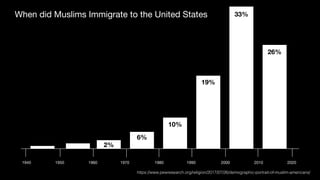
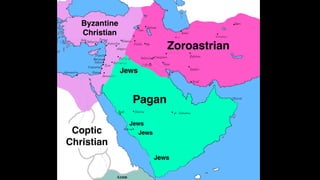
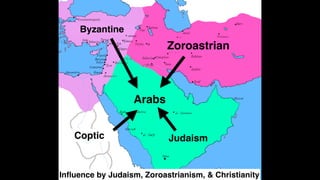
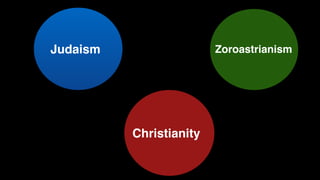
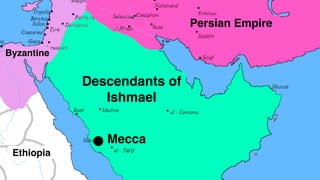
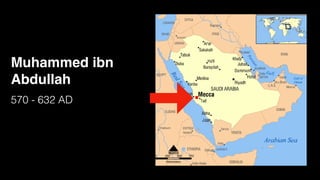
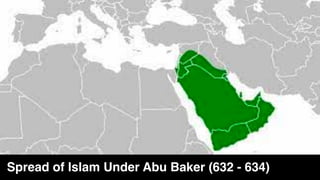
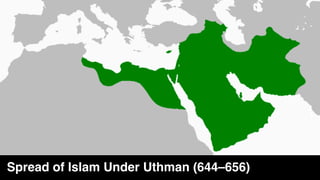
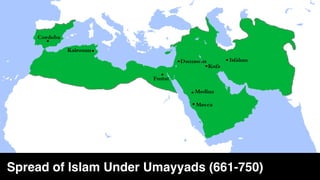
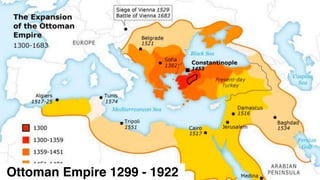
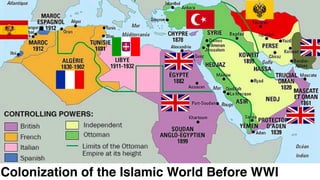
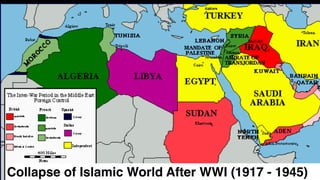
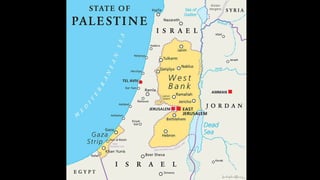
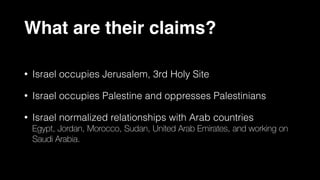
The document provides demographic information about Muslims worldwide and in the United States. It states that there are approximately 1.9 billion Muslims globally, making up 24% of the world's population. In the United States, there are over 4 million Muslims, with populations of 50,000-60,000 in Arizona. The document then discusses the Muslim community in the US, noting that most American Muslims are now established citizens who value education and hard work.


















![[Isaac] grew and was weaned. And Abraham made a great feast on the
day that Isaac was weaned. But Sarah saw [Ishmael] the son of Hagar the
Egyptian, whom she had borne to Abraham, laughing. So she said to
Abraham, “Cast out this slave woman with her son, for the son of this
slave woman shall not be heir with my son Isaac.” (Gen 21:8-11 ESV)
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int-244topic3aislam-240208164239-b672eda6/85/INT-244-Topic-3a-Islam-20-320.jpg)
![And the thing was very displeasing to Abraham on account of his son. But
God said to Abraham, “Be not displeased because of [Ishmael] because
of your slave woman. Whatever Sarah says to you, do as she tells you, for
through Isaac shall your o
ff
spring be named. And I will make a nation of
[Ishmael] also because he is your o
ff
spring.” (Gen 21:11-13 ESV)
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int-244topic3aislam-240208164239-b672eda6/85/INT-244-Topic-3a-Islam-21-320.jpg)
![So Abraham rose early in the morning and took bread and a skin of water
and gave it to Hagar, putting it on her shoulder, along with [Ishmael] and
sent her away. And she departed and wandered in the wilderness of
Beersheba. (Gen 21:14 ESV)
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int-244topic3aislam-240208164239-b672eda6/85/INT-244-Topic-3a-Islam-22-320.jpg)
![When the water in the skin was gone, she put [Ishmael] under one of the
bushes. Then she went and sat down opposite him a good way o
ff
, about
the distance of a bowshot, for she said, “Let me not look on the death of
the child.” And as she sat opposite him, she lifted up her voice and wept.
(Gen 21:15-17 ESV)
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int-244topic3aislam-240208164239-b672eda6/85/INT-244-Topic-3a-Islam-23-320.jpg)
![And God heard the voice of the boy, and the angel of God called to
Hagar from heaven and said to her, “What troubles you, Hagar? Fear not,
for God has heard the voice of [Ishmael] where he is. Up! Lift up [Ishmael],
and hold him fast with your hand, for I will make him into a great nation.”
(Gen 21:17-18 ESV)
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int-244topic3aislam-240208164239-b672eda6/85/INT-244-Topic-3a-Islam-24-320.jpg)
![Then God opened her eyes, and she saw a well of water. And she went
and
fi
lled the skin with water and gave [Ishmael] a drink. And God was
with the boy, and he grew up. He lived in the wilderness and became an
expert with the bow. He lived in the wilderness of Paran, and his mother
took a wife for him from the land of Egypt. (Gen 21:19-21 ESV)
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int-244topic3aislam-240208164239-b672eda6/85/INT-244-Topic-3a-Islam-25-320.jpg)























































































































































































![1. In the Name of Allah the Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful.
2. [All] praise is [due] to Allah, Lord of the worlds -
3. The Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful,
4. Sovereign of the Day of Recompense.
5. It is You we worship and You we ask for help
6. Guide us to the straight path-
7. The path of those upon whom You have bestowed favor, not of those
who have evoked [Your] anger or of those who are astray.
Quran 1:1–7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int-244topic3aislam-240208164239-b672eda6/85/INT-244-Topic-3a-Islam-227-320.jpg)