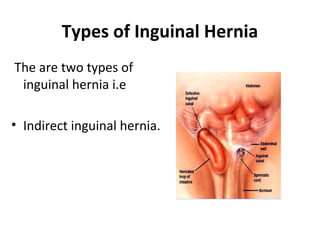
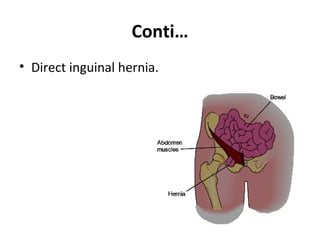
An inguinal hernia occurs when part of the intestine or abdominal fat protrudes through a weak area in the lower abdominal wall muscles into the groin. There are two main types of inguinal hernia: indirect and direct. Risk factors include congenital defects, heavy lifting, straining, obesity, and chronic coughing. Symptoms include a bulge or discomfort in the groin area that may increase with straining. Treatment options include surgery to repair or replace the weak muscle wall, with risks of complications like infection, recurrence, and pain.