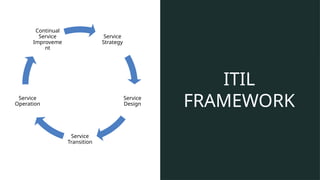
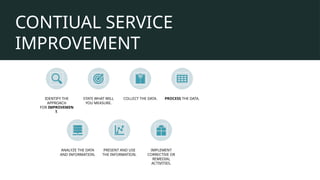
The document outlines the ITIL training agenda, highlighting key ITIL concepts, service lifecycle stages, and the history of ITIL's development from the 1980s to its current version, ITIL 4. It emphasizes the importance of ITIL for improving service quality, aligning IT with business goals, and enhancing customer satisfaction through structured IT service management. Additionally, the document provides insights into various ITIL processes such as service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continual service improvement.