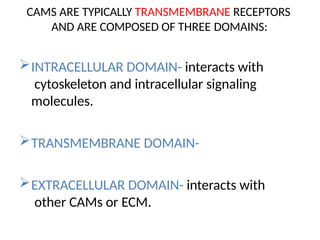
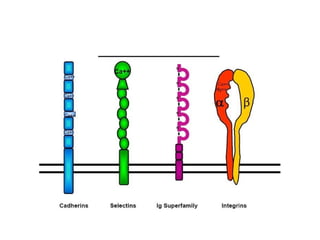
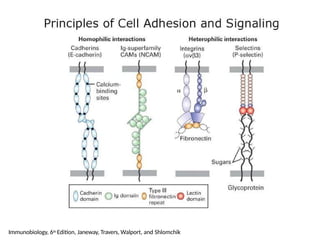
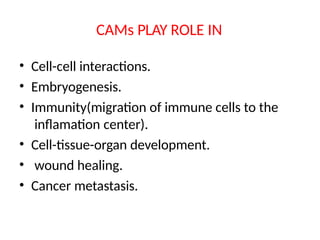
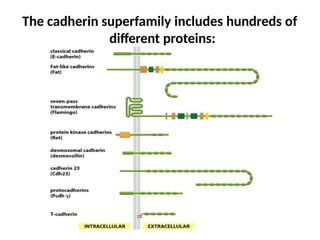
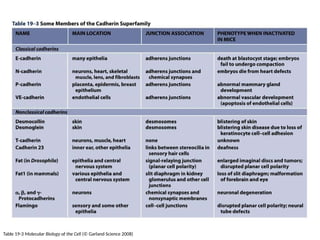
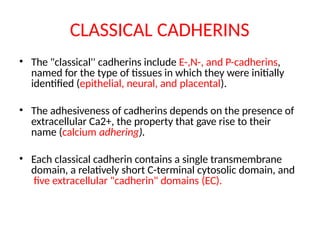
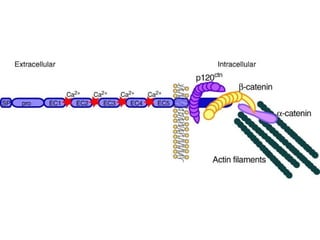
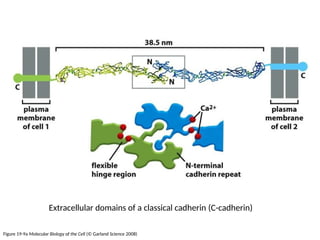
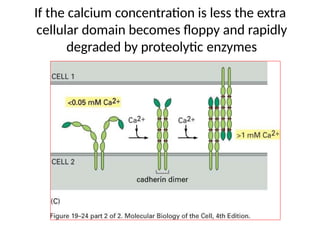
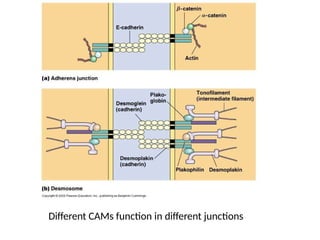
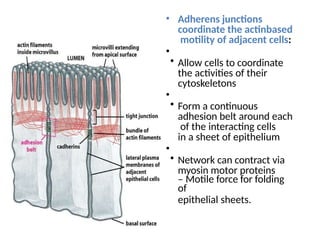
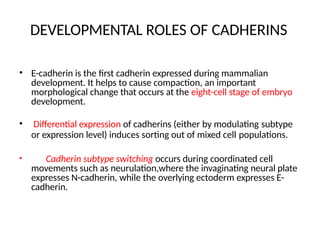
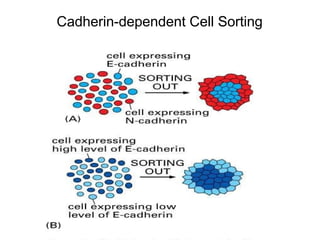
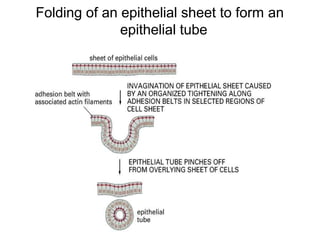
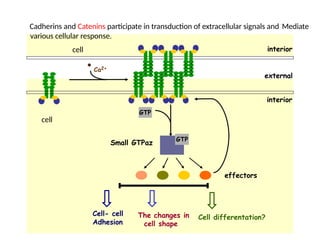
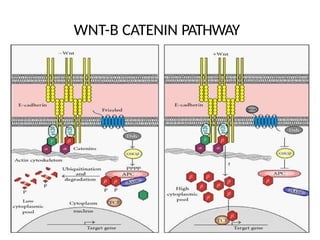
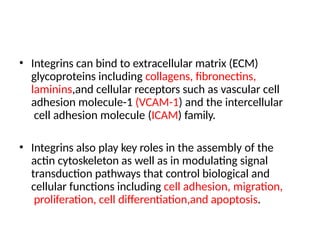
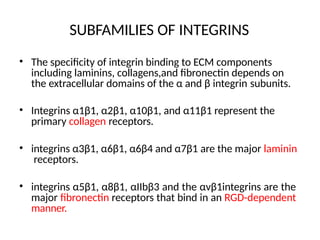
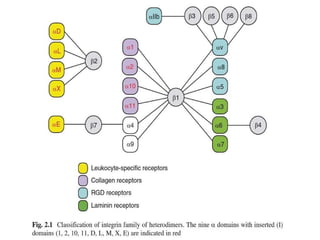
