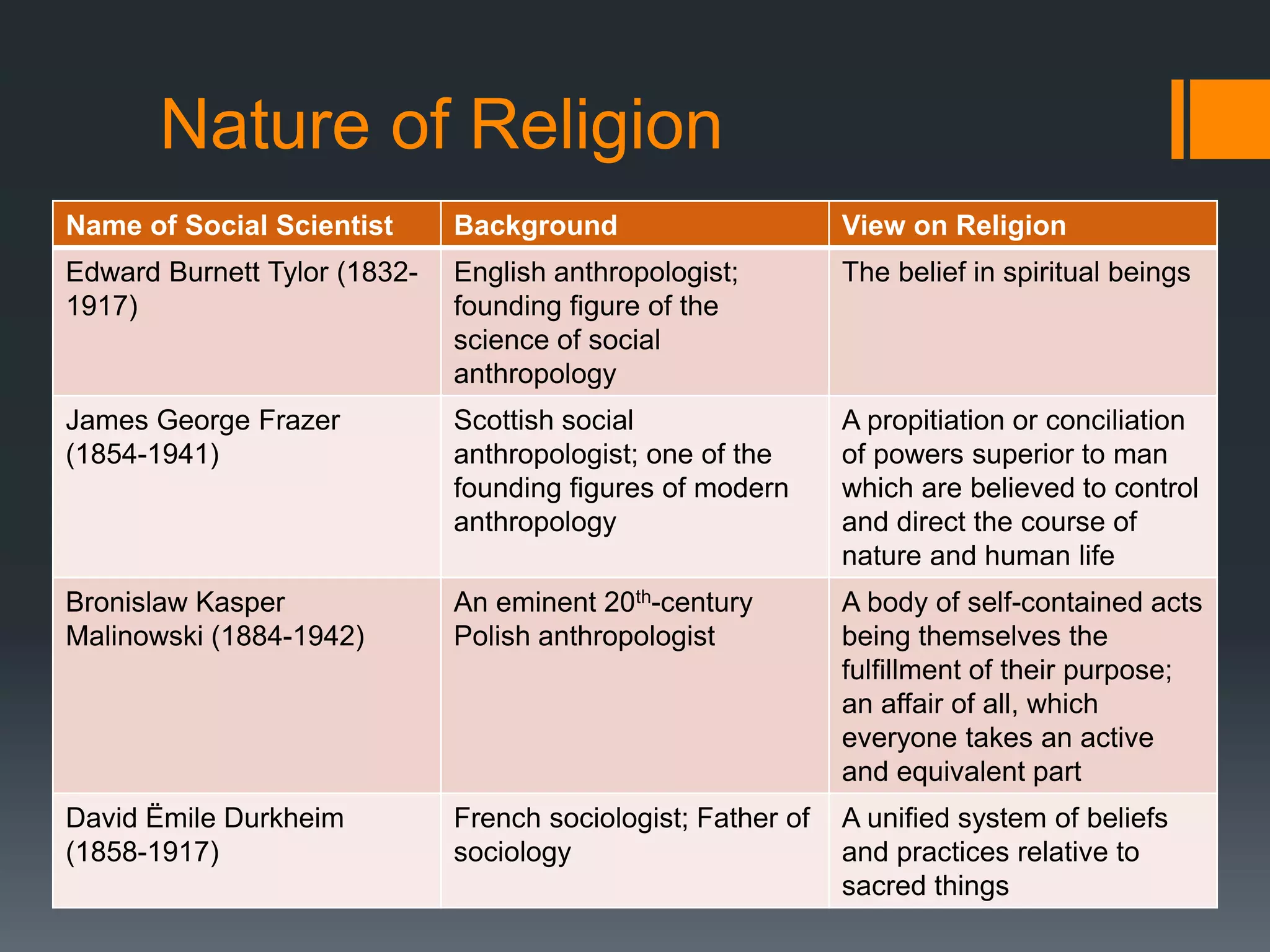
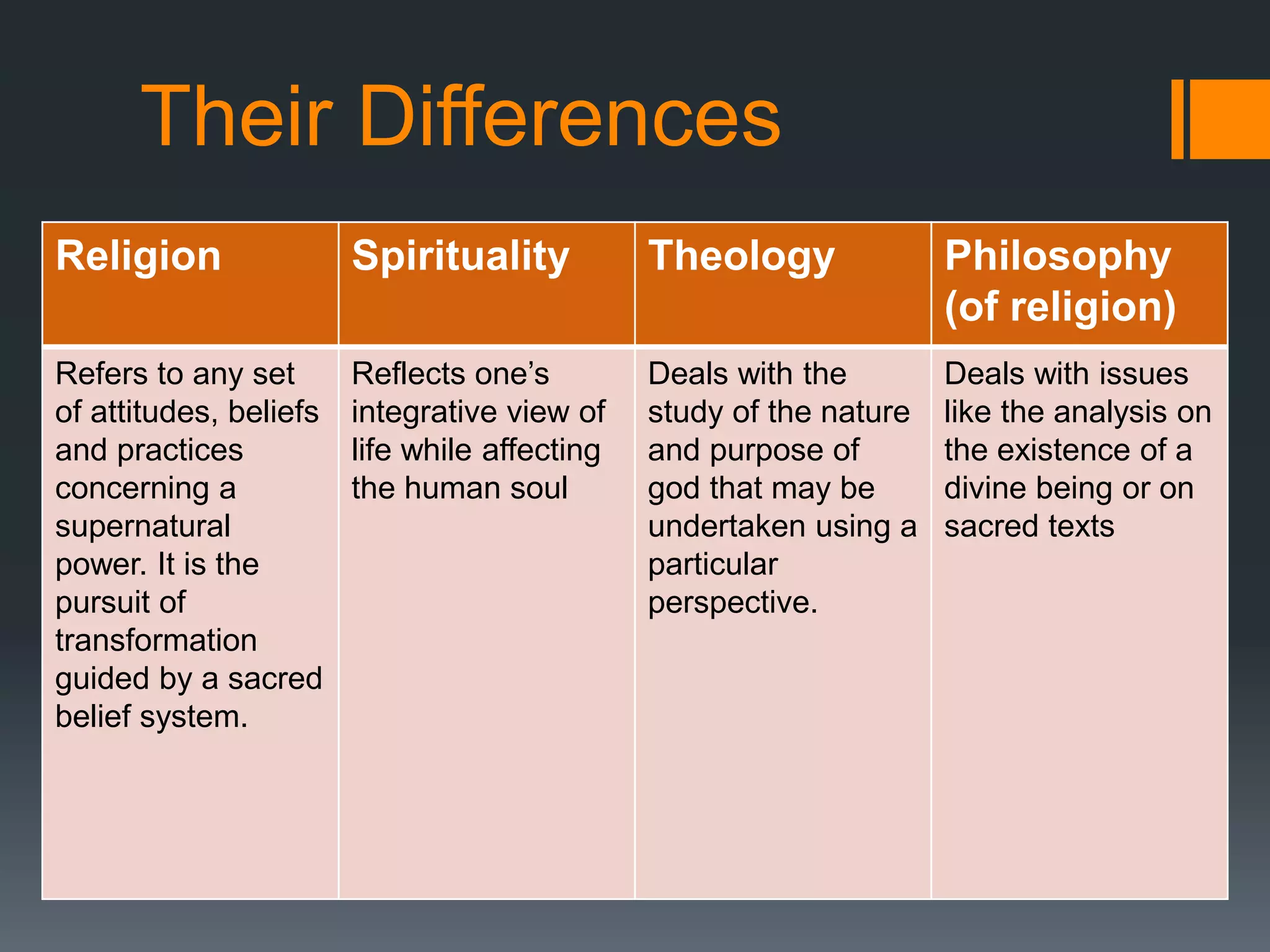
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to understanding religion. It defines religion and discusses worldviews, different belief systems like monotheism and polytheism, the nature and origins of religion, elements and theories of religion, and the differences between religion and spirituality. It also includes reflection questions and an enrichment activity. The key points are: religion involves organized beliefs and practices for worshipping gods, social environment and upbringing shape religious views, and the four common elements among religions are belief in deity, doctrine of salvation, code of conduct, and rituals.