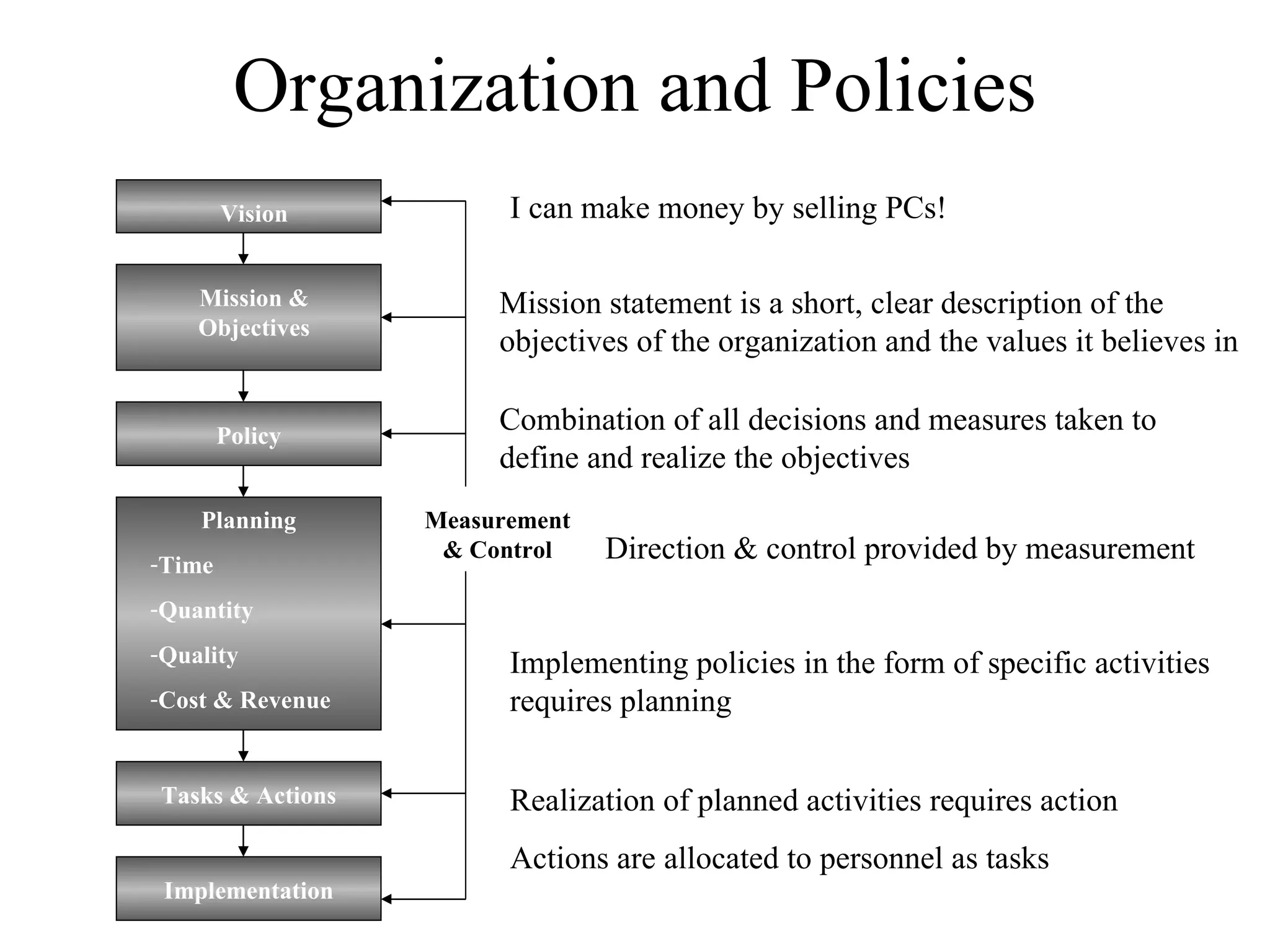
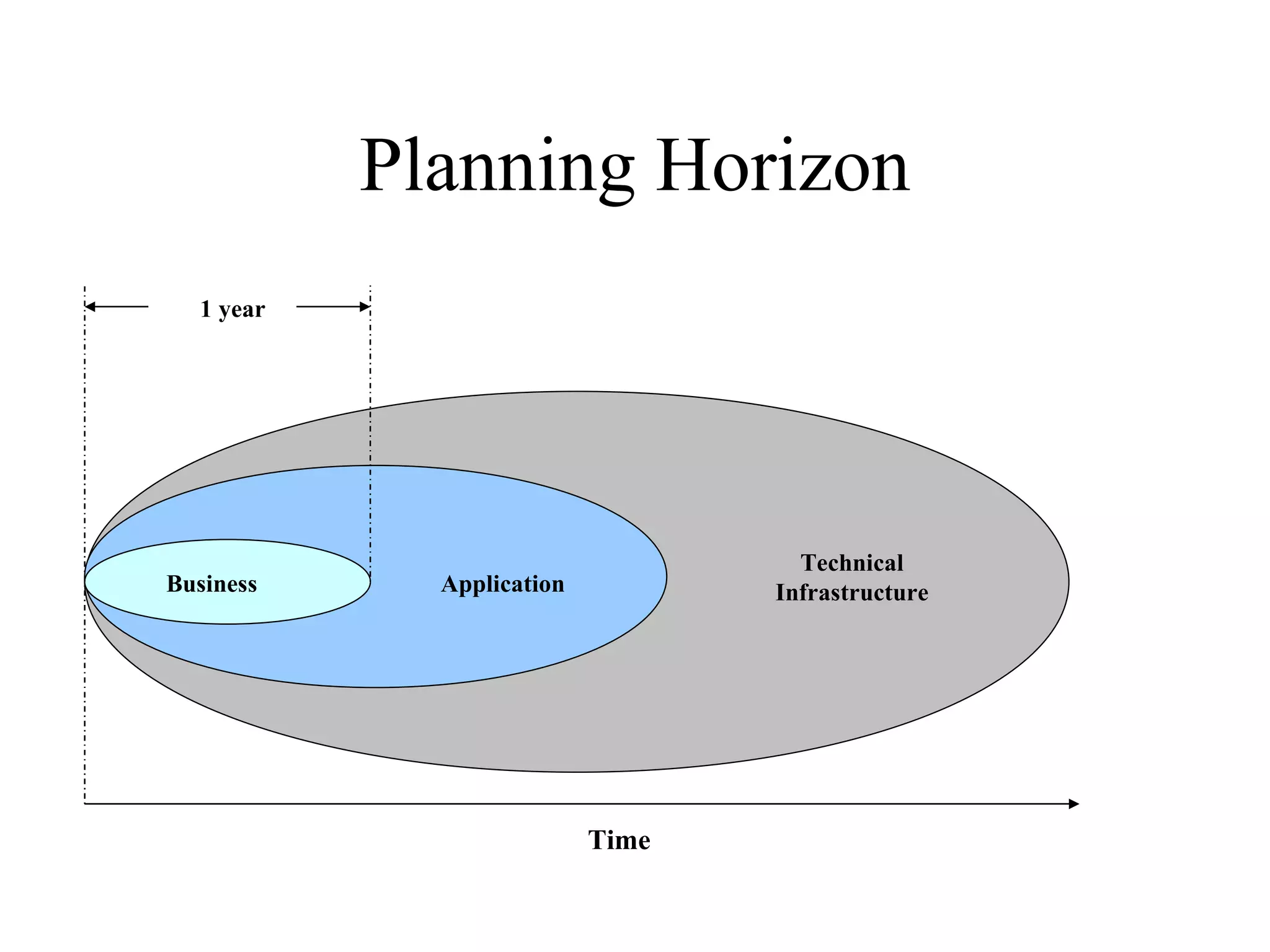
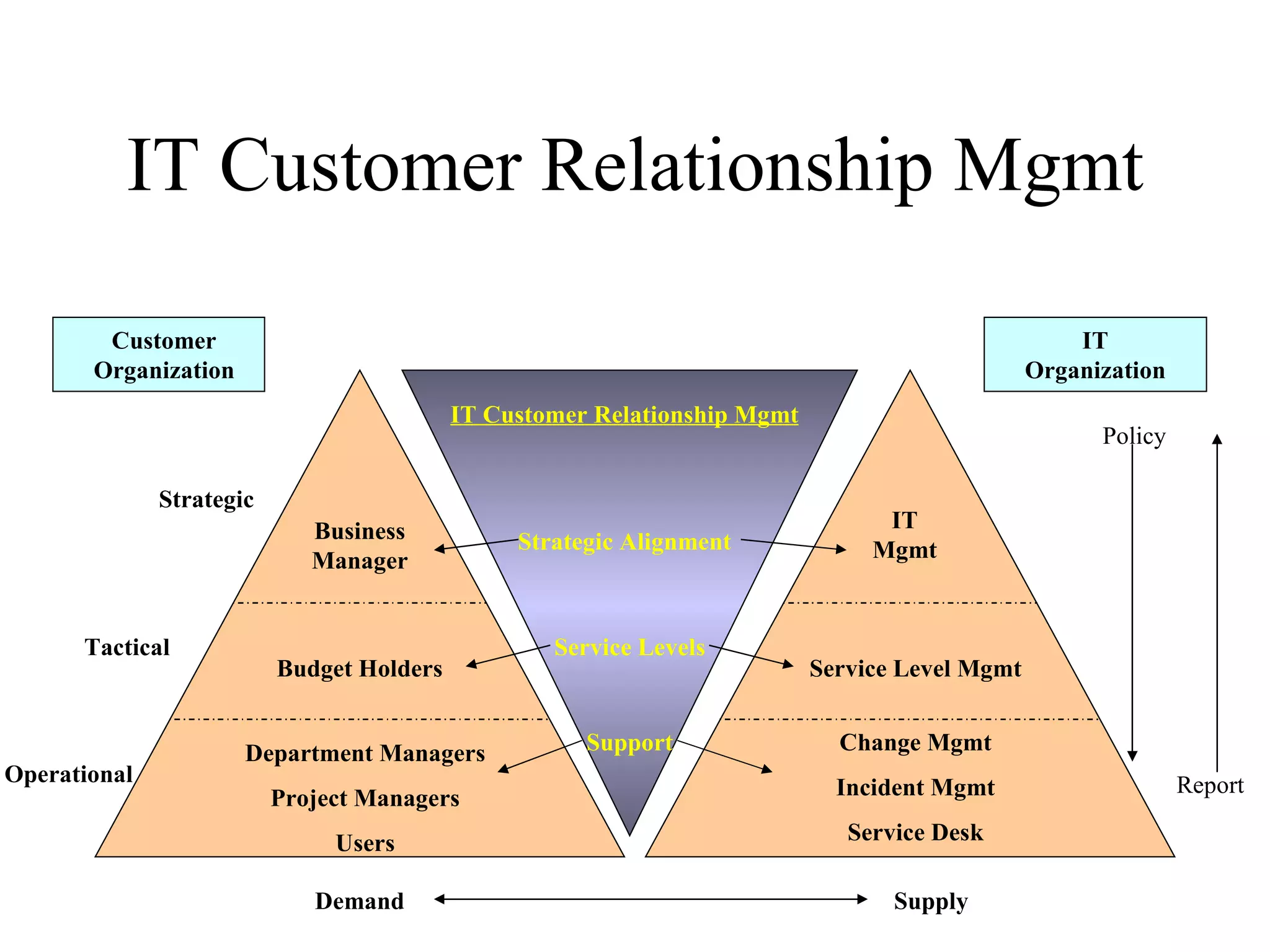
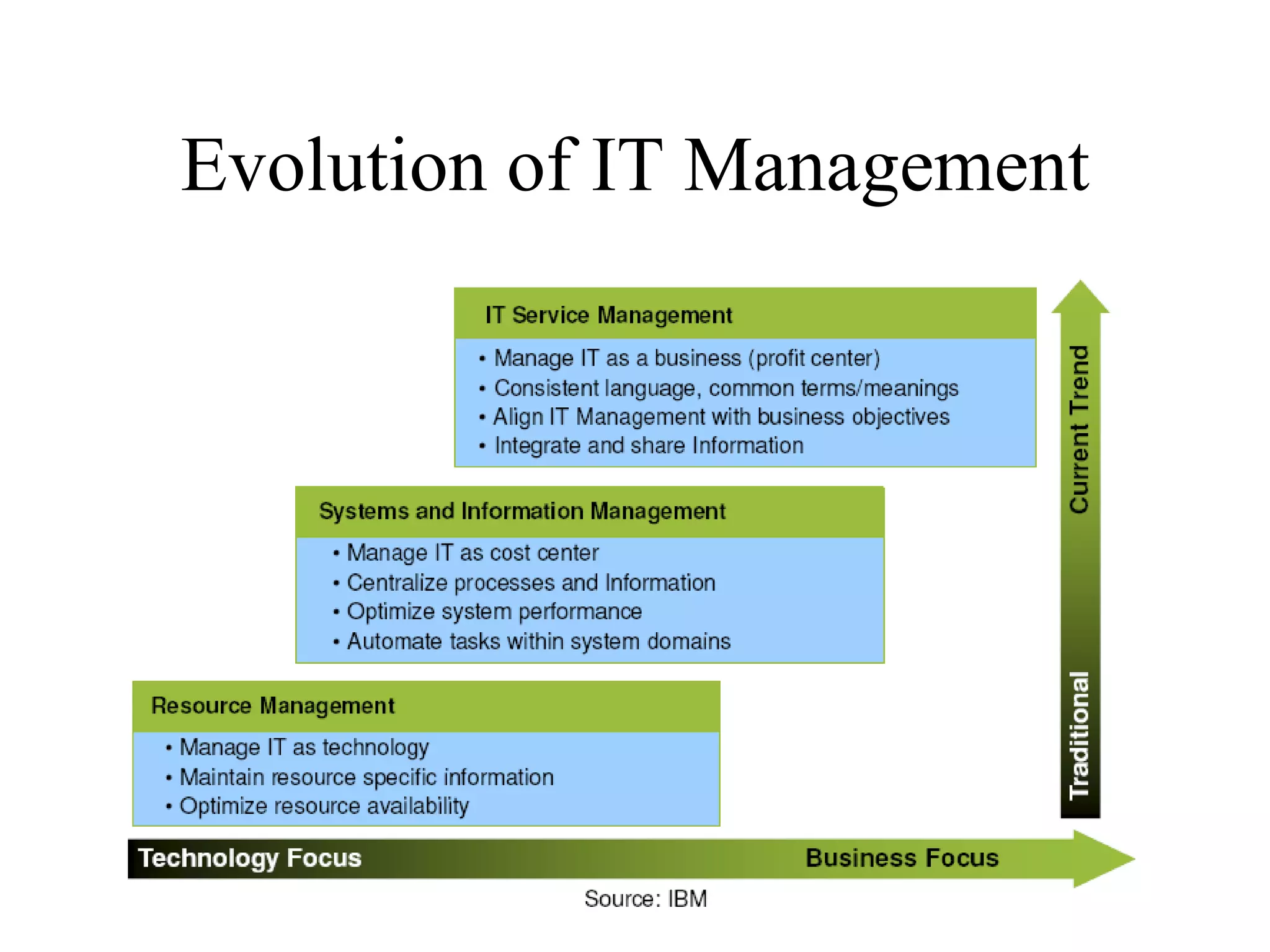
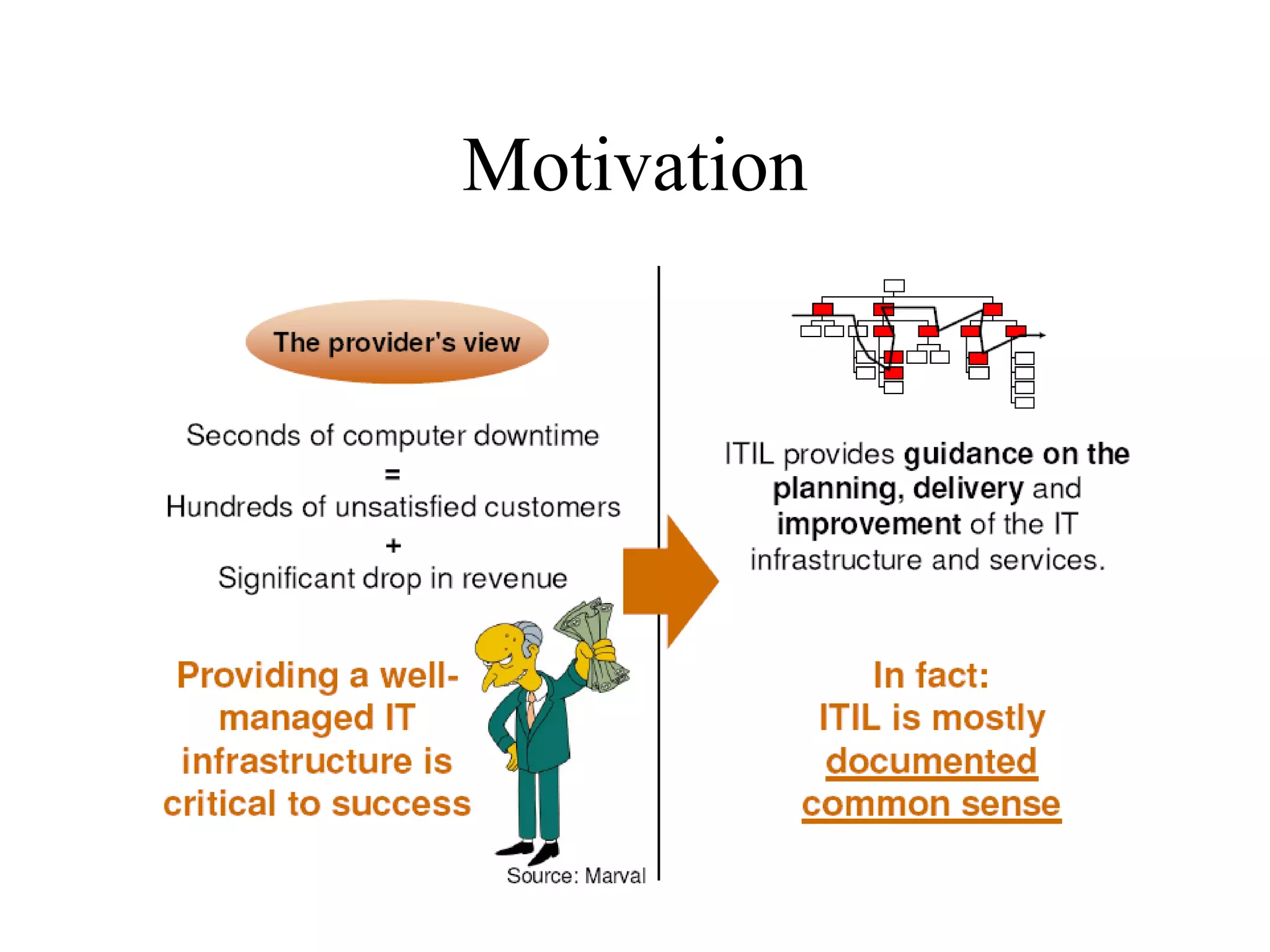
