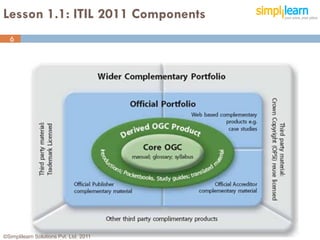
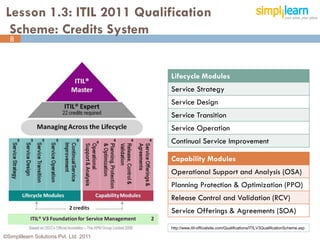
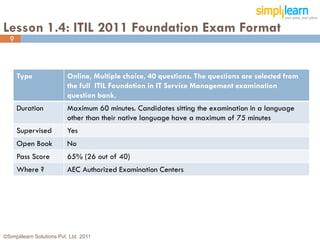
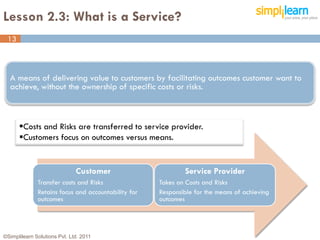
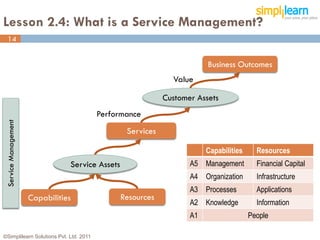
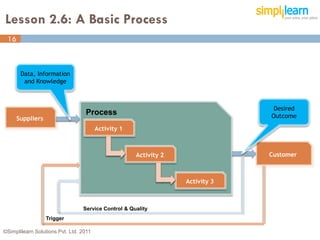
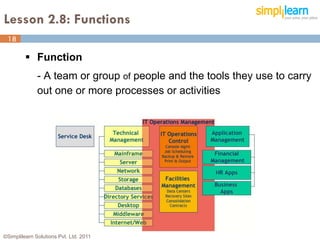
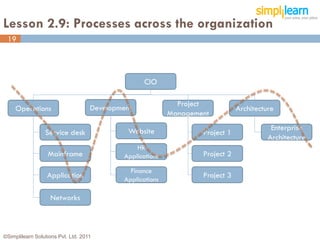
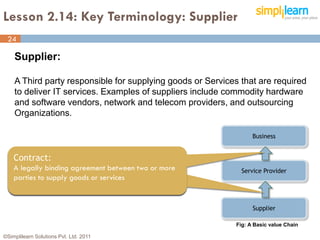
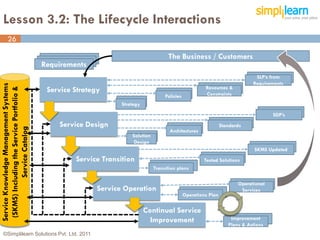
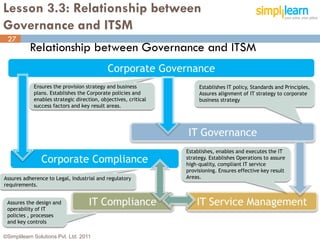
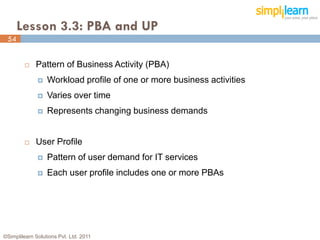
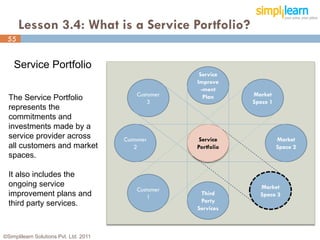
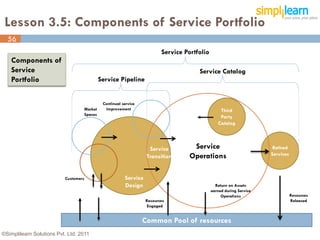
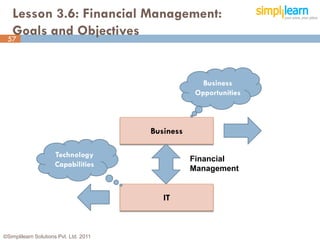
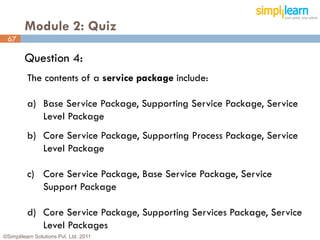
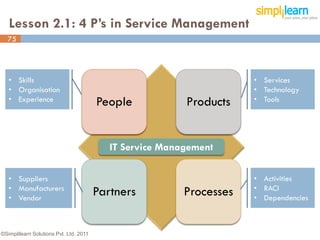
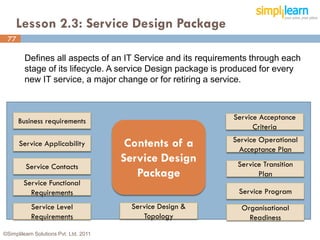
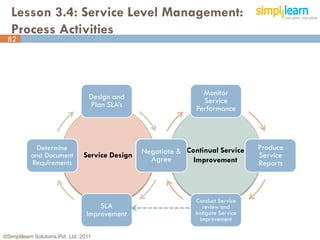
