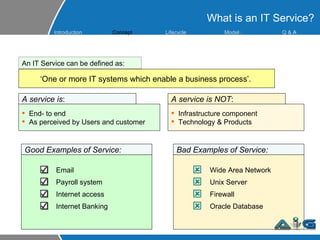
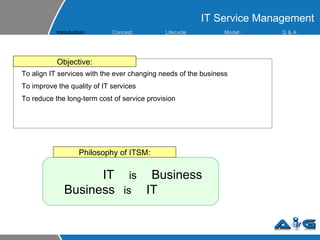
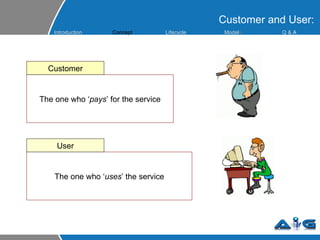
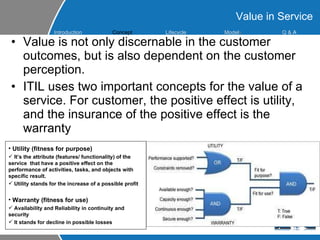
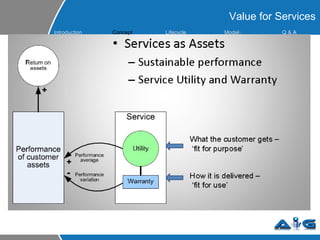
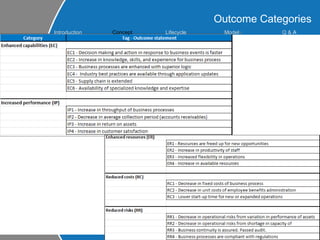
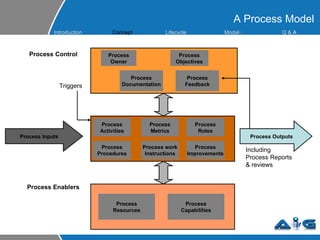
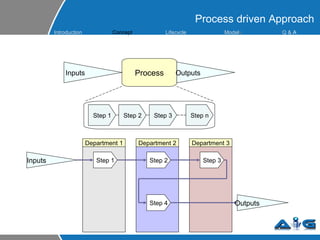
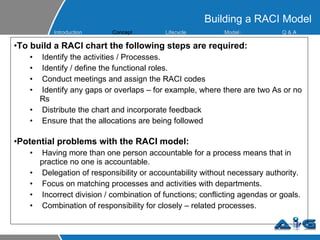
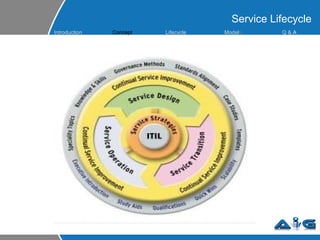
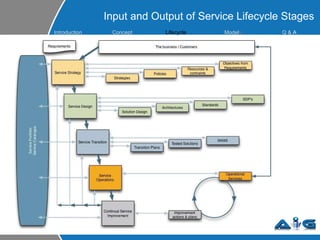
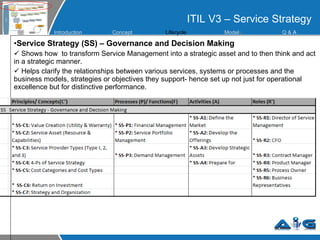
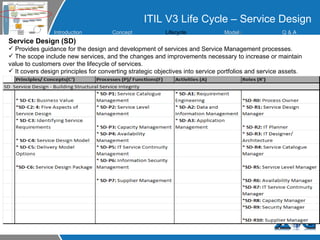
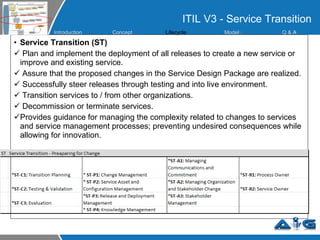
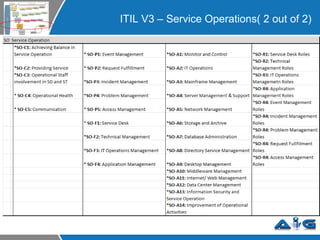
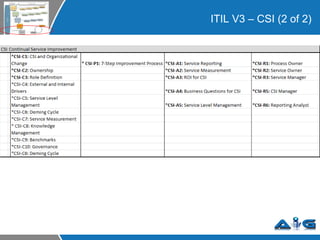
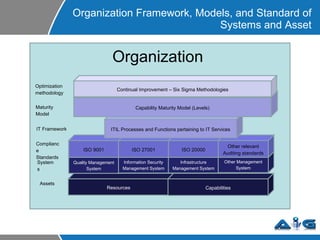
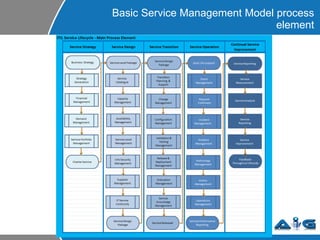
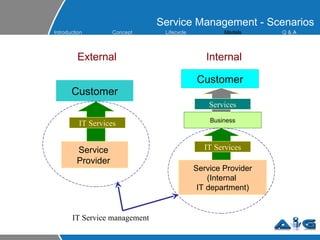
