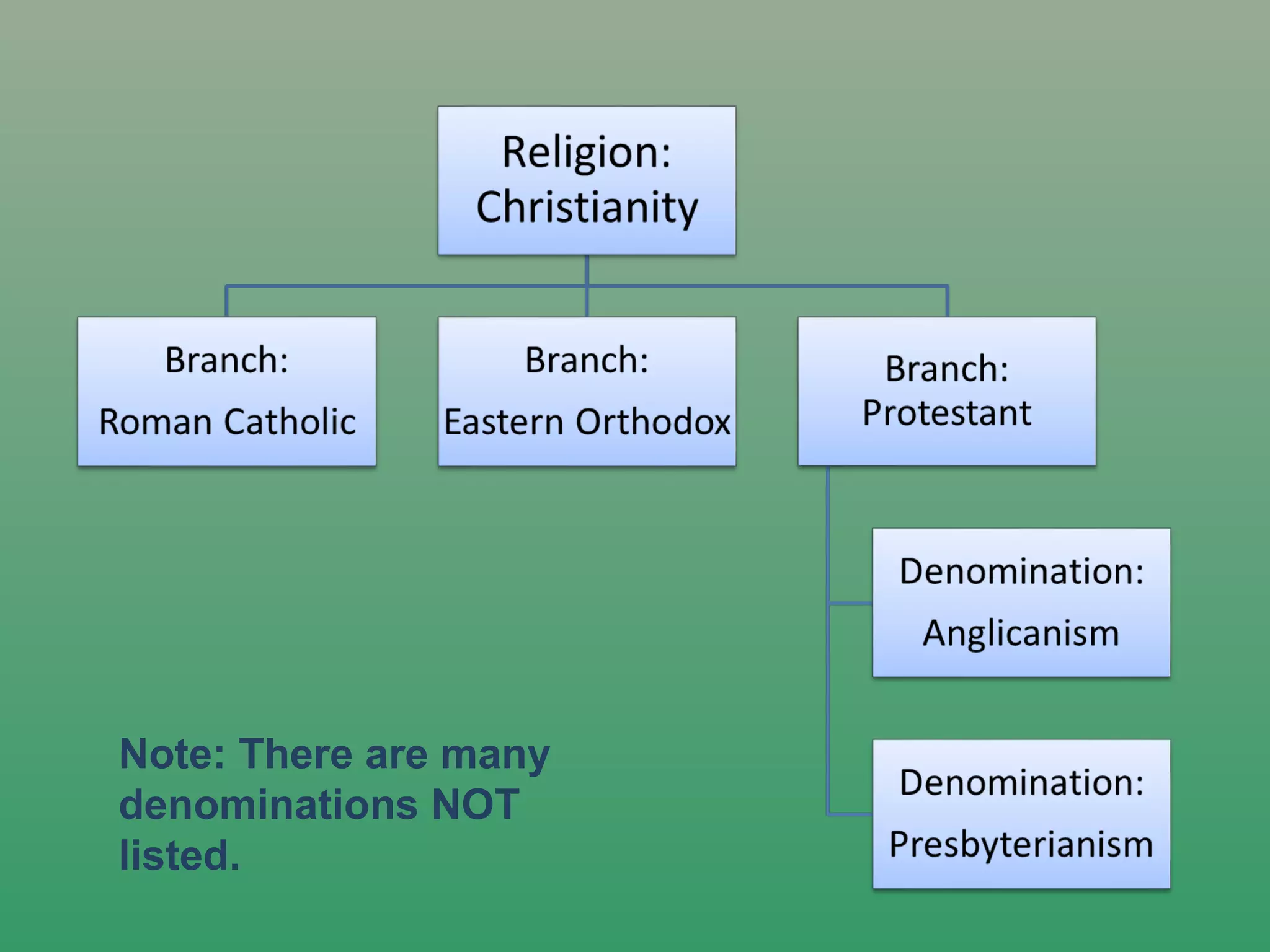
Religion is defined as a system of beliefs and practices that seeks to order life in terms of culturally perceived priorities. It often includes established symbols, rituals, and sacred texts that explain the origin of life, the universe, or the meaning of life. The document then provides overviews and examples of different types of religions including universalizing versus ethnic religions, examples of orthodox and syncretic religions, cultural hearths where major religions originated, and maps showing the diffusion and current distribution of adherents to major world religions. It also discusses concepts like fundamentalism, extremism, indigenous religions, and the rise of secularism.