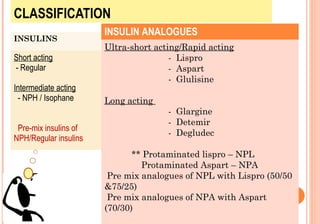
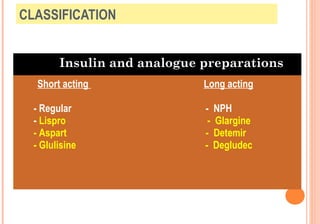
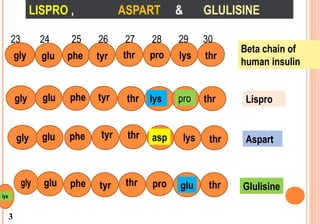
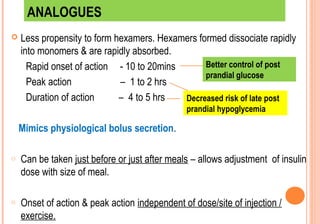
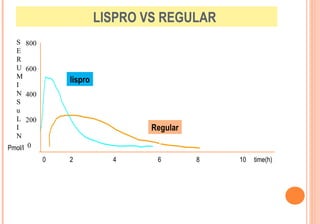
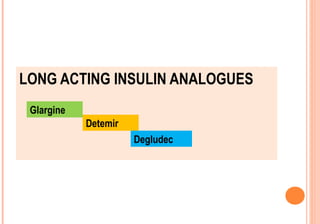
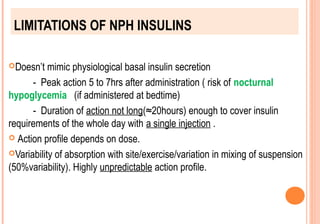
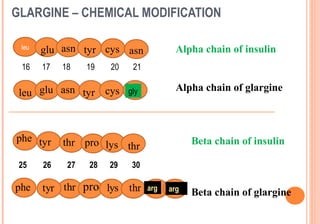
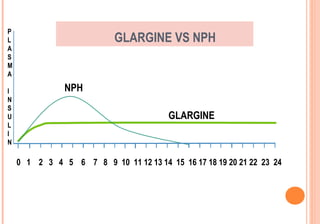
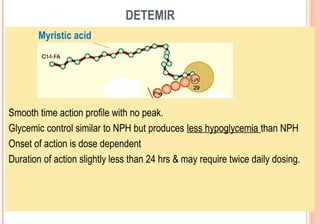
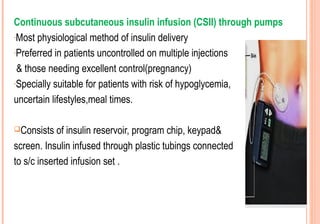
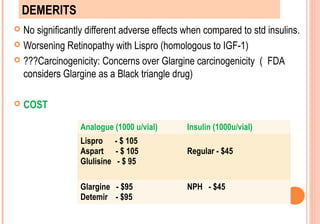
This document discusses insulin analogues, which are genetically engineered versions of human insulin that have altered pharmacokinetic properties. It describes the classification of insulin analogues as either short-acting like lispro, aspart, and glulisine, or long-acting like glargine, detemir, and degludec. Insulin analogues were developed to overcome limitations of standard insulins like regular and NPH insulins in order to better mimic the body's natural insulin secretion and reduce risks of hypoglycemia. While analogues provide benefits like improved glucose control and flexibility, their higher cost is a drawback.