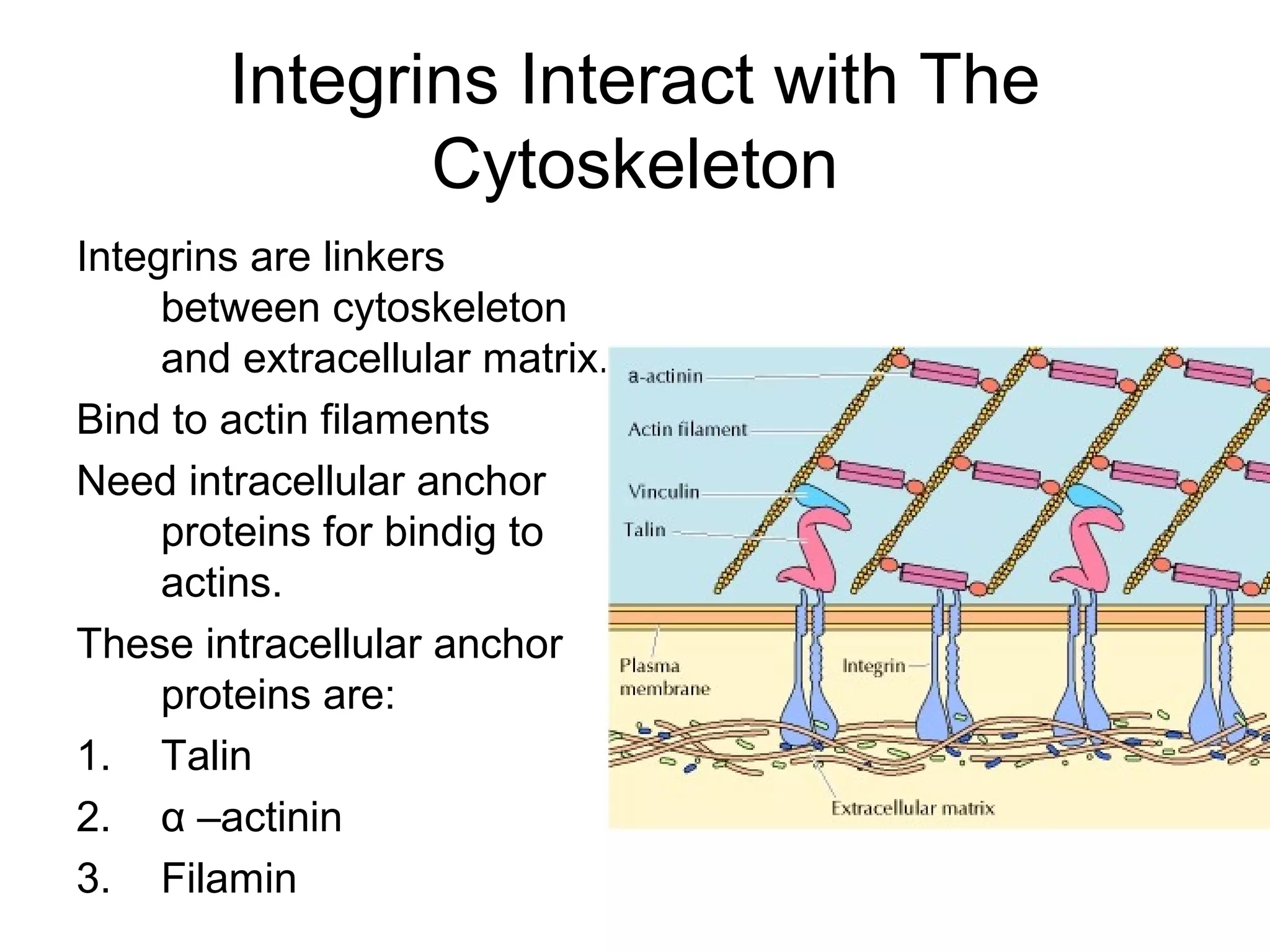
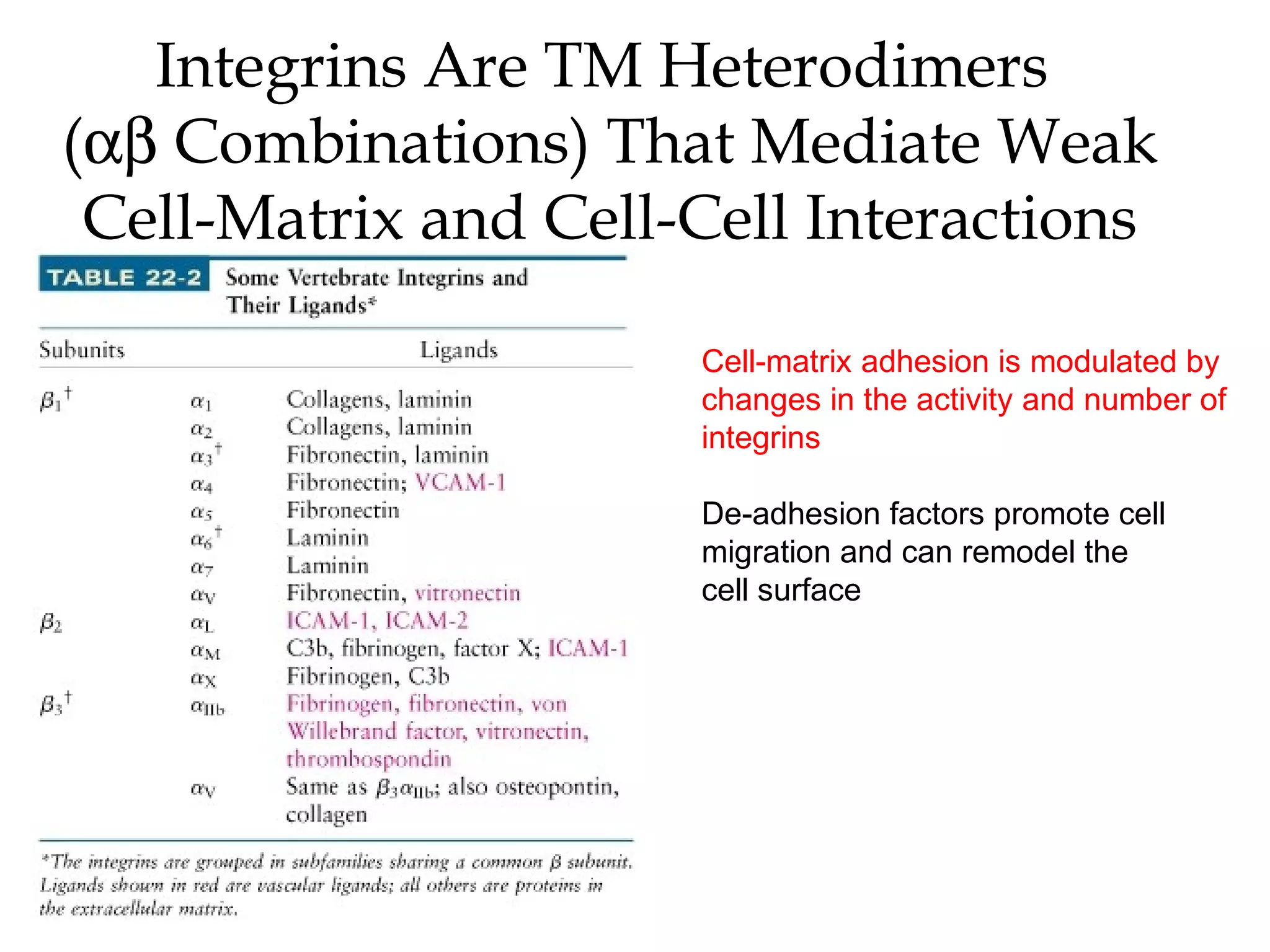