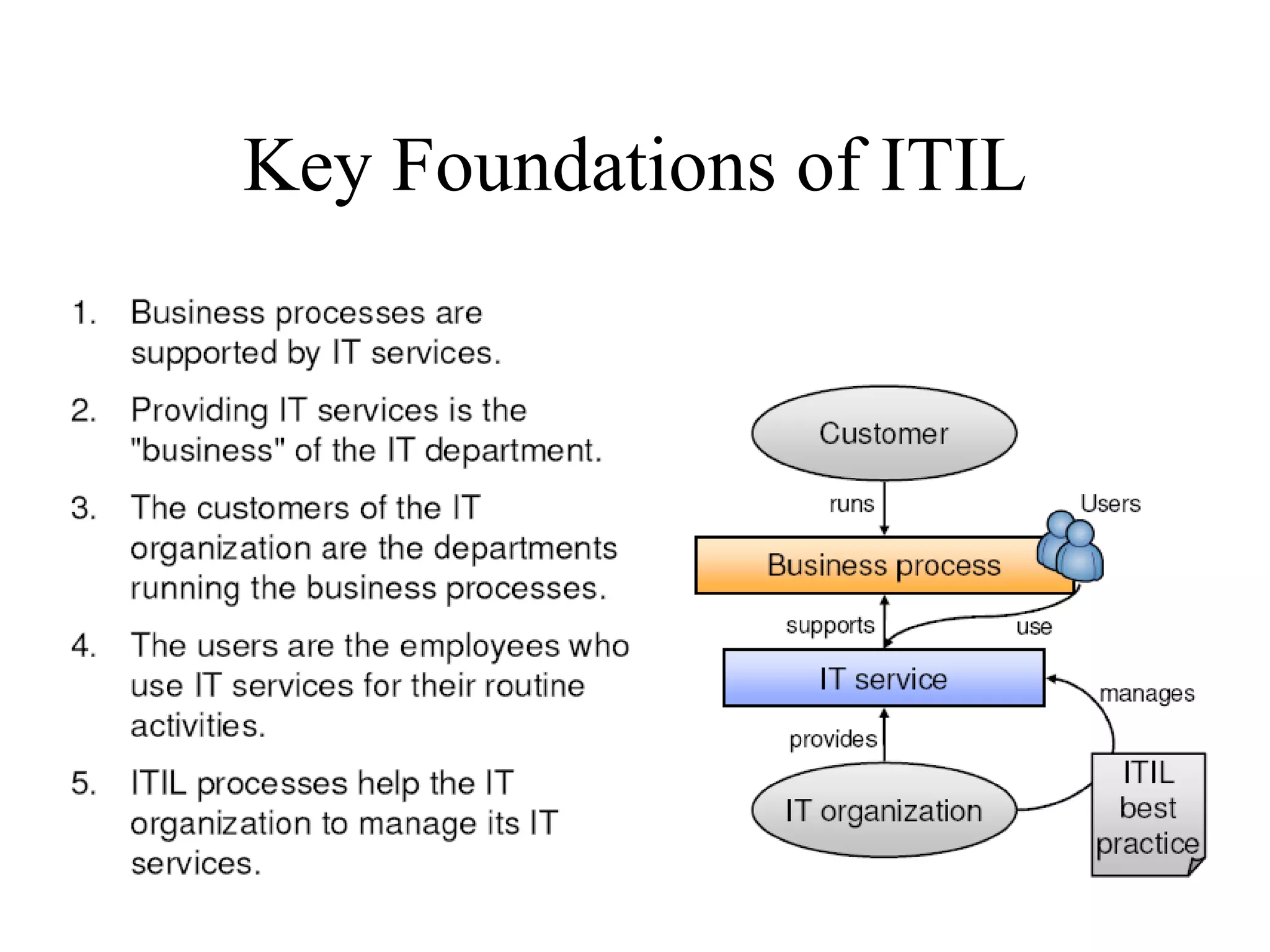
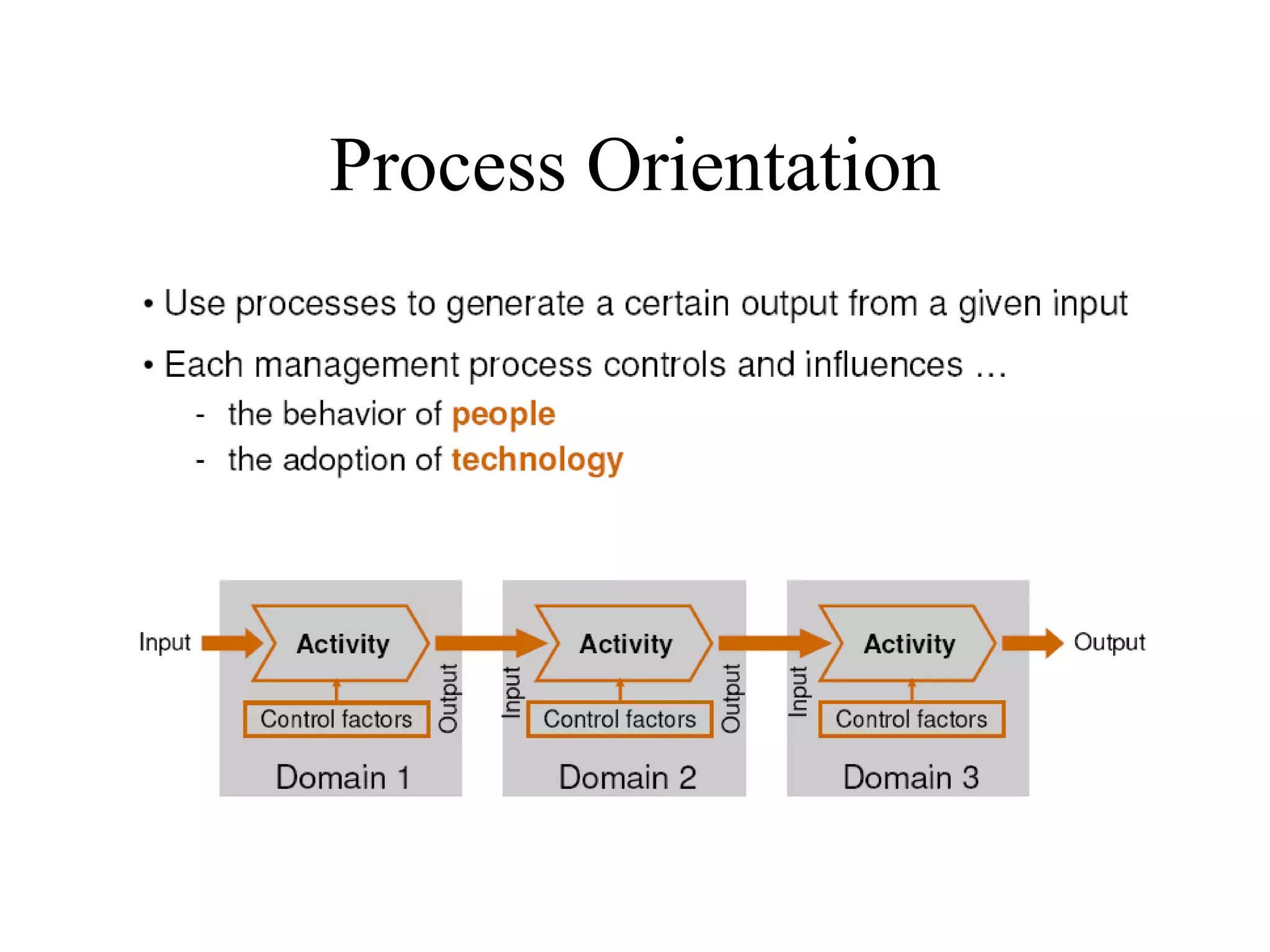
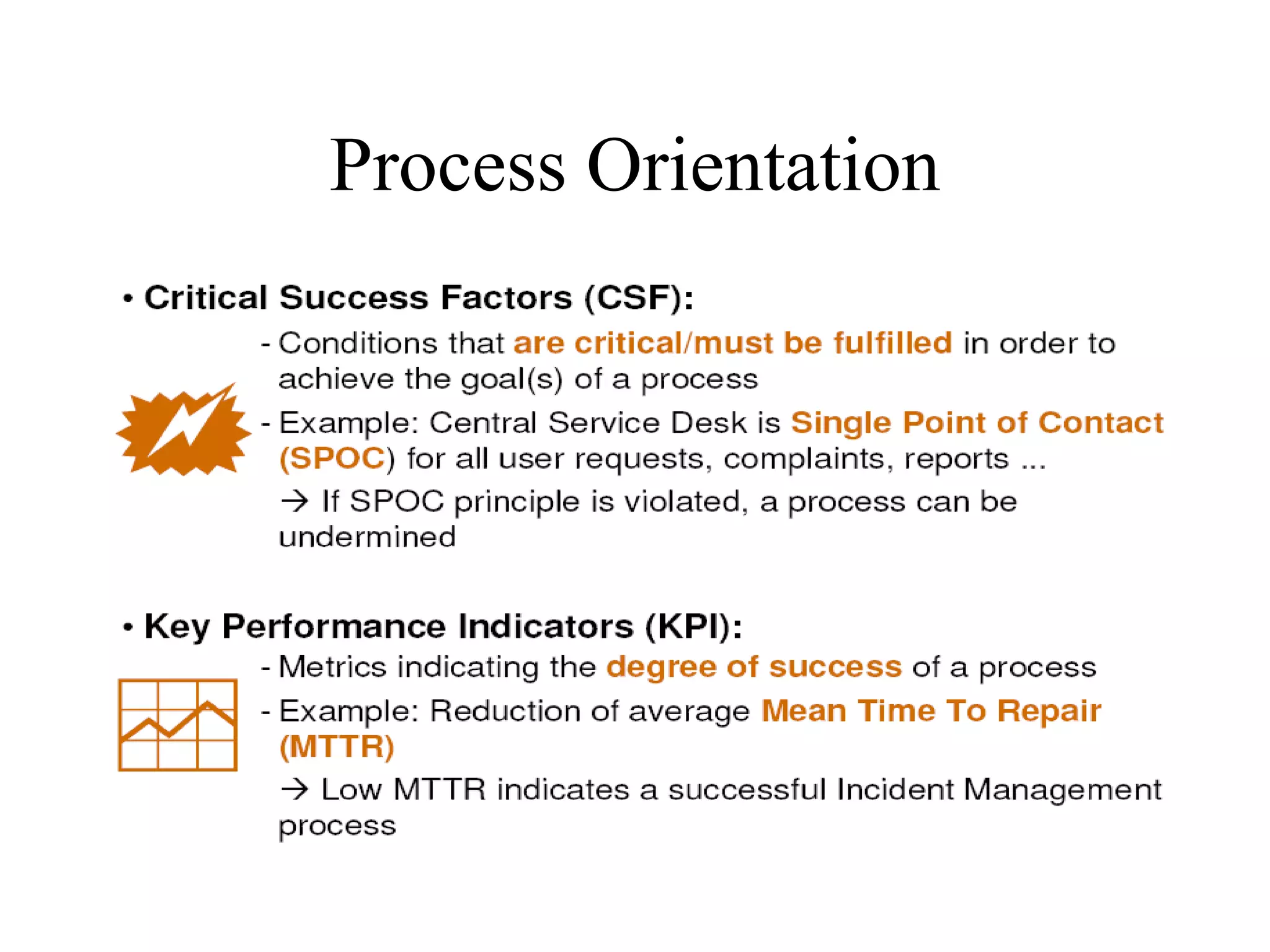
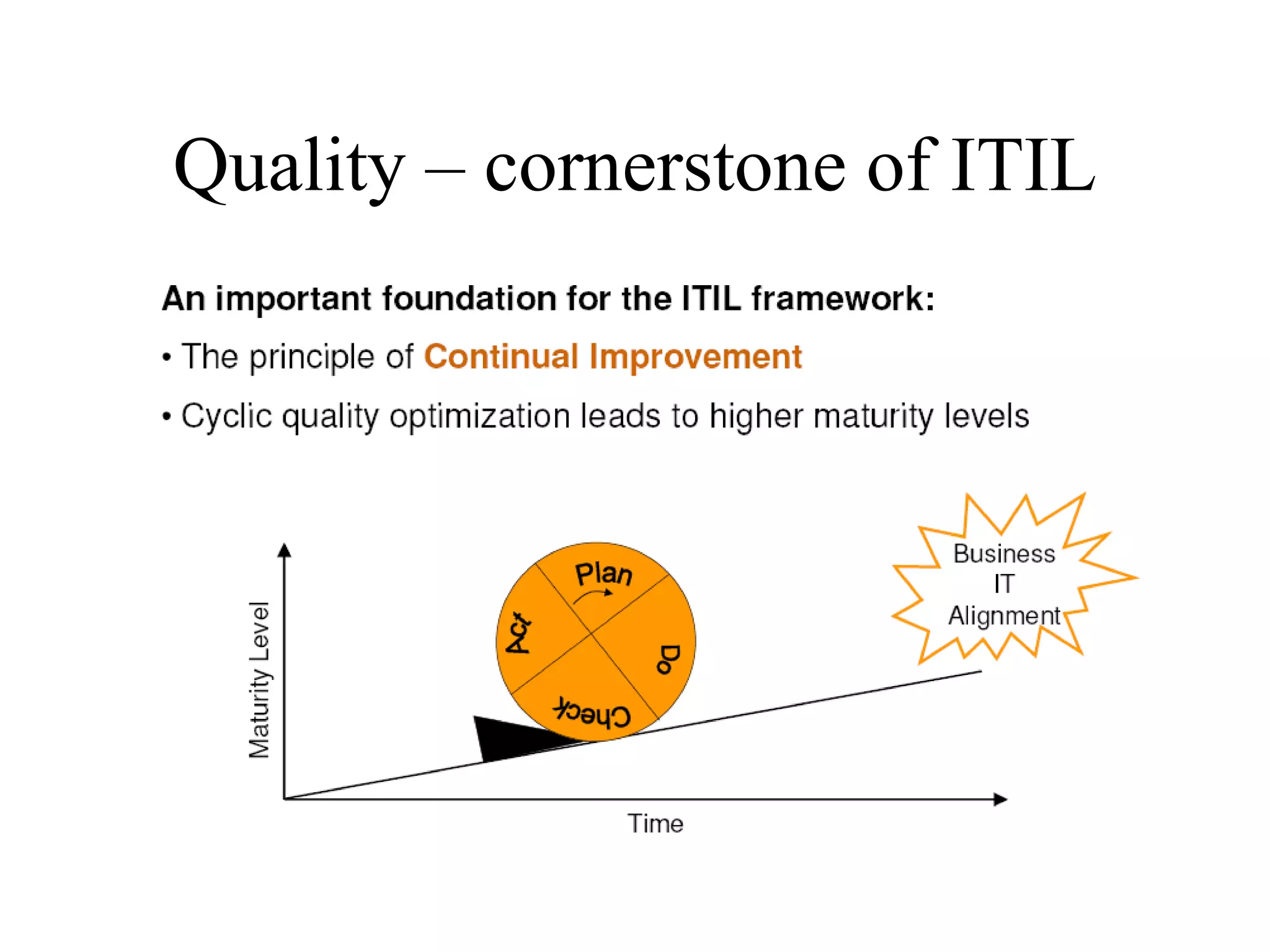
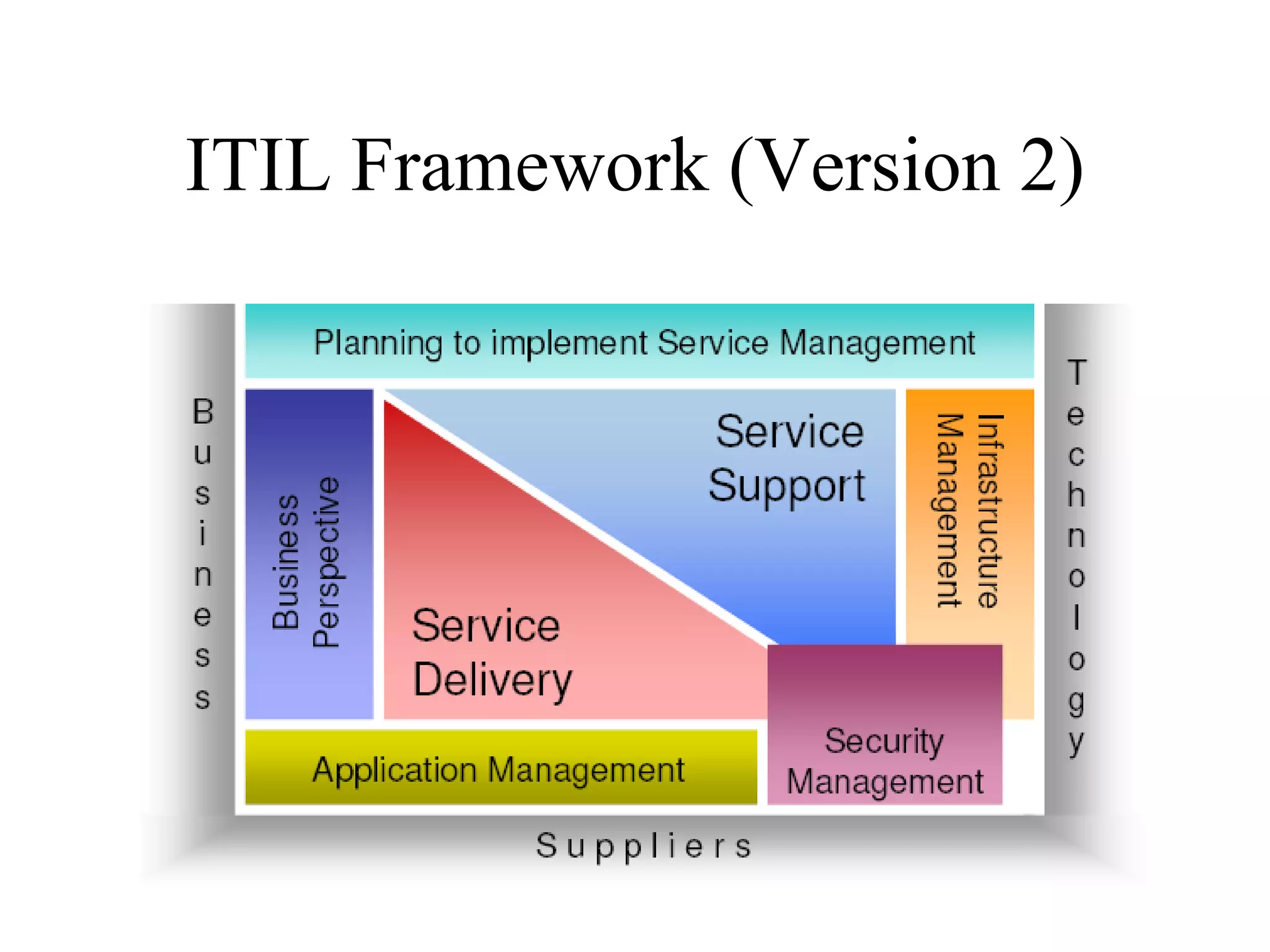
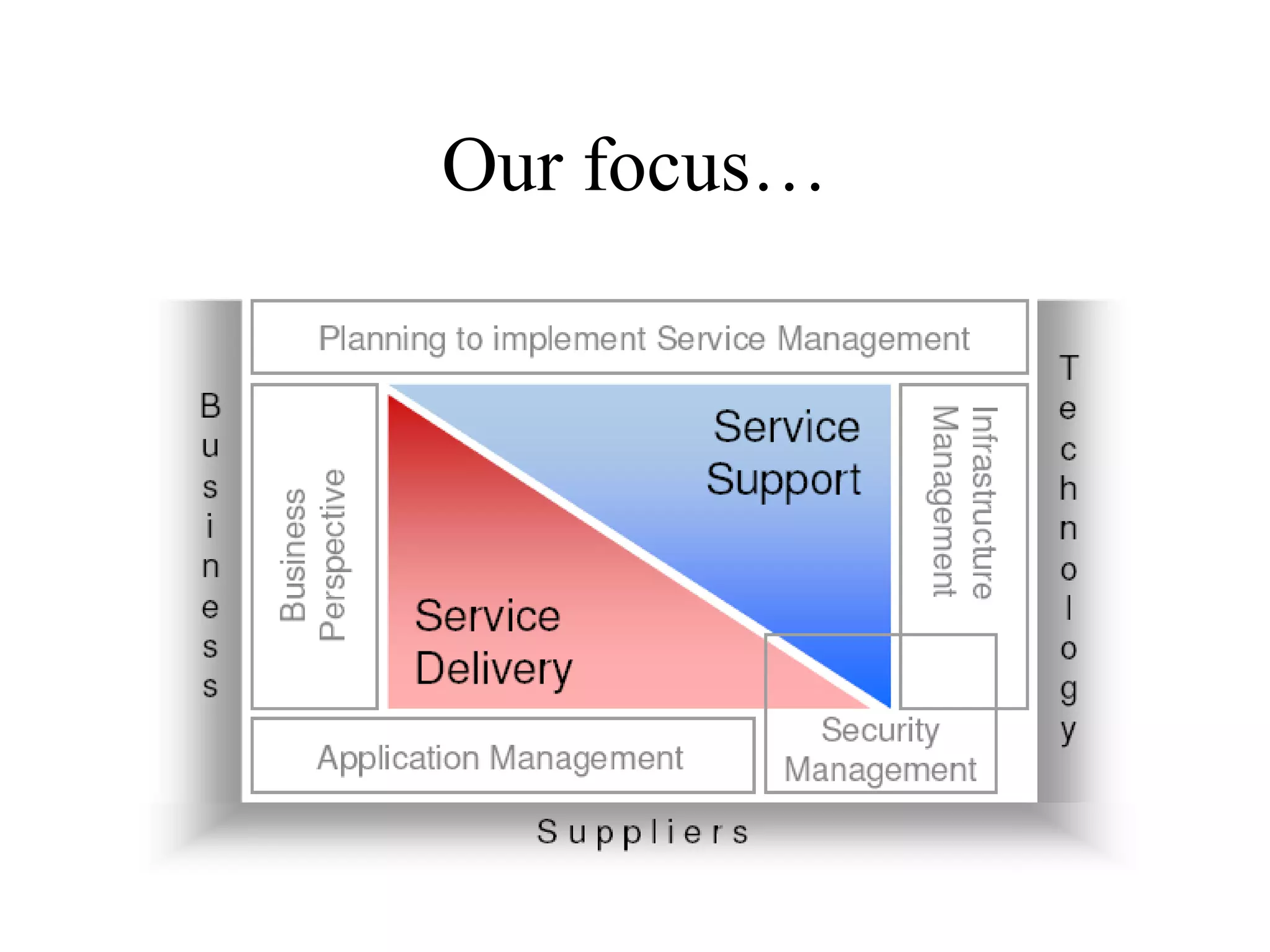
