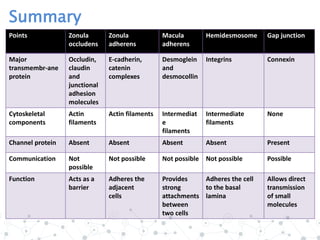
This document summarizes different types of cell junctions, including their structure, location, functions, and major proteins. It discusses tight junctions (zonula occludens), which form a seal between cells and control molecule passage. Adherent junctions (zonula adherens) firmly anchor cells together. Desmosomes (macula adherens) provide strong intermediate filament coupling between cells. Gap junctions allow exchange of molecules between cells. Hemidesmosomes anchor the cell cytoskeleton to the basal lamina.