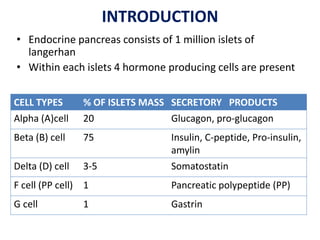
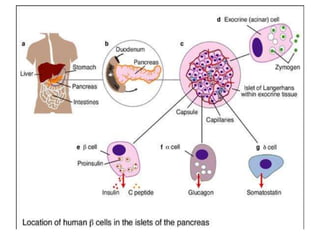
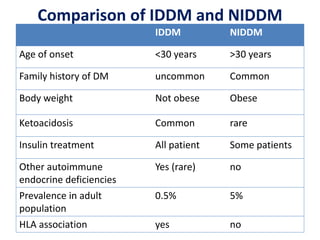
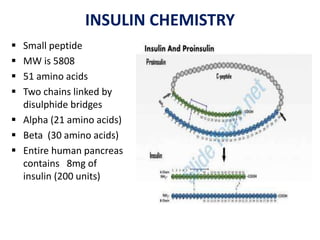
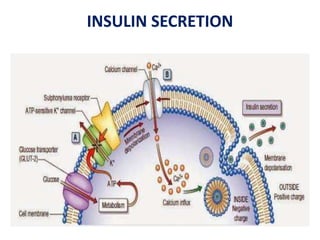
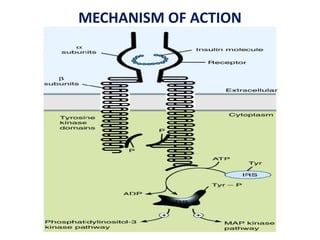
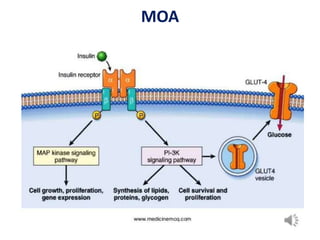
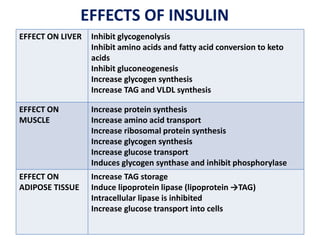
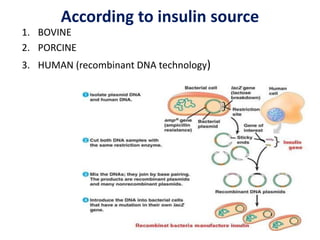
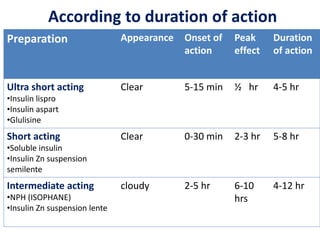
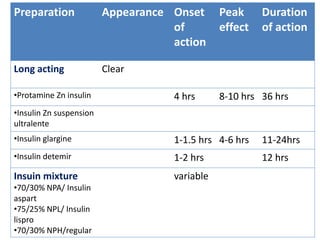
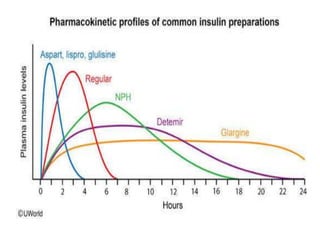
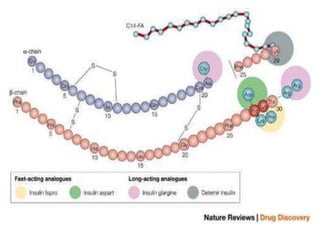
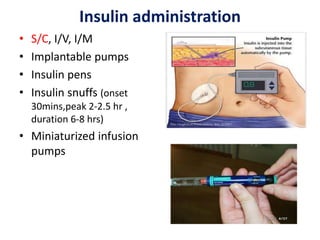
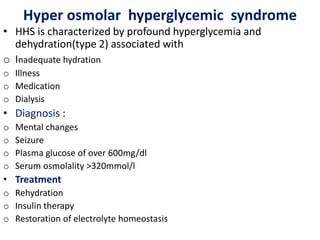
Insulin is a hormone produced by beta cells in the pancreas that regulates blood glucose levels. There are different types of insulin classified by source and duration of action that are used to treat diabetes, from fast-acting to long-lasting varieties. Insulin administration through injection or pump must be carefully titrated to each patient's needs and lifestyle to control blood sugar without causing hypoglycemia. Complications can arise from improper insulin dosing or resistance.