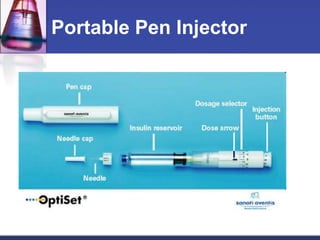
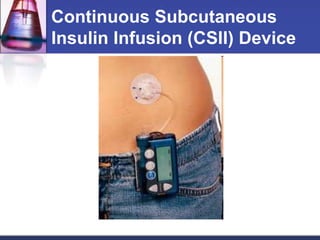
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels. There are different types of insulin preparations categorized by their onset and duration of action: rapid-acting insulin has an onset of 15 minutes; short-acting insulin has an onset of 30-60 minutes; intermediate-acting insulin has an onset of 1-2 hours; and long-acting insulin has an onset of 2-8 hours. Insulin can also be administered as a combination of short-acting and intermediate/long-acting insulins to better control blood glucose throughout the day. Insulin is usually administered via subcutaneous injection in the arm, thigh, or abdomen using a syringe or portable pen device.