The document discusses the study of religion, including:
- A passage from the Bible describing Nebuchadnezzar taking captives from Israel to Babylon for education.
- Components of religion like sacred stories, texts, rituals, beliefs, and people.
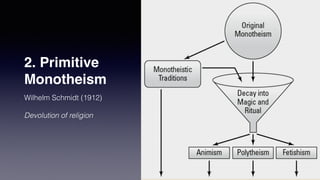
- Two theories on the origins of religion - evolution from animism to polytheism to monotheism, and primitive monotheism that devolved over time.
- The challenge for Christianity of believing in one truth while living in a pluralistic world, with approaches like inclusivism, dialogue, and respectfully sharing one's faith.



![[In 586 BC] Nebuchadnezzar the king of
Babylon came to Jerusalem and besieged it.
And the Lord gave Jehoiakim king of Judah into
his hand, with some of the vessels of the house
of God. And he brought them back to Babylon,
to the house of his god, and placed the vessels
in the treasury of his god.
(Dan 1:1–2 ESV)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int-244topic1part2studyofreligions-220112231352/85/INT-244-Topic-1-Part-2-4-320.jpg)