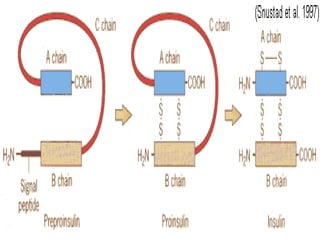
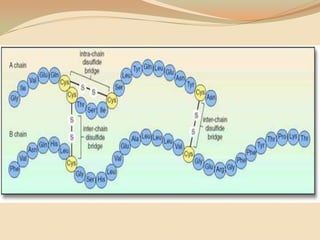
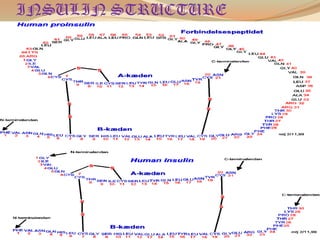
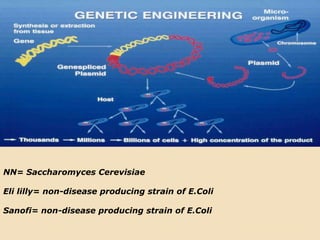
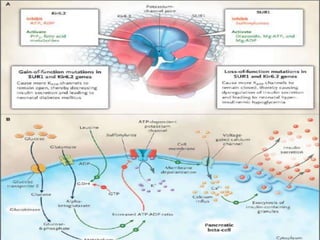
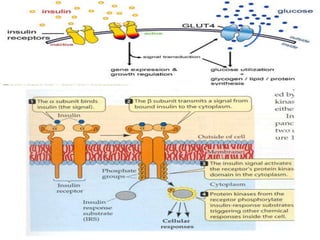
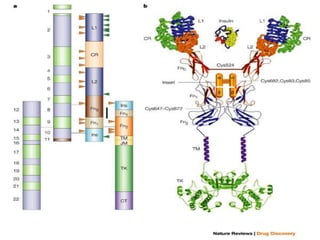
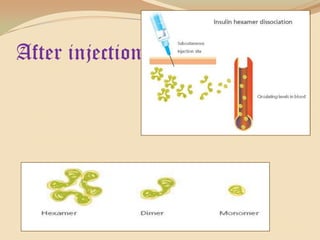
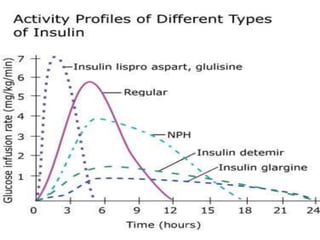
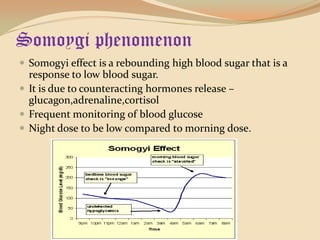
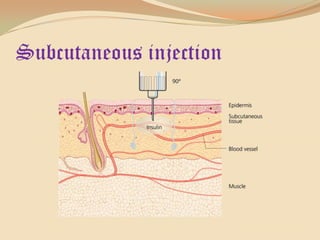
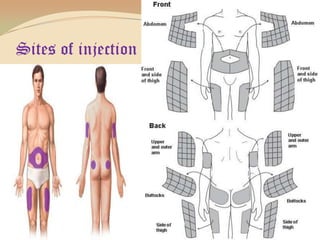
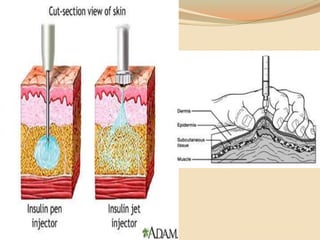
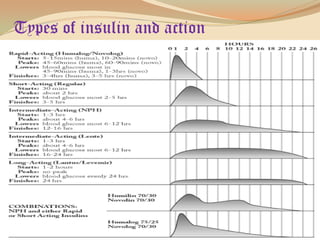
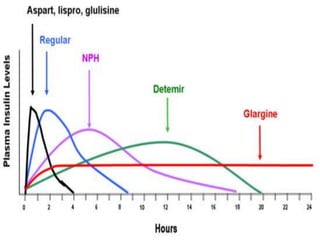
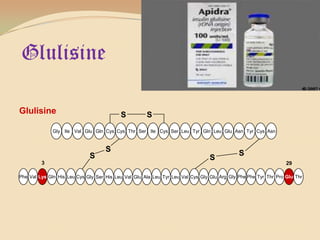
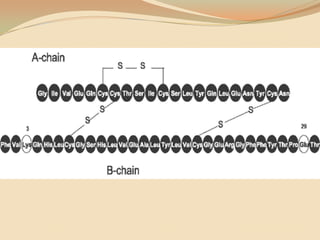
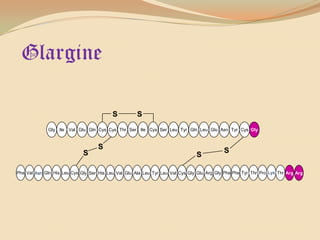
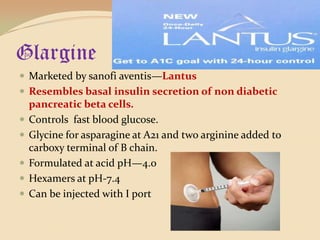
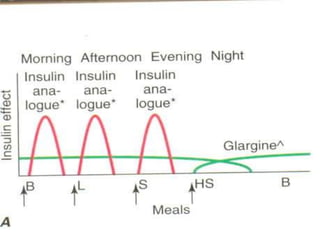
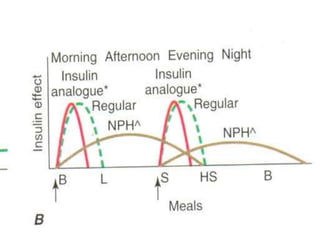
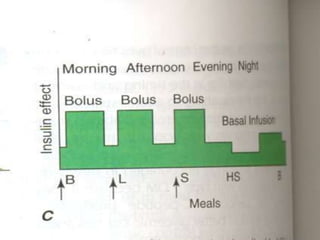
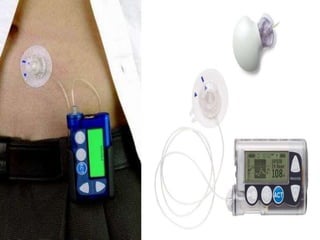
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. It allows the body to use and store carbohydrates from food. Without enough insulin, blood sugar levels rise and a person develops diabetes. There are different types of insulin that work in various timeframes to mimic the body's natural insulin release and keep blood sugar stable. Insulin is essential for diabetes treatment but requires careful dosing to avoid hypoglycemia from too much insulin or hyperglycemia from too little insulin. New delivery methods like insulin pens and pumps aim to more closely match a person's changing insulin needs.