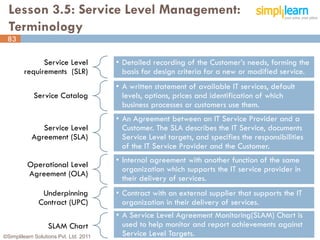
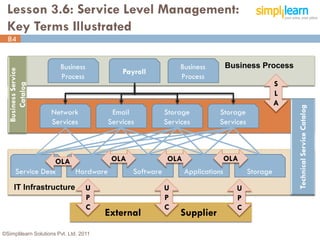
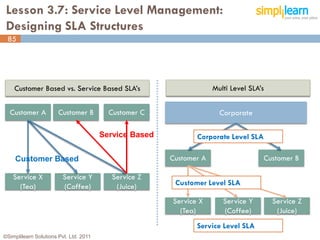
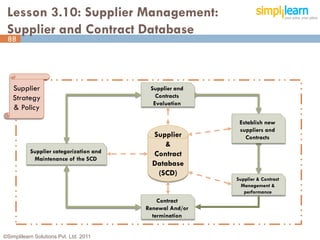
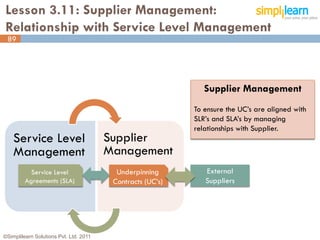
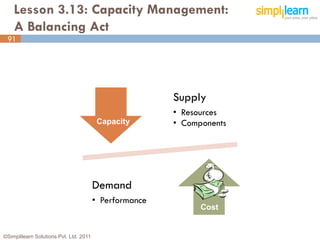
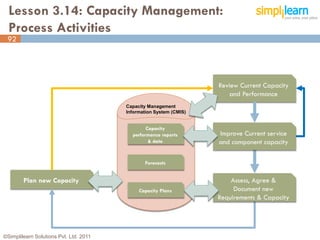
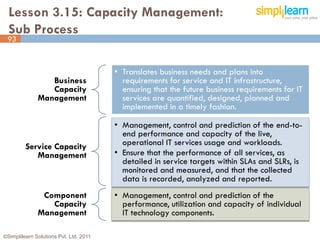
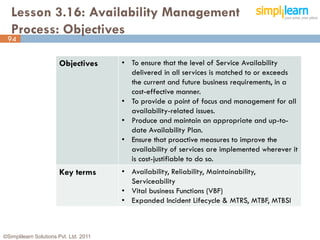
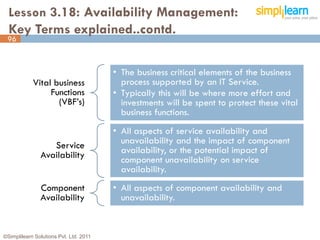
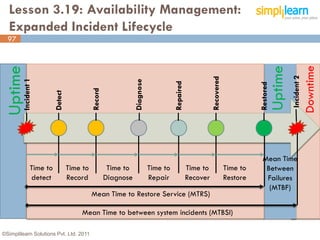
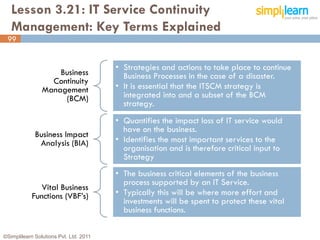
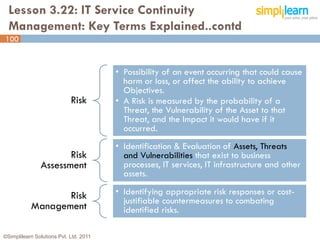
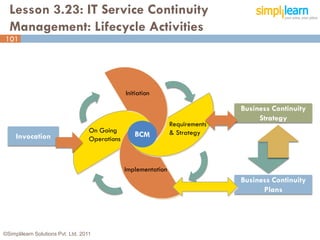
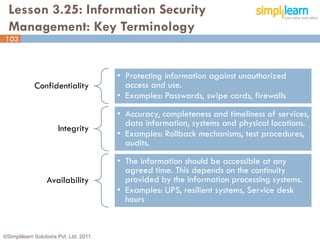
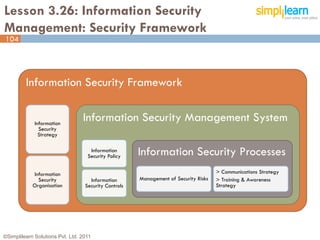
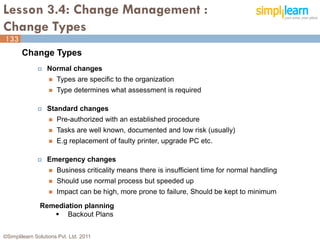
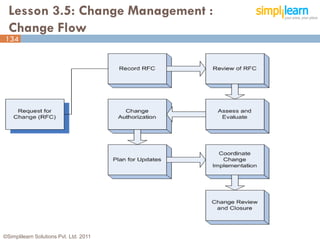
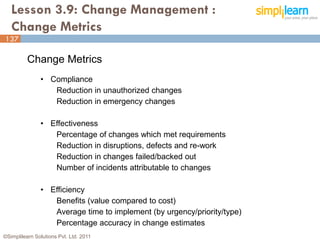
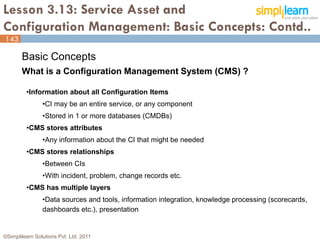