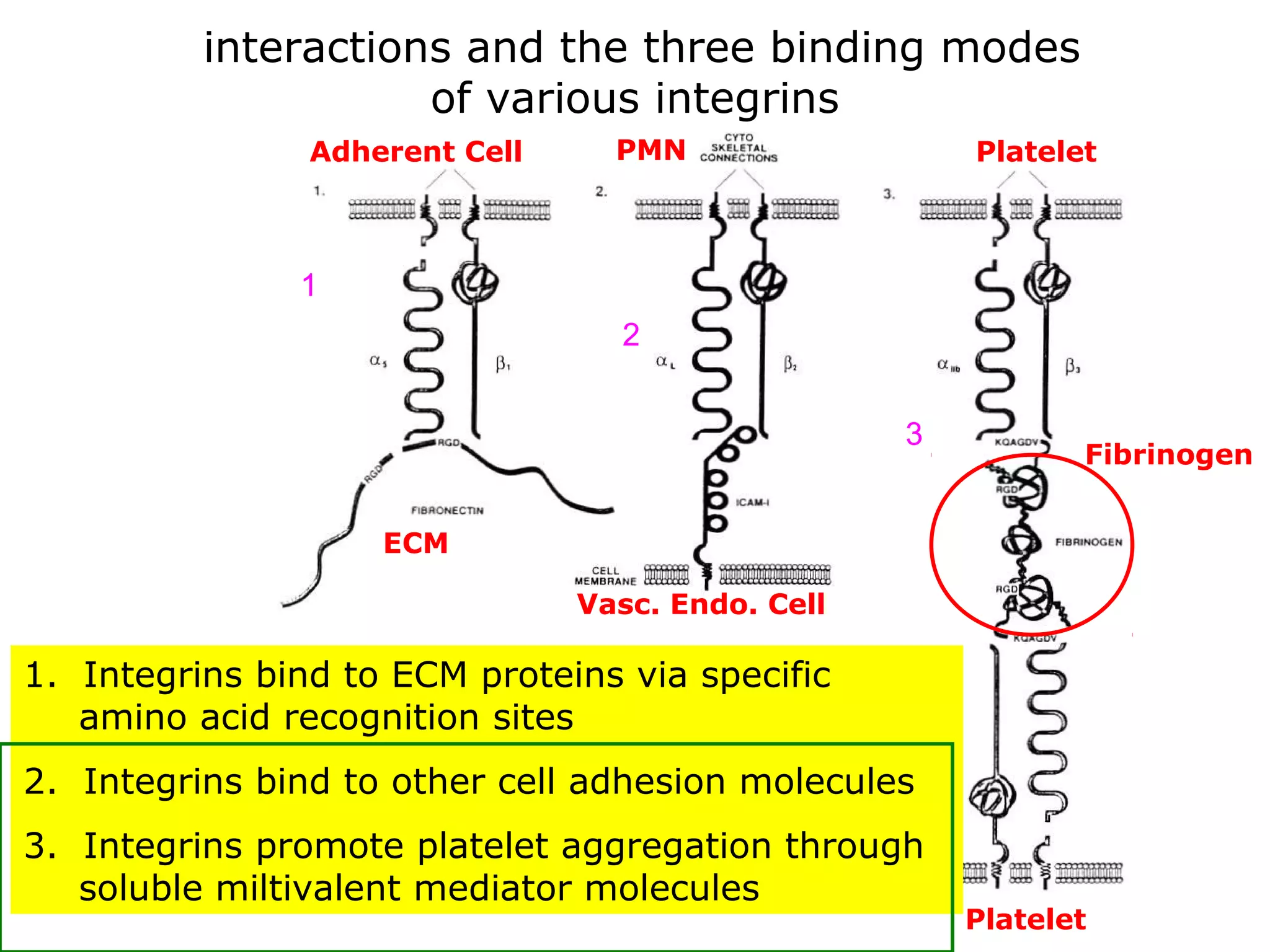
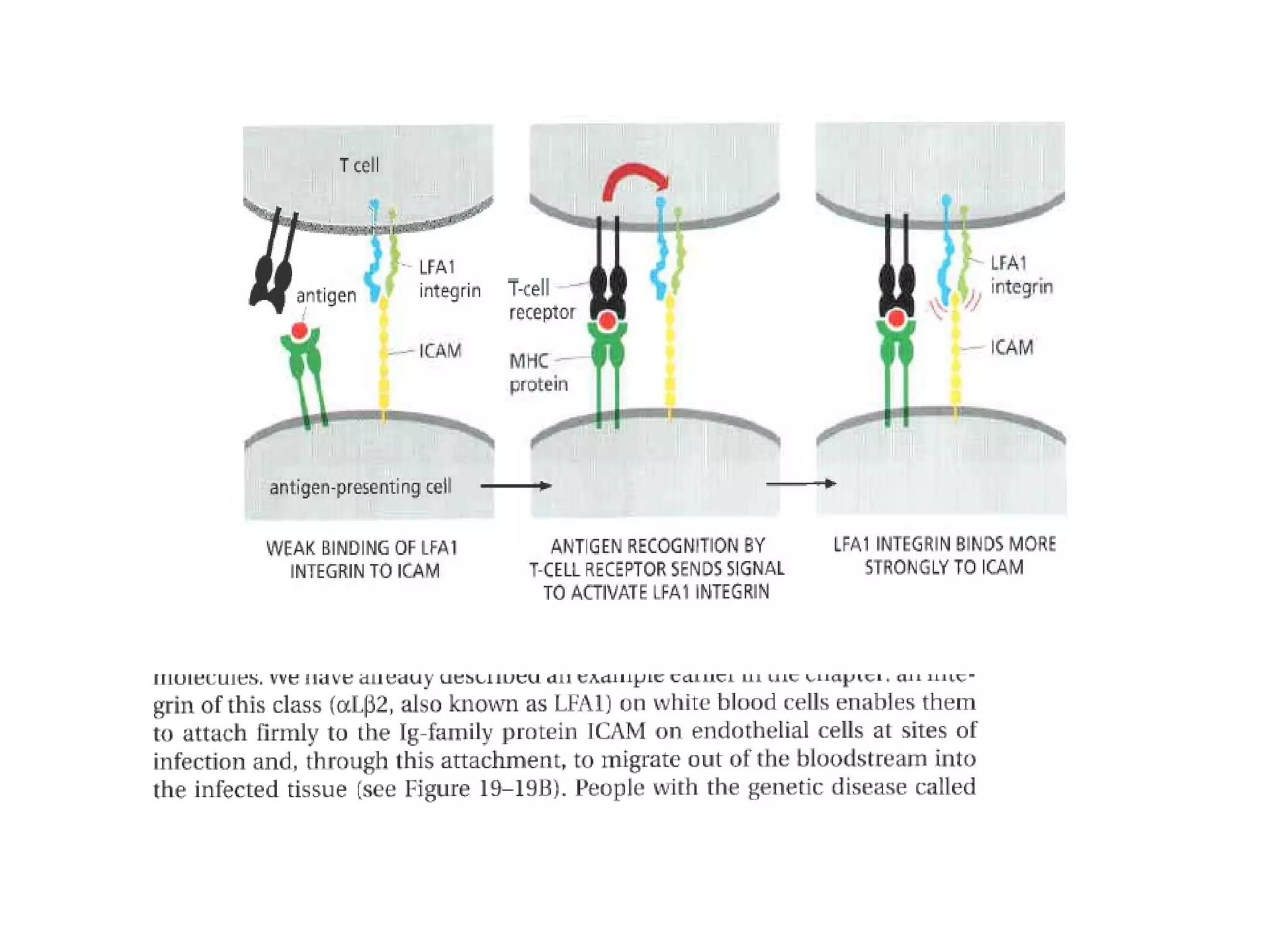