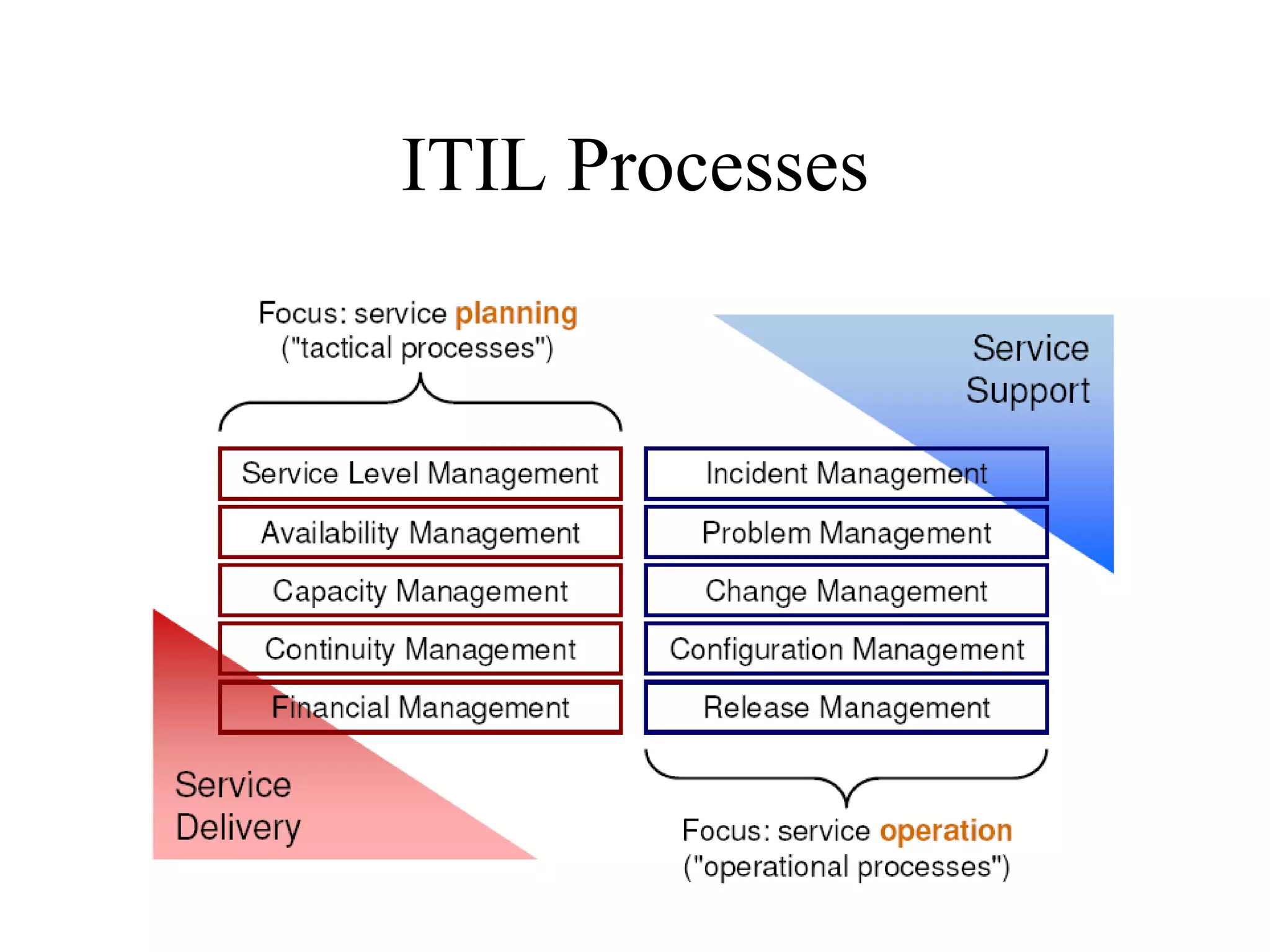
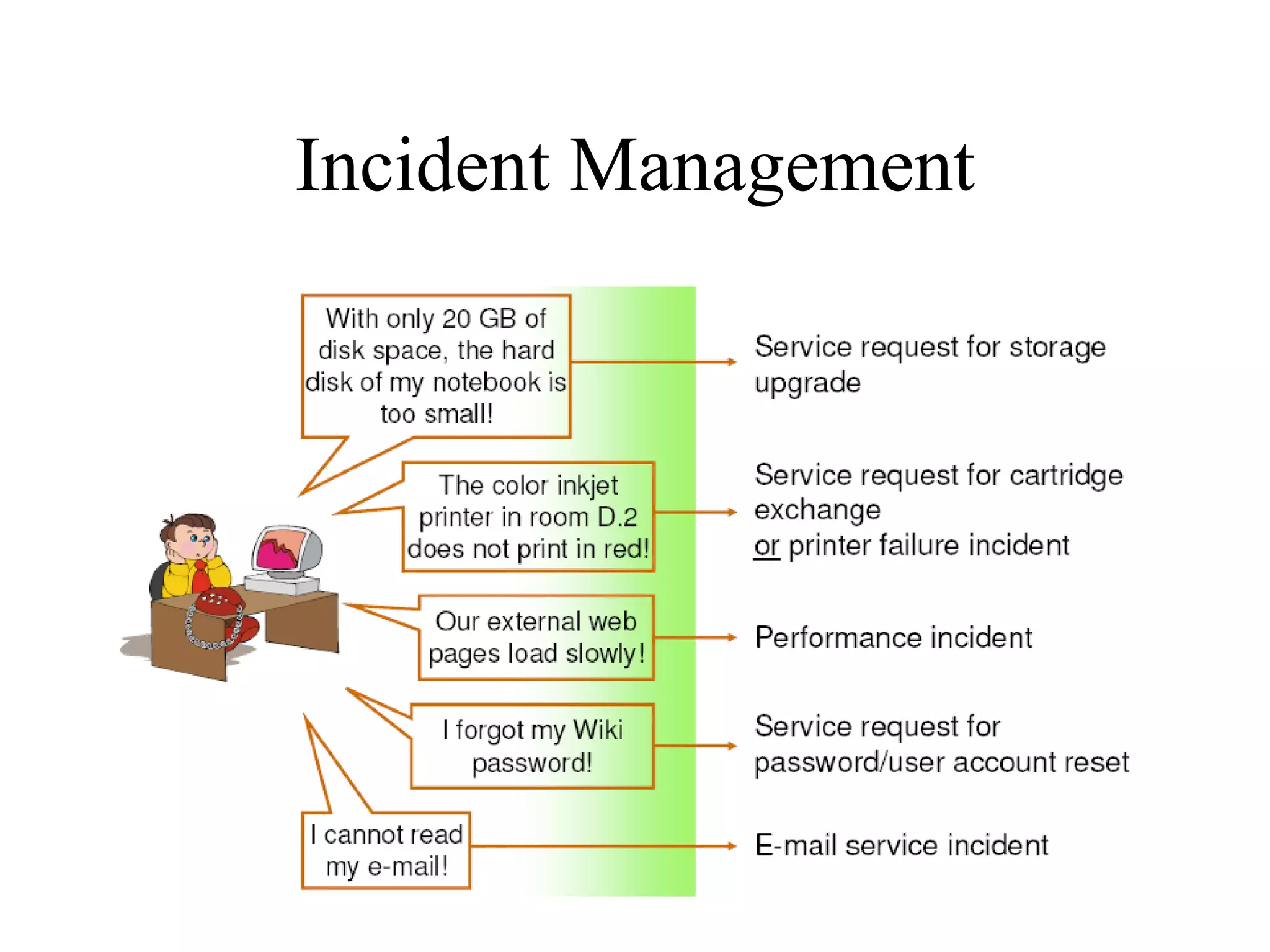
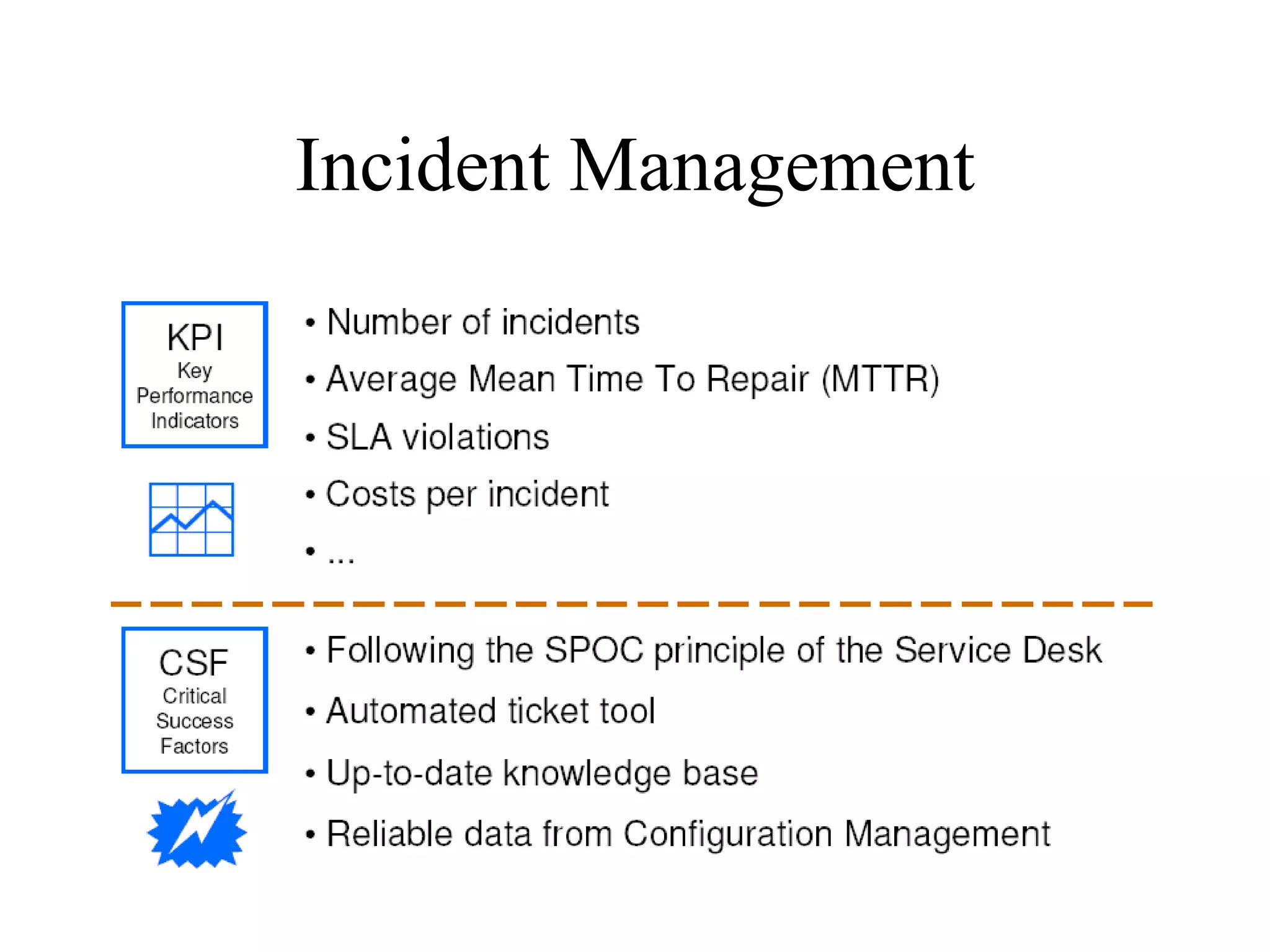
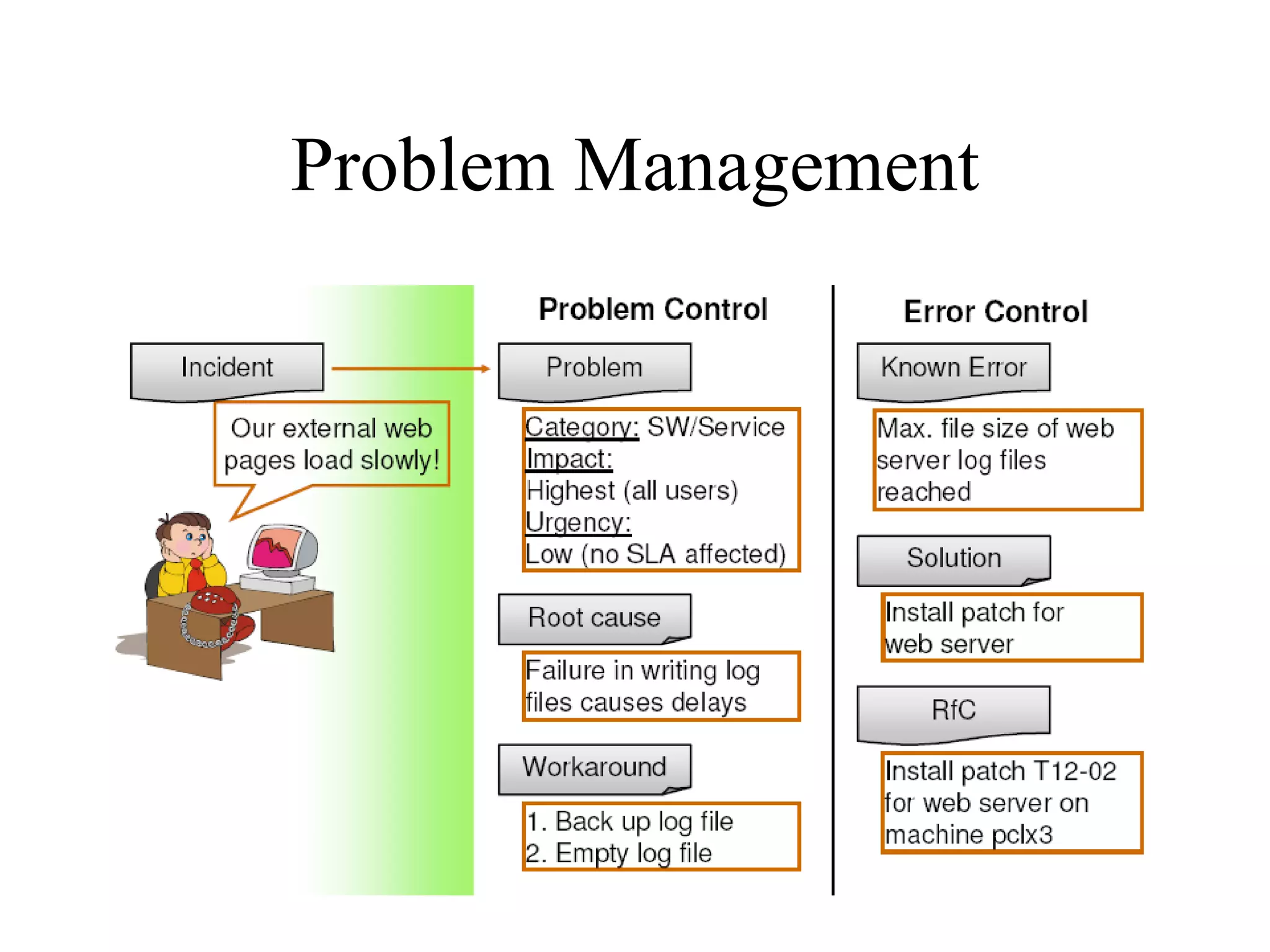
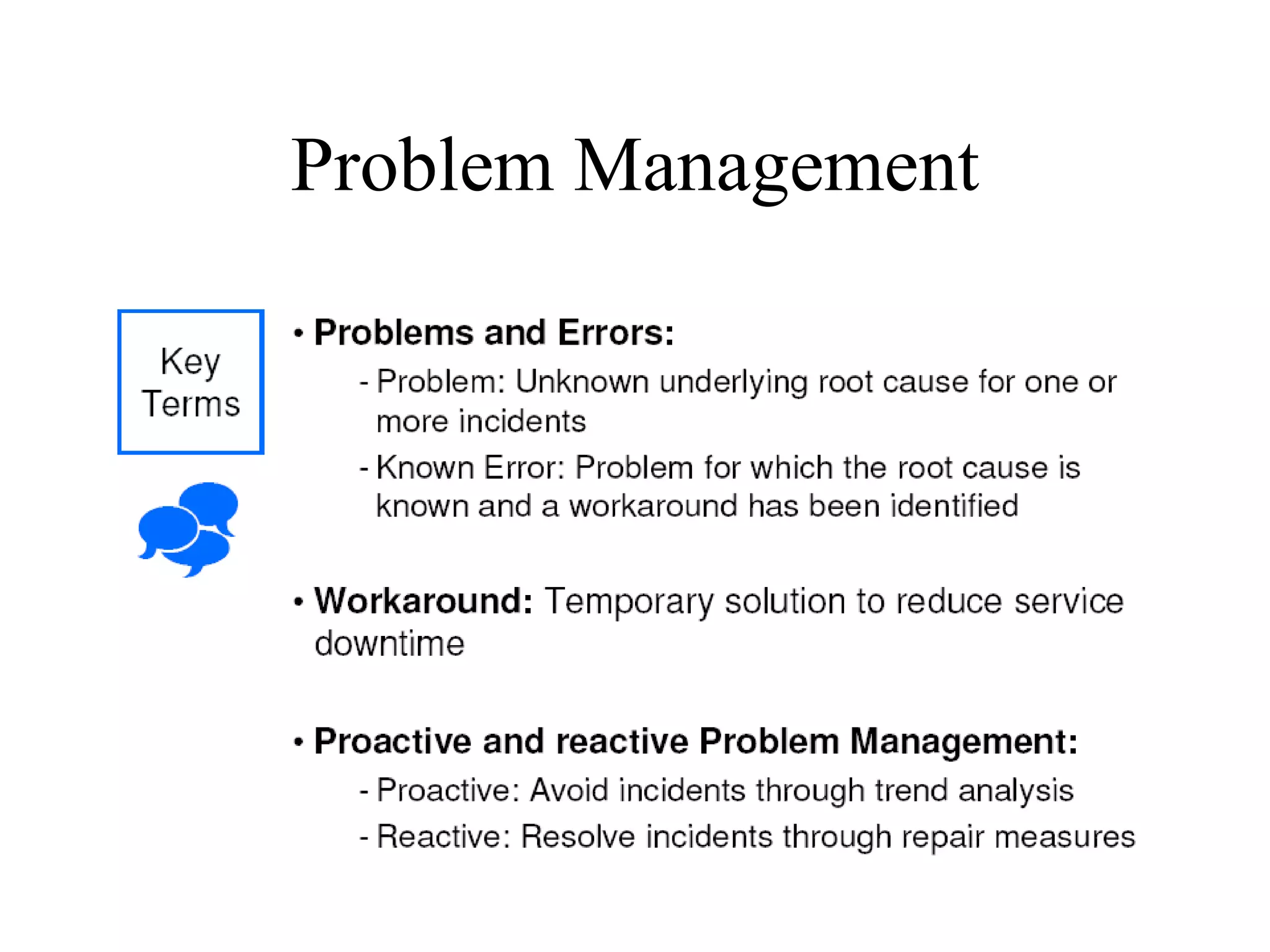
