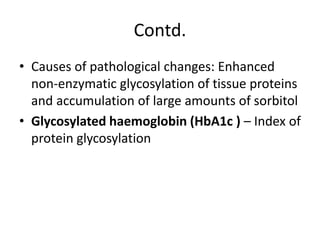
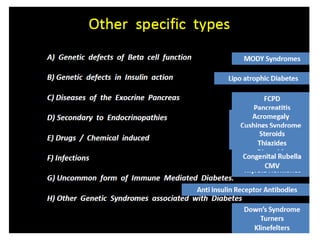
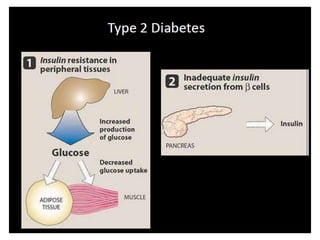
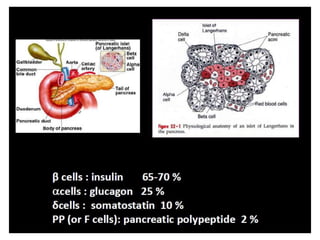
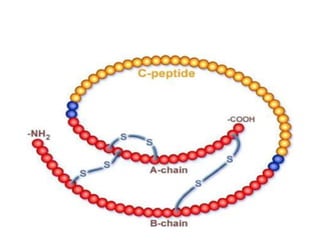
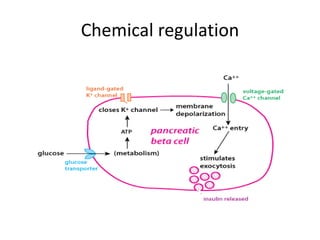
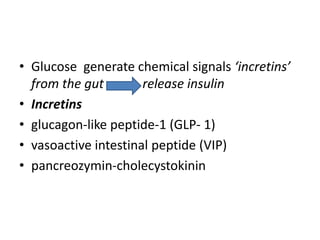
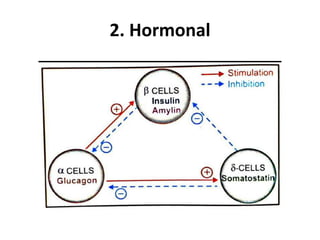
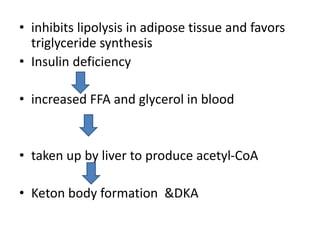
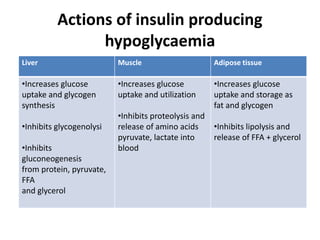
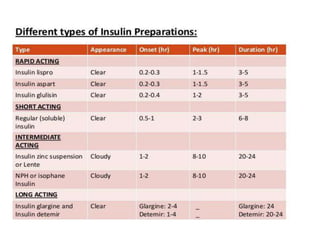
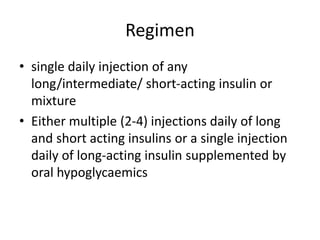
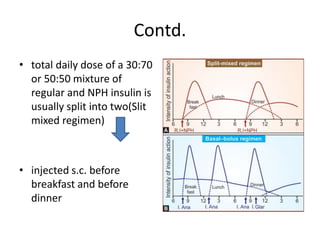
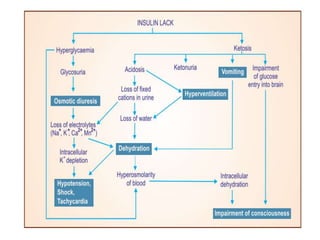
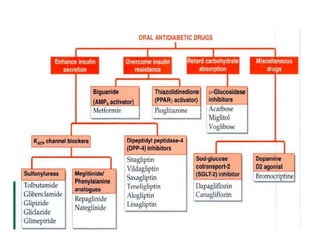
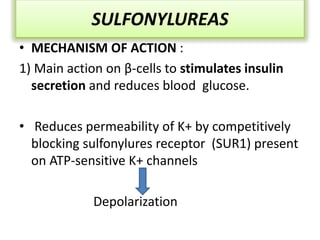
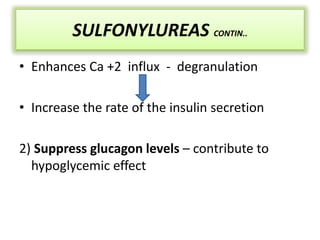
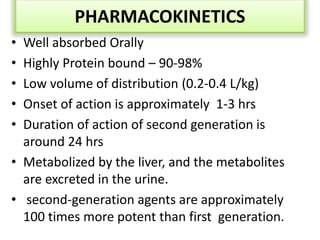
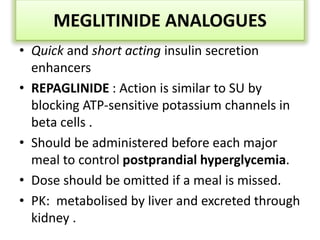
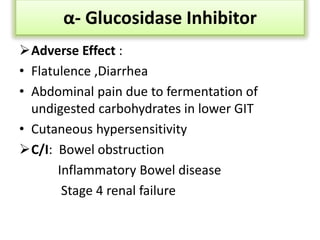
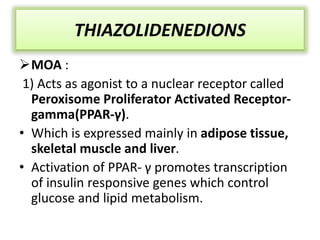
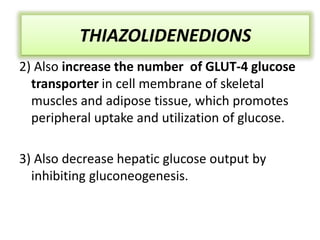
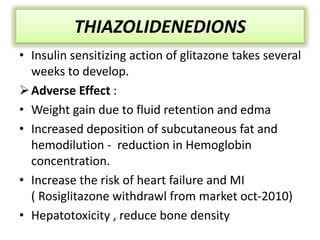
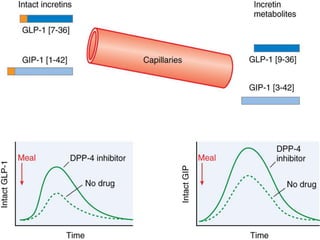
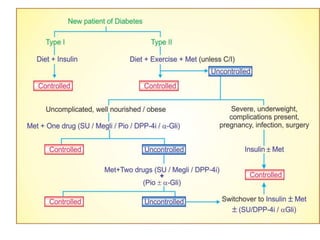
Diabetes is a condition characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from issues with insulin production or action. It can lead to pathological changes in tissues and complications like retinopathy, neuropathy, and cardiovascular disease. Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas that regulates glucose metabolism. It works by increasing glucose uptake and storage and inhibiting gluconeogenesis and lipolysis. Different insulin preparations have been developed with varying durations of action. Treatment of diabetes involves restoring normal metabolism through insulin administration and preventing complications.