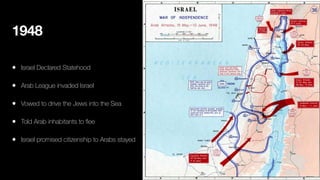
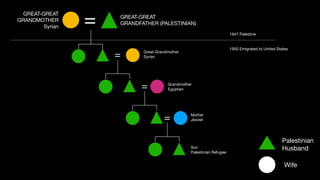
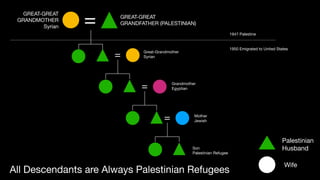
1. Early Zionists knew a Jewish state would displace Arabs but had no plan to expel them as they themselves had been refugees.
2. As fighting broke out in 1947-1948, upper and middle class Arabs fled cities, causing working class Arabs to panic.
3. Subsequent defeats of Arab militias by the IDF led to widespread panic and abandonment of villages.
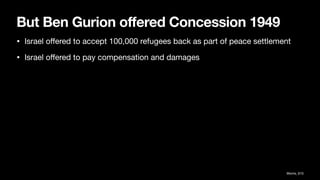
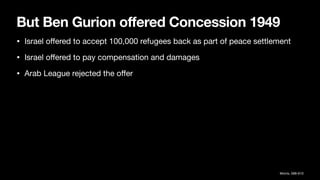
4. Ben Gurion later ordered some expulsions of hostile villages to secure lines of communication and prevent return of refugees. Offers were made to allow return of some refugees but rejected by Arab leaders.

































































































![Every attempt [by Israel] to hold on to [the West Bank and Gaza]…leads
us to become either a nondemocratic or a non-Jewish state. If the
Palestinians vote, then Israel becomes a binational state. If Palestinians
don't vote Israel becomes an apartheid state.
Ehud Barak, 1999
Jimmy Carter, “Don’t Give Up on Mideast Peace” [Op Ed], New York Times (April 12, 2012). https://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/13/opinion/dont-give-up-on-mideast-peace.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/israel-palestinepart2-240213153936-8301c200/85/Israeli-Palestinian-Conflict-Part-2-112-320.jpg)















![Bibliography
Anera. “What Are Area A, Area B, and Area C in the West Bank?,” 2023. https://www.anera.org/what-are-area-a-area-b-
and-area-c-in-the-west-bank/.
Carter, Jimmy. “Don’t Give Up on Mideast Peace [Op Ed].” The New York Times, April 12, 2012, Online edition, sec.
Opinion. https://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/13/opinion/dont-give-up-on-mideast-peace.html.
Clinton, Bill. My Life. New York: Knopf, 2004.
Clinton, Bill. “Statement: Death of Yasser Arafat.” Clinton Foundation (blog), November 11, 2004. https://
www.clintonfoundation.org/press-and-news/general/statement-death-of-yasser-arafat/.
Israel’s Central Bureau of Statistics. “Demographic Characteristics,” 2024. https://www-cbs-gov-il.
Morris, Benny. The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited. 2nd edition. New York: Cambridge University
Press, 2004.
Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics. “Press Release,” July 2022. https://www.pcbs.gov.ps/portals/_pcbs/
PressRelease/Press_En_InterPopDay2022E.pdf.
Shyovitz, David. “The 2000 Camp David Summit.” Jewish Virtual Library, 2020. https://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/
the-2000-camp-david-summit.
Virtual Jewish Library Editors. “Israel International Relations: International Recognition of Israel.” Jewish Virtual Library,
2023. https://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/international-recognition-of-israel.
130](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/israel-palestinepart2-240213153936-8301c200/85/Israeli-Palestinian-Conflict-Part-2-130-320.jpg)