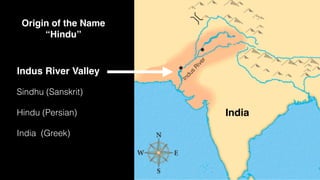
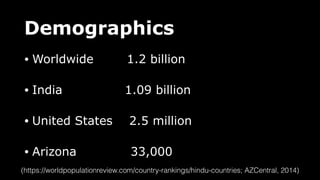
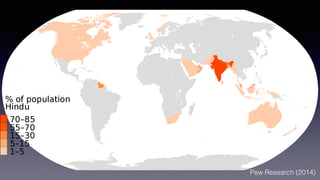
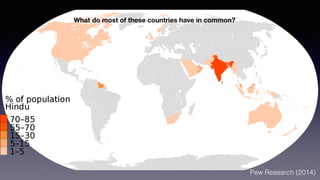
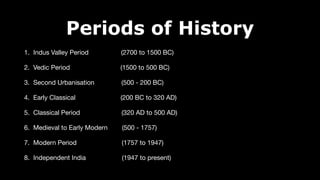
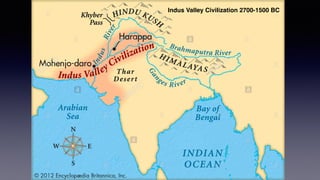
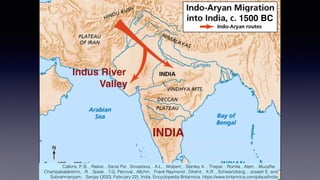
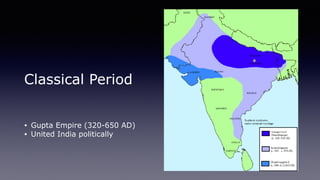
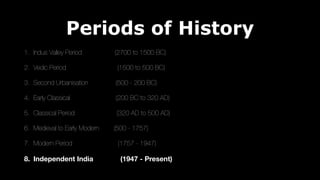
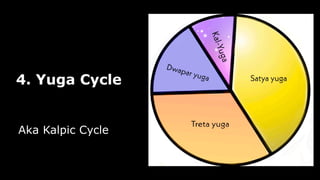
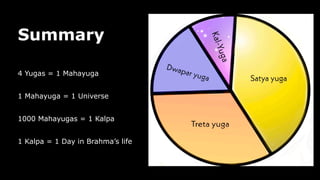
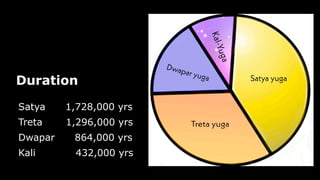
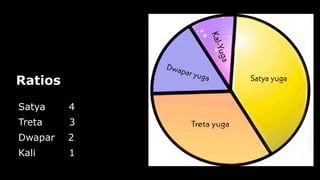
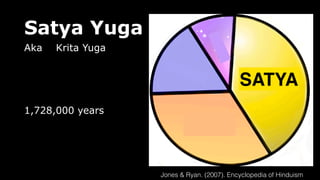
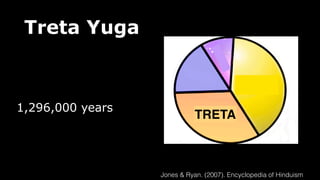
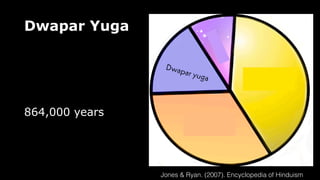
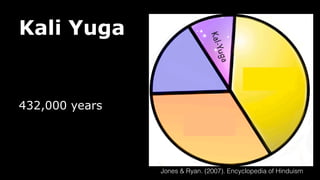
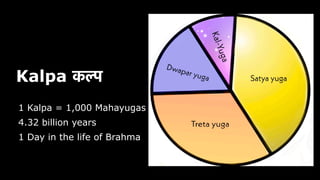
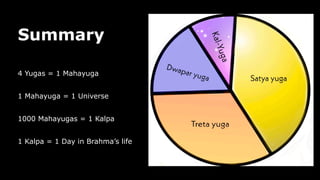
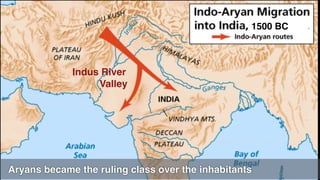
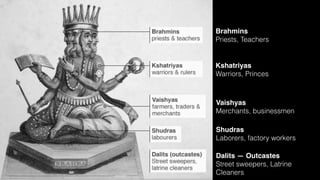
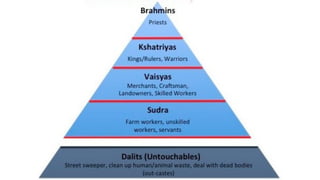
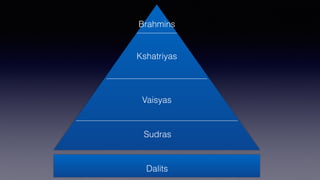
This document provides an overview of Hinduism through its history, beliefs, and practices. It covers the major periods in Hinduism's development from the Indus Valley Civilization through modern India. Key beliefs discussed include Brahman, Atman, karma, and the concept of cyclic time through the Yuga cycle. The document also looks at Hindu scriptures, the Trimurti gods, and comparisons with Abrahamic religions. Overall, it serves as a comprehensive introduction to Hinduism for educational purposes.