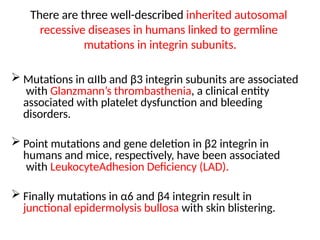
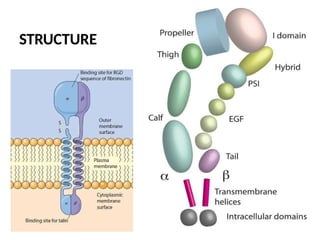
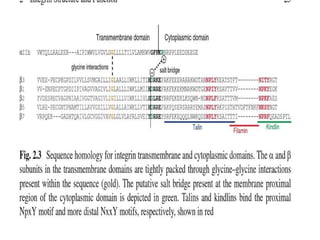
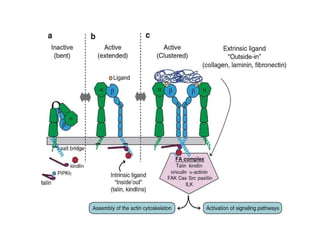
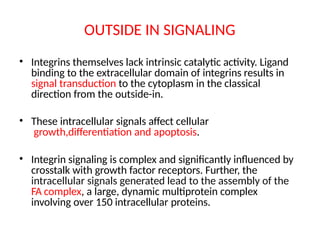
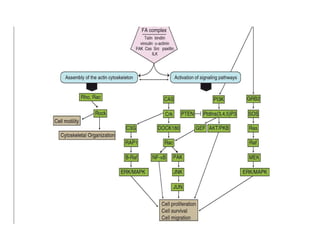
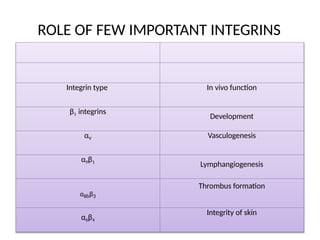
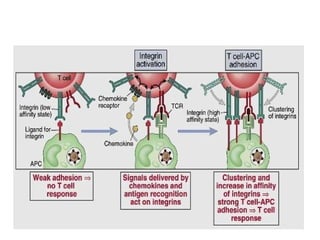
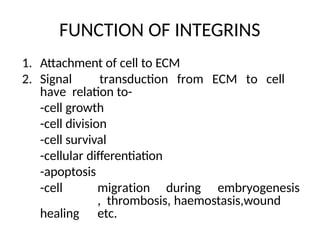
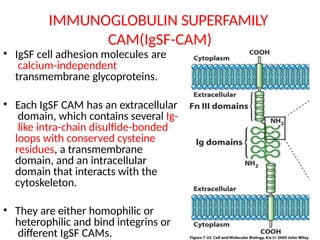
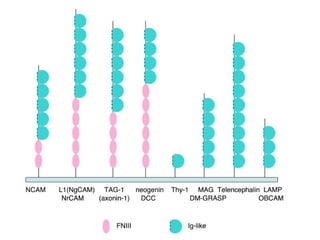
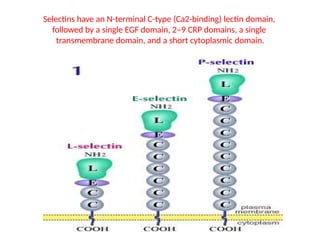
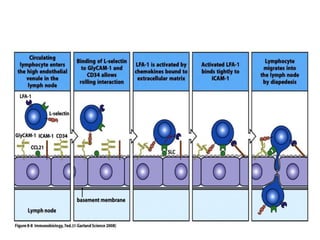
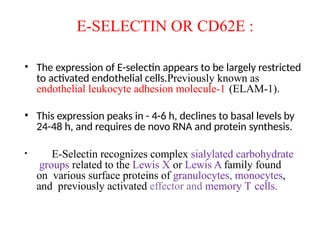
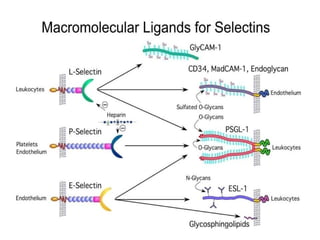
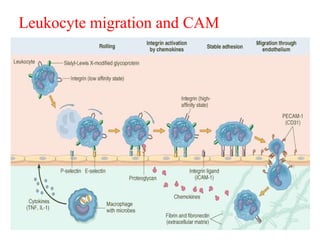
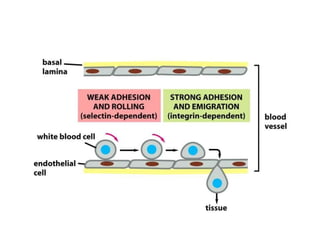
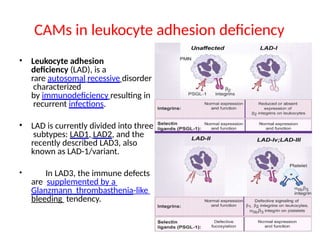
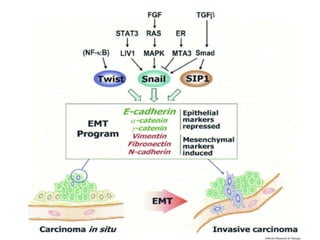