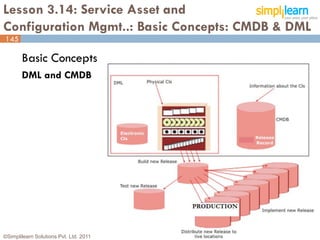
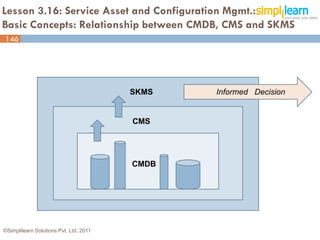
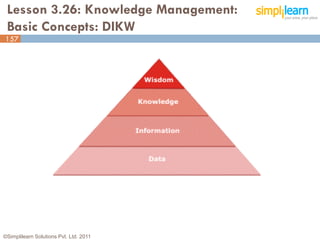
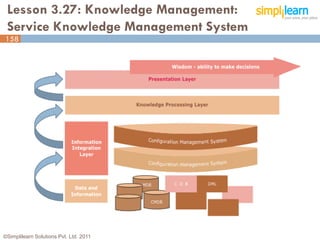
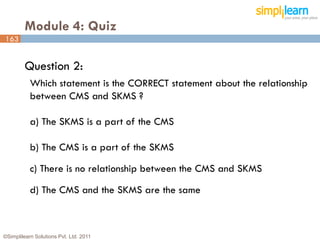
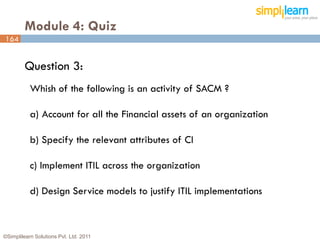
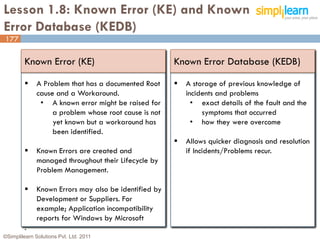
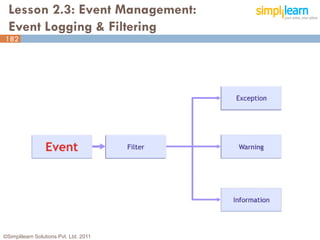
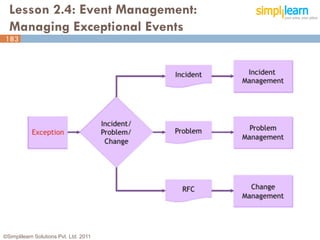
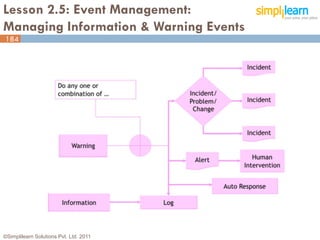
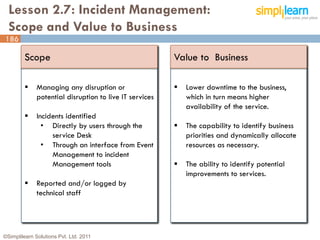
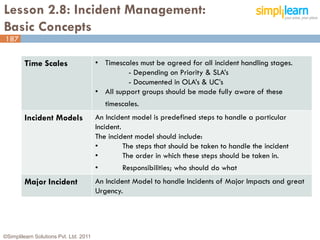
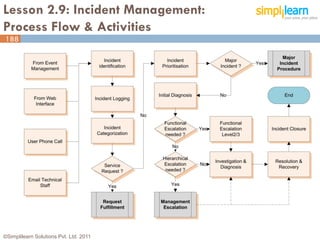
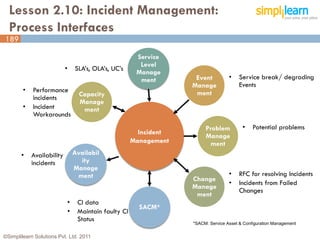
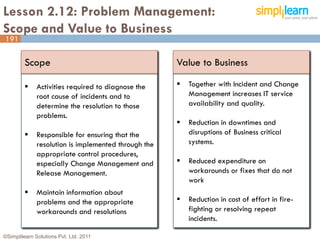
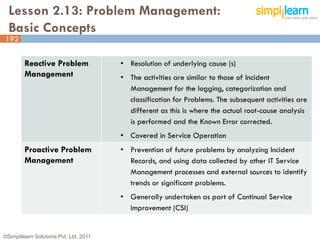
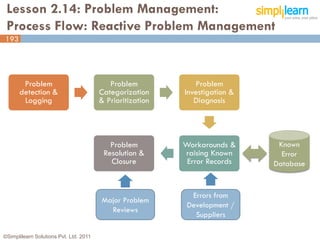
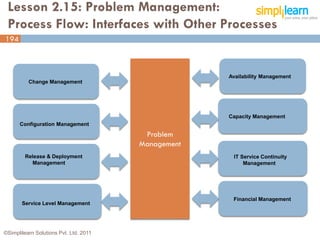
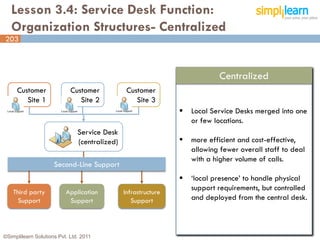