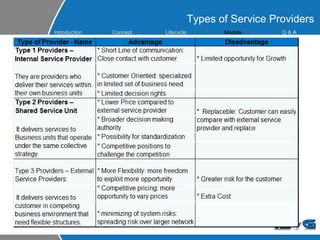
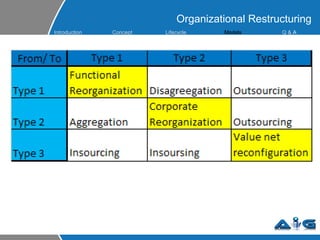
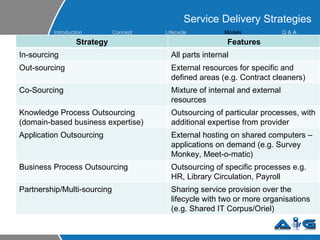
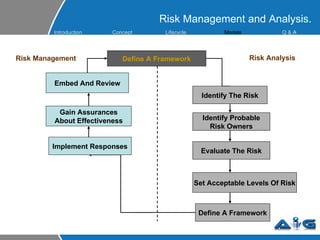
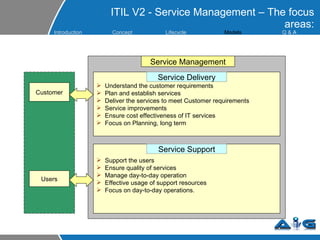
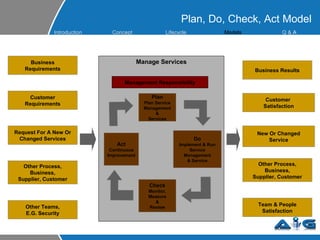
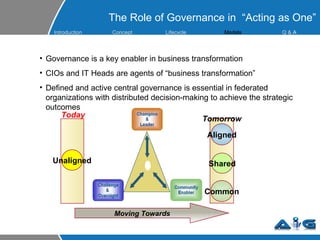
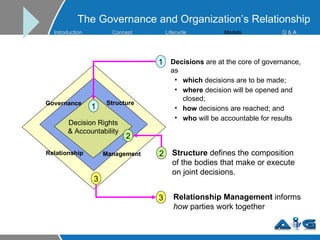
This document provides an overview of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) concepts including the ITIL service lifecycle. It defines key terms like service, service management, and discusses ITIL versions 2 and 3. It also covers ITIL principles such as focusing on customer satisfaction and the strategic role of IT. Process models, organizational roles, and the five stages of the ITIL service lifecycle are outlined.