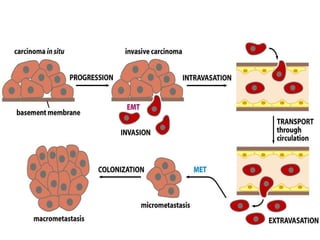
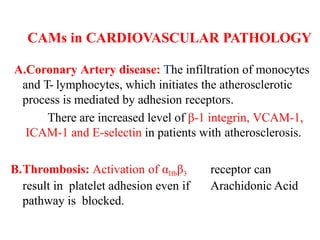
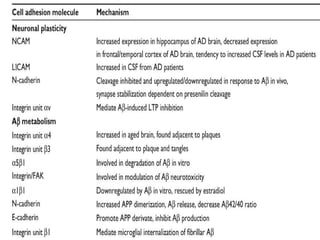
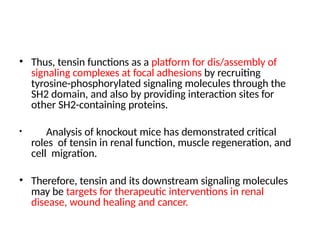
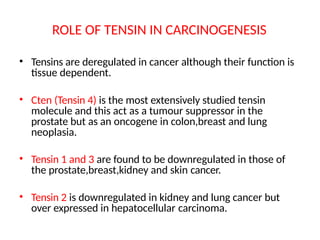
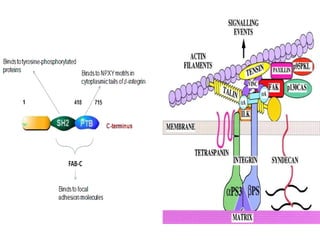
This document discusses the essential roles of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) in tissue formation, cellular communication, and various biological processes including embryogenesis, immunity, and cancer metastasis. It highlights the classification of CAMs into families such as cadherins, integrins, immunoglobulin superfamily, and selectins, and details their structures, functions, and significance in health and disease. The document also emphasizes the importance of specific CAM interactions in cellular stability and signaling within tissues and organs.