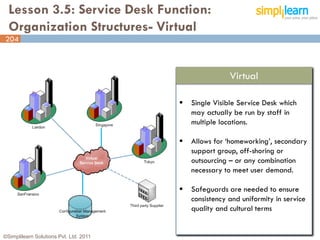
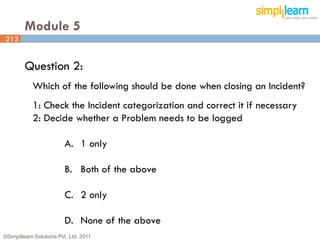
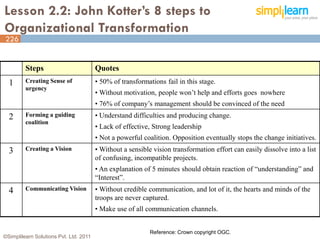
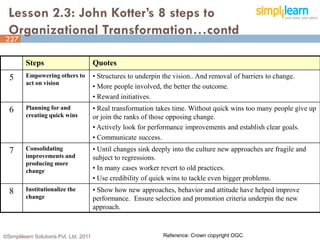
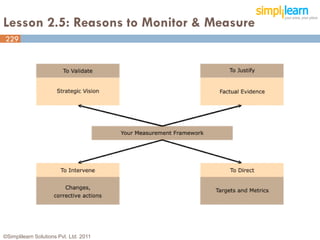
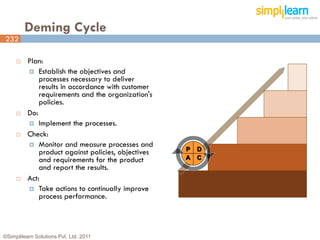
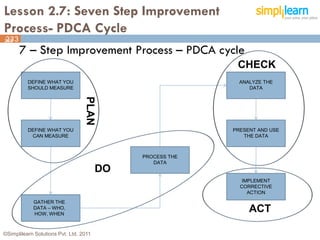
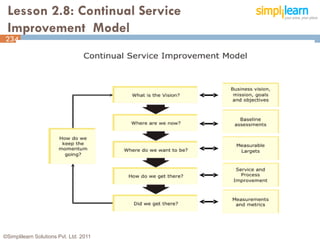
The document outlines the ITIL® 2011 Foundation certification course offered by Simplilearn, detailing course objectives, module outlines, exam formats, and key concepts of IT service management. Participants will learn about the lifecycle of IT service management, including processes, roles, and the importance of good practices versus proprietary methods. By the end of the course, candidates should be prepared to successfully pass the ITIL 2011 Foundation exam.