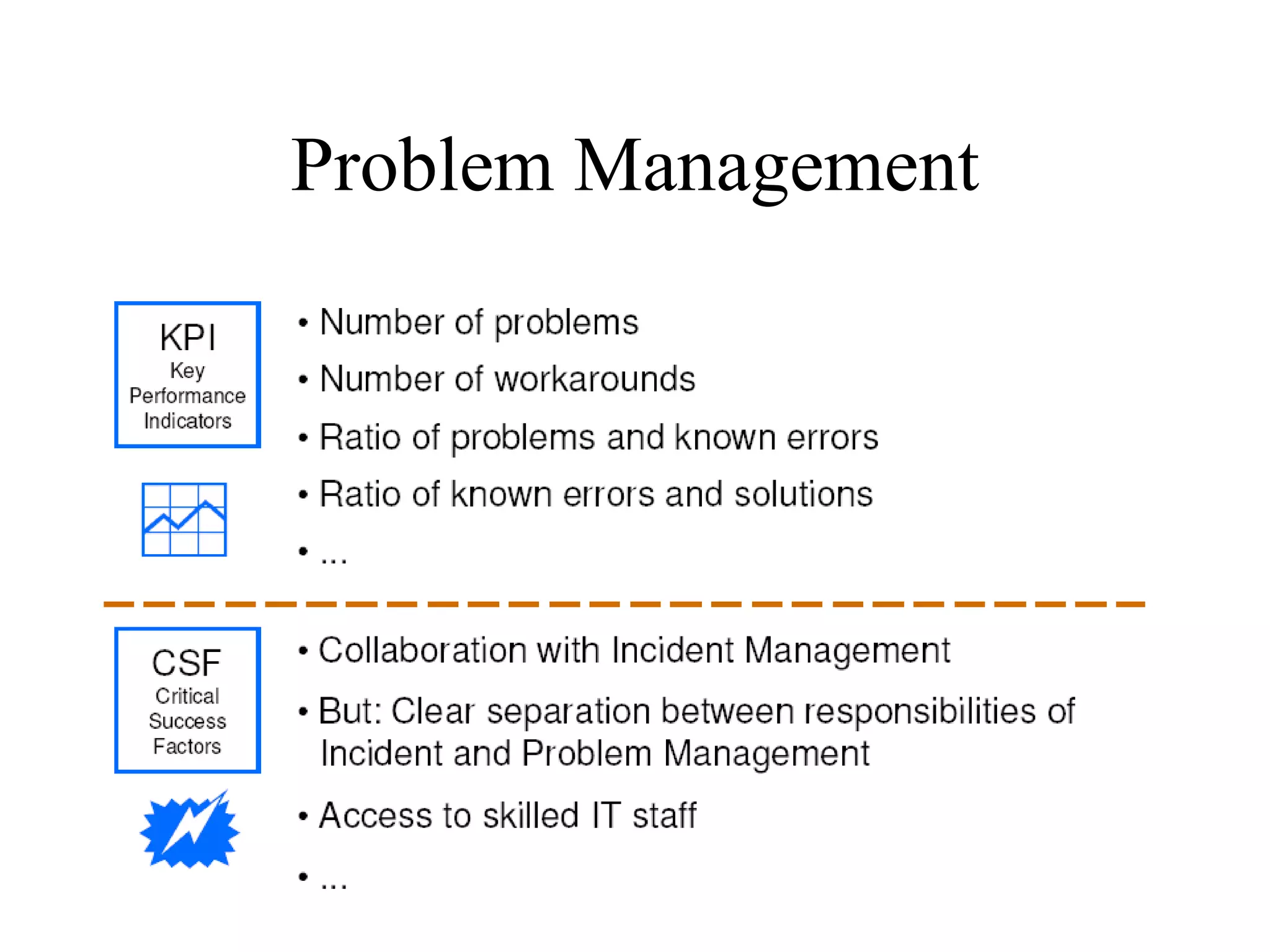
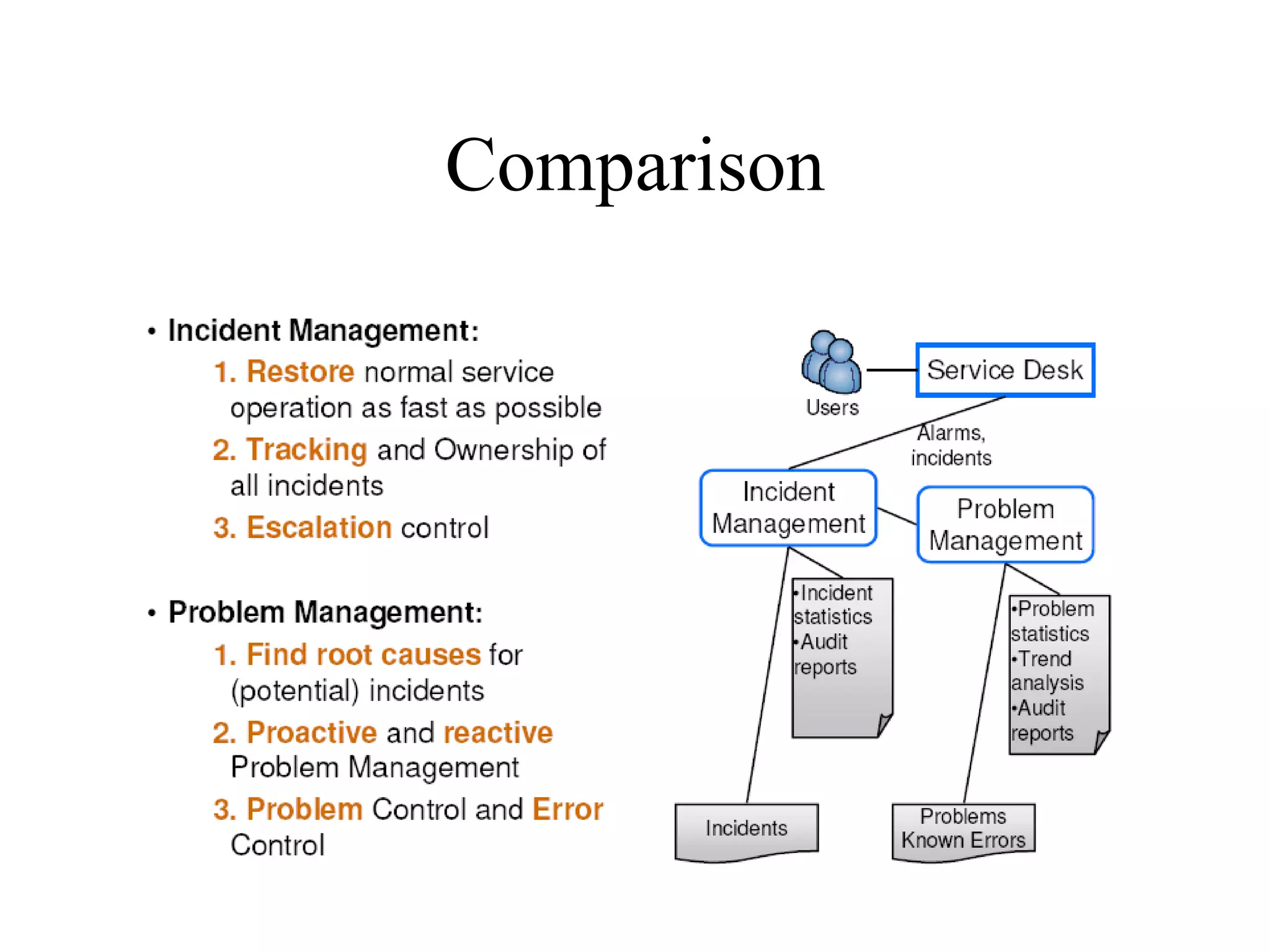
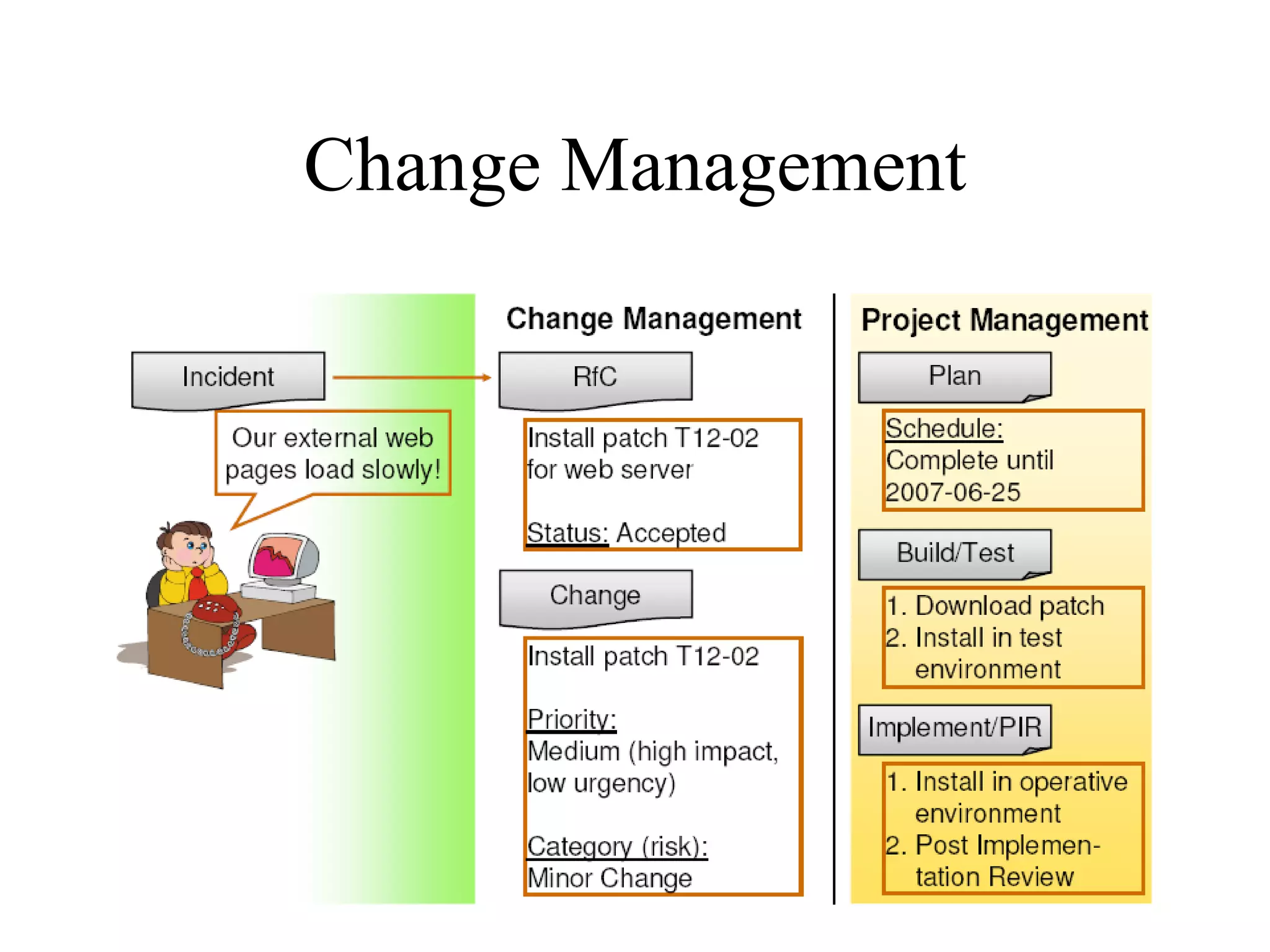
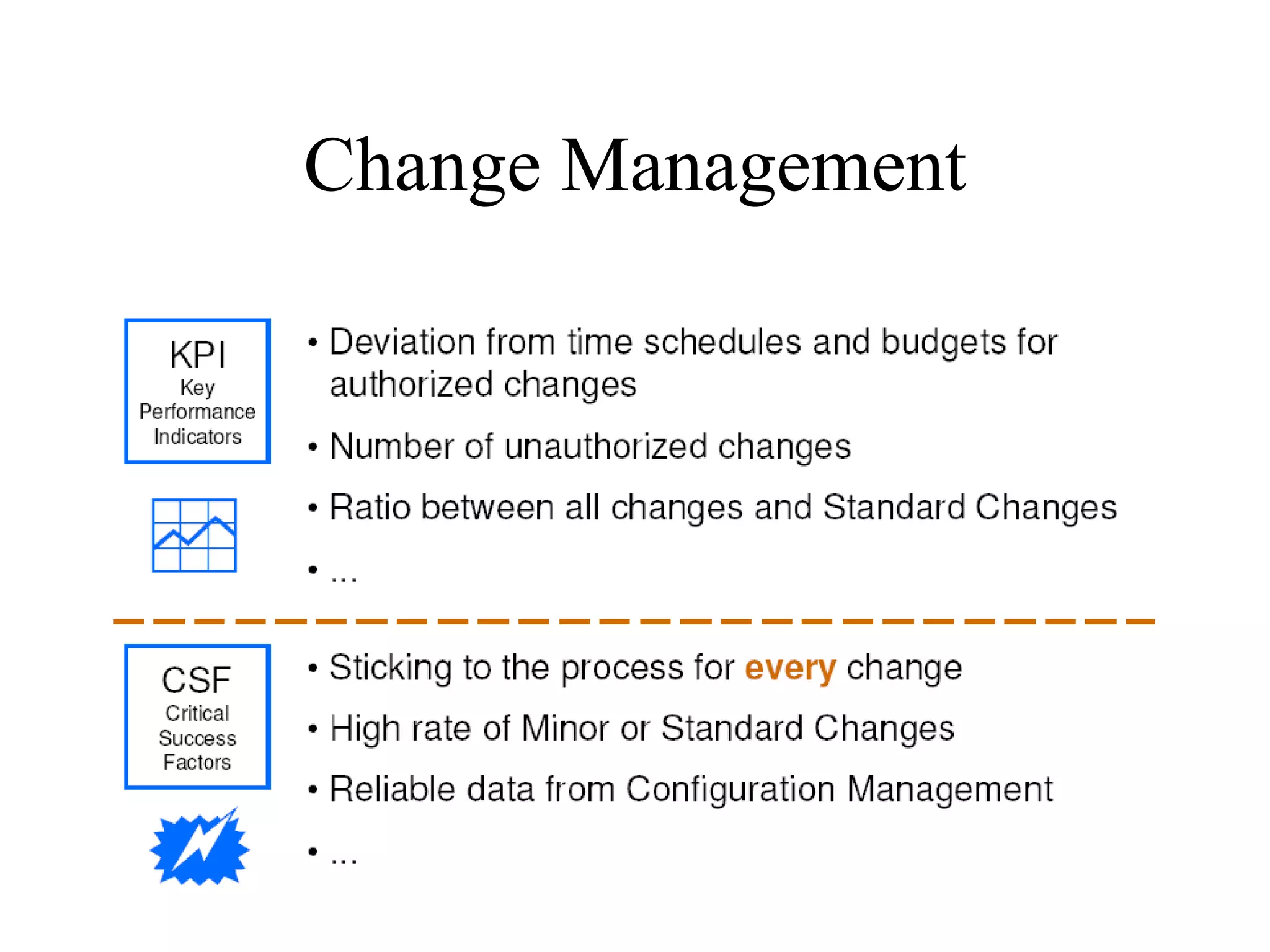
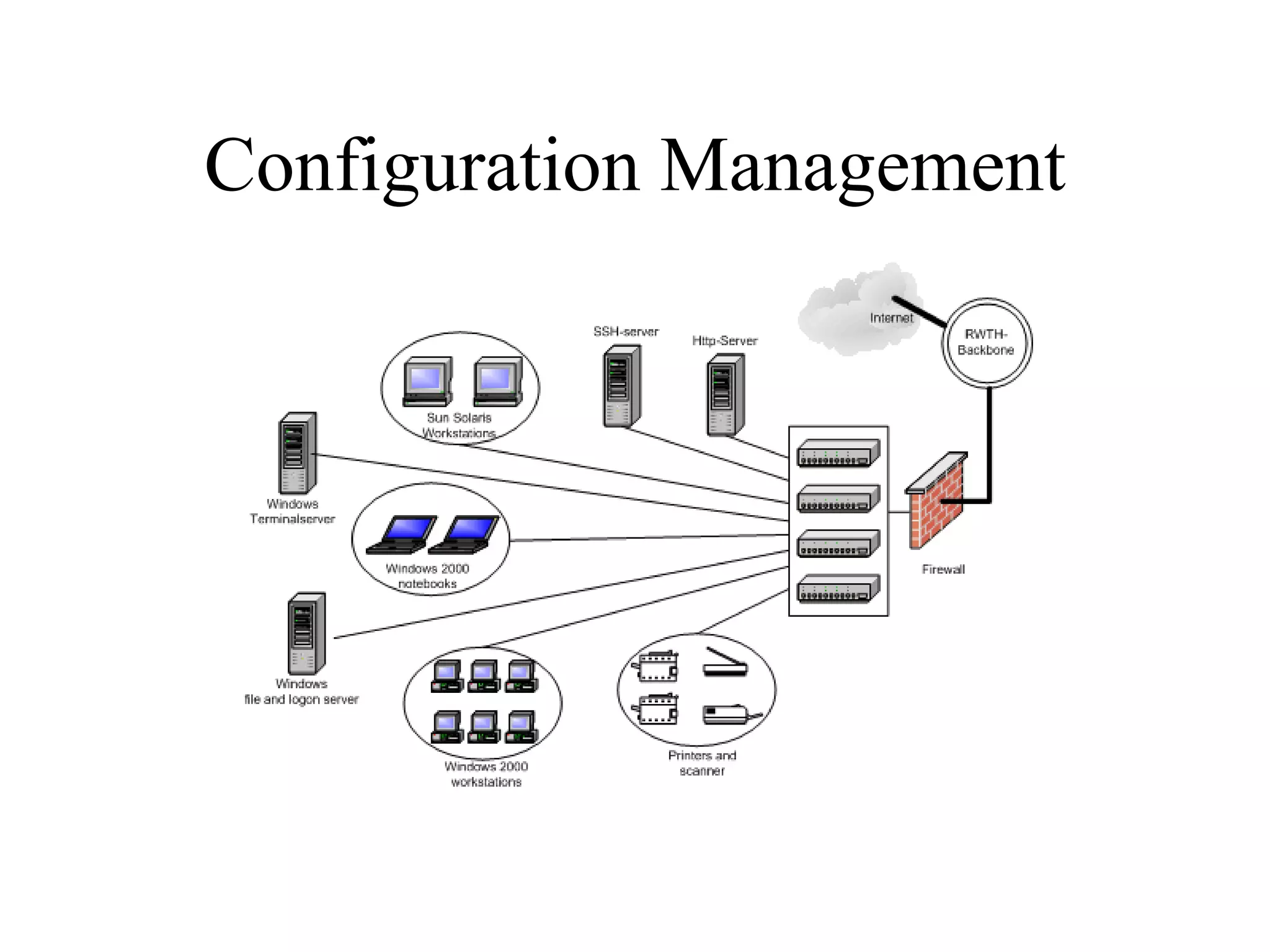