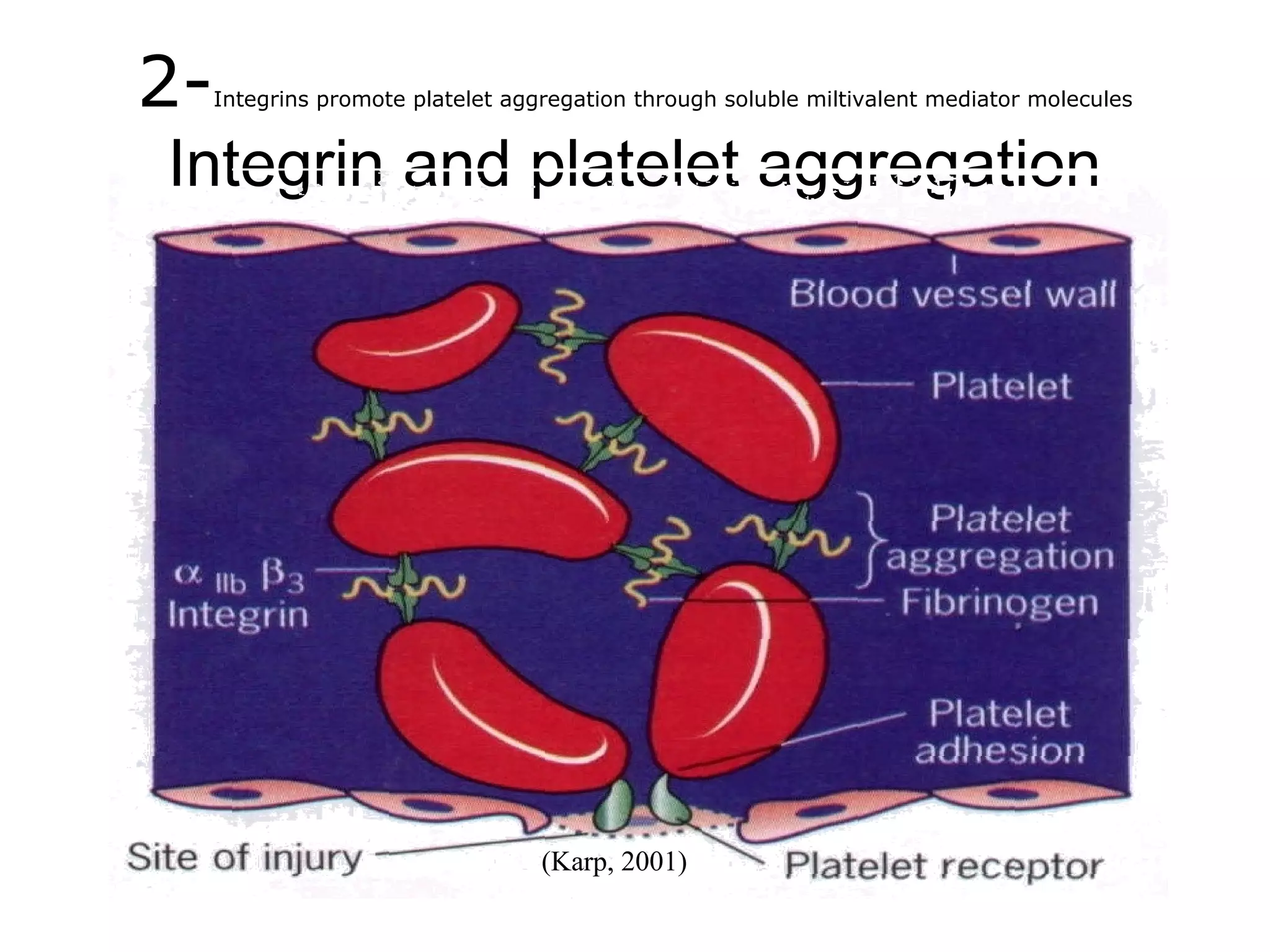
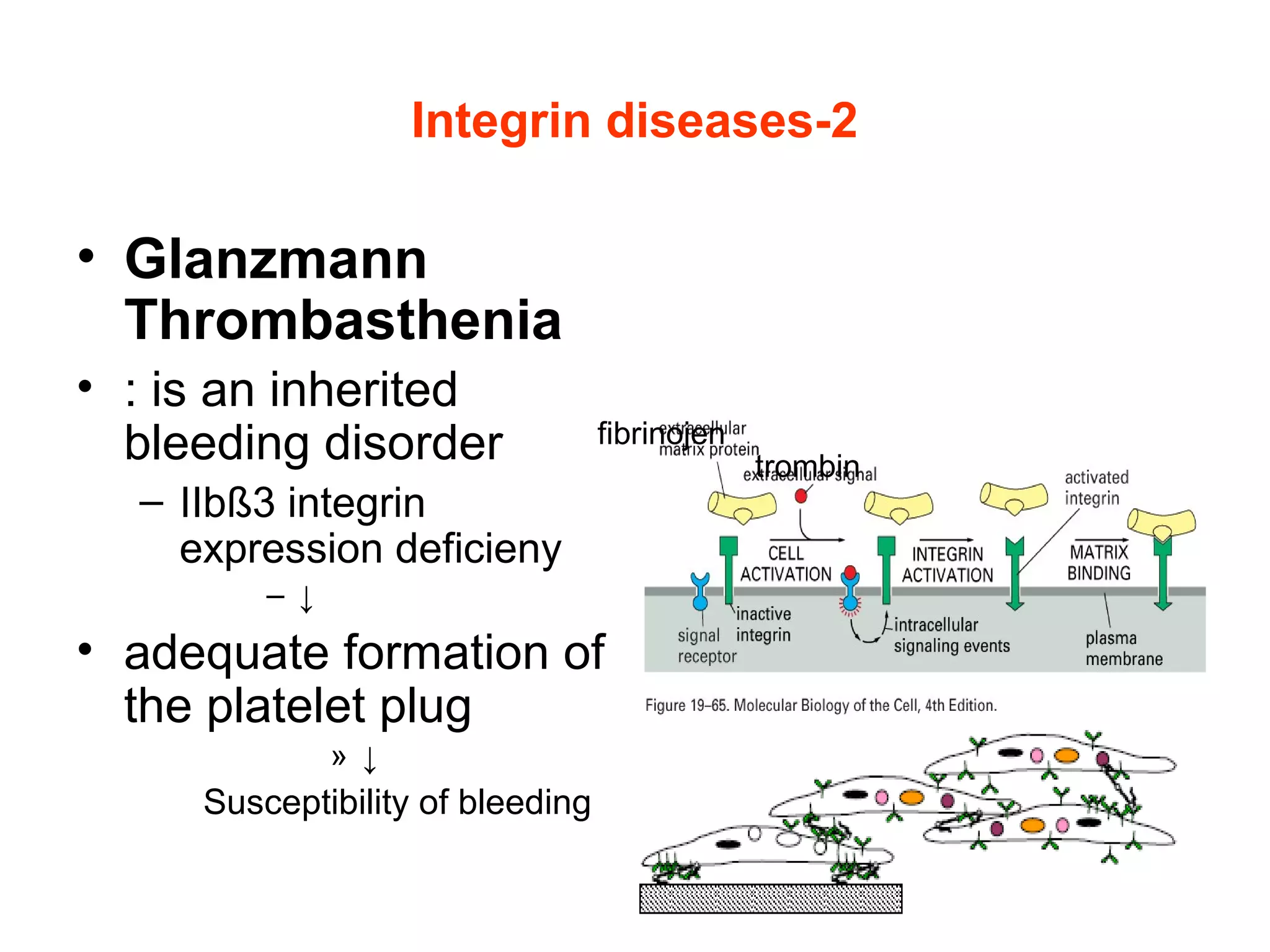
3) Integrins are heterodimeric CAMs composed of alpha and beta subunits. They mediate calcium-dependent adhesion between cells and the extracellular matrix by binding ligands like fibronectin and laminin. Integrins also