This document provides information about insulin, including:
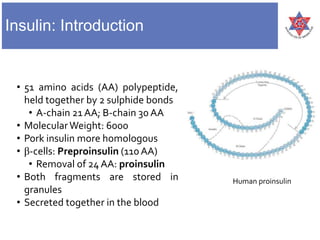
1) It describes the structure of insulin as a 51 amino acid polypeptide made of an A-chain and B-chain, held together by disulfide bonds.
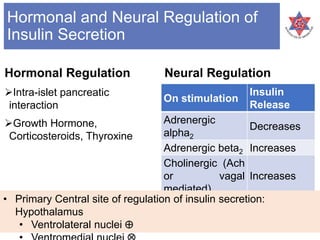
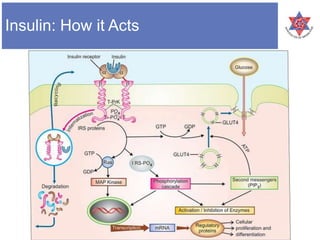
2) It explains that insulin secretion is regulated by both chemical and hormonal/neural mechanisms in response to glucose levels, including the roles of glucokinase and ATP-sensitive potassium channels.
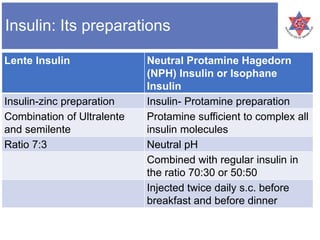
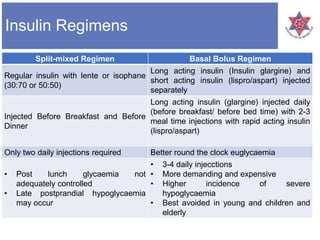
3) It lists the different types of insulin preparations available, including regular insulin, NPH insulin, and rapid-acting insulin analogues like insulin lispro, aspart, and glulisine, as well as the long-acting insulin glargine and detemir.