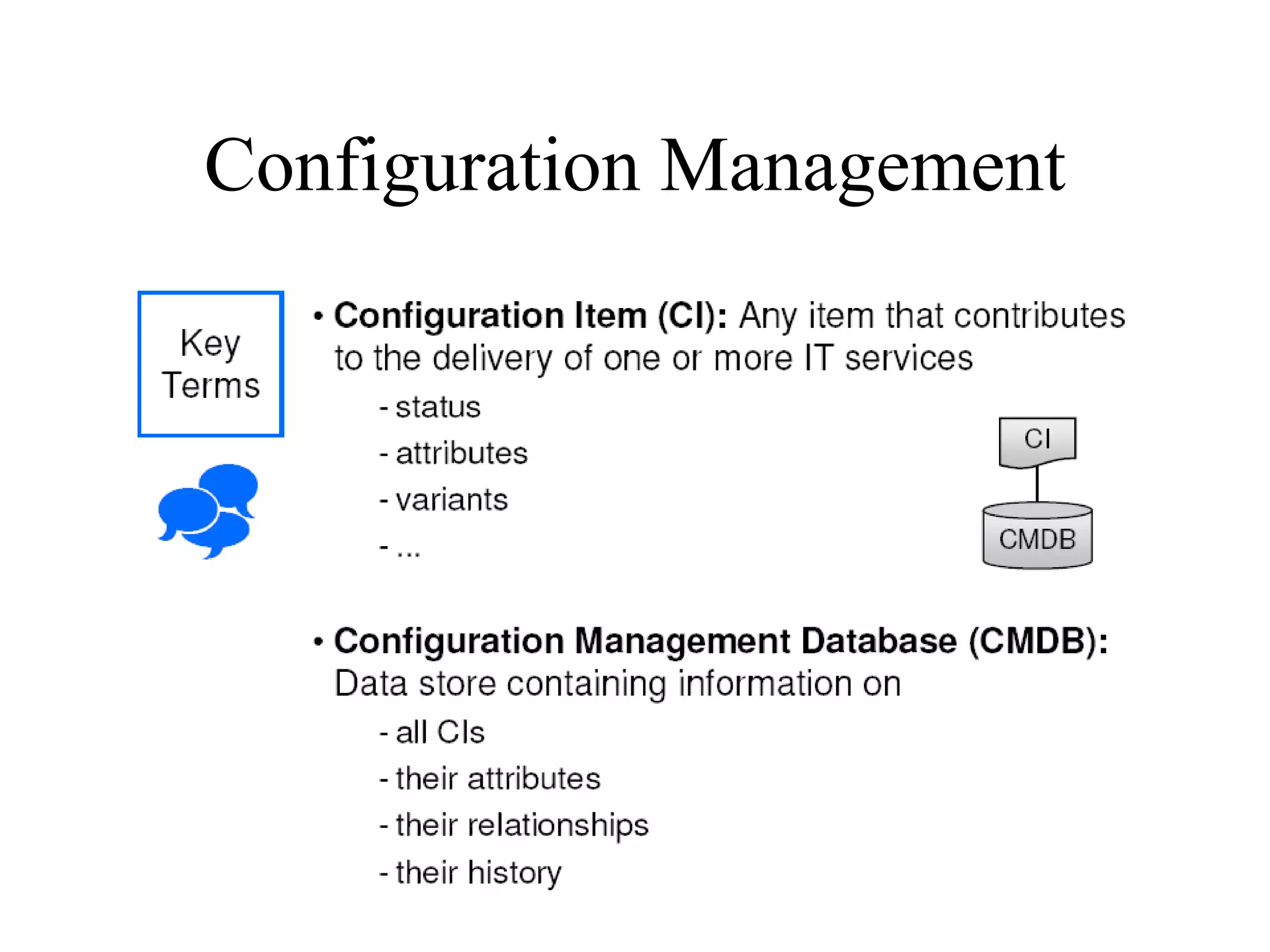
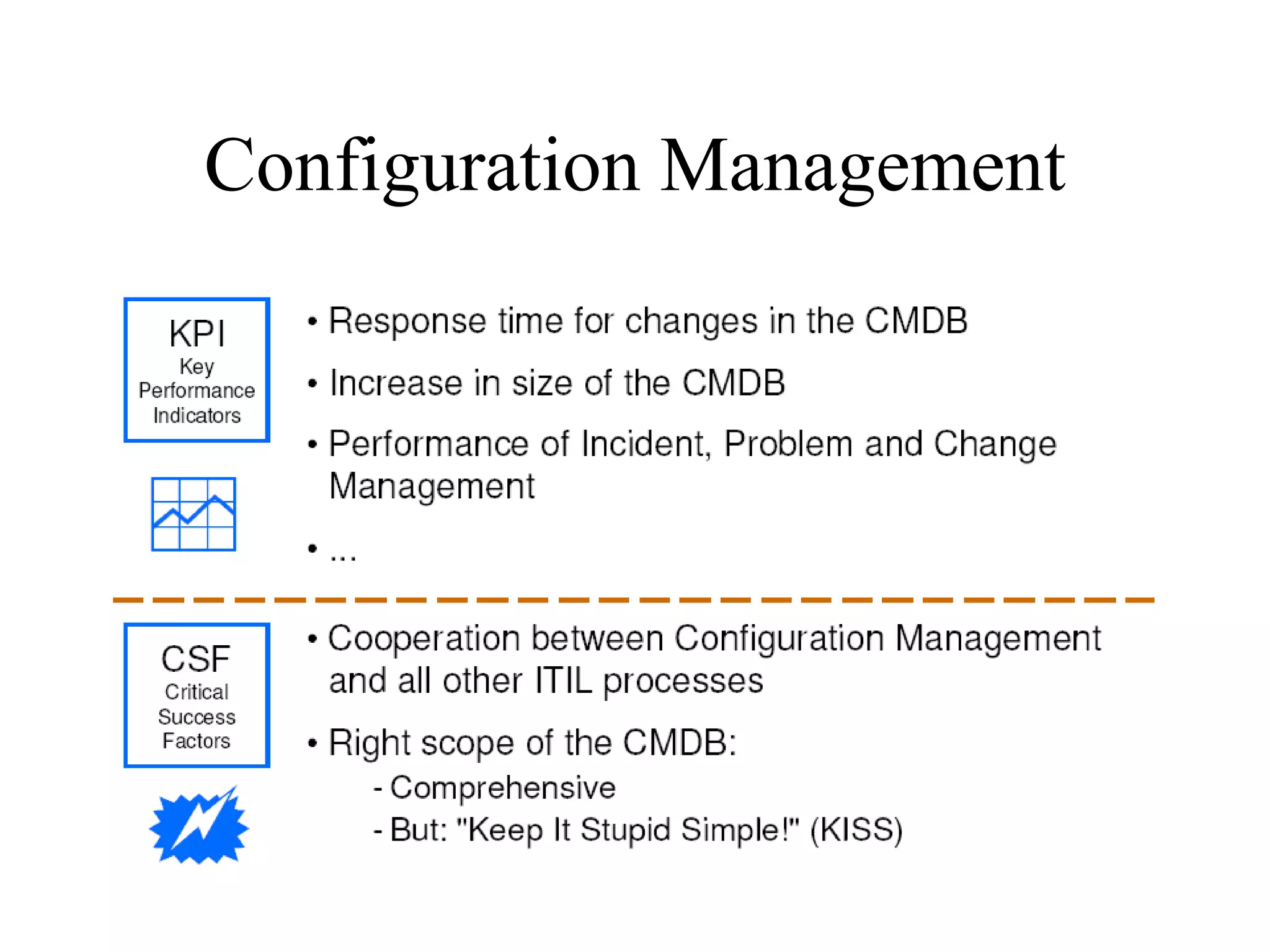
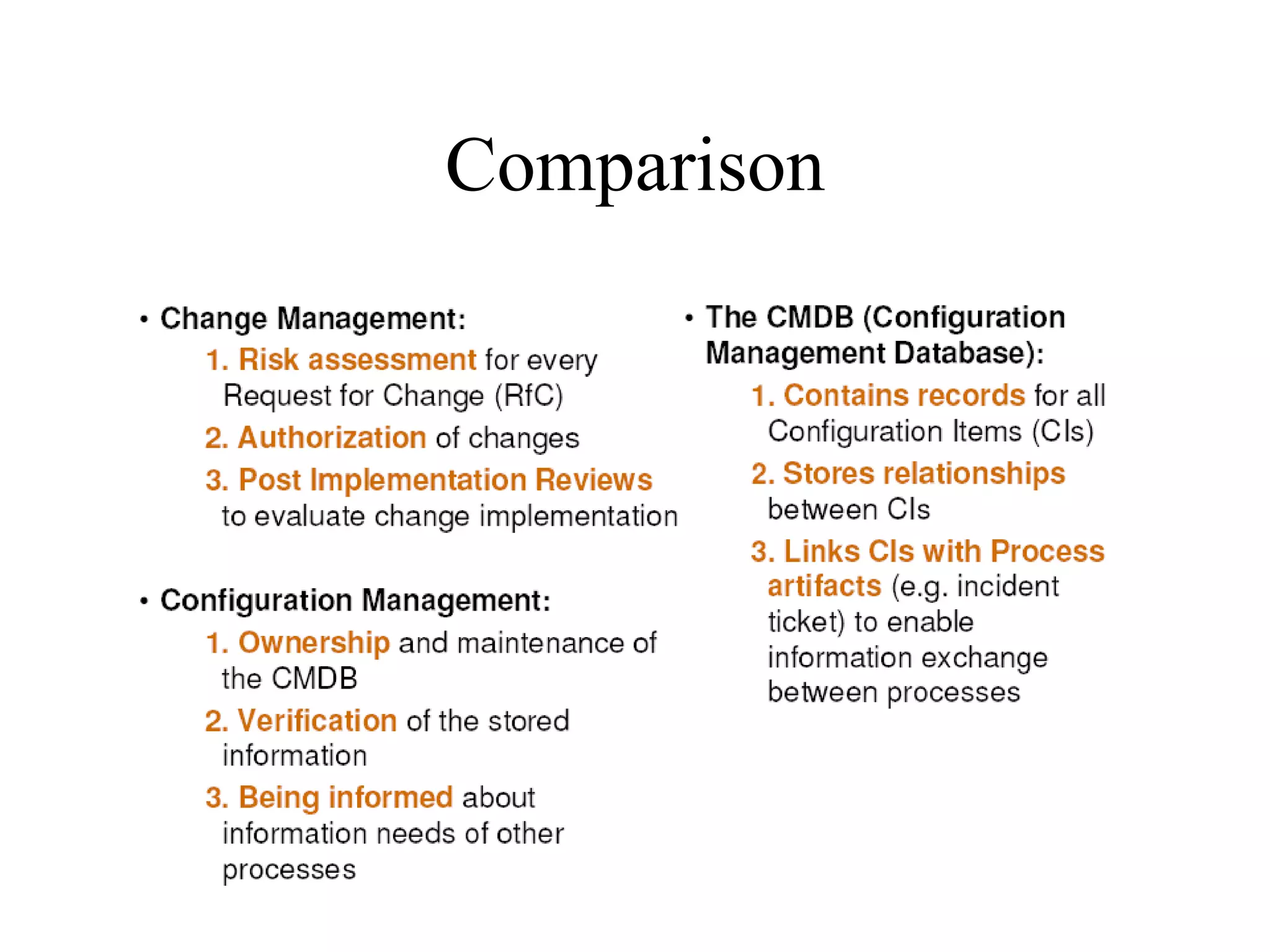
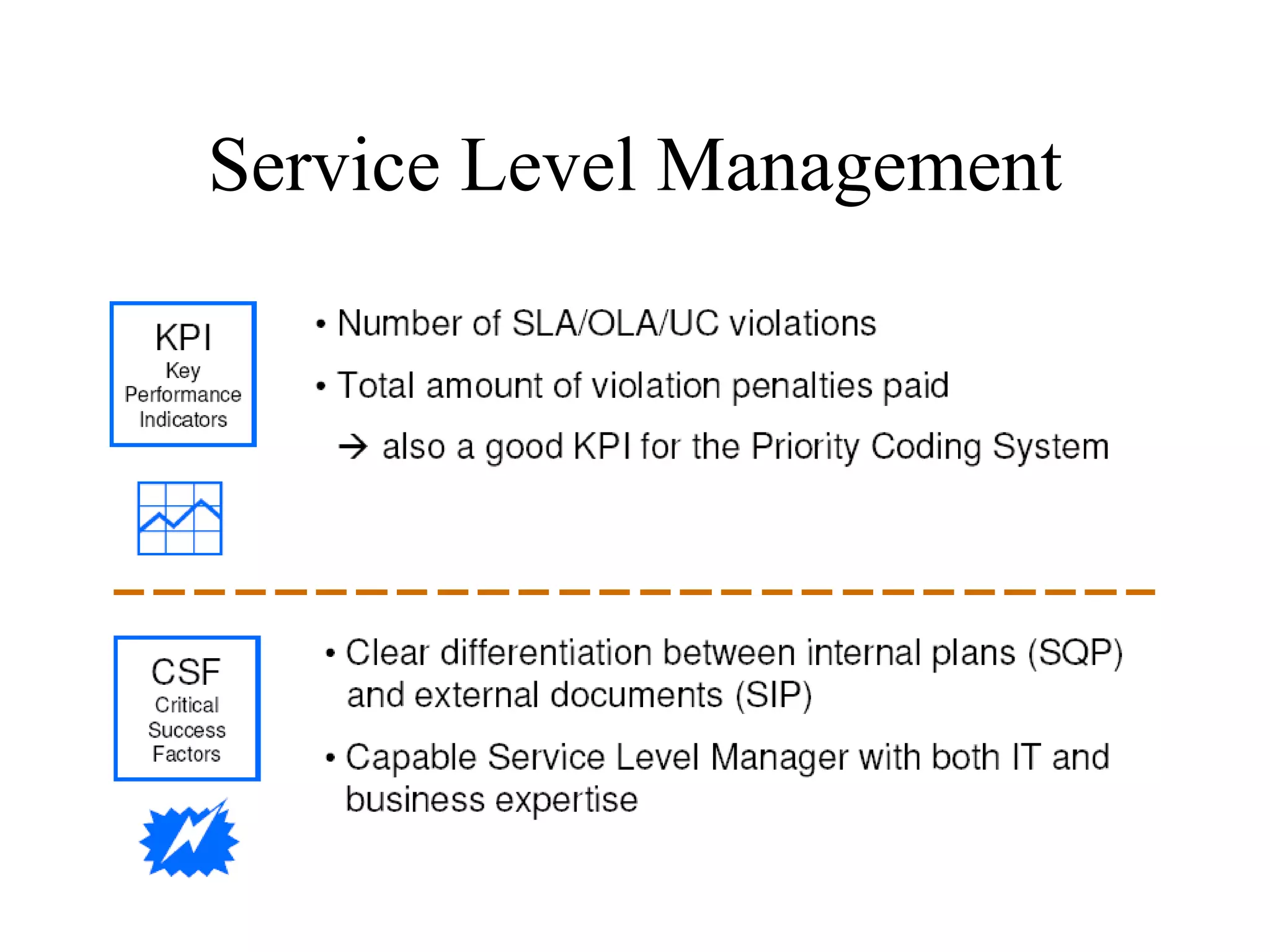
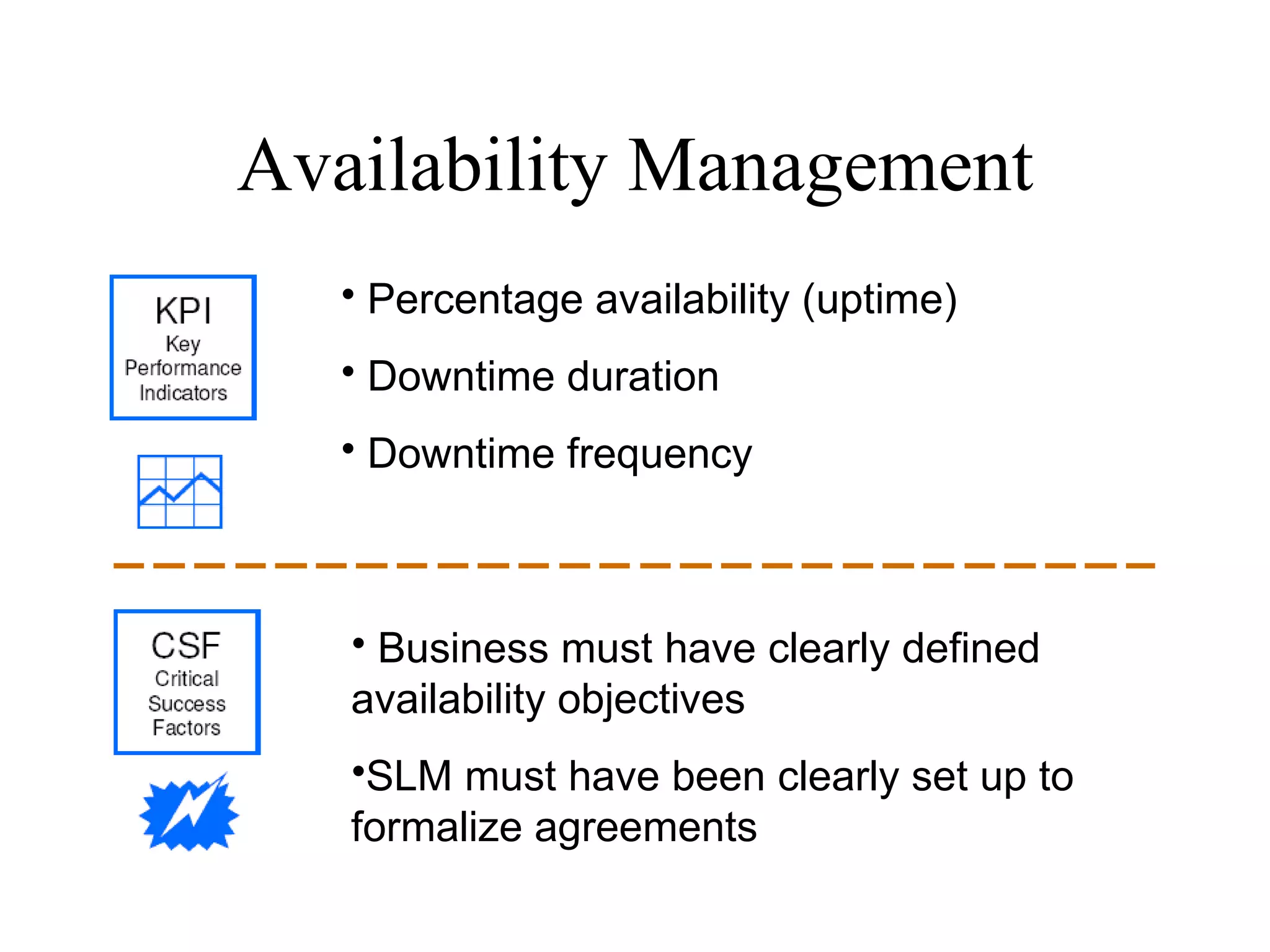
