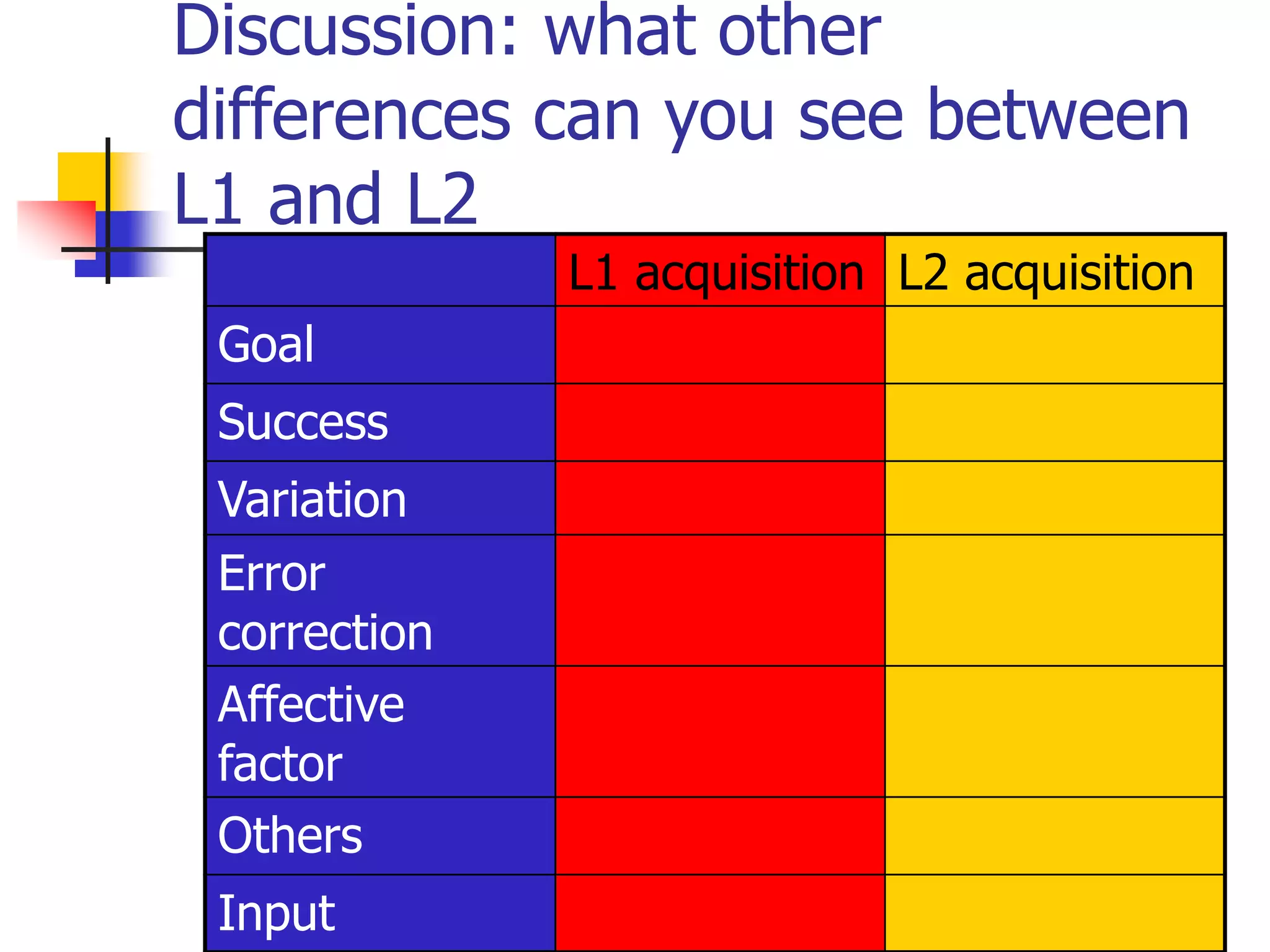
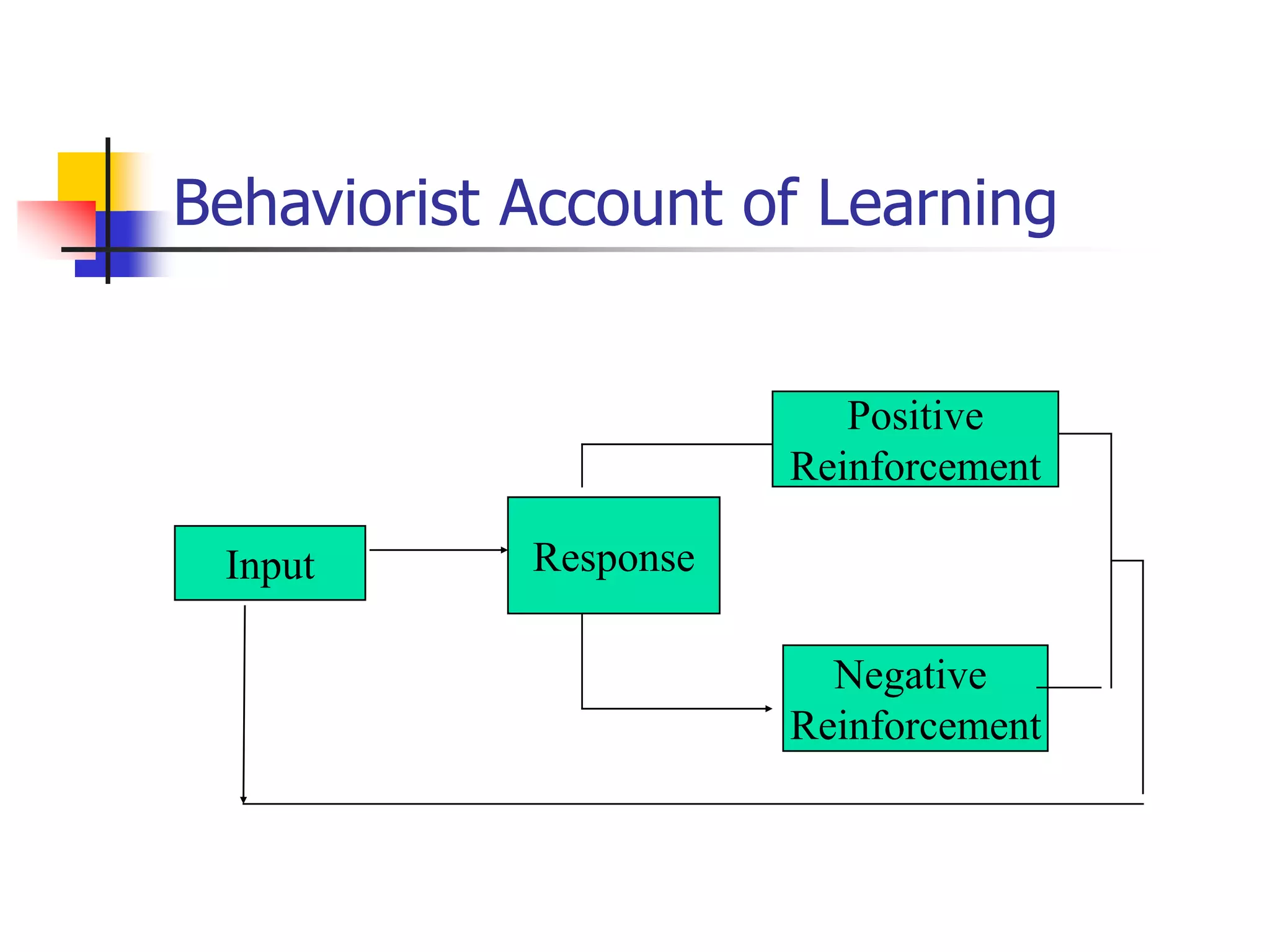
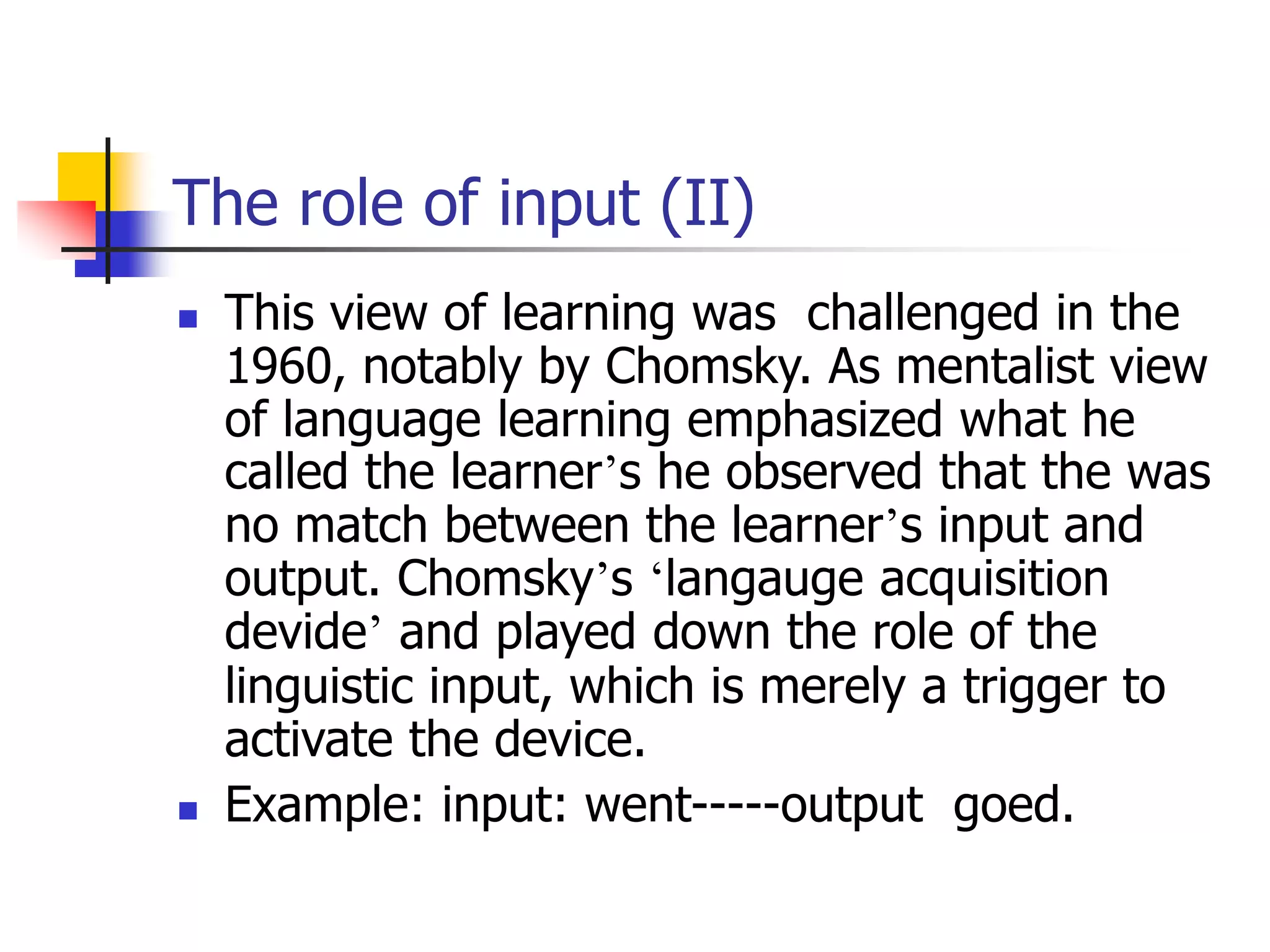
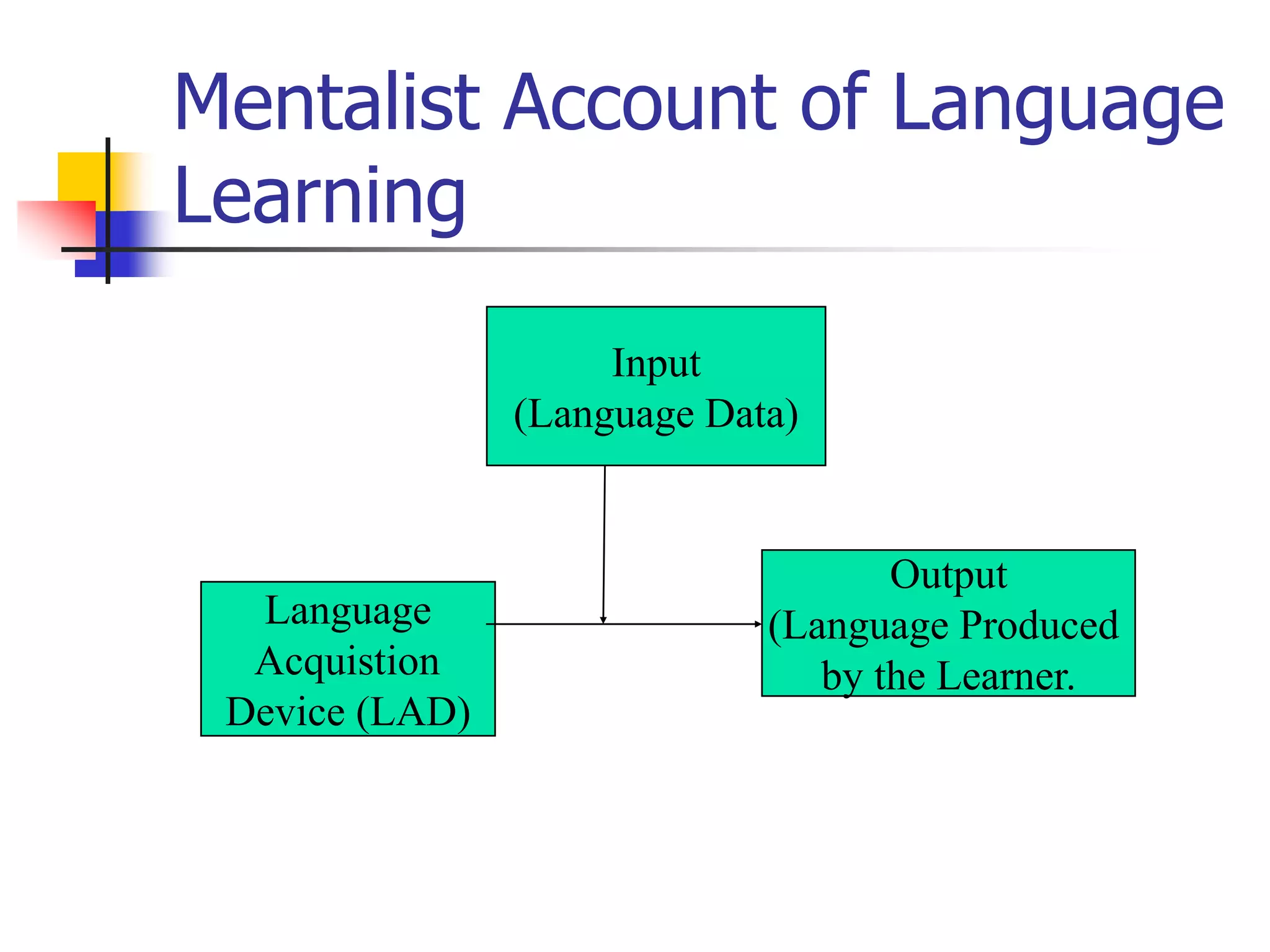
This document outlines theories of language learning, covering historical background, basic concepts, key issues, and approaches. It discusses the shift from practice-oriented to theory-oriented study, and the development of related fields. Key concepts covered include the differences between L1, L2, and FL. Approaches discussed include the linguistic approach, functional-typological approach, information processing/cognitive approach, and socio-cultural approach. Current issues focus on the cognitive underpinnings of L2 learning and representation of multiple languages in the brain.