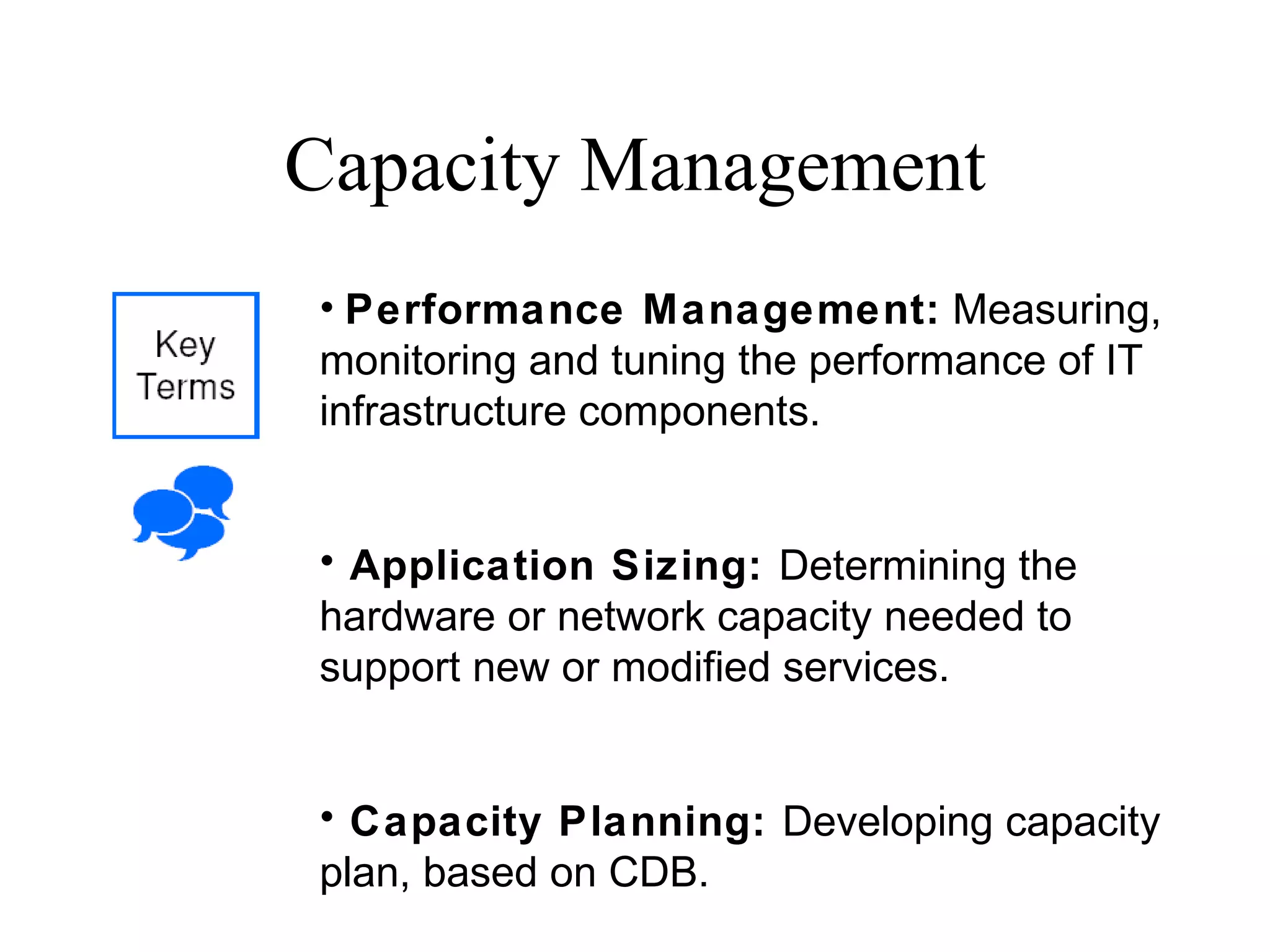
The document provides an overview of IT systems management and the ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework. It discusses key areas like IT service management, ITIL processes like incident management, change management and configuration management. It outlines the benefits of adopting ITIL practices like improved customer focus, quality and cost reductions. Some organizations that implemented ITIL successfully saw reductions in costs, outages and improvements in service levels. Reasons for failure included lack of management support, being too ambitious or not properly implementing processes.